Inventory of goods in trade
Suvorina V.M.
KSTU
Topic 7. Inventory of goods in trade
Lecture outline:
1. Inventory of stocks.
2. Documentation and accounting of inventory revaluation.
3.Accounting for the results of inventory of goods and containers.
1.Inventory is one of the elements of the accounting method, which involves checking the assets of a trading enterprise and their calculations, and comparing them with accounting data. Depending on the completeness of coverage of funds, the inventory is divided into complete and partial. The full one, as a rule, is carried out once a year, usually before the preparation of the annual report, its purpose is to ensure that the assets and liabilities of the trading enterprise are reflected realistically in the balance sheet. Partial inventory covers only part of the inventory items. An inventory of inventory items is carried out for the purpose of monitoring and checking the availability of inventories on a certain date by an inventory commission appointed by the head of the trading organization. The frequency, timing of inventory, and the composition of the inventory commission are approved in the accounting policy.
When storing goods in isolated premises at one financially responsible linden, inventory is carried out sequentially by storage location. After checking the supplies, the premises are sealed and the commission moves on to work on the next premises.
During the inventory, all operations with inventory goods and unauthorized persons are not allowed into the premises where the inventory is being taken.
In large warehouses during long-term inventory in exceptional cases and only with the written permission of the head of the organization. During the inventory process, goods may be released in the presence of members of the inventory commission. These goods are entered into a separate inventory list under the name “inventory issued during inventory count.” This inventory should be drawn up in the same way as documents for incoming supplies during inventory. A note is made in the expenditure documents with the signature of the chairman of the inventory commission.
Goods received during the inventory are accepted by the financially responsible person in the presence of members of the inventory commission.
Inventory inventories are reflected for each item, indicating the item number, type, group, article, grade and quantity. It is not recommended to enter data on the balance of goods into inventory lists from the words of the materially responsible person or according to accounting data without checking their actual availability.
Inventories belonging to other entities and held in custody are inventoried simultaneously with their own goods, and another inventory list is drawn up for them, in which a reference is made to the relevant documentation confirming the acceptance of these stocks for custody.
Inventories stored in warehouses of other organizations are entered into inventory records on the basis of documents confirming the delivery of these goods for safekeeping, indicating their name, grade, and type.
Inventory records are compiled separately for goods in transit.
Inventory of goods in transit, shipped but not paid for on time by buyers, located in the organization’s warehouse, consists of checking the validity of the amounts listed on the relevant accounts.
Only amounts confirmed by properly executed documents can remain on inventory accounts (in transit, goods shipped, etc.). In inventories for inventories shipped and not paid for on time by buyers, for each shipment the name of the buyer, the name of the goods, the date of shipment, the date of issue, the number and amount of the invoice are given.
When taking inventory of stocks issued for individual use to employees, it is allowed to draw up group inventory lists indicating in them the persons responsible for these items, for whom personal cards are open, with a receipt for them in the inventory.
Containers are included in the inventory by type, intended purpose and quality condition (new, used, in need of repair, etc.).
The work of the working inventory commission is documented in a protocol that reflects the results of the inventory, as well as checks to ensure the safety of goods. Inventory lists can be filled out using computers and other equipment, or manually.
It is not recommended to make any blots or erasures.
It is not recommended to leave blank lines in inventory records. In the last sheets of the inventory, unfilled lines are crossed out.
In cases where the financially responsible person discovers errors in the inventory records after the inventory, he can report this to the inventory commission before opening the warehouse, storeroom, or section. A statement from the financially responsible person that the shortage or surplus was caused by an error in the name, omission, miscalculation, etc., is accepted before the opening of the warehouse, storeroom, section where the inventory was carried out. The inventory commission checks the specified facts and, if confirmed, corrects the identified errors in the prescribed manner.
Errors are corrected in all copies of the inventory by crossing out incorrect entries and placing correct entries above the crossed out ones. Corrections are negotiated and signed by all members of the inventory commission and the financially responsible person. If necessary, inventory control checks are carried out, in which both members of inventory commissions and the financially responsible person take part. Inventory statements are submitted to the accounting department, where a reconciliation is carried out with the balances reflected in the accounting records and a matching statement is drawn up for those positions for which deviations from the accounting data are identified.
2.Revaluation of inventories is carried out in order to reduce prices (markdown) or increase prices (revaluation). Reasons for revaluation of goods:
– changes in demand and supply for them;
– inflationary process;
– partial loss of the product’s original consumer properties;
– moral aging, etc.
The procedure for conducting and recording inventory revaluation depends on the type of accounting price of goods used, established in the accounting policy of the entity. If an enterprise accounts for inventories at purchase prices, then the results of revaluation in accounting, as a rule, are not reflected, with the exception of the case provided for by IFRS No. 2 “Inventories” - inventories are valued at the lower estimate of cost and net realizable value. Net realizable value is used when the cost cannot be restored due to the fact that these goods are obsolete and have partially lost their original quality or their selling price has fallen below their purchase price. In the balance sheet, these goods are valued at their realizable price, i.e. must be discounted by the end of the reporting period and reflected in accounting at sales cost (market prices).
Business entities have the right to re-evaluate inventory balances from the moment of their acquisition to the moment of processing or sale, taking into account the level of inflation. The amount of revaluation taking into account the level of inflation is used to replenish own working capital and is not included in taxable turnover.
The basis for revaluation of inventories is the order of the manager. For the revaluation of goods, an inventory list-act is drawn up, in which the commission fills in the name of the goods, grade, quantity, price and value of the goods at old prices, the price and value of the goods at new prices, the amount of the difference from the revaluation (markdown or revaluation). The procedure for reflecting the revaluation of goods in accounting also depends on the method of analytical accounting of goods used at the enterprise. If goods are accounted for in physical value terms, then the accounting records reflect:
firstly, writing off goods at old prices;
secondly, the posting of goods at new prices;
thirdly, the difference from the revaluation of goods in value terms.
If analytical accounting of goods is carried out in total terms, then only the difference from the revaluation of goods is reflected in accounting.
Based on inventory records, information on the revaluation of goods is reflected in the accounting accounts.
Accounting for inventory results
| No. | Contents of business transactions | Document | Account correspondence | |
| Debit | Credit | |||
| When accounting for goods in physical value terms. | ||||
| 1. | The markdown of goods is reflected: | An inventory list is an act for the revaluation of goods. | ||
| A) at new prices; | 1330 | 1330 | ||
| B) the difference from the markdown of goods; | 7210 | 1330 | ||
| 2. | Revaluation of goods is reflected: | Same. | ||
| A) at old prices; | 1330 | 1330 | ||
| B) the difference from the revaluation of goods. | 1330 | 6280 | ||
- In order to ensure the reliability of accounting and financial reporting data, entities must conduct an inventory of goods and containers at least once a year. The number of inventories in the reporting year and the dates for their implementation are established by the entity independently. Mandatory inventories are carried out:
— when changing materially responsible persons;
- when establishing facts of theft or abuse, as well as damage to supplies;
— in case of natural disasters, fire, accidents or other emergencies caused by extreme conditions;
— upon liquidation (reorganization) of an entity before drawing up a liquidation (separation) balance sheet and in other cases provided for by the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The results of the inventory are revealed by comparing the actual balances of goods and containers indicated in the inventory list with the balances according to accounting data at the time of the inventory. For goods and packaging for which deviations of actual balances from accounting balances have been identified, a matching statement is drawn up.
If a natural value analytical accounting scheme is used to account for goods, then the inventory results are displayed separately for each name and type of product. When maintaining cost analytical accounting of goods, the inventory result is determined not for each product, but as a whole based on the total cost of all goods.
Discrepancies between the actual availability of property and accounting data identified during the inventory are recognized by the entity:
— surpluses are income and are subject to capitalization;
- shortages - expense.
Offsetting shortages of some goods with surpluses of other goods is possible in exceptional cases with the permission of the manager. In this case, the following requirements for mutual offset of misgradings must be met:
— it was identified during the same audit period;
- established by the same financially responsible person;
-subject to overlap of the same product name and in identical quantities.
In case of mis-grading, as well as in all cases of identified shortages and surpluses of goods, financially responsible persons provide detailed written explanations.
When shortages are identified for those goods for which norms of natural loss during storage and sale are established, the accounting department calculates these losses and indicates them in the matching sheet, after which the final inventory result is displayed.
The results of the inventory must be reflected in the records of the month in which the inventory was completed.
The procedure for reflecting inventory results is presented in the table.
Accounting for inventory results.
| № p/p | Contents of business transactions | Document | Account correspondence | |
| Debit | Credit | |||
| 1. | Excess goods and packaging are included in income. | Comparison statement, order. | 1330 | 6280 |
| 2. | Shortage of goods written off: | |||
| — within the limits of natural loss (without creating a reserve); | ––»–– | 7110 | 1330 | |
| — within the limits of natural loss norms (when creating a reserve to cover losses); | ––»–– | 1360 | 1330 | |
| — in excess of the norms of natural loss; | ––»–– | 7470 | 1330 | |
| Uncompensated losses of goods due to natural disasters, fires, etc. | Act | 7210 | 1330 | |
| 3. | Reflection of shortages recognized by financially responsible persons: | Comparison statement, order. | ||
| a) at collection prices; | 1250 | 6280 | ||
| 4. | Reflection of shortages not recognized by financially responsible persons and referred for consideration to judicial investigative authorities. | Lawsuit. | 7210 | 1280 |
| 5. | Reflection of the amount of shortfalls by decision of the judicial authorities: | |||
| - awarded for recovery from financially responsible persons; | The court's decision. | 1250 | 1280 | |
| - recognized as unfounded and subject to write-off at the expense of the subject. | 7210 | 1280 | ||
Basic literature [1-13]
Further reading [1-9]
Test tasks for SRS
1. Inventory of stocks.
2. Documentation and accounting of inventory revaluation.
3.Accounting for the results of inventory of goods and containers.
GLAVBUKH-INFO
The inventory of goods is carried out in accordance with the Methodological Guidelines for the Inventory of Property and Financial Liabilities, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 13, 1995 No. 49, which must be applied taking into account the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88.The inventory of goods is carried out by a commission with the obligatory participation of financially responsible persons. Inventory of goods consists of checking their actual availability in kind at the locations of the goods.
Goods are entered in the inventory for each individual item, indicating the type, group, quantity and other necessary data (article number, grade, etc.).
The commission, in the presence of the warehouse manager (storekeeper) and other financially responsible persons, verifies the actual availability of goods by mandatory recalculation, reweighing or measuring. It is not allowed to enter into the inventory data on the balance of goods from the words of financially responsible persons or according to accounting data without checking their actual availability.
In general, the inventory of goods is carried out in the same manner as for the inventory of materials and other inventories.
Containers are included in the inventory by type, intended purpose and quality condition (new, used, in need of repair, etc.).
For containers that have become unusable, the inventory commission draws up a write-off report indicating the reasons for the damage.
Inventory inventory data is used to compile matching statements, in which the actual inventory data is compared with accounting data.
Comparison statements are compiled when discrepancies are identified between accounting data and data from inventory records and acts.
When taking inventory of goods, the following unified forms of inventories and acts are used:
Form No.
| Form name | |
| INV-3 | Inventory list of inventory items |
| INV-4 | Inventory report of shipped inventory items |
| INV-5 | Inventory list of inventory items accepted for safekeeping |
| INV-6 | Act of inventory of payments for inventory items in transit |
To reflect the results of the inventory of goods for which deviations from the accounting data are identified, matching statements of form No. INV-19 “Matching statements of inventory results of inventory items” are used.
The matching statement is drawn up in two copies by the accountant, one of which is kept in the accounting department, the second is transferred to the financially responsible person.
All business transactions and inventory results are subject to timely registration in accounting accounts without any omissions or withdrawals.
The results of the inventory must be reflected in the accounting and reporting of the month in which the inventory was completed, and for the annual inventory (carried out before drawing up the annual financial statements) - in the annual financial report.
Discrepancies between the actual availability of goods and accounting data identified during the inventory are regulated and reflected in the accounting accounts as follows.
Identified surplus goods are accepted for accounting at market value on the date of the inventory and are credited to the financial results of the organization. This operation is reflected in the debit of account 41 “Goods” in correspondence with account 91 “Other income and expenses” (subaccount 91–1 “Other income”).
When identifying surplus goods, financially responsible persons must provide appropriate explanations for them.
Losses and shortages of goods may occur in the following cases:
a) shortages and damage to goods discovered upon acceptance from suppliers:
- within the limits of natural loss;
- above the norms of natural loss;
b) shortages and damage to goods identified during inventory and inspections:
- within the limits of natural loss;
- above the norms of natural loss;
c) loss of goods as a result of emergency circumstances (accidents, fires and natural disasters);
d) loss of goods from containers;
e) waste generation.
Shortages and losses from damage to goods are accounted for in the debit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” and are written off from the specified account in the order depending on the moment of their detection (identification).
If shortages and damage to goods are detected upon acceptance from suppliers, then the amounts of shortages and losses from spoilage within the limits of natural loss norms are written off as selling expenses. If the supplier of the goods has provided a discount to compensate for possible losses of goods, the amount of shortages and losses from damage to goods (in excess of the norms of natural loss) discovered upon their acceptance may be written off as selling expenses within the limits of the amount of the discount provided.
If shortages and damage to goods are identified during inventories and inspections, as well as as a result of accidents, fires and natural disasters, then they are written off in the following order.
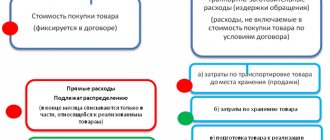
Amounts of shortages and losses of goods are written off from accounting accounts at their actual cost, which includes the contract price of the goods and the share of transportation and procurement costs related to this product.
The procedure for calculating the specified share is established by the organization independently.
In accounting, this operation is reflected in the debit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” and the credit of the goods accounting account.
Shortages of goods and their damage are written off from account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” within the limits of the norms of natural loss for sales expenses, in excess of the norms - at the expense of the guilty persons. If the perpetrators are not identified or the court refuses to recover damages from them, then losses from shortages of goods and their damage are written off to the financial results of the organization.
Write-off of commodity losses within the limits of natural loss norms is carried out only in cases where such norms are approved in the prescribed manner. In the absence of approved norms of natural loss, losses are considered as losses in excess of the norms of natural loss.
The shortage of goods within the established norms of natural loss is determined after offsetting the shortage of goods with surpluses based on re-grading.
In the event that, after a re-grading offset made in the prescribed manner, a shortage of goods was still identified, the norms of natural loss should be applied only for the item of inventory for which the shortage was identified.
The materials submitted to formalize the write-off of shortages of goods and damage in excess of the norms of natural loss must contain documents confirming appeals to the bodies of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, judicial authorities, etc. regarding the facts of shortages, and decisions of these bodies.
In addition, a conclusion on the fact of damage to goods received from the relevant services of the organization or specialized organizations must be attached.
Mutual offset of surpluses and shortages as a result of regrading can be carried out by decision of the organization’s management only for the same audited period, from the same audited person, in relation to goods of the same name and in identical quantities.
Financially responsible persons provide detailed explanations to the inventory commission about any misgrading.
In the case when, when offsetting shortages with surpluses by re-grading, the cost of the missing goods is higher than the cost of the goods found in surplus, then the specified difference is attributed to the guilty persons.
If the specific culprits of the shortage are not identified, then the differences are considered as a shortage in excess of loss norms and are written off to the financial results of the organization.
Identified shortages are taken into account in the debit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” and the credit of account 41 “Goods” and are written off in the following order:
- if there is a basis, a claim (claim) is presented to the supplier and the corresponding amount is written off as a debit to the account for accounting for settlements of claims;
- natural loss within normal limits is written off as selling expenses;
- the amount of shortfall in excess of the norms of natural loss is written off in the manner described above.
When preparing goods for sale, waste is generated when releasing goods from containers, paper wrappers, and binding materials; when cleaning contaminated surfaces, weathered cuts, the upper yellowed layer of fats; sugar crumbs (when selling weight sugar and sprinkled caramel), etc.
The cost of waste is written off on the credit of account 41 “Goods” to the debit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables.”
Losses from waste recorded in account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” are written off from the specified account:
- within the limits of norms - for selling expenses;
- above the norm - in the manner described above.
It should be noted that transactions to write off shortages and losses from damage to goods are reflected in accounting in the same manner as transactions to write off shortages and losses from damage to materials.
| < Previous | Next > |