Issuance of money on account at any time
Amendments have been made to clause 6.3 of the Procedure for conducting cash transactions. Before the changes were made, issuing money to an employee who did not report on the previous report was fraught with a fine under Art. 15.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
The accountable person was obliged, no later than three working days after the expiration of the period for which the money was issued against the report, to present to the chief accountant an advance report with attached supporting documents. The report was checked by the accounting department and approved by the head of the organization. After this, the final payment was made. At the same time, the issuance of new money on account was possible only if the accountable person fully repaid the debt on the previously received amount.
This rule has now been abolished. The presence of debt on the part of an employee is no longer an obstacle to issuing new sums of money on account. To issue them, it is enough to issue an administrative document. Meanwhile, it is still not recommended for employees to accumulate debts. The fact is that inspectors (IFTS and Social Insurance Fund) can regard such debt as the employee’s income and charge additional insurance premiums and personal income tax on it. Therefore, it is better to repay debts on accountable amounts in a timely manner and without delays.
How can you pay off endless reporting?
Do not set a cash limit
Small enterprises, on the basis of paragraph 10, clause 2 of Bank of the Russian Federation Directive No. 3210-U, have the right not to set a cash limit - and keep as much cash as they want in their cash register and independently decide on the need to deposit it into a current account.
To do this, it is enough to issue an order stating the cancellation (!) of the limit (and not that it is equal to “0”). Without this document, the tax authority will consider the limit to be zero, and any excess of it, even by 1 kopeck, will be recognized as a violation, which should be punished under Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. And then you can “sin” with endless reporting, but still not abuse it!
An entrepreneur can also cancel the limit. But it is much easier for him to do otherwise: at the end of each working day he can completely reset the cash balance in the cash register, taking it for personal needs . And this is not prohibited. Moreover, there are no restrictions on the amount, but only on the condition that the cash order will indicate “for personal needs.”
Draw up an interest-free loan agreement
You can, for example, draw up an interest-free loan agreement. This option is only suitable for organizations . This operation will allow you to close the debt on accountable amounts of the head of the company.
But there are some disadvantages:
- With an interest-free loan, an employee receives a material benefit in the form of savings on interest (clause 1, clause 1, Article 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And this is subject to 35% personal income tax;
- To avoid material gain, you will need to set interest on the loan. But then the company will have taxable income;
- Moreover, a loan will only delay the solution to the problem with endless reporting - after all, the loan will still need to be repaid someday.
It is worth recalling that, according to Directive of the Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3073-U, loans can be issued only from those funds that were withdrawn from the current account for this purpose. Therefore, in order not to pay extra money, they only make records on paper in the form of an offset:
D account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” subaccount “Provided loans” Account. 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” - the debt on accountable funds has been covered by a loan agreement executed with the debtor.
In fact, the debt on the accountable amount simply changes its form. But first, the accountable amount must be recognized as a debt by the enterprise and the debtor himself. To do this, you should draw up a reconciliation report and sign it.
In addition, the employee's written consent to set off between obligations will be required. After all, there was no actual receipt of the loan, just as there was no deposit of it into the enterprise’s cash register to pay off the debt under another obligation.
And as soon as the debt on accountable funds is closed, you should not be afraid of inflating the paperwork: you need to make another act of reconciliation with the closed debt on account 71, which the debtor must sign. In addition, with the resumption of endless reporting, it is worth waiting until the loan is closed.
Recognize the debt of the accountable person
There is another option for resetting the endless reporting: the organization can recognize the debt of the accountable person and claim it in writing. In this case, the accountable person himself must agree with this debt and enter into an agreement with the company on the gradual repayment of this debt from his salary.
Moreover, Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows this to be done. In this case, it is even possible to establish an installment plan for repaying the debt if there is agreement between the debtor and the organization.
What does this give? First, it makes perpetual reporting safe because it is officially recognized as debt. Secondly, this amount is gradually returned to the enterprise and is not subject to any taxes or contributions.
But it’s not worth issuing an endless report again until the previous “debt” is repaid. In addition, the reporting person will have to accept some losses from his earnings.
Or you can do it differently: forgive the debt and write it off. But then the reporting person will have taxable personal income tax in the amount of the entire endless sub-account that is registered with him. And from this entire amount you will have to collect 13% personal income tax (clause 1 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, insurance premiums will have to be charged on the amount of debt forgiven by the enterprise (letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated May 17, 2010 No. 1212–19).
In addition, the organization will not be able to:
- recognize as hopeless;
- and write it off as non-operating expenses!
Conclude a lease agreement for employee property
You can draw up a lease agreement for the employee’s property, so that later “on paper” or actually pay off the endless sub-account using this money. Rent will be subject to 13% personal income tax, but not insurance premiums. Moreover, these payments will go to the expenses of the enterprise.
But it is only necessary that the property be available, transferred by deed to the enterprise and accepted by it for off-balance sheet accounting in account 001 “Leased fixed assets”, and the rental amount should not exceed the current market one.
Rent payments will allow you to gradually close the endless reporting:
D sch. 001 – property rented from an employee has been accepted for off-balance sheet accounting;
D sch. 26 “General business expenses” Account 73, subaccount “Rent of employee property” - reflects monthly rent accruals (if the property is rented from the head of the company),
or
D sch. 97 “Future expenses” To account 73, subaccount “Rent of employee property” - reflects the annual rent. This amount will then be written off monthly as expenses in the amount of 1/12;
D account 73, subaccount “Rental of employee property” Account. 51 “Current accounts”, 50 “Cash” - if actual payments are made. But you need to remember: if real estate is rented from an employee, then you can pay under this agreement in cash only if it is withdrawn from the current account. Not from cash proceeds !
And then from this money the debt is repaid for accountable amounts, issued by a receipt order with the wording “Debt repayment for accountable funds.” And if rental payments and debt are immediately offset against accountable amounts, bypassing the cash register and current account, then the following posting is made monthly:
D account 73 subaccount “Rental of employee property” Account. 71 “Settlements with accountable persons.”
In this case, it will not be superfluous to periodically draw up and sign with the debtor a reconciliation report for account 71, which will reflect the gradual repayment of the accountable amount.
Issuance of money on account without statements
Amendments have been made to clause 6.3 of the Procedure for conducting cash transactions. Previously, the issuance of money on account (for expenses related to the activities of an organization or individual entrepreneur) was carried out strictly on the basis of an application from an employee. For example, in order to purchase office supplies or equipment for a company, an employee had to write an application in any form. The application must contain a record of the amount of cash, the period for which it is issued, as well as the signature of the head of the organization.
Now an application for the issuance of accountable amounts is not required. Money can be given to an employee from the cash register, or transferred to his “salary” card on the basis of an administrative document. The Central Bank does not specify what such a document is. Accordingly, money can be issued based on any order of the organization’s management. For example, an order from a director to send an employee on a business trip. At the same time, as before, employees will be able to receive accountable money based on their application. The amendments leave this possibility.
Didn't return the report on time - pay personal income tax
Accountable amounts not returned by the employee on time are reflected as his debt to the company. This debt may be attributed to the employee before the expiration of the statute of limitations in accordance with Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. They are not the employee’s income and are not subject to personal income tax, which a company can withhold only in two cases:
- if it forgives the employee’s debt for unrepaid amounts;
- if the statute of limitations for debt collection has expired.
But if a subordinate does not return the unspent account for a long time, does not provide accounting documents confirming expenses, and the company does not take any action to collect the debt, then with a high degree of probability the tax authorities will recognize this debt as the employee’s income and charge personal income tax.
An example of this is the latest ruling of the Supreme Court, which stated: if there are no documents to confirm expenses on the issued report, then personal income tax must be withheld from unaccountable amounts (determination dated February 3, 2021 No. 310-ES19-28047).
Personal income tax must be withheld from an unreturned report even from the director
Read more…
Let us add that tax can be charged on an unreturned report no earlier than the limitation period of three years has expired (letter from the Federal Tax Service of the Moscow Region dated September 14, 2021 No. 16-10/).
Registration of the cash book by an authorized person
Amendments are made to paragraph. 3 clause 4.6 Procedure for conducting cash transactions. In accordance with the previously existing procedure, all entries in the cash book were made strictly by the cashier. The cashier made entries in the book for each incoming and outgoing cash order issued for cash received and issued.
Now the circle of people who can fill out cash books has been significantly expanded. In fact, any authorized employee of the organization can keep books. To do this, you will need to issue an appropriate order or order authorizing the employee to make entries in the book.
BUKH.1S is now in the Telegram messenger! You can join the channel
via the link: https://t.me/buhru (or type
@buhru
in the search bar in Telegram).
Refund without order
Amendments are being made to clause 4.1 of the Procedure for conducting cash transactions. Before the changes, the issuance of cash from the cash register, for example, when returning goods by the buyer, was carried out using cash receipts. For each amount returned to the buyer, the organization was obliged to draw up a debit order (clause 6 of Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014).
Now in such cases there is no need to draw up separate expense orders. According to the amendments, all orders can be issued upon completion of cash transactions. That is, at the end of the work shift based on fiscal documents (cash receipts issued by the online cash register). In other words, to issue money for returned goods, it will be enough to issue a check containing a note about the return (the sign is “return of receipt”).
More responsibilities for a cashier
Amendments are made to paragraph. 4 pp. 4.6 The procedure for conducting cash transactions and concerns changes in the procedure for reconciling the data contained in the cash book.
Previously, at the end of the working day, the cashier was required to verify the data contained in the cash book with the data of cash documents. He was also obliged to display the amount of cash balance in the cash book and sign it. Now the cash book data is verified not only with the data of incoming and outgoing orders, but also with the actual amount of cash in the cash register.
The main document that establishes the rules for issuing funds on account is the Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014 “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions” (hereinafter referred to as the Directive). By order of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 4416-U dated June 19, 2017, significant changes were made to it, which became effective on August 19.
The main innovation: you can draw up an expense cash order not only on the basis of a written application from the accountable person, but also on the basis of an administrative document of the company or individual entrepreneur (subclause 6.3 of the Instructions). In addition, the ban on issuing accountable amounts if the accountable person is in debt has been lifted.
But no one forbids giving employees money on account “the old fashioned way”, based on their written application.
Can they be punished for this?
First of all, it is worth recalling that paragraph 1 of Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation punishes an ordinary organization only for:
- for cash settlements with other organizations or entrepreneurs in amounts exceeding those established by the Directive of the Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3073-U dated 07.1013. cash payment limit – i.e. 100 thousand rubles (in Russian currency) and an amount equivalent to 100 thousand rubles if payments are made in foreign currency. It should be borne in mind that this limit applies to settlements under any civil contracts concluded between organizations and (or) entrepreneurs;
- for complete or partial failure to receive cash to the cash register, any money, not just revenue;
- for violating the procedure for storing available funds. According to paragraph 7, clause 2 of Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014. free cash means cash that exceeds the cash limit established by the enterprise and is actually in the cash register. And such funds should only be stored in a bank account;
- for the accumulation of cash in the cash register in excess of the cash limit established at the enterprise. The exception is the accumulation of funds on days when salaries, scholarships and other remunerations are paid that are included in the wage fund (according to the methodology used to fill out statistical observation forms), and when social funds are paid. On these days, when paragraph 8 of clause 2 of Directive No. 3210-U is allowed to exceed its limit at the cash desk, they also include the day of withdrawal of cash from the bank account to make the specified payments. In addition, it is allowed to store money in excess of the limit in the cash register on non-working holidays and weekends, but only if organizations and entrepreneurs conduct cash transactions on these days.
Among the above violations, there is no liability for violations of the rules for issuing accountable funds .
In particular, this is confirmed by the conclusions made in the Resolution dated March 26, 2014 of the Seventh Arbitration Court of Appeal of the Russian Federation in case No. A67-5875/2013.
The essence of the issue considered in this Resolution was that the enterprise periodically issued, on account to its manager, funds that exceeded the established cash limit. The head of the company did not provide a report on the accountable funds he had previously received.
The tax inspectorate considered this behavior to fall under Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. But the court expressed the opinion that in the actions of the head of the company there are violations only in the procedure for issuing cash on account, but there are no violations, which are provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, i.e. there is no reason to believe that in this way the enterprise accumulated money in excess of the limit and violated the procedure for storing available funds.
Moreover, the Court concluded that cash is free until it is issued for reporting to an authorized person for the purpose of the company’s activities.
Thus, after these funds are issued for reporting, they lose their “free” status, which means that these amounts are not subject to the obligation to store them in the company’s bank account and the punishment provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation does not apply.
However, it is too early to rejoice . The court in the considered Resolution rejected the tax inspectorate only because it charged a violation in the form of accumulation of excess funds by issuing an endless sub-account, but in fact proved that the enterprise did not have the right to issue money to its manager on account without providing a report on previously issued amounts.
But there are decisions in favor of the tax authority . For example, the Decision of the Moscow City Court dated August 14, 2013 in case No. 7-1920/2013. In this case, an infinite sub-account was also identified, i.e. the head of the company handed over the accountable money to the cashier and immediately received it in a larger amount again on account. These transactions were documented with incoming and outgoing cash documents.
The tax authority concluded that the company was violating the procedure for storing available funds. And the court supported this conclusion, citing the fact that:
- cash issued on account was not spent, including on the needs listed in Directive No. 3073-U of the Bank of Russia;
- the head of the company did not submit advance reports, from which the very fact of spending funds and their intended or inappropriate use would be visible;
- the funds “left” the cash register for a short period of time and were returned in full.
Thus, the head of the company, in the opinion of the court , when registering the excess balance of money as issued on account for business needs, acted fictitiously and actually replaced himself with a credit institution, keeping free funds (i.e., above the limit) at home. As a result, the company and its director were punished on the basis of clause 1 of Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation .
Why aren't entrepreneurs punished for such offenses ? Because they do not allow them: unlike a legal entity, an entrepreneur can write off for his own needs at the end of the day all the cash from the cash register, down to the penny! And he doesn’t need to file endless reports. Moreover, Bank of Russia Directive No. 3073-U does not even provide for a limit when issuing cash to an entrepreneur for personal purposes.
We authorize the issuance
So, supporters of this approach, let’s call them “conservatives,” must obtain a written statement from the employee - addressed to the manager, in any form. The text of the application must reflect the amount of cash and the period of issue.
The manager must agree on the release of money and put his signature and date on the application.
As for the “innovators” who decide to take advantage of the new opportunity provided to them by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, they must issue an administrative document on the issuance of money. The composition of the details of administrative documents and the general requirements for their execution are currently established by “GOST R 6.30-2003”, adopted and put into effect by Resolution of the State Standard of the Russian Federation dated 03.03.2003 No. 65-st. It is this document that the Bank of Russia recommends to be guided by. The administrative document must contain the following information:
- last name, first name and patronymic (if any) of the accountable person;
- amounts of cash;
- the period for which they are issued;
- manager's signature;
- date and registration number of the document.
We give out money
After receiving the application, issue a cash receipt order. The form of the order (KO-2) was approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88.
The order can be issued by the chief or “ordinary” accountant, and in their absence - by the manager (subclauses 4.2, 4.3, clause 4 of the Instructions). The cashier checks the order. If there are no errors, then after presenting a passport or other identification document, the employee is given cash (subclause 6.1, clause 6 of the Directions).
The cash order is signed by the recipient and the cashier. If the company does not have a cashier (an employee whose job responsibilities include conducting cash transactions), then the manager can sign the cash order and issue cash (clause 4 of the Directions).
According to the issued order, an entry is made in the cash book.
Understanding the employee's report
We are patient and wait for the employee to report for what he received. If the money is issued for a business trip, then the advance report must be submitted by the employee within three working days from the date (subclause 6.3, clause 6 of the Directive, clause 26 “Regulations on business trips”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 No. 749) :
- expiration of the period for which the money was issued;
- returning from a business trip;
- returning to work (for example, after vacation or illness, if the deadline for issuing money fell during this period).
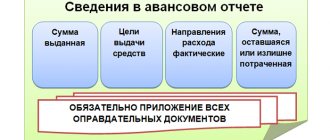
Documents confirming expenses (for example, sales and cash receipts) must be attached to the report. The advance report is presented to the chief accountant or accountant, and in their absence - to the manager.
The person to whom the advance report is presented checks the intended use of funds, the availability of supporting documents, the correctness of their execution and the calculation of amounts. After this, the expense report is approved by the manager.
The period during which the verification of this report, its approval and final payment is carried out is established by the head (subclause 6.3, clause 6 of the Directions).
After approval of the advance report, the accountable amounts are written off.
However, it happens that the employee spent less or more money than he received on the report. If less is spent, then in order to accept the remaining money, the chief accountant should draw up and sign a cash receipt order, which, in particular, reflects the amount of money being returned.
If more is spent, after approval of the advance report by the head of the organization, the overexpenditure should be returned to the employee using an expense cash order, the details of which are entered in the advance report.
If the advance report is not approved (for example, due to the lack of supporting documents) or the balance is not returned, then the money can be
The maximum period for issuing money on account
- is it set in 2021? The procedure for issuing and returning reporting funds directly depends on the answer to this question. Let's figure out what regulatory documents and regulatory authorities say about this in our article.
How to take into account cash payments with accountable persons?
The issuance of cash on account and the acceptance of expenses incurred from it are reflected in accounting (budget) accounting as follows:
| Debit | Credit | |
| Cash issued against cash register report | 0 208 00 567 | 0 201 34 610 off-balance sheet account 18 |
| Expenses were accepted for accounting based on the approved advance report | 0 401 20 000 0 109 00 000 0 105 00 000 0 106 00 000 | 0 208 00 667 |
| The unspent balance of the accountable amount was returned to the cashier | 0 201 34 510 off-balance sheet account 18 | 0 208 00 667 |
| Overexpenditure on the advance report was reimbursed from the cash register | 0 208 00 567 | 0 201 34 610 off-balance sheet account 18 |
Example 1.
An employee of an autonomous cultural institution was given cash from the cash register for travel expenses:
- daily allowance – 700 rub. (7 days x 100 rub.);
- accommodation – 4,900 rubles;
- travel – 3,000 rubles.
Upon returning from a business trip, the employee completed an advance report, attaching to it an act of accommodation services provided and a cash receipt in the amount of 4,900 rubles, as well as travel tickets in the amount of 2,700 rubles, which were also accepted as confirmation of the actual period of his stay in business trip (7 days). Unspent cash balance in the amount of RUB 300. entered into the cash register.
According to the accounting policy, travel expenses are included in general business expenses.
Transactions are carried out within the framework of income-generating activities.
In the accounting records of an autonomous institution, these transactions will be reflected as follows:
| Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | |
| Cash issued from the cash register for travel expenses: | |||
| – daily allowance | 2 208 12 567 | 2 201 34 610 off-balance sheet account 18 (code 212 KOSGU) | |
| - accommodation | 2 208 26 567 | 2 201 34 610 off-balance sheet account 18 (code 226 KOSGU) | 4 900 |
| – travel | 2 208 26 567 | 2 201 34 610 off-balance sheet account 18 (code 226 KOSGU) | 3 000 |
| Travel expenses were accrued based on the approved advance report: | |||
| – daily allowance | 2 109 80 212 | 2 208 12 667 | |
| - accommodation | 2 109 80 226 | 2 208 26 667 | 4 900 |
| – travel | 2 109 80 226 | 2 208 26 667 | 2 700 |
| The unspent balance of cash (3,000 – 2,700) rubles was returned to the cash desk. | 2 201 34 510 off-balance sheet account 18 (code 226 KOSGU) | 2 208 26 667 |
What deadlines for accountable funds are established by law?
The procedure for issuing cash on account is fixed in clause 6.3 of the Bank of Russia directive “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions by legal entities and the simplified procedure for conducting cash transactions by individual entrepreneurs and small businesses” dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U.
Moreover, this procedure clearly establishes a single period - the one during which the reporting employee is obliged to account for the funds received from the employer. It is equal to 3 days, counted from the last day of the period for which the accountable cash was issued.
IMPORTANT! The 3-day rule must be observed by absolutely all employees of the company, and the manager is no exception (even if he is the owner of the company).
For information on what a reporting director’s statement looks like, see the article
.
Separate mention should be made of cases of sending employees on a business trip. In this case, 3 days are counted from the date of return of the business traveler (clause 26 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On the peculiarities of sending employees on business trips” dated October 13, 2008 No. 749).
NOTE! This period cannot be increased.
Our publication will help you prepare an advance report.
Neither instruction No. 3210-U nor other regulatory sources establish any more deadlines. Does this mean that money issued on account can be returned at any time?
What operations may be of interest to controllers
Despite the fact that there is no limit on the amounts issued for reporting, unlimited and unreasonable reporting in 2019-2020 may attract the attention of regulatory authorities. First of all, when monitoring the correctness of reporting, inspectors will be interested in the following operations:
- Issuance and return of funds from the account, made on successive days (as a rule, this is done in order to hide excess cash in the cash register when the established limit is exceeded).
To learn how the cash limit is determined, read the publication “How to calculate the cash balance limit?”.
- Issuing amounts for a long period (several months, several years).
- Issuance of an amount significantly exceeding the average monthly expenses of the company.
- Issuance of an amount significantly exceeding the amount of expenses for which it was issued.
- Direction of amounts issued to the account for inappropriate use.
IMPORTANT! The auditors may ignore a single performance of such transactions, since their implementation is not prohibited. However, their repeated repetition, and especially systematic ones, will definitely arouse suspicion and become a reason for close study and identification of the true essence of these operations.
Should I set a deadline for issuing money under the report?
Any answer to this question has its positive and negative consequences. It is worth understanding that by determining a specific deadline for issuing accountable money, the company will be obliged to comply with it. Otherwise, there is a high chance of filing claims from tax authorities for failure to receive funds to the cash register. The fine for this violation is 4–5 thousand rubles. for officials and 40–50 thousand rubles. for legal entities (clause 1 of article 15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, such claims cannot be considered absolutely justified, since such a violation as untimely return of accountable funds is directly contained in Art. 15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation is not provided for. However, such a risk exists and must be kept in mind.
Read more about possible penalties for violations when handling cash in the article
.
In turn, if the deadline for the return of accountable cash is not recorded anywhere, then the controllers cannot have any claims for its untimely return. True, in this case, problems with the tax authorities are not excluded. Thus, in letter No. 04-1-02/704 of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 24, 2005, tax officials expressed the opinion that if the deadline for issuing cash on account is not specified, such a period is considered equal to 1 day. However, they do not justify their position with any legal acts.
In connection with the above, making a decision at the level of local internal corporate acts on establishing (or not establishing) deadlines for issuing reports is based on an assessment of one’s own economic situation and possible risks.
Find out whether it is necessary to fill out an application to receive accountable amounts.
How to draw up an order on the timing of the issuance of accountable funds?
Typically, an order is not drawn up separately to set deadlines, but to describe the entire procedure for issuing accountable amounts. In such an order it is necessary to indicate:
- the amount of amounts issued;
IMPORTANT! The maximum amount of accountable amounts to be issued is also not established by law. This, as well as the deadline for issuing money on account, is determined by business entities independently.
- the terms for which funds are issued to accountants;
- a list of employees entitled to receive accountable money;
- description of the procedure for submitting advance reports.
It should be borne in mind that the deadlines for which funds will be issued to accountants may be the same for all employees of the company, or set for each of them individually.
You can download an approximate example of an order on accountable persons from this link:
IMPORTANT! All organizational issues relating to the procedure for issuing and returning accountable funds should be fixed only in orders, but not in accounting policies. Otherwise, changing this procedure if necessary will be problematic (Clause 6, Article 8 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
Is it possible to issue money on account for long periods?
The law does not prohibit giving money to accountants not only for a few days or months, but also for several years. At the same time, it is worth understanding that excessively long periods of time for funds to remain with the accountable must be justified by production necessity, and the funds themselves must be spent on targeted expenses. Otherwise, there may be a risk that regulatory authorities will reclassify accountable amounts as income or an interest-free loan, which entails the need to withhold personal income tax from income (or material benefits).
Such requalification can only be challenged in court. At the same time, arbitration practice on this issue is ambiguous and largely depends on the conditions accompanying a particular situation involving accountable funds.
IMPORTANT! Pay attention to the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 14, 2013 No. 03-04-06/4-5, in which the department reports that until the management approves the advance report, it is impossible to unambiguously determine whether the employee will have income subject to personal income tax and what the amount of this income will be .
Is it possible to issue accountable amounts in 2021 if there is no report on previous amounts received under account, find out from the article
.
Results
Neither the minimum nor maximum terms for issuing money to accountables are established by law. Business entities have the right to determine them independently. These deadlines can be recorded in the local acts of the enterprise. However, the law does not oblige the enterprise to draw up such administrative documents.
For the legislative framework relating to the sphere of settlements with accountables, see the article
.
What is the issuance of money under reporting, and what is the maximum amount that can be issued to an employee under reporting in 2021? What reasons could there be for this, and what does the legislation say about accountable funds?
No organization can do without issuing funds to employees for various purposes. These could be business trips or entertainment expenses.
But in order to control the finances of the enterprise, it is necessary to keep correct records of expenses. All this is the responsibility of the accountant.
Moreover, in 2021, new rules for issuing funds on account began to take effect, which you should be aware of.
Required information
You should be aware that some changes have begun to take effect in 2021. For example, now accountable funds can be easily transferred to a bank card ().
To do this, the employee must specify in his application that the money should be transferred to his salary card.
Accountants often make a fatal mistake by not filing a refund to the company's cash desk. Even more often, employees simply do not return funds out of ignorance or on purpose.
To be on the safe side, it is better to include this clause in or oblige employees to provide.
In some cases, its absence can have serious consequences for the company. The report must be accompanied by documents that can confirm the expenses incurred (checks, etc.).
An accountant or other authorized person checks the report and confirms that the funds were spent without violations.
The form of this document is approved by law and such calculations cannot be made without it ().
Therefore, the issuance of money from the cash register of an enterprise may be regarded by the tax authorities as a serious violation of the procedure. What to do if the employee has not returned the remaining money?
In this situation, there is only one way out - withholding a certain amount from his salary. All this happens exclusively legally ().
But you should know that you must adhere to the following rules:
- obtain the employee’s consent to deduct funds from wages ();
- no later than a month later, issue a corresponding order;
- Be sure to familiarize the employee with this document.
If he does not give his consent to deduct the debt from his salary, this issue should be resolved in court. Also, do not delay with the order, otherwise you will also have to go to court.
According to the Labor Code (), a one-time deduction from wages should not exceed 20%. What if the employee quit and did not repay the debt?
The law establishes that the statute of limitations is 3 years, during which the organization can go to court ().
If this period has expired, then the company will have to write off this money. According to this amount, this amount should be included in the so-called non-operating expenses.
Often accountants insist that the employee sign a special document.
It is believed that such a document can guarantee the company a full refund. In fact, when issuing money on account, this procedure is completely useless. Money can still be withheld from wages.
The list of employees with whom a liability agreement should really be concluded is contained in the appendix to.
Definitions
Accountable funds are money that is issued to an accountable person for expenses related to the activities of the enterprise.
These expenses mean:
- economic needs;
- business trips;
- entertainment expenses.
An accountable person is an employee of the enterprise who receives money for certain expenses. Previously, funds could only be issued to full-time employees. True, in some cases, accounting departments of organizations circumvented this rule.
Therefore, from 2021, organizations are allowed to issue money to employees with whom they are concluded (clause 5 of the Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2021).
By receiving funds from the organization for implementation or other needs, the accountable person assumes certain obligations.
First of all, they relate to spending money according to its intended purpose. This must be documented. Failure to return money or inappropriate spending leads to serious consequences.
Grounds for extradition
Naturally, the organization keeps track of all expenses, including unplanned ones. And everything must be documented.
Therefore, the basis for issuing money is the employee’s statement or (when crediting money to the card).
It is first necessary to check whether the employee has any debt for funds previously issued to him. If it is available, then funds are not issued to such an employee.
In the case where there are no debts, the company's accountant issues and disburses the money. The form of the application is not established by law, so it is written in any form.
Most often this document looks like this:
If the manager of the enterprise needs the funds, he is also obliged to write a statement.
This is necessary even if the general director of the company requests the release of funds. By following the established procedure, you can avoid problems with the tax authorities in the future.
Legal grounds
The legislation of the Russian Federation controls the issuance of funds and reports using.
In addition, the reporting procedure for issuing money is regulated.
To whom can accountable amounts be issued?
Accountable persons are individuals who are given funds from the cash register or using bank cards to cover expenses related to the operation of the institution.
The following may be accountable:
- any employees of the institution;
- individuals with whom the institution has entered into a civil contract, for example, performers, contractors (Letter of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated October 2, 2014 No. 29-R-R-6/7859);
- individuals engaged by institutions to perform certain powers without concluding employment contracts or civil law contracts with them, for example, students of educational institutions, accompanying persons.
The list of accountable persons can be fixed within the accounting policy of the institution.
It is not allowed to issue funds to accountable persons who have overdue debts on previous advances (clause 214 of Instruction No. 157n).
How much money can be issued for reporting in 2021
In the Russian Federation, all payments in national currency that are carried out within the framework of one agreement should not exceed 100 thousand rubles.
And it is believed that this limit cannot be exceeded. But there are also some nuances. Many people are still interested in the question of what is the maximum amount that can be given to an employee reporting more than 100,000 rubles?
The fact is that this limit on expenses is established for settlements between organizations and individual entrepreneurs. But it does not apply to settlements with individuals, who in this case are employees of the enterprise.
This includes wages, social benefits, personal needs of the head of the organization and the issuance of funds on account.
Video: settlements with accountable persons
The main thing is that the employee does not exceed the limit of 100 thousand when making payments with other companies or private entrepreneurs.
This means that this amount is not limited by the legislation of the Russian Federation. Therefore, the maximum amount of funds issued to the account is established by the head of the organization.
The same applies to what amount can be reported to the director for 2019. It all depends on the financial capabilities of the enterprise.
Who sets the limit?
If in a budget organization
Receiving funds on account in budgetary organizations is no different from this procedure in private organizations.
If the money goes to travel expenses, then their size is determined either by or by the relevant regulatory act ().
The amount is also issued solely on the basis of the employee’s application. You should definitely make sure that the employee has accounted for previous expenditures of budget money.
The only thing that an employee needs to remember is that when making payments on behalf of an organization with private entrepreneurs and legal entities, the limit of 100 thousand rubles cannot be exceeded.
Responsibility for violations
The organization is obliged to bear responsibility for violations of any of the paragraphs of Regulation No. 373. It consists of imposing the following fines on the company:
Issuing money on account is an important area of accounting, without which no enterprise can do.
From time to time, various changes are made to these rules by law that you need to be aware of.
Otherwise, any, even the smallest mistake, can lead to a violation of the law and subsequent liability.
If there is a need to give employees money on account, you should understand the intricacies of this financial procedure. This is necessary in order to correctly reflect it and avoid claims from the tax service. Moreover, sometimes you have to give money in this way to persons who are not employees of the enterprise. In our article we will talk in detail about who can give money on account.
Payments made by notaries through accountants
Let's consider the situation. The employer-notary plans to issue cash on account to the employee for the purchase of a computer worth more than 110,000 rubles. Does he have the right to do this and can the seller refuse to accept the full amount in cash to the notary office employee?
In this case, there will be no restrictions on the amount of amounts - neither on the amount reported (since there are no such restrictions in principle), nor on the amount paid. The fact is that notarial activity is recognized as a legal activity performed on behalf of the state and is not recognized as entrepreneurial, since it is not accompanied by the extraction of profit (Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 1998 No. 15-P).
At the same time, privately practicing notaries are equated to entrepreneurs only in tax legal relations (Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In other cases (including those related to cash payments), notaries are not subject to the rules established for individual entrepreneurs (letter of the Federal Tax Service for Moscow dated 04/08/2011 No. 17-26/034104). Therefore, an employee of a notary office who has received cash on account from his employer can pay in full with it, even if the purchase price is more than 100,000 rubles.
Funds issued for reporting always attract increased attention from tax authorities. That is why it is very important to correctly prepare all documents and mutual settlements with accountable persons. ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to do this. Get trial access to the K+ system and go to the Guide for free.
Why issue
The disbursement of funds under the report refers to the transfer of money from an organization to an employee or other person, which must be spent on specific purposes related to the needs of the company. Russian legislation does not limit the amount of funds that can be issued. Everything here is at the discretion of the head of the company. Finance can be issued either in cash or non-cash. This monetary transaction is regulated by Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-11-11/42288. It sets out the procedure for conducting cash transactions. And here it is indicated for what needs the enterprise can give money:
- Economic needs of the company.
- For branches of the company that do not have their own balance sheet.
Money for production needs for non-employees
The literal interpretation of the provisions of clause 6.3 of the Russian Instructions deserves special attention, from which it follows that money is issued to an employee of the enterprise on account. The Bank of Russia did not provide for the possibility of providing financial resources to another person who is not in an employment relationship with the company.
The Ministry of Finance of Russia, by order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000, approved the Instructions for the application of the chart of accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations. From the contents of this Instruction it follows that the accountable persons are company employees. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation did not provide for the possibility of issuing money for production needs to other persons.
It should be noted that the provisions of the above-mentioned regulations do not contain a direct prohibition on the issuance of money for production needs to other persons who are not in labor relations with enterprises.
The same Instructions directly provide for the execution of transactions not specified in the explanations for accounts 60 - 75, using account 76. The issuance of funds on account to persons who are not employees should be carried out using account 76.
The position of the Ministry of Finance of Russia, set out in letter dated July 2, 2012 No. 02-06-10/2476, deserves attention. According to the logic of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, each enterprise independently resolves the issue of the possibility of issuing money for production needs to persons who are not employees of the company.
In the opinion of the Ministry, it is advisable to provide for the procedure for providing and accounting for such funds in the accounting policies of the organization.
Issue features
The company has the right to issue money on account not only to its employees, but also to other persons with whom a civil law agreement has been concluded. But the status of these categories is different, which the company’s management should remember. If your employee working under an employment contract can be sent on a business trip with the payment of daily allowance or accountable money from the salary, then such things are not done with those who work under a civil contract. To avoid confusion, it is best not to give money to the employee on account, but to use the execution of the concluded contract. Thus, the basis for extradition may be a person’s application for reimbursement of expenses spent on carrying out the organization’s instructions.
An employee working under a civil contract cannot be sent on a business trip with the payment of daily allowance or withholding accountable money from wages.
Officially, it is forbidden to issue money to non-employees on account, as stated in the Bank of Russia instruction on conducting cash transactions No. 3210-U. According to this document, the contractor is also an employee of the company, and therefore funds can be transferred or issued to him in cash or non-cash form. For example, a contractor may order materials that he will then use to renovate the organization’s premises.
Local acts of the enterprise can establish the procedure for issuing accountable amounts to contractors. In addition, this point must be spelled out in detail in contracts with the contractor. It is worth remembering that the instructions of the Bank of the Russian Federation regarding cash transactions only state that cash can be issued for reporting purposes. Therefore, if a company needs to issue money by non-cash method (), it is necessary to record this procedure in the local acts of the company.
What does the tax office see in this?
As soon as, when checking the procedure for conducting cash transactions, the tax inspectorate sees the issuance of funds to the head of the company for reporting and the return of this money in a day or two to the cash desk of the enterprise, then it is considered that the enterprise thus stores excess cash.
Tax authorities base their arguments on the basis that:
- money is not spent at all, including on the needs of the enterprise;
- the advance report is not submitted;
- in the application for receiving funds from the cash register (if there is such an application at all) a fictitious purpose is indicated. And the application itself is needed only for formal compliance with the requirements of the Directive of the Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U.
And even if a zero advance report is submitted, the tax authority will focus on the absence of actual expenditure of accountable money . It is this fact that will serve as the main evidence that the actions of the head of the company have replaced the obligation of the enterprise to keep excess money in a bank account.
Especially if several tens or hundreds of thousands of rubles are “issued” for the report, and this amount increases from time to time. As a result, it is immediately clear that the entire procedure for the return and subsequent issuance of cash for reporting is fictitious!
Moreover, the tax authority may question the actual availability of these funds . After all, very often, in order to avoid paying extra taxes on the income of the founders, the payment of dividends to them is hidden behind the issuance of endless reporting.
In addition, during an on-site audit, tax authorities may consider substantial accountable amounts that the head of the company does not spend at all as income, with all the ensuing problems. Those. calculate personal income tax on this amount! Moreover, there is judicial practice that favors the tax authorities.
Representatives of extra-budgetary funds can do the same when conducting their audit - charge insurance premiums for these amounts.
How to avoid such problems? First of all, you need to find a way to reset the existing infinite sub-report and find a way to avoid it altogether, using completely different operations.