1. Dividends and their policy 2. What is leverage? 3. Other types of income and expenses
The amount of income received from the sale of products and the correctness of its application directly affects the final indicator and the level of efficiency of the enterprise. About 24% of the enterprise's income goes to the budget fund to pay mandatory taxes, and the rest of the income is the net profit of the enterprise. Therefore, part of the net profit must be used correctly.
There are several ways to use net profit:
- Organization of a public needs fund;
- Contribution to the development of organizational performance;
- Payments in the form of dividends for shareholders of the enterprise;
- Payment of financial assistance to employees of the enterprise;
- Creation of a reserve fund
If you carry out a comparative description of the income received, you can determine the main factors that lead to an increase in income taxation and, as a result, a decrease in the part of the income that remains within the enterprise. The main factors that influence this are divided into external and internal.
External factors include income tax, contributions to the reserve fund, and sources of financing. Internal factors are considered to be the profitability indicator, the availability of investments, productivity costs, own and borrowed capital, sales of enterprise materials, and depreciation funds.
What is a cumulative total when calculating income tax?
The tax base for income tax is the monetary expression of the organization's profit (clause 1 of Article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When determining the tax base, taxable profit is determined on an accrual basis from the beginning of the tax period (clause 7 of Article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Tax is calculated based on the annual base.
Advances based on the results of reporting periods are calculated based on profits calculated on an accrual basis from the beginning of the tax period to the end of the reporting period (clause 2 of Article 286 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Cumulative total means that the profit of the reporting quarter is determined based on income and expenses received/incurred from the beginning of the year to the reporting date. That is, it actually includes both the profit/loss of the previous reporting period and the profit/loss of the current one.
Find out how to correctly calculate advance payments for income tax in ConsultantPlus. If you don't have access to the system, get a free trial online.
About the cumulative total in another report, read the material “6-NDFL is filled in with a cumulative total from the beginning of the year.”
Use of net profit of MUP
Readers' questions are answered by Intercom-Audit Yekaterinburg LLC
(343) 290-51-02, 290-51-12, 290-51-22
[email protected] www.audit-ekb.ru Can municipal unitary enterprise (retail trade) use part of the net profit of the enterprise (account 84-2) for the development and expansion of financial and economic activities, if this is stated in the Charter, in particular, the purchase of retail furniture: account. 76 – count. 51 payment for furniture; sch. 10.9 – count. 76 furniture was capitalized (account 10.9 – low-value equipment and household supplies); sch. 44.2 – count. 02.7 depreciation of low-value inventory. Is it possible to post the account? 84.2 – count. 02.7 instead of posting the account. 44.2 – count. 02.7? If not, why not?
According to Art. 2 of the Federal Law of November 14, 2002 No. 161-FZ “On State and Municipal Unitary Enterprises” by a unitary enterprise
A commercial organization is recognized that is not vested with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it by the owner.
Only state and municipal enterprises can be created in the form of unitary enterprises.
The property of a unitary enterprise belongs by right of ownership to the Russian Federation, a subject of the Russian Federation or a municipal entity.
Art. 16 of Law No. 161-FZ establishes the obligation
at
a unitary enterprise, at the expense of the net profit remaining at its disposal, create a reserve fund
in the manner and in the amounts provided for by the charter of the unitary enterprise.
Reserve fund funds
are used
exclusively to cover losses
of the unitary enterprise.
A unitary enterprise also creates other funds from its net profit
in accordance with their list and in the manner
provided for by the charter
of the unitary enterprise.
Facilities
, credited to such funds,
can be used
by a unitary enterprise
only for the purposes
determined by federal laws, other regulatory legal acts and
the charter of the unitary enterprise
.
In accordance with Art. 17 of Law No. 161-FZ owner
property of a state or municipal enterprise
has the right to receive part of the profit
from the use of property under the economic control of such an enterprise.
The municipal enterprise annually transfers part of the profit to the municipal budget
, remaining at his disposal after paying taxes and other obligatory payments, in the manner, in the amount and within the time frame determined by local government bodies.
Constituent document
of a unitary enterprise is its
charter
.
In accordance with Art. 9 of Law No. 161-FZ The charter of a unitary enterprise must contain, among other things, a list of funds created by the unitary enterprise, the size, procedure for the formation and use of these funds.
Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation dated August 25, 2005 No. 205 approved the Model Charter
federal state unitary enterprise based on the right of economic management.
Clause 3.11 of the Model Charter indicates which funds and in what order a unitary enterprise can create.
For example
:
– a social fund, the funds of which are used to address issues of improving the health of enterprise employees, including the prevention of occupational diseases.
– housing fund, the funds of which are used for the purchase and construction (equity participation) of housing for enterprise employees in need of improved housing conditions
– and other funds.
The size, procedure for the formation and use of funds are established by a collective agreement
on the basis of the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
In clause 3.9 of the Model Charter it is stated that the enterprise disposes
results of its activities, including
net profit received
.
To fulfill its statutory goals, the enterprise has the right
in the manner established by the current legislation of the Russian Federation:
– purchase or lease fixed and working capital at the expense of
its available financial resources, credits, advances and other sources of financing;
– provide material and technical support for production and development of social facilities;
– plan your activities and determine development prospects based on the enterprise’s activity program, approved in the prescribed manner, as well as the presence of demand for the work performed, services provided, and products manufactured.
Thus, the profit of a unitary enterprise is managed by the owner of this enterprise and it is he who determines the procedure for spending the profit
.
If the Charter states that the enterprise can dispose of net profit
, then it can, among other things, be used for the development and expansion of financial and economic activities, including the purchase of commercial equipment, commercial furniture, even without creating an appropriate fund.
Accounting for commercial furniture purchased by you depends on whether it is a fixed asset
or refers
to inventories
(inventory and household supplies).
Fixed assets
According to PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets”
, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n,
an asset is accepted
by the organization for accounting as fixed assets
if the following conditions
:
A)
the object is intended for use in the production of products, when performing work or providing services, for the management needs of the organization, or to be provided by the organization for a fee for temporary possession and use or for temporary use;
b)
the object is intended to be used for a long time, i.e. a period exceeding 12 months or the normal operating cycle if it exceeds 12 months;
V)
the organization does not intend the subsequent resale of this object;
G)
the object is capable of bringing economic benefits (income) to the organization in the future.
Assets
in respect of which
the conditions for recognition of fixed assets are met, and with a value within the limit
established in the accounting policy of the organization, but
not more than 40,000 rubles per unit, may be reflected
in accounting and financial statements
as part of inventories
.
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 257 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
for profit tax purposes,
fixed
assets are understood as part of the property used as means of labor for the production and sale of goods (performing work, providing services) or for managing an organization with an initial
cost of more than 100,000 rubles
.
Property that does not meet all these requirements is not taken into account as part of the fixed assets and is not depreciated.
.
The cost of this
property in accounting or tax accounting is accordingly
taken into account in expenses when it is transferred into operation
.
Purchased commercial equipment (commercial furniture), which simultaneously meets all the criteria provided for in paragraph 4 of PBU 6/01, is registered as an item of fixed assets.
In accordance with clauses 7, 8 of PBU 6/01, an asset is accepted for accounting at its original cost, formed from the actual costs of acquiring it and bringing it to a state suitable for use.
Acceptance of OS for accounting and tax accounting
is drawn up with
an act of acceptance and transfer of property
(
OS-1
)
and an inventory card
(
OS-6
).
Accounting entries for the purchase of commercial equipment and cash payments to the supplier's representative are made in accordance with the Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts
accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, and are shown below in the table of transactions.
| Wiring | Operation |
| D 60 – K 51 | OS payment |
| D 08 – K 60 | The costs of acquiring (constructing) the OS are taken into account and are to be included in its initial cost |
| D 01 – K 08 | OS accepted for accounting |
| D 19 – K 60 | Input VAT is reflected on the costs of purchasing OS |
| D 68 - K 19 | VAT is accepted for deduction |
In accordance with clause 17 of PBU 6/01, the cost of an asset is repaid through depreciation
.
Depreciation charges are recognized in accounting as expenses for ordinary activities in the month of their accrual (clauses 5, 8, 16, 18 PBU 10/99 “Organizational Expenses”
, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n, clause 64 of the Methodological guidelines for accounting of fixed assets).
Since depreciation charges
are recognized in accounting as expenses for ordinary activities, then
their write-off to account 84.02 “Retained earnings” is not provided for by law
.
| Wiring | Which fixed assets are depreciated? |
| D 44 – K 02 | OS used for selling goods (works, services) |
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 256, paragraph 1, art. 257 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
fixed assets are depreciable property.
The amount of accrued depreciation is recognized monthly as part of expenses associated with production and sales ( clause 3, clause 2, article 253, clause 2, article 259, clause 3, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
Inventories
According to PBU 5/01 “Accounting for inventories”
, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 06/09/2001 No. 44n,
the following assets are accepted as inventories
:
– used as raw materials, materials, etc. in the production of products intended for sale (performance of work, provision of services);
– intended for sale;
– used for the management needs of the organization.
Inventories are accepted for accounting at actual cost.
In accordance with the Chart of Accounts on subaccount 10-9 “Inventory and household supplies”
the availability and movement of inventory, tools, household supplies and other means of labor are taken
into account, which are included in the funds in circulation
.
Assets included in inventories are not depreciable property
.
Therefore, in this case there cannot be wiring D 44 K 02.
| Wiring | Operation |
| D 10 – K 60 | MPZ purchased |
| D 19 – K 60 | VAT presented by the supplier of goods and materials is reflected |
Balashenko E.V. , Director of Intercom-Audit Ekaterinburg LLC
Example of tax base calculation
Let us explain this with an example.
Let's say the reporting periods for an organization are quarter, six months and 9 months.
For the first quarter, its income amounted to 900 thousand rubles, and expenses - 750 thousand rubles.
For the second quarter: income - 600 thousand, expenses 800 thousand rubles, respectively.
For the third quarter: 1 million and 700 thousand rubles.
For the fourth quarter - 700 thousand and 800 thousand.
Let's present the calculation of the tax base in the table:
| I quarter | Half year | 9 months | Year | |
| Revenues, thousand | 900 | 1500 (900 + 600) | 2500 (900 + 600 + 1 000) | 3200 (900 + 600 + 1000 + 700) |
| Expenses, thousand | 750 | 1550 (750 + 800) | 2250 (750 + 800 + 700) | 3050 (750 + 800 + 700 + 800) |
| Financial results, thousand | +150 | -50 | +250 | +150 |
Thus, during the year the organization received both profit and loss, but as a result, the cumulative total was a profit.
See also: “How is profit before tax calculated (formula)?”
What is leverage?
The concept of “leverage” from an economic point of view is explained as a “lever”, which, having even the slightest influence, can radically change the performance indicators of an enterprise. The relationship between fixed and variable costs for the cost of finished products depends on the strategic processes of the organization, from a technological and technical point of view. The relationship between production volumes, variable and fixed costs is reflected in the leverage indicator.
Did not you find what you were looking for?
Just write and we will help
According to scientist V.V. Kovalev, production leverage is the presence of a probable opportunity to manage gross income through changes in the cost of goods. The level of production leverage is calculated using the formula:
\(Kpl=ΔП%/ΔК%\), where Kpl is the gross profit from changes in production volume;
\(ΔП%\) - income growth rate; \(ΔК%\) — sales growth rate
If you increase the level of production leverage, this will increase the risk associated with obtaining the income necessary to calculate expenses.
As an example, we can make a comparative analysis of three different enterprises. The tables below show that the production leverage ratio will be higher for the enterprise that has a higher dependence of fixed costs on variable costs. Regardless of the percentage of increase in product production, this allows for an increase in gross profit.
Thus, it should be said that if the level of productivity decreases, the income of the third enterprise will gradually decline, approximately 1.6 times faster than that of the first enterprise. From this there is only one conclusion: the third enterprise is most subject to the highest possible risk.
What's in the declaration?
The income tax return is also drawn up on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year (clause 2.1 of the Completion Procedure, approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 23, 2019 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] ).
Important! The declaration for 2021 must be submitted using a new form.
In it you reflect the income and expenses accumulated from January 1 to the reporting date, and the amount of tax or advance payment calculated from them.
The amount of tax (advance) payable is shown minus payments of the previous reporting period. As a result, the difference between the current payment and the payment of the previous reporting period goes to the budget.
If you have access to ConsultantPlus, check whether you have filled out your income tax return correctly. If you don't have access, get a free trial of online legal access.
Find recommendations for preparing and an example of filling out an income tax return here.
Option 3: every month with additional payment per quarter
second year on the market. In 2021, she paid advances once a quarter - the amount of income allowed it. But she now had to switch to monthly advance payments for her income taxes because she exceeded the income limit for quarterly payments in 2019. No notice was given in advance regarding the calculation of advances on profits received. Therefore, they will have to be calculated based on expected income.
During the first quarter, the same amount of advance payment must be paid as in the fourth quarter of last year. This amount is reflected in the income tax return for 9 months of the previous year (sheet 02, line 320). Even if it becomes clear that the period will be unprofitable, the advance cannot be reduced.
For the fourth quarter of 2021, Gamma LLC paid an advance on income tax in the amount of 2 million rubles. Therefore, during the first quarter of 2019, you need to pay the same amount. Monthly advance payments for income tax are made as follows:
- the amount of the quarterly payment is divided into 3 equal parts;
- payment is made no later than the 28th day of each of the three months of the quarter.
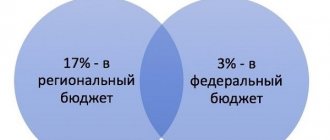
This means that in the first quarter I must transfer 666.67 thousand rubles each by January 28, February 28 and March 28. The amount must be distributed between budgets:
- 566.67 thousand rubles (17%) - to the regional;
- 100 thousand rubles (3%) - to the federal one.
The following quarterly advances are calculated as follows:
- in the second quarter the amount is equal to the advance for the first quarter;
- in the third quarter: advance for the first half of the year - advance for the first quarter;
- in the fourth quarter: advance for 9 months - advance for half a year.
When the quarter ends, the advance payment for the period and the amount of the additional payment are determined based on how much income was actually received. The additional payment is calculated according to the formula: Advance for the current period - (Advance for the previous period + Amount of monthly advances for the current quarter). For example, for 9 months the additional payment is calculated as follows: Advance for 9 months - (Advance for half a year + Monthly advance payments for the third quarter).
How Gamma LLC needs to calculate the total monthly advance payments for income tax in 2021 and the additional payment at the end of the quarter is shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Calculation of advances for income tax of Gamma LLC for 2021
| Periods | Tax base on an accrual basis, thousand rubles | Amount of the quarterly advance on an accrual basis, thousand rubles (base * 20%) | Amount of monthly advances payable during the quarter, thousand rubles | Additional payment based on the results of the quarter, thousand rubles |
| I quarter | 17 000 | 3 400 | 2,000 (according to the fourth quarter of 2021) | 3 400 — 2 000 = 1 400 |
| II quarter | 42 000 | 8 400 | 3 400 | 8 400 — (3 400 + 3 400) = 1 600 |
| III quarter | 70 000 | 14 000 | 5 000 | 14 000 — (8 400 + 5 000) = 600 |
| IV quarter | 110 000 | 22 000 | 5 600 | 22 000 — (14 000 + 5 600) = 2 400 |
Using this method may result in an overpayment of the advance payment. If the monthly amount paid plus the advance for the previous period is greater than the payment based on the results of the current period, then there is no need to pay anything extra to the budget.
Results
Calculation of tax on an accrual basis means that the calculation must be based on income and expenses received (made) from January 1 to the reporting date. The tax return is filled out using the same principle. The amount of tax payable also increases, since when determining it, payments from previous reporting periods are taken into account.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 23, 2019 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Dividends and their policy
Dividend policy promotes the efficient use of enterprise income. As practice shows, paying dividends in large quantities is a guarantee way to attract a business entity. If you look at situations from the other side, such actions can affect the inhibited development of the enterprise. This occurs by reducing the portion of income that is used to expand the enterprise.
Is it difficult to figure it out on your own?
Try asking your teachers for help
Solving problems Tests Essays
In the theory of dividend policy, there are several main approaches, namely:
- Payment of dividends is carried out after investment processes, which will increase their level in the future;
- Paying minimum dividends for a certain period of time will reduce the possible level of risk for the organization's shareholders.
To choose a more effective and relevant approach for an enterprise, you should analyze external and internal factors, consider the goals and objectives of the subject of activity and assess further prospects in terms of its development.
In the process of analyzing the use of income, it is also necessary to evaluate the movement of the necessary indicators and determine a number of actions that will increase the growth of share capital and the return on capital indicator within the enterprise. After this, you need to determine the reserves for income growth. Basically, this is an increase in sales volumes of finished products, a reduction in their cost, an increase in product quality and sales on favorable market conditions.