With accounting, the process is streamlined: they hire an accountant, he handles everything. Sometimes they try to blame the management on the accountant as well. Usually, because they don’t see the difference, but it’s like asking a developer to fix Wi-Fi in the office, because “well, he’s a computer guy.”
Let's face it - accounting is a scary thing and no one wants to get into it. Accountants are holy people, without whom a business will be mired in penalties, fines and audits.
There is no need to put management accounting on the shoulders of an accountant. Yes, a great accountant will be able to do both, but these are two different forms of reporting and two functions in the company. You don’t want an accountant to do twice as much work, which will take twice as long, require twice as many skills and a completely different frequency. It's just not his job.
Let's try to figure out whose and why to complicate our lives so much.
Why you need to keep both records, why different specialists should do this, how to build a full-fledged accounting system in a company and not spend millions on it, Mikhail Smolyanov (“Finologist”) and Alexey Fitiskin (“My Business”) will tell you at the free webinar “Accounting and management accounting: how do large companies keep records and why does small business need it?” September 11 at 17:00 Moscow time
Purposes of each type of accounting
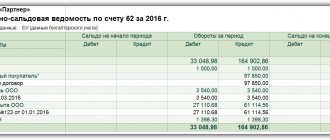
Accounting records transactions and transactions, financial results and cash flows.
It gives a rough idea of what is happening in the business. The main goal of an accountant is to correctly calculate taxes and report on the financial position of the organization on time. Accounting is focused on the past, since accounting works only with what has already happened or is happening now. It is unlikely that your accountant will predict revenue for at least the next month. Accounting does not have this capability, so it is not suitable for management.
Management accounting is aimed at operational analysis, understanding the state of affairs and planning further work.
It is important for management to collect information to make decisions that will help gain benefits in the future. Analysis of past periods helps to see the factors affecting the organization and predict the level of profit and loss in the future. The dynamics are monitored by three basic management reports:
- about cash flow;
- about financial results;
- forecast balance.
Periodicity
Financial statements
The deadlines are regulated by the state through the tax calendar, which specifies all dates for filing reports and paying taxes and contributions.
For example, here’s what an accountant needs to do in June:
- submit a report in form SZV-M for May 2021 before June 15, 2019 to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation at the place of registration;
- pay contributions from your salary for May 2021 until June 15, 2019 to the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration and to the Social Insurance Fund (injury contributions);
- make an advance payment of income tax for June 2019 by June 28, 2021 to the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration.
Management reporting
Ideally, it appears in real time. We need to strive for this and build a system that will allow us to see the big picture online.
In life, you can usually see some of the data quickly online, but the full data arrives with a week’s delay. This is a C grade option, because the meaning of the management report is lost.
Promptly obtaining data is necessary to quickly make important management decisions in business. Without this there will be no order and development. Imagine that you are driving a car or a bicycle, whichever you prefer. You are trying to drive, but instrument readings arrive in the “brain” of the car with a delay. You press the pedal or turn the steering wheel, and the car reacts only after half an hour. How far will you go?
Open data and trade secrets in accounting
Accounting is needed by tax authorities, statistics services, suppliers and other external users. Accounting data is no secret. They are even published publicly on the statistics website.
Management accounting is maintained for internal use by the director, manager or owner. Its data often becomes a trade secret, so even within the organization not everyone has access to it.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
Knowledge and competencies
Reporting has different functions, so the knowledge of the specialists who deal with each also differs.
Financial statements
The accountant speaks the language of the state and knows the rules of the state. It brings business actions into compliance with government regulations. Let's look at two life situations: employee business trips and acquiring.
1. Business trips
Nikolai and Alexey go to Moscow for negotiations on the project. Everything is paid for by the company. After negotiations, Nikolai leaves, and Alexey remains on his business in Moscow for two more days and demands that the company pay for his return tickets, accommodation and travel allowances.
The accountant’s task is to pay travel allowances to both employees and deal with Alexey separately. What an accountant needs to do:
- Understand whether it is legal to include additional hotel expenses and daily allowance for Alexey.
- Calculate daily allowance for each employee.
- Monitor the preparation of an advance report for each employee and generate payments for overruns.
To understand whether it was possible to pay Alexey for two days in Moscow, the accountant studied the legislation, internal documents on employees and business trips and was convinced that he could:
- pay for tickets from Moscow with a date shift of two days;
- include this expense in reducing taxable income;
- not to pay Alexey travel allowances for two extra days;
- not to pay for Alexey’s hotel for two extra days.
2. Acquiring
A simple operation “attached a card - the purchase price was written off - returned the goods” in the world of an accountant looks like this:
1. The client paid for goods in the store with a card. Postings are generated about the write-off of goods and the bank's debt to the organization, because the money arrives at the bank with a delay of 1-3 days.
2. The money arrived in the company’s bank account within 1-3 days. The bank deducts its acquiring fee. Postings are generated about the write-off of the bank's debt to the organization.
3. The bank commission must be allocated because it is withheld from the buyer's money. It is issued in a special way - as part of the proceeds.
The accountant sets up the cash register for the taxation system, and in addition to the cash register, an acquiring terminal appears. At the end of the day, the devices issue reports, on the basis of which the accountant makes accounting entries and draws up a cash book, in which he receives revenue and deposits it with the bank.
Management reporting
A financial model is a language for describing a business through numbers. A specialist who deals with management accounting must understand business processes.
When a person knows how marketing, sales and production work, he understands the essence of the processes and knows how to digitize them. He can ask the right question, talk to every manager, find an error in the calculations. Unlike an accountant, he is not required to thoroughly understand taxes.
At the free webinar “Accounting and management accounting: how do large companies keep records and why does small business need it?” On September 11 at 17:00 Moscow time, Mikhail Smolyanov (“Finologist”) and Alexey Fitiskin (“My Business”) will analyze in detail when, where and for what purpose accounting and management accounting are used, what is the difference between them:
— Specialist competencies and tools for accounting automation.
— Specialist competencies and tools for automation of management accounting.
Is it possible to combine all functions in one person or service and how much does it cost? Three examples of companies for which management accounting helped solve and avoid problems will be given.
Fixed and free forms of accounting
Accounting requirements are defined in detail: it is regulated by laws, regulations, standards, tax clarifications and other documents. The deadlines for compiling and the form of reporting are strictly defined. Accounting is mandatory for all organizations; you simply have no choice whether to do it or not.
Management accounting is simply your right. It is not subject to rules from above; it can be conducted in a way that is convenient for you, based on the specifics of the activity and your own goals. The main thing is that you understand the reports and indicators yourself. The frequency of compilation can be any: week, quarter or even year.
Tasks
The presented type of accounting can be organized to quickly and efficiently solve the following complex problems:
- regulate the planning of economic activities through budgeting;
- control and optimize costs by quickly obtaining fresh data;
- perform an analysis of the deviation of real values from planned values, based on report data.
The goals and objectives of management differ in the methods of their implementation:
- operational accounting;
- budgeting;
- management reporting, that is, internal;
- financial reporting, external.
They are implemented using:
- cash flow budget;
- budget of expenses and profits;
- planned balance.
The management balance sheet differs from the accounting balance sheet: in the latter, the classical models of management reporting format are completely absent. In this regard, if an enterprise needs to manage its balance sheet, it has to take the balance sheet and take measures to improve it - for example, expand analytics.
Budgets that are used in domestic conditions practically do not use management automation. This opportunity allows you to monitor the enterprise as a whole, analyze the implementation of plans, deviations of real indicators from budget ones, make timely adjustments and make decisions with greater efficiency.
The completion of the planned period is characterized by the preparation of:
- profit and loss statement;
- balance;
- report on the movement of financial resources.
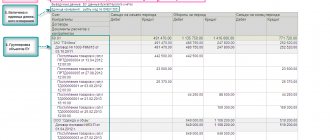
Scheme
The reality of data in accounting
We reflect in accounting what is written in the contract. And in management accounting we focus on the real meaning of the operation.
For example, sale with subsequent repurchase: the contract is concluded with the condition that the seller can buy the goods from the buyer at any time and retains all the risks and benefits of owning the goods. Such a transaction is a disguised loan or financing. There is no point in recognizing revenue from such a transaction in management accounting, since the revenue figure will be higher than in reality. But in accounting you will have to do this.
Formation of management information
The needs of enterprises for management information change according to certain patterns associated with the evolution of the organization itself. The stages of generating management reporting can be formulated as follows:
- collection of individual elements of management information (receipt of money and debts of specific clients, urgent payments, etc.);
- distribution of revenue by divisions;
- distribution of costs across departments;
- formation (approximately) of the budget and analysis of the profitability of divisions;
- distribution of revenue from individual goods and services;
- analysis of the profitability of individual goods and services;
- forecasting income and expenses;
- preparing and periodically adjusting a fairly realistic budget;
- preparation of individual management decisions (for example, investments) taking into account management accounting information;
- assessment of various options for strategic decisions based on management accounting information.
The gradual implementation of management accounting is due to the need to master the information received and develop the skill to analyze it.
Graduality and simplicity are the key to the effectiveness of the implementation and development of management accounting. Many companies begin to implement management accounting only when faced with economic difficulties. This problem is expressed in the works of the famous economics publicist S. N. Parkinson, who formulated many laws of business life, including his famous “laws.” When the influx of money is large and seemingly unlimited, the only economy that takes place is an economy of thought. In the second half of the 20th century. Parkinson described evolution, the period of the last 50-70 years.
In Russia, the events he describes probably fit into 10-15 years of development of a market economy. Parkinson described that “money used to be spent on organizing banquets and maintaining dancers. But there are (at least theoretically) some physiological limits to such excesses. There are no such restrictions on administrative innovations; administrative staff and various consultants can be kept in such numbers that the mistresses only become annoying and generally become intolerable.”
As the author notes, the habit of large incomes and large expenses quickly adjusting to them leads to peculiar innovations in accounting, when money is spent that actually does not exist. In Russia since the early 1990s. and until 1998, this was a critical feature of the development of many companies. Then the situation began to gradually change. During periods of economic reforms, when financial flows are significantly reduced, there is an increase in efficiency: companies put their “household” in order, establish normal accounting, etc. But periods of difficulties, of course, are a catalyst for the process of realizing the need to collect and analyze information that contributes to improving the quality of management decisions.
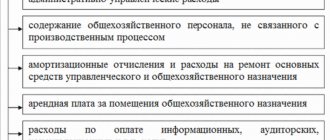
The right level of detail
Accounting evaluates the entire enterprise and combines information about all departments, products, and employees.
Management accounting can look at the entire company or individual divisions - in depth and in more detail. This allows you to better understand the business from the inside and know what is happening in it and why. You see not just the overall flow of funds in the company, but also indicators by department and even employee. Not just see the profit, but understand its sources. Don’t just take into account goods, but divide them into groups and types.
Setting up management accounting
There are several stages in the process of organizing management accounting.
The first stage is the creation of a working group. It should include the heads of all departments affected by the reform. It is best if the group is headed by the first person of the company (or his deputy). All participants are required to devote some part of their time (from 10 to 50%) to working on the project. Meetings should be held regularly; when making a decision, it is necessary to appoint someone responsible for its implementation and set deadlines for completing the work.
At this stage, the current state of affairs is analyzed, existing information flows are studied and the goal of the project is determined. This is the stage of diagnosing and formulating the concept of accounting, including accounting policies and management chart of accounts. Functional diagnostics and model development require special technologies that ensure speed, completeness and coherence of the result, so it is advisable to involve consultants. The company can do the rest itself.
The second stage is the separation of financial responsibility centers (FRC): costs (for example, IT service), income (for example, sales department), profit (for example, a branch) and investments. At this stage, it is necessary to determine exactly where and by whose decision income and costs arise so that the center manager, for example, is not responsible for uncontrollable expenses. Managers of financial responsibility centers are informed of the indicators that they are required to achieve. From a pragmatic point of view, it is enough to distinguish two types of units - income-generating and infrastructural.
The third stage is ensuring the necessary document flow, in particular the development of a methodology (who enters what information, in what form and column) and the creation of regulations (what information is received, in what time frame and to whom, what he does with it, to whom and when in what form transmits). All this is formalized in the form of regulations on management accounting.
The fourth stage is training to work with the management accounting system for personnel directly involved in the process. Training can be carried out in parallel with the generation of management reporting.
The fifth stage is automation. Moreover, it should be carried out only at the very last stage of implementation of management accounting. Experts recommend working in any standard local program, such as Excel, for at least a year, and only then, provided that the costs of the software are justified, proceed to deeper automation.
Metrics to Track
Accounting is carried out in monetary terms and is governed by numbers. Management accounting includes natural and even verbal indicators: the number of defects, productivity, customer and employee satisfaction, staff turnover, average order size and others. These indicators affect the business just as much as numbers, so they need to be monitored and adjusted. Often this becomes the main tool in optimizing the operation of the entire enterprise.
A web service for small businesses, Kontur.Accounting, helps you keep records, pay salaries and submit reports, and also generates five management reports. Monitor business development and automate routine accounting operations. All new users can get acquainted with the system and work in Accounting for free for two weeks.
Features of professions
Accountants
There is a wide choice of where to go to study: in Russia there are 1,015 universities studying to become accountants, specializing in economics, accounting and auditing. There are many face-to-face and distance learning courses for aspiring accountants.
According to Rosstat, as of October 31, 2021, the number of working specialists in accounting operations and accounting is 44,182 people, and specialists in processing statistical, financial and insurance information and conducting settlements are 11,274 people.
Salary depends on competencies, industry, volume of work and city.
In 2018-2019, the position of a leading specialist in Moscow is estimated at 110,000 - 150,500 rubles. In St. Petersburg they offer 107,600 – 137,500 rubles. A Muscovite who deals with cash and fixed assets can count on 51,500 - 75,000 rubles a month, a St. Petersburg resident - no more than 60,000 rubles.
The demand for professionals even with little work experience is quite high. The main thing in the profession is attentiveness and stress resistance, because an accountant is responsible for all inaccuracies and errors in accounting. An accountant always has room to grow; many, after several years of being employed, open their own business and become entrepreneurs.
Financial analysts
Financial analysts and directors are generalists whose responsibilities vary greatly depending on the company they work for. Analysts draw up a plan, advise the manager, and analyze.
Analysts are paid the most in the Smolensk region - an average of 100,000 rubles. In Moscow the maximum is 82,000 rubles, in the Leningrad region 56,000 rubles.
Financial directors in Moscow and St. Petersburg receive up to 600,000 rubles. per month. There is a very wide range of salaries in the market, it all depends on the company. For example, large industrial companies pay 1.5 million per month.
The best universities that train financiers are NES, National Research University Higher School of Economics, and Russian Economic University. G.V. Plekhanov, St. Petersburg State Unitary Enterprise and VAVT of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia.
Requirements for organizing the process
The organization of management is based on various parameters of the enterprise's management policy. These parameters are:
- production cycles and their frequency;
- continuity of data and more than one use;
- creating reporting values that are relevant to all levels of management;
- use of budgeting;
- efficiency, breadth and reliability of data, as well as the ability to analyze them;
- use of identical units of measurement;
- the ability to evaluate the performance of certain structural departments.
Note! The automated process, which is increasingly being introduced in enterprises, has its own requirements regarding the organization of the process.
Today they are:
- understandability for any user;
- timeliness of identifying and sending information;
- reality and completeness of provision of all parameters of economic activity;
- regularity of information collection;
- compliance of indicators with expectations.