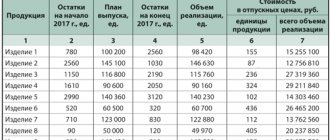
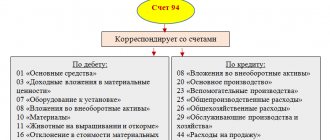
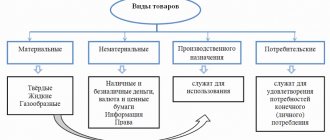
Every store has the most popular products. They make up approximately one fifth of the total assortment, and bring in up to 80 percent of profits. A good supplier strives to ensure that popular products in the store are in stock. After all, if the next delivery fails, the shelves will be empty, and disgruntled customers will go to another store. The goods will appear on the display case if the order is placed on time and accepted correctly. Today we will talk about the acceptance of goods.
You walk into a hypermarket and see shelves lined with brightly colored packages of different shapes and sizes. The shelving extends far and wide. How did the goods get on the shelves? They've come a long way. The buyer zone is just the tip of the iceberg. Our blog already had an article about organizing a retail space, and now we will tell you what happens behind the scenes of a store, namely, what mistakes stores make during reception.
Let us immediately note that it is extremely incorrect to talk about the acceptance of goods as a separate event. This is just part of a very long chain, which professionals call the supply chain.
Supply chains can be divided into two types:
The overwhelming percentage of Russian retailers work according to the first scheme, since building their own distribution centers is very expensive. Therefore, we will consider acceptance using the example of the first supply scheme.
The assortment of each store is divided into two groups:
- FMCG (fast movement consumer goods) – consumer goods with high turnover;
- other goods that the store owner needs to diversify the assortment (because the shelves should never be empty).
What will the store owner achieve?
The store owner will try to ensure that the most popular goods (FMCG) are always in abundance. How to make sure that they are always in the right quantity? It is necessary to observe all the details of delivery and receipt of goods. Where is the failure possible?
In a small store everything is simple. The owner often serves as both a merchandiser and a seller. He knows very well which products are worth ordering for future use. The owner manages the assortment manually and has no problems; the picture looks quite rosy - to calculate the needs, just fill out a table in Excel (or even in a notebook).
The canvas takes on darker shades as we reach the scale of the supermarket. There is no person who keeps the order in his head.
Large stores use electronic goods accounting systems, which collect information about the volume of purchases, product balances and many other data. Questions about what goods need to be brought, where and at what time should not arise. One mistake in documents will provoke a whole galaxy of difficulties.
Always place your order carefully
The supplier must find out the exact quantity of goods, in what packaging and on what transport they will be delivered. There should be no discrepancies in price.
The application must indicate the type of transport. The dimensions of the car must correspond to the dimensions of the entrance area. The truck will not be able to unload in a narrow street. In response, the supplier must inform the customer of the delivery date and time.
Pay attention to every little detail, and then creating a safe flow of goods will not be difficult.
Safe stock is an emergency supply that is used up in the event of a supply disruption. Each product has its own safe stock calculated. It depends on trade turnover and supply chain. Stock depends on the dynamics in the choice of suppliers. For example, a supplier may have 10 contracts for the same product from different companies. It will be cheaper to buy somewhere, but it will take longer to transport. You can experiment, but always think two steps ahead and remember that no one is immune from emergency situations.
Where do stores store goods?
Think back to your last trip to the supermarket. All these huge shelves and thousands, thousands of products. Where does all this lie before it gets to the trading floor? Probably in the warehouse?
No. Most large stores do not have warehouses at all. If there are warehouses, they are very small. Each square meter of retail space brings tens and hundreds of thousands of rubles - no one is interested in losing profit by sacrificing valuable space. It is more profitable for the store to give as much space as possible to customers. Therefore, immediately after acceptance, the goods move to the sales floor.
Ultra-fresh food (fresh vegetables, fruits and chilled meat) and dairy products get there especially quickly - they immediately try to take them into the hall. And goods with a long shelf life are placed somewhere in the corridors and technical rooms. Of course, they interfere with everyone and increase the chaos that is natural for the reception area.
As you understand, not every store has a spacious warehouse. This makes it very difficult to order goods in advance.
Setting up a warehouse group
Important . It is possible to register the receipt of goods with one document to different warehouses only if these warehouses are included in one group of the directory “Warehouses and stores”.
Let's open the directory “Warehouses and shops”.
Master data and administration / Master data / Warehouses and stores
Let's assume that our directory already has a group that contains two retail warehouses. Let's edit its settings.
Advice . To change the details of a group of any directory, select this group and select the “Change” command in the context menu.
The group form will open. Since we need to register receipt in one document for the warehouses of this group, in the subsection “Selecting this group” we will put o. Then we will record and close the group.
Advice . If changing the form details is not available, you can use the “More – Allow editing details” command in this form.
When creating a new group, it is also possible to enable the option to select a group in orders and invoices.
The receiving area replaces the warehouse
The receiving area is the most vulnerable part of the store. Everything depends on her, but they treat her with disdain. There are always not enough employees. Managers prefer to send subordinates to the sales floor so that they beautifully display goods on the shelves. There is also a lack of equipment - data collection terminals, which could significantly speed up acceptance, are also sent to the sales floor.
What happens is this: everyone is running around, fussing, frantically opening boxes and counting whether everything is in place. Somewhere grain spills out, bags of potatoes are torn. And then suddenly the next car arrives and the situation completely gets out of control.
Meat carcasses are thrown where the potatoes were carried. And boxes of washing powder are being unloaded nearby. Of course, there is no talk of any sanitary standards; everyone only dreams of getting this over with as quickly as possible.
Fresh foods instantly absorb odors, especially fish. Different types of goods must have their own unloading zones. Unloading household chemicals and food products at the same time and placing them side by side is not the smartest method.
To prevent the reception from sinking into the abyss of chaos, it is enough to follow some rules
Follow the acceptance schedule
The entire work shift (and there are usually three of them a day: morning, evening and night) must be clearly scheduled. Which company will arrive, when and in what vehicle, what cargo will it bring. Which employee is responsible for unloading, whether to put everything in the back room or immediately carry it to the sales floor.
The schedule is often violated due to unscrupulous receivers. If the store is large, then cars with goods from different suppliers arrive constantly. Congestion occurs, and “resourceful” receivers sell seats. They negotiate with some drivers and, for money, let them skip ahead in line. Because of this, the schedule is destroyed.
Organize a convenient unloading area
The small area of the unloading zone is a scourge for the entire acceptance process. The larger the receiving area, the easier it is to control the process.
It is worth creating separate zones for “anchor” products. Do you sell a lot of fish and they constantly bring it to you? Organize at least a small “fish” space for reception. Create favorable sanitary conditions in it. This way you will not only improve the acceptance process, but also improve the quality of the products on the shelves of your store.
Appoint those responsible for acceptance and provide them with equipment
Employees will always have time to place goods on store shelves. Now the goal is to unload the truck with goods as quickly as possible and without errors.
Situations where a driver arrives and waits a long time for their car to begin unloading are unacceptable. Assign responsibility for working with different suppliers. So that by the time specified in the schedule, employees approach the reception area and begin work. If you arm them with data collection terminals, then things will go even faster.
Acceptance of goods is greatly slowed down by paperwork
The order has accompanying documents: delivery note and invoice. Receivers must check the goods and count the amount of defects. We accept only intact products that have not lost their presentation.
If it turns out that ten bottles of beer were broken, then the number of bottles indicated on the invoice is no longer valid. The receivers do not stand on ceremony with the documents and write directly on them, with a pen, the number of bottles that will end up on the sales floor.
Then the documents are sent to the accounting department. Even just one change makes the documents no longer relevant, and the accountant contacts the supplier, records the discrepancies and expects corrected documents from him. Without them, the accountant cannot enter purchase data into the accounting system.
Until the receiver puts the store's stamp on the papers, the driver is responsible for the goods. Situations arise when the driver shifts responsibility for the defect to the store employees and refuses to sign documents.
To save time and nerves, we recommend that you introduce electronic document management. This eliminates all bureaucratic delays - all changes to the accompanying documents can be made literally “on the fly” - without extra hours of waiting and litigation.
Large stores negotiate with suppliers and predict in advance the possible percentage of defects. On average, five to ten percent of the quantity of goods from a batch is allocated for the so-called shrinkage (or shaking). This approach is convenient, but it requires building mutual trusting relationships with suppliers.
There is an important nuance - not only the quantity of goods, but also prices, names of goods, details or store addresses may differ in the accompanying documents. Errors here are also unacceptable. One mistake, and the documents lose their validity. In principle, electronic document management solves many problems. But with incorrect prices, things are not so simple. According to papers, goods may turn out to be more expensive than the store expected.
This is not critical - in order not to redo documents, the supplier and customer agree on the maximum threshold of discrepancies. But since the store is a large mechanism, the gears of which are living people, it is not immune to errors. Yes, you can negotiate price discrepancies, but with so many products from different suppliers, it's easy to miss that some products may have margins of three, two, or even one percent. And it turns out that by agreeing on a five percent price discrepancy for all goods, the store will sell some products at a loss.
Acceptance to warehouse
After getting acquainted with the main documents, it is necessary to talk about the procedure for accepting the goods. First of all, it is worth mentioning the deadlines for receiving products. As a rule, if the vehicle and the warehouse are located in the same city, then it is allowed to transport the goods within ten days. It is important to note that this clause does not apply to products with a limited shelf life. For intercity transportation, the time range increases to twenty days.
During the acceptance of goods, both qualitative and quantitative checks are carried out. According to Article 513 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to carefully check all the data that came with the product. Since the possible duration of transportation was mentioned above, the first document that you should pay attention to is an act confirming the conditions of cargo transportation, as well as a certificate of conformity with the quality of the delivered products or a technical passport. To control compliance, it is also permissible to selectively open the box for the purpose of visual inspection and identification of goods.
Quantitatively, the conformity of the goods is checked through recalculation, external inspection of the container in which the products were received and weighing. A mandatory requirement is the presence of markings on each container. If a shortage is detected, the consignee has the right to stop acceptance and the verification procedure upon receipt is resumed. If the products have been received in the volume corresponding to the invoice, then the responsible employee signs the paper, stamps it and puts a stamp on the date of receipt of the goods.
Also, it is important to emphasize that the legal relationship between the supplier-carrier and the recipient is regulated by the supply agreement, which includes an inventory of the products and their configuration. Since the legislation does not provide a mandatory form of agreement for both parties, companies apply two directives of the USSR State Arbitration Court. Other issues can be resolved through personal agreements.
Acceptance requires a systematic approach
The system will develop when a transparent scheme for forming needs after the sale appears. The requirement is formed into an order and sent to the supplier in the correct form. You may have 25 different suppliers, they all provide different information, and it definitely needs to be structured.
You have a retail outlet. Take into account the average turnover per month. Although this indicator is the same as the average temperature in a hospital, in general it can be operated on.
You also have an average daily order requirement. You know that within a week so many trucks with different goods should arrive at the store. This is simple arithmetic - just think a little, and then the acceptance process will no longer be chaotic.
The item was purchased for cash. How to confirm expenses
The item was purchased for cash. How to confirm expenses
The LLC ships the goods to the individual entrepreneur (STS, income minus expenses). The goods were purchased in cash. In this case, the LLC issues an invoice with the allocation of VAT and issues only the counterfoil for the receipt order. There is no cash register; they are motivated by the fact that the organization uses UTII. I can’t prove to them that they (LLC) are wrong. I am interested in the actions of my tax office, since I do not have a cash receipt.
Let's start with the seller.
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs who are taxpayers of the single tax on imputed income for certain types of activities, when carrying out the types of business activities established by clause 2 of Art. 346.26 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
,
can carry out
cash payments and (or) payments using payment cards
without the use of cash register equipment
.
This is established by the Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 346.26 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
The taxation system in the form of UTII is applied
to retail trade
.
In accordance with Art. 346.27 Tax Code of the Russian Federation under retail trade
refers to business activities related to the trade of goods (including in cash, as well as using payment cards) on the basis of
retail sales contracts
.
Under a retail purchase agreement
a seller engaged in business activities of selling goods at retail undertakes to transfer to the buyer goods intended for personal, family, home or other use not related to business activities (clause
1 of Article 492 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
).
If the buyer purchases goods for use in business activities or for other purposes not related to
with personal, family, home and other similar use, then such activity is carried out on the basis of a
supply
.
Both retail and wholesale trade are not related to the form of payment.
In both cases, payments can be made both in cash and in non-cash form.
The main thing is the purpose of using the purchased product.
The main criterion
What distinguishes wholesale trade from retail trade is the use by legal entities of purchased goods for the purpose of their processing and further sale in professional (entrepreneurial) activities to generate income (Resolution of the
Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District
dated May 12, 2009 No. F09-2292/09-C2).
Since an entrepreneur purchases goods for use in business activities, the relationship between the seller and the buyer is governed by a supply agreement
.
Indirect confirmation that the transaction took place within the framework of the supply agreement is also the fact that the seller issued an invoice to the buyer and presented the amount of VAT
(The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation often refers to this fact).
Due to the fact that UTII payers have the right not to use cash registers only
in relation to the types of activities specified in
paragraph 2 of Art.
346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (including
in relation to retail trade
), then in relation to types of activities
not specified
in
clause 2 of Art.
346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (including in relation to trade carried out under a supply agreement),
the seller is obliged to use cash register systems
when making cash payments.
Therefore, in your situation, the seller should have given you a cash receipt.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 346.26 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
the expenses specified in this article are accepted subject to their compliance with the criteria specified in
paragraph 1 of Art.
252 Tax Code of the Russian Federation .
Expenses are recognized as justified and documented expenses.
Documented expenses mean expenses supported by documents drawn up in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
In Art. 9 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ “On Accounting” stipulates that all business transactions carried out by an organization must be documented with supporting documents. These documents serve as primary accounting documents on the basis of which accounting is conducted.
Primary accounting documents
are accepted for accounting if they are compiled in accordance with the form contained in the albums of unified forms of primary accounting documentation, and documents whose form is not provided for in these albums
must contain the following mandatory details
:
A)
Title of the document;
b)
date of document preparation;
V)
name of the organization on behalf of which the document was drawn up;
G)
content of a business transaction;
d)
measuring business transactions in physical and monetary terms;
e)
the names of the positions of the persons responsible for the execution of the business transaction and the correctness of its execution;
and)
personal signatures of these persons.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in a letter dated September 17, 2008 No. 03-03-07/22 indicated that cash receipts
are recognized for tax accounting purposes
as primary accounting documents
confirming the actual cost of purchasing goods (work, services) in cash.
But if there is a decoding of the list of goods
.
Receipt cash order (form No. KO-1)
, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88, is
a unified form of primary accounting documentation
for recording cash transactions.
Receipt for cash receipt order
is a document
confirming actual payment
of costs incurred.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation is convinced that the expenses of a taxpayer applying the simplified taxation system, made in cash, on the basis of invoices, invoices and receipts for a cash receipt order, can be taken into account when determining the tax base only if there is a cash receipt
(letter dated February 21, 2008 No. 03-11-05/40).
However, the fact that tax legislation does not contain
provisions that a cash receipt is the only document that can confirm the taxpayer’s expenses when making cash payments, the courts say.
FAS Ural District
, for example, indicates that
the taxpayer’s
failure to submit cash receipts in the presence of other documents
does not in itself refute the fact of payment of cash and the presence of corresponding expenses.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not establish a list of documents that must be drawn up when a taxpayer carries out certain expense transactions, nor does it impose any special requirements for their execution (filling out).
The decision on the possibility of accounting for certain expenses if they are connected with the taxpayer’s activities in making a profit for tax purposes depends on whether the documents available to the taxpayer confirm the fact of the implementation of the expenses declared by him or not (resolution dated July 3, 2007 No. F09 -4997/07-С3, dated October 18, 2007, No. Ф09-8532/07-С3, dated 07/31/2008, № Ф09-5433/08-С3).
Therefore, receipts for cash receipt orders
are acceptable evidence of expenses incurred.
In addition, in clause 3.7 of the Procedure for filling out the Book of Income and Expenses of organizations and individual entrepreneurs applying the simplified taxation system, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 2008 No. 154n, among the primary accounting documents
, confirming the costs of acquiring fixed assets and intangible assets,
receipts for cash receipts are indicated
.
Thus, the documents you have from the seller can serve as primary accounting (supporting) documents accepted for tax purposes.
Sometimes they come back
A box of markers was delivered to the store. Carelessly, the employees pushed it into a cluttered corner and forgot about it. The person responsible for acceptance shook his head, the employees threw up their hands, the markers were written off, and the cost was deducted from the employees’ salaries (or written off as a defect). This happens all the time and causes severe headaches.
Because sooner or later the box will still be discovered (for example, during inventory). And then the accountants will have to perform complex arithmetic somersaults so that the figures in the documents agree. Avoid such situations to avoid further problems.
Types of main primary documents
- Contract – specifies your rights and obligations, working conditions
- Banking and cash documents - these documents are used to receive and withdraw funds from the enterprise’s cash desk
- Invoice - these documents indicate the arrival and departure of goods
- Invoice – confirms the fact of performed service or acceptance of goods. To be completed by the customer. Required for VAT accounting
- Certificate of completed work – confirms the compliance of the services performed with the terms of the contract
- Advance report – confirms the expenditure of the advance, its balances or overspending. So that you can write it off later
Distribution centers greatly simplify logistics
At the beginning, we mentioned that there is another supply scheme - when suppliers bring goods to the distribution center of a retail chain. The distribution center itself calculates the safe flow both at home and in its stores. It has its own employees, its own special equipment.
In stores, no one counts anything; the accounting department immediately prepares the documents. A car arrives from the distribution center, and the goods are immediately put on the shelves. This is a single organism.
This approach allows you to reduce prices by almost half, because there is no competition for the shelf, and the cost of advertising and packaging is not included in the price of the product.
Material liability
During the course of the article, a lot was said about the progress of inspections of both documentation and the product itself. Now let's touch on the topic of financial responsibility of persons working in the warehouse.
The financially responsible person is considered to be the employee who accepts the goods at the warehouse, or the person who has received a power of attorney to carry out acceptance. From a legal point of view, such an employee bears full financial responsibility for the products in the warehouse. In the event of theft or damage to property, the employee compensates for losses to the employer in full or in the amount of monthly wages (Article 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
It is important to understand that the employment contract with such an employee must contain a clause on his financial responsibility. This provision is stated either directly in the contract itself or in an additional agreement.
Such measures will protect you and your company from losses and unpleasant consequences in the form of a damaged business reputation.
Summarize
What is important is a real connection between the receiving area and those people and information systems (back office, ERP) from which the order is generated. You can work without this, but when you reach a serious level, reception and logistics will be disrupted.
The capacity and area of the receiving area must allow receiving at least a certain amount of goods at the same time. At least a few cars. Accordingly, people and free space are needed there.
- adhere to the delivery schedule;
- provide staff with data collection terminals;
- divide acceptance into areas of responsibility for different employees;
- do not skimp on acceptance;
- introduce electronic document management.
The situations we described are not isolated cases, but a harsh reality for 90 percent of stores.
Unsolved problems together form a big snowball. Sooner or later the lump will turn into an avalanche and cover the entire store. Follow the rules and keep the reception area under control.