What is tax accounting
The definition of tax accounting is given in Article 313 of the Tax Code.
Thus, tax accounting is a system for summarizing information to determine the tax base for a tax based on data from primary documents, grouped in accordance with the procedure provided for by this Code. As can be seen from the definition, tax accounting is necessary in order to calculate income tax. But the rules established by Chapter 25 of the Tax Code are such that it is impossible to do this on the basis of accounting data alone.
The main task of tax accounting is to generate complete and reliable information about how each business transaction is taken into account for tax purposes.
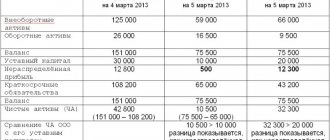
The accounting regulation “Accounting for income tax calculations” (PBU 18/02) requires organizing accounting in such a way that it can be used to determine taxable profit.
However, it does not exempt the company from maintaining tax records.
note
Since 2012, the concept of “consolidated group of taxpayers” has been introduced into the Tax Code. If a company is a responsible member of a group, it is required to maintain tax records for the entire group. However, this does not mean that the remaining members of the group do not have to keep records. They maintain tax records and provide their data to the responsible group member.
From tax accounting data it should be clear:
- how the company determines income and expenses;
- how an enterprise determines the share of expenses taken into account for tax purposes in the reporting period;
- what is the amount of the balance of expenses (losses) to be attributed to expenses in the following reporting periods;
- How does the company form the amount of reserves?
- what is the amount of income tax debt to the budget.
Tax accounting data is confirmed by primary documents, tax base calculations, and analytical tax accounting registers.
Tax accounting is a system for summarizing information to determine the tax base for a tax based on data from primary documents, grouped in accordance with the procedure provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Maintaining tax records is the responsibility of all companies, including those applying special tax regimes.
It is tax accounting that makes it possible to generate complete and reliable information about the accounting procedure for tax purposes of business transactions.
Tax accounting is carried out in special forms - tax registers.
Taxpayer organizations independently form their own tax accounting system.
The procedure for maintaining tax accounting must be prescribed in the accounting policy for tax purposes, which is approved by order (instruction) of the head of the company and is the main document necessary for calculating taxes.
The goals of tax accounting are:
1) generation of complete and reliable information on the amounts of income and expenses of the taxpayer, which determine the size of the tax base for the reporting (tax) period;
2) providing information to internal and external users to monitor the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of calculation and payment of taxes to the budget;
3) providing internal users with information that allows them to minimize their tax risks and optimize taxes.
In this case, the internal user of the information is the administration of the organization.
External users of information are tax authorities, which assess the correctness of the formation of the tax base, tax calculations, and also monitor the receipt of taxes to the budget.
The means of achieving the goal of tax accounting is the grouping of data from primary documents.
Tax accounting consists only of the stage of summarizing information. Collection and registration of information by documenting it is carried out in the accounting system.
Tax accounting data must contain the following information:
- the procedure for forming the amount of income and expenses;
- the procedure for determining the share of expenses taken into account for tax purposes in the current tax (reporting) period;
- the amount of the balance of expenses (losses) to be attributed to expenses in the following tax periods;
- the procedure for forming the amounts of created reserves;
- the amount of debt for settlements with the budget for taxes.
Tax accounting data is confirmed by:
- primary accounting documents (including an accountant’s certificate);
- analytical tax accounting registers;
- calculation of the tax base.
One of the main tasks of tax accounting is to determine the amount of payments to the budget and tax debts to the budget on a certain date.
The subject of tax accounting is the production and non-production activities of an enterprise, as a result of which the taxpayer has obligations to calculate and pay taxes.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation defines the following principles of tax accounting:
- principle of monetary measurement. Tax accounting reflects information on income and expenses, presented primarily in monetary terms;
- principle of property separation. Property owned by an organization is accounted for separately from the property of other legal entities owned by the organization.
- the principle of continuity of the organization's activities. Accounting must be maintained continuously from the moment of its registration as a legal entity until its reorganization or liquidation.;
- the principle of temporary certainty of facts of economic activity. The principle of temporary certainty of the facts of economic activity is dominant. Income is recognized in the reporting (tax) period in which it occurred, regardless of the actual receipt of funds, other property or property rights (accrual principle). Expenses accepted for tax purposes are recognized as such in the reporting (tax) period to which they relate, regardless of the time of actual payment of funds or other form of payment.;
- the principle of consistency in the application of tax accounting rules and regulations. The rules and regulations must be applied consistently from one tax period to the next. This principle applies to all tax accounting objects;
- the principle of uniform recognition of income and expenses. This principle assumes that expenses are reflected for tax purposes in the same reporting period as the income for which they were incurred.
The following tax accounting options are available:
- tax accounting is maintained separately from accounting. This option is most appropriate for use in large companies, where such records are kept in a special division of the organization;
- tax accounting is maintained on the basis of accounting, which presupposes the maximum convergence of tax and accounting; special tax registers are maintained only in cases where tax legislation provides for other accounting rules;
- tax accounting is carried out by adjusting accounting data: tax registers reflect only the difference between accounting and tax accounting data in situations where such deviations arise;
- tax accounting is maintained in a special tax chart of accounts. This method involves the development and introduction of additional tax accounts to the working chart of accounts. This method is the most optimal and is most often used in small and medium-sized organizations.
*Article borrowed from the site https://www.audit-it.ru/terms/taxation/nalogovyy_uchet.html
What are tax registers
Tax accounting registers are forms in which all the information necessary to calculate income tax is entered (Article 314 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is taken from primary documents or accounting registers.
There is no single form of registers, so each company must develop them independently and approve them as an annex to the order on accounting policies for tax purposes.
Each register must contain mandatory details. Here they are:
- Name;
- period (date) of compilation;
- transaction meters in physical (if possible) and monetary terms;
- name of business transactions;
- signature (decryption of the signature) of the person responsible for compiling the register.
When developing tax accounting registers, you can use the recommendations of the Ministry of Taxes of Russia (now the Federal Tax Service of Russia) “Tax accounting system recommended by the Ministry of Taxes of Russia for calculating profits in accordance with the norms of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.”
Tax accounting registers can be maintained either manually on paper or electronically on a computer. Each register must be signed by the person responsible for its preparation. They can be either a company accountant or a specialist directly involved in tax accounting.
How to keep tax records
The Tax Code gives an organization the right to choose the option of creating tax accounting registers.
There are two ways:
1. It is most advisable to build tax accounting on the basis of accounting. To do this, first of all, you need to clearly define in what ways the tax and accounting rules are the same and in what ways they differ. For more information about this, see the “Income Tax” section.
Then it is necessary to bring accounting and tax accounting policies as close as possible to the maximum possible extent: establish the same methods for depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets, write-off of inventories for production, determination of the production cost of products, assessment of work in progress and finished products in the warehouse, etc. Then many transactions reflected in accounting will simultaneously participate in the calculation of income tax.
However, do not forget: bringing tax and accounting closer together is not always beneficial. So, for example, if a company chooses a single depreciation method for accounting and tax accounting—linear—then the accrued amounts are reduced compared to other methods, and as a result, the amount of property tax increases.
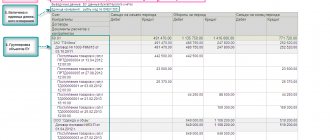
The account card, turnover sheet and other accounting documents can be used as tax accounting registers. The Tax Code does not prohibit doing this. If the accounting registers contain insufficient information to determine the tax base, then additional details can be entered into them.
2. It is possible to organize separate tax accounting, that is, to build an independent tax accounting system that is in no way connected with accounting. In this case, you will have to develop tax accounting registers for each business transaction. The same transaction will need to be recorded simultaneously in both the accounting and tax registers.
Primary tax accounting documents and their features
Tax accounting involves the use of primary documentation.
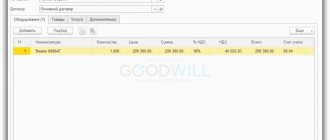
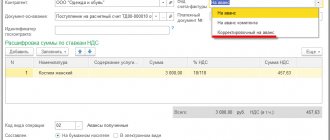
Basically, the primary documents of tax accounting are the same documents as in accounting. A special place among the primary tax accounting documents is given to such documents as invoices, sales and purchase books. These documents are consolidated primary documents. This category also includes certificates of income of an individual, cards for individual accounting of the amount of accrued payments, etc.
Note 2
A characteristic feature of documents of this type (except for invoices) is that they are not displayed in the accounting account, but are only one of the indicators for calculating tax.