Home / About the company / Articles / Labor protection at the enterprise: legal requirements and organizational features
Article 212 of Chapter 34 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation requires employers to ensure safe work, that is, the preservation of the life and health of subordinates. The regulation also obliges employees to comply with established rules. What should be done to create optimal working conditions at the enterprise, what measures should be taken and who should be appointed responsible for compliance with labor safety standards?
What is labor protection?
Labor protection is a regulation, adherence to which should provide citizens with the best working conditions. In short, its main goal is to ensure safety for the life and health of performers at work .
The concept of OT includes the following provisions:
- providing working conditions that minimize the negative impact on the employee’s body;
- identifying the causes of possible harm that contribute to occupational diseases;
- identifying unsafe practices that increase the risk of injury;
- creating relatively favorable working conditions, minimizing the influence of harmful factors to acceptable limits;
- equipping the employee’s place of work to enable him to perform his job functions safely;
- issuing personal protective equipment to performers;
- pursuing policies aimed at improving working conditions;
- compliance with standards governing production safety;
- compliance with the rules established by the state regarding conditions in places intended for work;
- assessing risks and applying measures to reduce them.
Thus, OSH is aimed at complying with the measures taken for the safety and well-being of workers and provides guarantees in unforeseen adverse cases.
Watch the video about occupational safety:
Legislative regulation
Processes related to occupational safety are set out in section 10 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- Art. 211 obliges all citizens and firms to comply with state requirements, regardless of the field of activity;
- Art. 212 regulates a set of measures aimed at obtaining the necessary conditions that must be fulfilled by the employer. Including the creation of internal Regulations on Labor Protection;
- Art. 213 speaks of mandatory preliminary and routine medical examinations;
- Art. 214 obliges the contractor to strictly comply with labor protection rules;
- Art. 217 provides for the introduction into the staff of an employee or department responsible for occupational safety if the number of employees exceeds 50 people;
- Art. 219 gives the employee the right to work in conditions created taking into account all required standards. For example: a properly equipped workplace; payment of insurance premiums in case of illnesses and injuries; education; obtaining protective equipment; preservation of earnings during absence due to medical examination.
- Art. 220 – the employer cannot require work to be performed if the necessary protective measures have not been taken. Downtime in such a situation is paid;
- Art. 225 - all employees of the company, including directors, must familiarize themselves with the safety instructions;
- Order of the Ministry of Labor No. 438n of 2021, GOST 12.0.230-2007 established a standard form of the Regulation on labor protection. This is an internal act drawn up in the company. It contains: information about sources of finance; training plan with number of hours; list of planned measures; action plan.
Here you can find a sample of a standard Regulation on labor protection at an enterprise.
Event Registration
All planned and implemented labor safety actions should be carefully documented, otherwise the company will face proceedings and fines during the next visit of inspectors. To avoid problems, it is important to organize a systematic and optimized document flow. It is necessary to develop and publish regulations, instructions and orders, programs and lists, maintain journals and personal cards. The list is not closed; you can use any other documents depending on the nature of the company’s activities and needs.
Requirements
Labor safety requirements must be observed in any company, regardless of its form of organization. Thus, an employee has the right to safe work in an LLC, an individual entrepreneur, and a large enterprise.
Work certification
According to the Law “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions” No. 426 - Federal Law dated December 28, 2013, a procedure for declaring work places . Certification of occupational safety work was abolished with the advent of the new Law. Now a certificate is issued for the fact that the place of work meets accepted standards.
Conducted by specialized companies after completion of workplace certification. The certificate is issued for three years if there are no violations. If there are, then only after they have been eliminated. In the next three years, the enterprise carries out scheduled monitoring by the same company .
From this article you can learn in detail about the certification of workplaces in the organization.
If violations are found during the inspection, the certificate is suspended until corrected. If no measures are taken, the document will be cancelled. Lack of a certificate is an administrative offense. Responsibility is imposed under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Differences in employee number requirements
The number of performers that must be kept on staff for labor protection is determined based on the norms of Resolution of the Ministry of Labor No. 10 of January 22, 2001.
Requirements for companies regarding the number of OT employees are different. They depend on the total number of employees, the level of danger, as well as the nuances of the company’s activities.
For example, if a company involves toxic or explosive substances in its production, the safety department may be staffed with a large number of employees.
The dependence on the total number of employees is manifested in the following ratio:
- for companies with up to 20 employees , it is permissible to hire a part-time employee from another company;
- from 20 to 50 people - the work of the service can be done by the director or his deputy;
- for a company with a staff of over 50 , an on-staff employee is required. Engineering and technical education is required.
- if the number is more than 700, you need to organize an OT bureau of 3-5 people.
Service structure
Management makes a conclusion about what the structure will be based on the above factors. The feasibility of maintaining a department depends mainly on the total number of personnel.
Functions in this area can be performed:
- a third-party employee, including workers under a GPC agreement;
- the director himself or deputy director;
- one employee on staff, possibly part-time;
- department of several employees.
When a decision is made to introduce an entire division - department or bureau, the structure will be as follows:
- director of the firm;
- The head of the department reports to him;
- Ordinary performers of the OT department report to the head of the department.
If the number of employees is no more than 700 people and the production is not associated with hazards or increased risks, it is not practical to maintain a department .
For most companies, one person is enough. Moreover, he will report directly to the director of the enterprise , since the director is responsible for the organization, and he also exercises control over the activities of the labor protection service.
Intersectoral headcount standards
The act approved by the resolution of the Ministry of Labor dated January 22, 2001 No. 10 serves to resolve the following issues:
- determining the optimal number of participants and type of structure;
- division of tasks between performers.
This recommendation for organizing the work of the OT service should be followed by all companies.
The standards cover the following areas of the service:
- control;
- organizing actions to prevent accidents and illnesses that occur at the place of work; familiarization with instructions and other types of training; testing employee positions for suitability; testing employee knowledge;
- drawing up an action plan;
- control : compliance with the rules of conditions at work places; for employees to follow the law;
- accounting and proceedings in unforeseen situations.
Personnel training procedure
This important stage in the prevention of industrial injuries includes three main aspects:
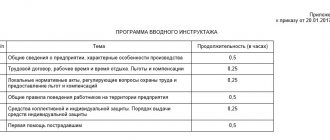
Occupational safety briefing
When starting a job or transferring from another production unit, each employee must undergo on-the-job training. Students undergoing internships and seconded specialists from other organizations receive the same training.
Initial instruction is carried out according to a program that details information about the technological process and hazardous production factors. In addition, requirements for the prevention of electrical injuries and occupational diseases are provided.
Trainees become familiar with the procedure for preparing a workplace for work, investigating accidents, issuing and recording personal protective equipment. Separately, measures are given to prevent industrial injuries, accidents, fires and the sequence of actions in the event of such situations.
A lot depends on the quality of the initial briefing, so it should be carried out by the immediate supervisors (producers) of the work (foreman, foreman, teacher, etc.), who have undergone occupational safety training in the prescribed manner and tested their knowledge of occupational safety requirements.
Unscheduled briefing
By decision of the employer, extraordinary instruction is carried out in the following situations:
- When introducing new or changing existing regulations or legislative acts in the field of labor protection.
- If technological equipment, tools, technologies are replaced that may affect personnel safety.
- In case of violation by workers and students of labor safety requirements, which can lead or have led to injury, accident, explosion or fire, poisoning.
- If production with hazardous working conditions was stopped for 30 days.
Targeted briefing
Targeted instruction is carried out when performing one-time work. They are not related to the direct responsibilities of the employee and represent the following types of activities:
- Unscheduled loading or unloading of materials, equipment, cleaning of the territory, work outside the enterprise.
- Elimination of consequences of disasters, accidents, natural disasters.
- Carrying out special types of work under a permit or other permit. Such instruction is carried out by the head of the department where such work is carried out. All types of instruction are recorded in a special journal.
Organization procedure
Basics of where to start organizing labor protection at an enterprise:
- determine how many employees are needed;
- create a division if more than one employee is needed;
- add to the staffing form the required number of units for the position “labor safety specialist”, one unit for the chief;
- define the terms of reference;
- create job descriptions;
- draw up internal acts;
- resolve the issue of territorial location of the service, equipping it with all the necessary attributes.
The list of documents for each specific enterprise may differ, but approximately it will consist of the following:
- orders on adding department staff positions to the staff;
- order on assignment of functions;
- job descriptions;
- management regulations;
- the procedure for announcing instructions and testing the level of knowledge;
- cards that will display the issued protective equipment;
- regulations governing the work procedure;
- a journal for recording situations that resulted in compensation for harm;
- medical examination schedule.
Sample order on the creation of a labor protection service:
An example of an order on the organization of labor protection work:
Stages of creation
1) Develop internal regulations on labor protection. The local regulatory act should include sections of Order of the Ministry of Labor No. 438 of August 19, 2021; adaptation of the text is possible.
2) Conduct an occupational risk assessment. Performed by occupational safety specialists, the employer or independent experts.
3) Purchase flushing agents, personal protective equipment, special machines and other necessary goods and devices. The list of specific items is determined by the specifics of the enterprise’s activities and the identified negative impact factors.
4) Draw up a schedule for maintaining and inspecting machines, issuing personal protective equipment, and performing scheduled preventive maintenance. The person responsible for each type of work is appointed by order.
5) Organize a special assessment of workplaces.
6) Tell specialists and management about methods and techniques for safe work, conduct briefings and internships, and test knowledge of labor protection requirements.
7) Train staff in first aid skills.
Important: it is advisable to conduct appropriate training with managers and specialists at least every 3 years, and with ordinary employees annually.
 Prepare local regulations on labor protection.
Prepare local regulations on labor protection.
In the future, it is necessary to monitor the proper functioning of the system and compliance with established requirements, as well as timely submit reports to the inspection authorities.
Control system
In accordance with Art. 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation creates a service and manages it by the director of the company. Based on this, it becomes clear to whom the labor protection service reports – the director.
The professional standard is a standard document indicating the functions and requirements for the performer.
He prescribes the following functions to the head of the safety service:
- providing the service with local regulatory documents;
- employee training;
- transfer of information for statistical research;
- implementing measures to minimize the risks of injury and illness;
- monitoring the condition of places intended for work;
- monitoring employee compliance with rules;
- accident investigation;
- distribution of responsibilities within the department and control over how they are performed;
- planning, making proposals to create more favorable conditions on the ground.
Requirements vary depending on the characteristics of the enterprise and the preparation of the performer:
- if the production is hazardous, the future boss is required to undergo industrial safety certification;
- A diploma of higher education in the specialty “Technosphere Safety” is required Its absence is also acceptable, but confirmation of specialized additional training in the field of occupational safety will still be required;
- in the latter case, when taking up a position, an essential criterion will be actual experience of more than 3 years . If you have a higher education, it is possible to get a job without experience.
Public administration
This policy direction is carried out by the Government through lower authorized bodies.
Occupational safety management involves the creation of laws that protect the rights of citizens to favorable working conditions. The main body performing this function is the Ministry of Labor. Its main tasks:
- implementing programs to improve working conditions;
- providing support for activities aimed at enhancing security;
- monitoring the strict implementation of legislative norms.
The Ministry of Labor develops regulations . For example, these:
- the procedure for compliance of ongoing activities with established requirements;
- rules for disclosing instructions and testing employee knowledge;
- list of actions subject to accreditation.
Basic Concepts
Legislation understands labor protection as a system of care for the life and health of enterprise employees when they perform their job duties. It can be considered as an element of labor relations, an institution of labor law or a subjective right of workers.
Occupational safety is designed to solve the main problem - to prevent injuries at work and the occurrence of occupational diseases, as well as to minimize social consequences. Through special measures, each workplace is guaranteed to have low or socially acceptable risk.
Ways to ensure labor protection
1. Legal. Includes a system of state safety standards and means of monitoring their compliance. Events are regulated by the Constitution, Labor Code, legal and by-laws of the Russian Federation.
2. Socio-economic. They are instruments for stimulating bona fide employers by the state. For example, in order to support those who do not violate labor safety requirements and standards, differential tariffs are provided for contributions to compulsory pension and social insurance, the possibility of reimbursement of costs from the social insurance fund, etc.
For reference: the list of expenses that are allowed to be compensated at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund is listed in Order of the Ministry of Labor 580n dated December 10, 2012 (Appendix). In addition, in 2021, in order to prevent coronavirus in organizations, employers can also count on reimbursement of funds spent on the purchase of PPE.
3. Organizational and technical. They imply the development by the enterprise of a policy to comply with the requirements of labor protection legislation, the identification of tasks and means of solving them.
4. Sanitary and hygienic. These are measures to reduce the degree of exposure to hazardous and harmful factors at work. These include environmental studies in laboratory conditions and with the help of special instruments, production control, and vaccination of personnel. By such means, management achieves the main goal - protecting the health and life of subordinates, creating and maintaining favorable working conditions.
5. Treatment and prophylaxis. These include psychiatric examinations, milk dispensing, medical examinations, etc.
For reference: replacing therapeutic and preventive nutrition with monetary compensation is prohibited by the rules approved by Order 46n of February 16, 2009 (clause 11).
6. Rehabilitation. Activities of this nature help restore the ability to work and health of employees if they have acquired chronic diseases or suffered due to an accident during the work process. Rehabilitation includes transfer to light work, sanatorium-resort treatment, payment for health procedures, etc. Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides a complete list of possible measures.
Occupational safety specialists
Responsibilities and rights
An employee in the OT department has the following rights:
- to undergo periodic training;
- to properly arrange your place of work;
- to social guarantees established by federal regulations and internal regulations;
- to participate in meetings in which topics affecting the work of the department are raised;
- to sign papers falling within his competence;
- to familiarize yourself with the orders issued by the director if they relate to labor protection;
- to receive information related to employee safety;
- to make proposals for improving measures.
The following responsibilities are imposed on the specialist:
- issuance by employees of materials necessary for protection;
- communicating to employees information about risks, features of the technological process, acceptable actions, etc.;
- control over strict adherence by company employees to legislation;
- analysis of technical conditions, equipment and safety on site, reporting this information to the manager;
- control of expenses from the budget, calculation of the cost plan;
- development and promotion of activities aimed at improving working conditions;
- referral for medical examinations;
- control over strict implementation of safety regulations;
- others.
Rights and responsibilities are enshrined in the job description and are provided to the worker for review and signature.
Authority
The service employee is authorized to:
- carry out inspections;
- issue an order based on the results indicating the violations identified;
- demand elimination of violations;
- monitor compliance with requirements;
- demand from heads of departments to remove from work citizens whose actions violate labor safety rules;
- make proposals to the director regarding the punishment of violators;
- initiate incentives for performers who help implement improvements in the field of occupational safety;
- ask department heads to participate in activities aimed at improving conditions;
- be a representative at meetings in government bodies.
Tasks and goals
The goal of an occupational safety specialist is to provide conditions for workers that minimize the risks of harm to health.
Based on this, its tasks are formed:
- participation in conveying instructions to performers on safety rules, in certification, in work related to the adoption of new equipment, in assessing the effectiveness of the service, in eliminating violations;
- coordinating the provision of citizens with means of protection, development of plans, referral for medical examinations, mental health checks, where required; control over strict adherence to laws;
- collection, analysis, transmission of information;
- service improvement;
- others.
What organizations do they interact with?
In accordance with Art. 218 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation creates a committee (commission) on occupational safety. The essence of education is that performers participate in the management of occupational safety . Created with the aim of creating maximum efficiency of the service.
Interaction is carried out with:
- labor inspection;
- technical labor inspection of trade unions;
- state regulatory and supervisory authorities.
What actions are illegal?
Despite the wide range of rights of an occupational safety specialist, he cannot independently perform a number of actions. For example:
- exempt from duties those persons who did not visit a medical institution for examination, instruction, or those who commit violations;
- impose liability on performers for violations;
- involve individual employees in assisting with events;
- reward financially for participation in improving service conditions.
The competence of an occupational safety specialist includes: making proposals, recommendations, providing information on the above issues. Direct execution is not required.
The final decision and implementation is carried out after approval by the head of the company and departments.
Employees who must undergo occupational safety training.
The employer is obliged to organize and promptly conduct training in safe work methods and testing the knowledge of labor protection requirements for employees (paragraph 7, part 2, article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1.7 of the Procedure approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education Russia No. 29).
All categories of employees must undergo occupational safety training, in particular:
- managers (including heads of organizations);
- specialists;
- workers.
In addition, employers-entrepreneurs are required to undergo labor safety training. This is stated in Part 1 of Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Attention: the organization should not allow employees who have not undergone training and instructions on labor protection to work (paragraph 8, part 2, article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An employee who has not undergone training and testing of knowledge on labor protection through no fault of his own must be suspended from work, and the organization is obliged to pay for the entire period of suspension from work as downtime due to the fault of the organization (paragraph 3, part 1, part 3, article 76 Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Stages of occupational safety training
As a rule, the occupational safety training procedure includes:
- labor safety briefing (mandatory for all employees);
- training in safe methods and techniques for performing work;
- training in first aid rules.
In addition, the employer is obliged to organize testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements. This conclusion can be drawn from the provisions of parts 1, 2 and 3 of Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
General training procedure The procedure for training employees and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements was approved by Decree of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29. At the same time, regional and local authorities may establish additional requirements for training and testing knowledge of labor protection ( clause 1.3 of the Procedure approved by the resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29).
The legislation provides for different procedures for training in occupational safety and health depending on the categories of employees:
- working professions;
- managers and specialists.
Occupational safety training for blue-collar workers
Employees of blue-collar professions are trained in safe methods and techniques for performing work within a month after starting work or upon transfer to another job. Training is carried out in the preparation of employees, retraining and training them in other working professions. This is stated in paragraph 2.2.1 of the Procedure approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
If the work is associated with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, then employees of blue-collar professions undergo training with on-the-job training and subsequent passing of exams. At the same time, employees who have had breaks in their profession (type of work) for more than a year undergo training and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements within the first month after being assigned to these jobs. This is stated in paragraph 2.2.2 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
Employees of blue-collar professions are trained to provide first aid to victims at least once a year. New employees must complete such training no later than one month after hire. This is stated in paragraph 2.2.4 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
The employer determines the form, frequency and duration of training for blue-collar employees independently, taking into account the requirements of regulations governing the safety of specific types of work (clause 2.2.3 of the Procedure approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 of January 13, 2003 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29 ). Responsibilities for training employees and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements are, as a rule, performed by the labor protection service (clause 7.14 of the Recommendations, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated February 8, 2000 No. 14).
Training of managers and specialists
The need for training managers (specialists) in labor protection arises:
- when hiring a new employee;
- when transferring an employee to another job;
- when improving the qualifications of a manager or specialist.
This is stated in part 2 of article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 3 of clause 2.3.6 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 of January 13, 2003 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
Managers and specialists must undergo special training in labor safety within the scope of their job responsibilities within the first month after starting work. Conduct repeated training as necessary, but at least once every three years. This is provided for in paragraph 2.3.1 of the Procedure approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29 of January 13, 2003.
There is an exception to this rule. Training and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements may not be completed within a year after starting a job:
- employees qualified as an engineer (specialist) in the safety of technological processes, production or labor protection engineer;
- specialists in labor protection of federal executive authorities, executive authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, state supervision and control;
- teachers of educational institutions teaching the discipline of labor protection;
- employees with continuous work experience in the field of labor protection for at least five years.
This is stated in paragraph 1.6 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
Before starting independent work, a new employee must be familiarized with:
- with job responsibilities (including labor protection);
- with internal local documents regulating the procedure for organizing work on labor protection (for example, Regulations on the labor protection service, Regulations on the procedure for training in labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements, Safety Instructions);
- with the state of working conditions at the facilities (structural units) entrusted to him.
This is stated in paragraph 2 of clause 2.3.1 of the Procedure approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
Managers and specialists are trained in occupational safety and health according to relevant programs. In this case, training can take place:
- in training organizations (educational institutions of vocational education or training centers if they have a license to teach in the field of labor protection, teaching staff in the field of labor protection and material and technical base);
- in the organization itself (if it has a special commission to test knowledge of labor protection requirements.
This is stated in paragraph 2.3.2 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
Training in training organizations
Some categories of employees must undergo training in training organizations of federal executive authorities and executive authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation in the field of labor protection (for example, Rostechnadzor). These include, in particular:
- employers (heads of organizations, entrepreneurs);
- deputy managers in charge of labor safety issues;
- engineering and technical specialists supervising the work;
- occupational safety specialists;
- members of labor protection commissions;
- organizers and supervisors of students' practical training;
- authorized representatives for labor protection of trade unions and other representative bodies of employees.
This is stated in paragraph 2.3.2 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
During the occupational safety training process, lectures, seminars, interviews, individual or group consultations, and business games are held. Besides,
Elements of self-study of the occupational safety program, modular and computer programs, as well as distance learning can be used. This is stated in paragraph 2.3.5 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
Employer training
Labor safety training in the organization is carried out according to programs approved by the employer. Develop these training programs based on sample curricula and training programs for occupational safety. This is stated in paragraph 2.3.4 of the Procedure approved by Resolution No. 1 of the Russian Ministry of Labor No. 1 and the Russian Ministry of Education No. 29 of January 13, 2003. For example, sample training plans for occupational safety and health training were approved by the Russian Ministry of Labor on May 17, 2004.
In addition, to conduct training in the organization, develop the following documents:
- order on organizing training of employees on labor protection;
- Regulations on the procedure for training in labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements.
This conclusion can be drawn from the provisions of paragraphs 21–23 of part 2 of article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Checking employees' knowledge of labor protection requirements
An organization can conduct a test of knowledge of labor protection requirements independently or in a specialized organization (clauses 3.4, 3.9 of the Procedure approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 of January 13, 2003 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29).
The procedure and frequency of testing knowledge of labor protection requirements depends on the category of the employee and the reason for the test.
For example, the next test of knowledge of labor protection requirements for managers and specialists should be carried out at least once every three years, and testing of the knowledge of workers in working professions in providing first aid to victims - at least once a year.
An extraordinary inspection is carried out in certain cases, for example:
- when legislation changes;
- with changes in technological processes;
- in case of transfer or emergence of new responsibilities for an employee;
- with a break in work for more than one year;
- when establishing violations by the employer in labor protection;
- with insufficient knowledge of occupational safety and health requirements;
- after accidents that have occurred in the organization.
Such rules are established in paragraphs 3.1–3.3 of the Procedure approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
Testing knowledge of labor protection requirements in the organization
The theoretical knowledge of occupational safety requirements and practical safe work skills of blue-collar workers are tested by their immediate supervisors. In this case, the employee must know the requirements of labor protection rules and instructions, and, if necessary, special safety and labor protection requirements. This is stated in paragraph 3.1 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
To test knowledge of labor protection requirements in an organization, create a commission. For this:
- issue an order to create a commission in any form;
- develop regulations on the labor protection commission.
The standard provision was approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated May 29, 2006 No. 413 (Article 218 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The commission must consist of at least three people. Members of the commission must undergo training and testing of knowledge on labor protection. The commission is formed of a chairman, deputy (deputies) chairman, secretary and members of the commission.
The commission may include:
- heads of organizations and structural divisions;
- occupational safety specialists;
- chief specialists (for example, technologist, mechanic, power engineer);
- representatives of the trade union and other employee representative bodies.
This is stated in paragraph 3.4 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
Check results
Document the results of testing the knowledge of employee labor protection requirements in a protocol (clause 3.6 of the Procedure approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 of January 13, 2003 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29). Its form was approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Russian Ministry of Labor No. 1 and the Russian Ministry of Education No. 29.
Employees who successfully pass the test will be issued a certificate of knowledge testing on labor protection. Its form was approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29. The chairman of the commission must sign the certificate and certify it with the seal of the organization. This is stated in paragraph 3.7 of the Procedure, approved by resolution of January 13, 2003 of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29.
If an employee does not pass the test, he is obliged to undergo a second knowledge test no later than one month (clause 3.8 of the Procedure approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 of January 13, 2003 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29).
Testing knowledge of labor protection requirements in a training organization
Training organizations can test the knowledge of occupational safety requirements only for those employees who have undergone training in occupational safety (clause 3.9 of the Procedure approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia No. 1 of January 13, 2003 and the Ministry of Education of Russia No. 29).
Responsibility for violation of labor safety rules
Violation of labor safety rules is subject to administrative and criminal liability.
In addition, an organization and its officials may be subject to administrative penalties for allowing employees to work who have not undergone training and testing of knowledge of labor safety requirements in the prescribed manner. This is provided for in parts 3 and 5 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offences.
How to conduct occupational safety training?
Mandatory instructions
Employees of the organization must be familiarized with labor protection requirements and safety rules in the workplace (Articles 212 and 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Instruction at the workplace is a mandatory procedure that all employees without exception must undergo (Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1.1 of the Procedure approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated January 13, 2003 No. 1, Ministry of Education of Russia dated January 13, 2003 No. 29 ).
Personnel must master safe methods and techniques of work, be able to provide first aid to victims, and firmly know what actions are prohibited in the workplace. When working with computers, you must comply with the rules and regulations (SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03), approved by Decree of the Chief Sanitary Doctor of Russia dated June 3, 2003 No. 118.
The rules of safe work and the procedure for familiarizing employees with them should be established in the labor safety instructions. Some industries have standard occupational health and safety regulations. For example, for employees of the fuel and energy complex (oil and gas industry, petroleum products supply), such standard instructions were approved by Order of the Ministry of Fuel and Energy of Russia dated July 4, 1995 No. 144.
Types of labor safety briefings
Instruction happens:
- introductory (conduct with newly hired employees; seconded to the organization; trainees and other persons who are accepted for permanent or temporary work);
- primary (carry out before starting independent work);
- repeated (carry out at least once every six months according to programs developed for initial instruction in the workplace);
- unscheduled (carry out in case of any changes, for example, if new legislation on labor protection appears or technological processes change, etc.);
- targeted (conduct with employees in cases where they need to perform one-time work, eliminate an accident, natural disaster or their consequences, etc.).
The introductory briefing must be conducted by a labor protection specialist or an employee who has been assigned these responsibilities by order of the head of the organization.
Primary, repeated, unscheduled and targeted briefings must be carried out by the employee’s immediate supervisor (foreman, foreman, teacher, etc.), who has undergone special training in labor safety.
These types of instructions are established in paragraph 2.1 of the Procedure approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated January 13, 2003 No. 1, Ministry of Education of Russia dated January 13, 2003 No. 29.
Training logs
The fact that the appropriate type of briefing has been carried out, knowledge and labor safety rules tested and the employee has received permission to work independently should be recorded in the introductory briefing logbook and the workplace briefing logbook.
Event Planning
Planning is carried out with the goal of optimally distributing the necessary activities in a specific time period. This increases the efficiency of the labor protection service and coordinates its work.
Planning can be:
- for the coming year;
- for the future. Affects longer periods;
- operational. It is carried out when conditions conducive to this arise.
When planning, organizations rely on the recommendations of departments and can make their own adjustments. The list of measures is approved by order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated March 1, 2012 No. 181n.
It may include the following:
- support for employees promoting a healthy lifestyle;
- marking hazardous areas with reflective signs;
- equipment upgrade;
- introduction of automatic systems for recognizing harmful substances;
- equipment of premises for conducting briefings;
- carrying out activities aimed at promoting health;
- installation of warning systems in case of situations dangerous to life and health;
- development of protective systems;
- others.
Occupational Safety Day
Holding occupational safety day is a tradition that appeared during the USSR . The purpose of the training is to consolidate knowledge about safety measures at work.
On this day, employers try to reduce the workload of their subordinates so that all team members can take part in the event . A script is prepared in advance, lectures and conversations are held on improving the quality of life and health. Inspections may also be carried out.
This event is not legally established. The employer independently establishes the frequency of carrying out the OT service in the Regulations.
In addition, the following are compiled:
- OT days program;
- order to carry out;
- list of participants;
- a list of violations identified during inspections with recommendations for elimination.
In small organizations such events are perhaps rare. companies attach greater importance to Occupational Safety Day
- with a high number of personnel;
- with hazardous production;
- with government sources of funding.
Stand and corner
separate spaces containing information as a reminder
The standards are enshrined in the resolution of the Ministry of Labor “On approval of Recommendations for organizing the work of the office and labor protection corner” dated January 17, 2001 No. 7.
The act makes the following requirements:
- creation of a labor protection office at enterprises with more than 100 employees; in industries with an increased risk of accidents using hazardous substances.
- the creation of a labor safety corner is permissible for organizations with less than 100 employees;
- These requirements also apply to enterprises that frequently change their location due to the nature of their work.
The design of the occupational safety corner can be presented in the form of a stand, which is a carrier of all the necessary information. According to the resolution of the Ministry of Labor, the materials on the stand have approximately the following content:
- algorithm of actions of employees in the event of a dangerous situation;
- notification of existing production factors that create health risks;
- the measures the company takes to ensure safety;
- internal package of company documents;
- list of state regulatory documents;
- detailing of technological processes;
- room layouts.
Occupational safety is a whole area in the work of an organization and contains nuances. Russian legislation has approved many norms both at the federal and departmental levels. Familiarization with them and implementation will be a good guarantee of the well-being of the company’s employees and the successful interaction of the company with regulatory authorities.