Loans provided: accounting and reporting
Note from the author! Before putting a facility into operation, all costs during construction are accumulated on capital investments, that is, on account 08.
Thus, the indicator for the line “Loans and credits” reveals the amount of short-term loans and credits received and not repaid by the enterprise, as well as the amount of interest payable on received loans and borrowings.
As the name suggests, loans can be divided according to repayment periods: Loans, in addition to cash, can be received as debt securities: In this case, the company pays the lender not interest, but a discount, that is, the difference between the nominal and real value of the security. Borrowed funds are considered to be money received from third-party sources, which will need to be returned back under certain conditions.
How to take into account other people's funds
As the name suggests, loans can be divided according to repayment periods:
- for long-term, that is, over 12 months;
- and short-term, that is, up to 12 months.
In this case, the company pays the lender not interest, but a discount, that is, the difference between the nominal and real value of the security.
The liability on accounts 66 and 67 is accounted for in two ways:
- Based on actual loan amount plus interest.
- At par value of debt securities.
In addition to the main body of the loan, interest on the loan, which is the income of the lender, is taken into account in separate subaccounts 66 and 67 of the account. Accrued interest is reflected on account 91 “Other income and expenses” as expenses, or on account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” as an increase in the cost of fixed assets:
- Debit 91.02 Credit 66, 67 – monthly interest accrued.
- Debit 08 Credit 66, 67 – the cost of the object under construction has been increased by the amount of interest.
Note from the author! Before putting an object into operation, all costs during construction are accumulated on capital investments, that is, on account 08. After completion of construction or additional equipment, the objects are entered into account 01 “Fixed Assets”.
For example, a company took out a loan for the construction of a bridge in the amount of 1,000,000 rubles for one year. The bank's annual interest rate is 18%. You need to calculate how much deductions to take into account each month:
- 1,000,000 * 18% = 180,000 rubles per annum;
- 180,000 / 12 months = 15,000 rubles – monthly interest accrual.
Since the loan term is one year, it is considered short-term, which means it will be displayed on account 66:
- Debit 51 Credit 66.01 – a loan was received in the amount of 1,000,000 rubles.
- Debit 08 Credit 66.02 – interest was accrued on the increase in the cost of the bridge in the amount of 15,000 rubles.
- Credit 66.02 Debit 51 – monthly payment to the bank of 15,000 rubles is transferred.
Displaying the company's borrowed funds in the balance sheet
The company has submitted a balance sheet, and in it the liability is not equal to the asset. The accounting is correct, the values are incorrect due to a program failure when the balance was sent.
For the amounts of repaid loans and borrowings, account 67 “Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings” is debited in correspondence with the cash accounts. Credits and borrowings not paid on time are accounted for separately.
As the borrower repays the debt, the lending organization writes off the corresponding amount of collateral received from account 008 “Collateral for obligations and payments received.”
The interest rate for using a loan is determined in the amount of 2/3 (two thirds) of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of Russia, existing for each last day of the billing period.
Articles on the topic (click to view)
- Correspondence with the debtor during the maintenance of the relationship
- Application for procedural succession, sample, how to write + example
The company has the right to issue a loan to another company or individual. This transaction is formalized in writing - a loan agreement.
- Purpose of the article: reflection of information about borrowed funds.
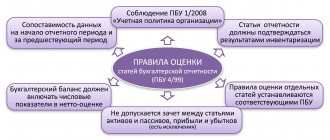
- Line number in the balance sheet: 1410, 1510.
- Account number according to the chart of accounts: credit balance of 66, 67 accounts.
Expert opinion
Kuzmin Vladimir Timofeevich
Legal consultant with 6 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
Is it possible to use the indirect cash flow statement to determine whether a company has non-cash flow transactions?
In this case, the company pays the lender not interest, but a discount, that is, the difference between the nominal and real value of the security.
Where to show interest on received and issued loans in the balance sheet line
And in both options there is a clause: “The borrower undertakes to pay interest on the use of the loan amount at a time when the loan is repaid.”
When filling out this line, it is necessary to take into account the repayment terms of not only the loan obligations themselves, but also the interest debt. If the organization has long-term debt obligations for which at the end of the year.
The amounts of interest due in accordance with the terms of the loan agreement are recognized by the organization for each expired reporting period as part of other income on the basis of paragraph.
When filling out the balance sheet, check the repayment terms of all long-term loans and credits recorded in the account. If the repayment period of any loans and credits is on December 31, the amount of debt on loans and credits is formed by both the amount of the principal debt and the interest due at the end of the reporting period. according to the terms of the contracts.
In accounting, on the date of issuance of the loan, an entry is made in the debit of account 58 “Financial investments”, subaccount 3 “Loans provided”, in correspondence with the credit of account 51 “Current accounts”. This follows from the norms of clauses 2, 3, 8 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for Financial Investments” (PBU 19/02), approved.
A loan represents funds transferred by a credit institution to a borrower. In this case, the latter pays interest for the use of such borrowed funds.
Loans and credits line Short-term loans and borrowings are accounted for in a separate account 66 “Short-term credits and borrowings”. Analytical accounting of short-term loans and borrowings is carried out by type of loans and borrowings, credit organizations and other lenders who provided them.
As with long-term loans and borrowings, when accounting for short-term loans and borrowings, interest on loans and borrowings, as well as loans and borrowings obtained by placing bonds, are accounted for separately.
Lines 1190 (for long-term) or 1230 (for short-term) of the balance sheet are intended for such loans. Any additional costs associated with the issuance of borrowed funds (for legal review of the contract, payment for consulting services, etc.) are taken into account as part of other expenses ().
Operations for issuing loans in cash are not subject to VAT.
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please use the online consultant form on the right or call the numbers provided on the website. It's fast and free!
- Long-term liabilities on the balance sheet
- Interest on a long-term loan in the balance sheet: in line 1410 or 1510?
- Short-term liabilities
- Short-term loans and borrowings
- Long-term loans and borrowings on the balance sheet – line
- Line 510 “loans and credits”
- Short-term and long-term liabilities on the balance sheet: what are they?
- Line 1510 “Borrowed funds”
The company entered into a loan agreement in 2014 and issued funds under it until 2021. According to the terms of the agreement, interest is also paid at the end of the agreement. those. in 2021.
The amount of an interest-bearing loan provided in kind should be determined based on the value of assets transferred or to be transferred by the organization. Such value is established based on the price at which, in comparable circumstances, the organization usually determines the value of similar assets.
A short-term loan is a loan for a period of no more than one year; it is the main source of additional funds for an organization for temporary needs. Borrowed short-term money is used for temporary replenishment of fixed and working capital, for inventory, as well as for other needs.
Expert opinion
Kuzmin Vladimir Timofeevich
Legal consultant with 6 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
A loan is issued for the purpose of generating income for the lender, that is, at monetary interest. Loans can be interest-free. There is no benefit for a lender to risk their money without even receiving additional income.
Debt on borrowed capital is shown in a separate line of the balance sheet, which all companies are required to submit at the end of the reporting period:
- line 1410 is intended for long-term loans and borrowings;
- line 1510 – for short-term obligations on loans and borrowings.
Naturally, we are talking about loans and borrowings received. After all, issued loans that meet the criteria for financial investments specified in paragraph 2 of PBU 19/02 are part of the organization’s assets.
At the same time, debt for settlements with buyers, customers and other debtors, secured by an overdue bill of exchange, continues to be recorded in the corresponding accounts receivable.
The debt on loans and credits received in the financial statements is shown taking into account the interest due at the end of the reporting period (clause 73 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n).
Credit balance of account 66 + Account balance 67
Redistribution of debt obligations
Each enterprise has the opportunity to transfer obligations that have a long maturity period to a short-term basis. This is acceptable when there are no more than 12 monthly payments remaining on the loan.
Important! Debt with a payment term exceeding 12 months cannot be included in accounts intended to reflect short-term loans and credits.
Overdue debt
When the borrower fails to repay the next payment on time, the accountant needs to transfer the remaining loan obligations to the status of overdue debt. In this case, the company may incur additional expenses:
- Paid consultations with credit experts.
- Verification of the loan agreement by third party specialists.
- Fines and penalties provided by the lender for late payments.
- Other expenses not covered by banking services.
Calculation of interest under a loan agreement: postings
Short-term loans and borrowings in accordance with the Chart of Accounts and the Instructions for its application are reflected in account 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings” (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). Therefore, we can say that the balance of short-term loans and borrowings, i.e.
i.e. the credit balance of account 66 as of the reporting date should be reflected on line 1410. And the remaining balance of account 67 (in terms of long-term loans and borrowings) should be transferred to line 1410 (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n).
Loans can only be provided by specialized organizations, that is, banks and other financial organizations.
Our farm operates on the Unified Agricultural Tax and is considered a small business entity. We conduct accounting and prepare reports in a simplified manner.
Other costs associated with loans and borrowings should be taken into account evenly throughout the entire term of the contract.
Calculation of interest under a loan agreement: postings The procedure for reflecting these transactions in the borrower’s accounting depends.
What is considered borrowed funds?
Depending on the type of organization that lent financial resources, they can be divided into two types:
- Loans.
- Loans.
The difference between types lies in the source of funding. Loans can only be provided by specialized organizations, that is, banks and other financial organizations. Loans can be issued by almost any legal entity and even an individual.
A loan is issued for the purpose of generating income for the lender, that is, at monetary interest. Loans can be interest-free. There is no benefit for a lender to risk their money without even receiving additional income. Therefore, an interest-free loan is found among affiliated and interdependent persons when several companies are united:
- to a corporation;
- holding;
- group.
Thus, you can divide the loans:
- Loans.
- Loans.
A loan is issued for the purpose of generating income for the lender, that is, at monetary interest. Loans can be interest-free. There is no benefit for a lender to risk their money without even receiving additional income.
The procedure for generating indicators according to the lines of section IV of the balance sheet liabilities
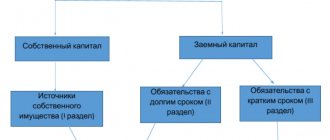
The organization’s liabilities (essentially its borrowed capital) are presented in two liability sections of the balance sheet, depending on their maturity date:
in Sect. IV “Long-term liabilities” – liabilities whose maturity is more than 12 months after the reporting date;
in Sect. V “Short-term liabilities” – obligations that must be repaid within the next year.
Section IV of the balance sheet consists of five lines.
This section should reflect information about the organization's obligations, the maturity of which is more than 12 months after the reporting date.
The lines of Section IV, for example, should reflect the amount of a loan or loan raised for a long period of more than a year, the amount of deferred tax and valuation liabilities of the company, as well as the amount of other long-term liabilities.
Let's consider the order of filling out these lines.
Line 1410 must reflect data on all long-term loans and borrowings received by the organization for a period of more than 12 months.
At the same time, this line reflects the amount of loans received both in cash and in kind, bank loans, and the company’s obligations under issued financial bills.
To fill out line 1410, take the credit balance of account 67 “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings.”
Moreover, this should be done only in that part of the debt for which the repayment period exceeds 12 months after the reporting date.
Line 1420 “Deferred tax liabilities”:
Line 1420 is filled out by companies applying PBU 18/02.
To fill out line 1420, take the credit balance of account 77 “Deferred tax liabilities.”
If an organization offsets deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities and presents them on a collapsed basis (balanced), it is necessary to fill out page 1420 only if the credit balance of account 77 “Deferred tax liabilities” turns out to be greater than the debit balance of account 09 “Deferred tax assets” (by the amount differences between them).
Line 1430 shows the amount of reserves created in accordance with PBU 8/2010.
For example, this line should reflect the amount of the reserve for warranty repairs.
In this case, this line should indicate only data on long-term estimated liabilities for a period of more than 12 months.
Line 1430 reflects the credit balance of account 96 “Reserves for future expenses” (in terms of obligations with a maturity period of more than 12 months) not written off as of December 31 of the reporting year.
Line 1450 should contain information about other long-term liabilities that were not reflected in the above lines of Section IV.
So, for example, on line 1450 you can indicate data on accounts payable to suppliers and contractors with a repayment period of more than 12 months.
This may be the credit balance of the following accounts:
Expert opinion
Kuzmin Vladimir Timofeevich
Legal consultant with 6 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” in terms of long-term accounts payable for installments or deferred payment provided by suppliers and contractors, if it is more than 12 months;
62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” - in terms of debt to buyers and customers, the repayment period of which exceeds 12 months (arising as a result of receipt of advances and prepayments for the upcoming supply of products, goods, performance of work, provision of services, including debt on commercial loans) ;
68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” - in terms of long-term debt for taxes and fees (for example, when providing an organization with an investment tax credit, deferment or installment plan for the payment of federal taxes and fees);
69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” - in terms of long-term debt on insurance contributions (for example, when restructuring debt to extra-budgetary funds);
76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” - regarding other long-term accounts payable and obligations;
86 “Targeted financing” – in terms of obligations the fulfillment period of which exceeds 12 months after the reporting date. Data on targeted financing is reflected here (account credit 86 “Targeted financing”) (for example, when developer organizations receive targeted financing from investors, which generates the developer’s obligation to investors to transfer the constructed facility to them).
Still have questions about accounting and taxes? Ask them on the accounting forum.
This indicator characterizes the efficiency of using only equity and long-term borrowed capital. When calculating return on equity, net profit is taken into account without expenses for servicing borrowed capital.
Capital and reserves: authorized capital (account 80), additional and reserve capital (if any, accounts 83 and 82), retained earnings (uncovered loss, account 84), revaluation of fixed assets (intangible assets), if such is carried out in the organization ( count 83). This line also reflects own shares purchased from shareholders for cancellation (account 81).
Explanation of credits and loans to the presented balances
After all, the Chart of Accounts and the Instructions for its application do not provide for the transfer of short-term credits and borrowings from account 67 to account 66 (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
For each balance line, you need to enter the corresponding code in the column. What code to put if a line includes several indicators, each of which has its own code? Clause 5 of Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance “On Forms of Accounting Reports of Organizations” states that the code corresponding to the largest share is assigned.
Let me tell you right away, this is not an easy task. First, I recommend checking the arithmetic calculations. If there are no problems with arithmetic, proceed to checking the accounting entries in OSV.
Regulatory and legislative acts on the topic
| Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n | Approval of the balance sheet form |
| clause 7.3 of the Concept approved by the Methodological Council for Accounting under the Ministry of Finance | On the grounds for the emergence of obligations |
| clause 19 PBU 4/99 | Definition of long-term liabilities |
| Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n | Algorithm for calculating indicators of items of long-term liabilities |
Financial investments on the balance sheet are.
Information in the balance sheet is divided item by item (approved by the Ministry of Finance). Opposite each item is the amount taken from the SALT on the reporting date; in 2 adjacent columns the itemized value of the property for the two previous reporting dates is indicated.
This line of the balance sheet reference section reflects the cost of inventory items that are in safe custody in the organization.
Long-term liabilities are accounts payable that are due in more than one year. Long-term liabilities include bank loans (but not bank overdrafts, which are repayable on demand) and unpaid lease amounts.
Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 002. On the same account, supplier organizations account for goods and materials paid for by buyers, which are left in safekeeping, issued with safe receipts, but not taken out.
Expert opinion
Kuzmin Vladimir Timofeevich
Legal consultant with 6 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
It is assumed that the latter are aimed at financing fixed assets and capital investments. All calculations are performed on a net balance basis.
This period begins on the 1st day of the month following the month in which the receivables are reflected in accounting. The total indicator of long-term debt is entered in line 230. Short-term debt is considered to be debt for which payments are expected within 12 months after the reporting date.
Line 1430 “Estimated liabilities”
The reference section of the balance sheet provides information about the values that are taken into account in off-balance sheet accounts. These are values that are temporarily at the disposal of the organization (leased fixed assets, material assets in safekeeping, in processing, etc.), conditional rights and obligations.
The formation of data on short-term loans, borrowings and long-term liabilities in the balance sheet occurs on line 1410 and 1510.
Despite the lack of activity, the balance will still not be completely empty. Not only the header will be filled in, but also some lines of liabilities and, possibly, assets.
Borrowed capital (LC) is part of the value of the organization’s property acquired as an obligation to return money or valuables equivalent to the value of such property to the supplier, bank, or other lender.
This line reflects the cost of goods accepted for commission under a commission agreement. Goods of the principal (principal, principal), accepted for sale in accordance with the commission agreement, are recorded in the off-balance sheet account 004 Goods accepted on commission.
Accounting for consignment goods is carried out at the prices specified in the contract or acceptance certificate.
Important! If a company uses borrowed funds obtained from different sources to achieve its goals, then they are displayed in separate lines. For each type of debt, its own sub-account is opened.
Analysis of the balance sheet and its indicators is a complex, multi-stage process. I told you how to do it above.
The results of the analysis help optimize the financial policy of the company. A high-quality analysis allows you to make competent management decisions.
When equity capital is insufficient, companies resort to obtaining additional financial assistance from third parties. Borrowed funds in the balance sheet are line 1510, which reflects cash receipts that do not belong to the enterprise.
They will need to be returned with payment of a certain percentage on the repayment period established by the contract.
At the same time, you have the opportunity to reflect deferred assets and liabilities on a net basis. That is, depending on what difference arose between the debit of account 09 “Deferred tax assets” and the credit of account 77.
If this difference is positive (debit 09 is greater than credit 77), fill out only line 1180 of the balance sheet asset. Put a dash in line 1420.
Long-term and short-term liabilities of the enterprise
To resolve financial issues, many companies attract internal and third-party sources of financing. In the second case, at a certain stage the company may have so-called long-term and short-term obligations.
If they exist, one of the main tasks of a company or enterprise is timely repayment of debts, while the funds received are not the property of the company, it simply uses them until the time for their repayment comes.
Signs of short-term liabilities
This type of loan has the following features:
- The total amount of borrowed funds largely determines the duration of the enterprise's production cycle. The more significant the short-term obligations of a business entity, the smaller amounts it will attract to use to pay current expenses in the course of the company's operation.
- The company's short-term liabilities replace a free source of borrowed capital.
- The total amount of debt is often determined by how successfully the company sells its products. An actively operating enterprise is forced to constantly spend money, so it often requires borrowed funds.
- When preparing the financial statements of a company, it is worth remembering that short-term liabilities on the balance sheet are “Liabilities”.
- In some cases, debts that are less than 12 months old can be paid off using current assets. These financial resources are used in the planned activities of a business entity, and in order to use them to pay off debts, they must be credited no later than 12 months from the date the debt was created.
- The amount of this type of debt depends on the frequency of payments on it, which makes it possible to quickly work with sources of funds when carrying out production activities.
- The size of short-term liabilities is difficult to estimate in the future; this situation arises from the impossibility of accurately calculating the amount of amounts that form the basis of debt obligations.