Bank operations for the issuance (issue) of bank cards, as well as for their distribution, are carried out on the basis of internal bank rules, which each credit institution develops independently, taking into account the current legislation of the Russian Federation. These rules are approved by the highest governing body of the bank and must contain the following provisions:
- the procedure for issuing payment cards by the bank;
- the procedure for the bank's activities when acquiring payment cards;
- procedure for distribution of payment cards;
- the procedure for carrying out all types of settlements for transactions with bank (payment) cards;
- risk management system when using payment cards;
- the bank's procedure in case of loss of a payment card by a client;
- document flow for transactions with payment cards, as well as technologies for processing accounting information;
- the procedure for storing payment cards purchased by the bank for their issue, the procedure for personalizing payment cards for issuance to clients;
- the procedure for lending to clients when using credit cards - establishing a credit limit, conditions for using the loan, the procedure for repaying the principal debt and interest on such loans;
- all other issues related to the use of payment cards by bank clients.
By credit cards
a separate agreement may be concluded with the client, which stipulates all the conditions for obtaining and repaying the loan and interest on it.
In accordance with the Regulation of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 266-P “... Client is an individual
carries out the following operations using a bank card:
- receiving cash in foreign currency or foreign currency in the territory;
- receiving cash in foreign currency outside the territory;
- payment for goods (work, services, results of intellectual activity) in rubles on the territory, as well as in foreign currency – outside the territory;
- other transactions in foreign currency in respect of which the law does not establish a prohibition (restriction) on their performance;
- other transactions in foreign currency in compliance with the requirements of currency legislation.
Client – legal entity, individual entrepreneur
carries out the following operations using payment (debit) cards and credit cards:
- receipt of cash in foreign currency, in accordance with the procedure established by the Bank of Russia, settlements related to the activities of a legal entity, individual entrepreneur, including payment of travel and entertainment expenses;
- payment of expenses in foreign currency related to the activities of a legal entity, individual entrepreneur, including payment of travel and entertainment expenses, in the territory;
- other transactions in currency in accordance with the law;
- receiving cash in foreign currency outside the territory to pay for travel and hospitality expenses;
- payment of travel and hospitality expenses in foreign currency outside the territory;
- other transactions in foreign currency in compliance with the requirements of currency legislation...”
All transactions on payment cards of bank clients are duplicated electronically and this is the basis for their execution and confirmation for reflection in the bank’s balance sheet. These documents reflect the following mandatory details:
- identifier of an ATM, electronic terminal or other technical means intended for performing transactions using payment cards;
- type of operation;
- transaction date;
- transaction amount;
- transaction currency;
- commission amount;
- authorization code;
- payment card details.
Recently, bank operations with “business cards”
clients of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs. The essence of these operations is quite simple. A plastic bank card (business card) is issued to the client (legal entity or individual entrepreneur), exactly the same type as cards issued for citizens (the public). This business card is linked to the client’s current account and has a spending limit. This tool is especially convenient for enterprises whose employees often make expenses in cash - purchase various goods in stores, fuel at gas stations, pay for hotels, meals in cafes and canteens, and make any other expenses in cash. If they use a business card, all payments for goods, services, etc. are made non-cash. The bank can issue any number of cards to a client for one current account. Also, employees of an enterprise can withdraw cash from any ATM using such a business card within the previously agreed upon limit, but in this case a commission is usually charged, which is identical to the checkbook commission for withdrawing cash from a current account. No transfers of funds from a business card to various personal cards of citizens are allowed. Also, the client, in agreement with the bank, can set daily limits for the use of funds for all his business cards, or for a month, etc., including cash withdrawal limits. Business cards issued by Russian banks can also be used to pay for goods and services in foreign countries.
You can also use business cards to top up your company’s current account through ATMs and payment terminals. The head of the enterprise and (or) the chief accountant can quickly receive a report on the use of funds on business cards, receiving notifications about completed transactions by phone or email.
Checking account
A current account is a kind of account designed to store available funds and make non-cash payments.
Both an individual and a legal entity can open a current account, but if individuals can themselves determine whether they need such an entry, then for a legal entity this is a mandatory procedure regulated by Russian law. For each legal entity, opening a current account allows for quick and convenient access to available funds, which can be terminated at any time through liquidation. It is important to open a current account for an LLC in a reliable and trusted bank, since only in this case will a legal entity that has decided to open a current account for an LLC have confidence in the safety of available funds and the ability to quickly access them. Opening a current account for an LLC is important regardless of the situation. You can open a current account for an LLC for several different purposes at once. For example, open a current account for an LLC in one currency, which will be intended for current expenses, and in the same bank open a current account for an LLC in a different currency, which no one will use on demand.
Accounting entries for commercial banking structures
The accounting entries of commercial banking structures are quite diverse. Let's look at the most common of them.
- Debit 20202 “Cash desk of credit organizations” (asset) Credit 40702 “Commercial organizations” (liability) – reflects the transfer of cash to the cash desk of a banking structure for crediting to some current account of a specific client;
- Debit 91207 “Forms” (asset) Credit 99999 “Account for correspondence with active accounts with double entry” (liability) – reflects the transfer of check books and forms to the cash desk of the banking structure;
- Debit 99999 “Account for correspondence with active accounts with double entry” (liability) Debit 91207 “Forms” (asset) – reflects the issuance of check books and forms from the cash desk of the banking structure;
- Debit 40702 “Commercial organizations” (liability) Debit 20202 “Cash desk of credit organizations” (asset) – reflects the write-off of funds from the client’s current account for issuing him cash from the cash desk of a commercial banking structure;
- Debit 20202 “Cash desk of credit institutions” (asset) Credit 20209 “Cash in transit” (asset) – reflects the receipt of cash from the cash settlement center to the cash desk of a commercial banking structure;
- Debit 20209 “Cash in transit” (asset) Credit 30102 “Correspondent accounts of credit institutions” (asset) - reflects the receipt by a commercial banking structure of an extract from the RCC on the withdrawal of cash support from the correspondent account of a financial institution;
- Debit 20209 “Cash in transit” (asset) Credit 20202 “Cash desk of credit organizations” (asset) – reflects the issue of cash from the cash desk of a commercial banking structure for its transfer to the cash settlement center;
- Debit 30102 “Correspondent accounts of credit organizations” (asset) Credit 20209 “Cash in transit” (asset) – reflects the receipt by a commercial banking structure of an extract from the RCC on the crediting of the amount of cash that was collected;
- Debit 20209 “Cash in transit” (asset) Credit 20202 “Cash desk of credit organizations” (asset) - reflects the transfer of cash from the cash desk of a commercial banking structure to bolster the branch cash desk;
- Debit 30302 “Settlements with branches located in the Russian Federation” (asset) Credit 20209 “Cash in transit” (asset) - the write-off of cash from the correspondent sub-account of the branch is reflected; cash was written off in exchange for the cash that was transferred to it;
- Debit 20202 “Cash desk of credit organizations” (asset) Credit 30302 “Settlements with branches located in the Russian Federation” (asset) – reflects the receipt of cash from the cash desk of a commercial banking structure;
- Debit 20208 “Cash in ATMs” (asset) 20202 “Cash desk of credit institutions” (asset) – reflects the issuance of non-greedy funds from the cash desk of a commercial banking structure to the ATMs of a financial institution;
- Debit 409026 “Collected cash proceeds” (liability) 47422 “Liabilities for other operations” (liability) - reflects the receipt of collected cash in the cash desk of the commercial banking structure.
As can be seen from the listed accounting entries, accounts in financial institutions differ from the accounts of commercial organizations: different numbering of business transactions, including the number of characters. Business transactions in banking structures are reflected directly on the same day, which means a complete ban on postings for the previous period.
Are you a student at any Russian university? We invite you to a paid interview! The topic of the interview is preparation for the session and problems that arise during this Find out more
Opening a current account
You can open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur without any extra effort, since this procedure, unlike liquidation, does not cause any difficulties. In order to open a current account for an LLC, it is enough to contact the bank and provide a number of documents, most of which every legal entity must have
- charter or agreement on establishment;
- certificates of tax registration and state registration;
- a copy of the passport of each person who will have access to the funds;
- extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
In addition, to open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur, other documents will be required. It is best to familiarize yourself in advance with what papers may be required for a particular legal entity so that you can open a bank account for an individual entrepreneur without any extra effort. Opening a bank account for a legal entity is not difficult, but sometimes this process can cause a lot of problems. It all depends on how prepared you are to open a bank account and who you entrust this process to.
HOW DOES THE BENEFICIARY KEEP ACCOUNTS?
The participation of the guarantor in the calculations does not create any special problems for the beneficiary creditor.
This will not affect the taxation of his profits in any way. And the accounting procedure is illustrated by another example. Example 6
Let's use the conditions of example 2 again. But now let's look at the situation from the seller's point of view.
Let’s assume he uses the “simplified” system, and the property is included in the list of goods. The accountant will make the following entries: DEBIT 008
- 10,000,000 rubles.
— a bank guarantee was received to ensure the buyer’s payment under the real estate purchase and sale agreement; DEBIT 68 CREDIT 51
- 15,000 rub.
— the state fee for state registration of the transaction is transferred; DEBIT 44 CREDIT 68
- 15,000 rub.
— duty is included in sales costs; DEBIT 62 CREDIT 90
10,000,000 rub.
– the debt of the buyer-principal is reflected; DEBIT 90 CREDIT 41
- 8,000,000 rub.
— the property is deregistered; DEBIT 76 CREDIT 62
- 10,000,000 rub.
– a demand was presented to the guarantor bank for payment under the contract due to non-receipt of money from the buyer; DEBIT 51 CREDIT 76
- 10,000,000 rub.
– payment has been received from the guarantor; LOAN 008
- 10,000,000 rub. – the used guarantee has been written off (subclause 1, clause 1, article 378 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
for reference
Bank guarantees are a very popular product among companies. Here are real figures for some banks that issued bank guarantees in the amount of:
10,000,000 rub. – St. Petersburg branch of GLOBEX Bank (Vnesheconombank Group);
790,000,000 rub. (including guarantees in US dollars and euros) – Irkutsk branch of VTB Bank;
RUB 3,600,000,000 – Penza branch of Sberbank of Russia.
Elena Dirkova
, for the magazine “Practical Accounting”
Practical accounting
A universal berator that contains complete and reliable information about accounting rules. Comprehensive information about the work of the company from creation to distribution of profits. Find out more >>
If you have a question, ask it here >>
Opening a current account for individual entrepreneurs and LLCs
An urgent opening of a current account for an individual entrepreneur will be required only if it is planned to carry out non-cash transactions. If in plans all work is carried out only through cash payment, then a current account for individual entrepreneurs is not required. In order for an account to be opened for an individual entrepreneur, you will need to collect a complete package of documents and submit it to the bank. The whole procedure takes quite a lot of time, so those who know that a legal entity never has time entrust this procedure to professionals who are able to independently solve the task and open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur in the shortest possible time.
Qualified specialists can open a current account for an LLC, just like for an individual entrepreneur, but it should be understood that not every company providing such services is able to open a current account for an LLC in accordance with all existing rules. If you decide to open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur with the help of a third-party organization, then there is a risk of encountering a large number of problems, which are very difficult to correct for each legal entity. To prevent this from happening, remember that only professionals who have proven themselves to be the best can open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur.
Opening a current account for an LLC, unlike an individual entrepreneur, is a necessity, without which it is impossible to run a full-fledged business. Opening a current account for an LLC is important for every legal entity, however, not every one of them is able to open a current account for an LLC on their own, so here you cannot do without the help of specialists who will not only be able to open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur, but will also provide detailed advice on how opening and closing are done, how the liquidation or unblocking process works, and what you need to do to succeed in a bank or treasury.
You can open a bank account for an LLC only with a pre-prepared package of documents. Any mistake made will result in you not being able to open a bank account for the LLC, which will require you to start over. That is why, in order to quickly open a current account for an LLC without extra effort, legal entities turn to specialized organizations that can open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur without extra effort.
Moscow State University of Printing Arts
1.
Topic 1. BASICS OF ORGANIZATION OF ACCOUNTING IN A COMMERCIAL BANK
In Russia there is a two-tier system - the Bank of Russia and commercial banks and other institutions.
The Bank of Russia performs the following functions of the Central Bank:
- pursues a unified state monetary policy aimed at protecting and ensuring the stability of the ruble;
- issues cash and organizes its circulation;
- is a lender to commercial banks and organizes a bank refinancing system;
- establishes the rules for making settlements, conducting banking operations, accounting, and reporting for the banking system;
- carries out state registration and licensing of credit organizations;
- supervises the activities of commercial banks;
- carries out currency regulation and currency control.
Commercial banks provide credit and settlement services to business entities. A commercial bank is a highly organized credit organization created to attract and place funds, precious metals, securities, funds of legal entities and individuals on the terms of repayment and payment, which meets the needs of society, reimburses expenses and makes a profit as a result of statutory activities. Statutory activity is the provision and sale of services to legal entities and individuals, who are called bank clients.
Accounting is based on economic information, the collection procedure, classification and directions of which are regulated by the laws of the Russian Federation and regulations of the government and the Bank of Russia.
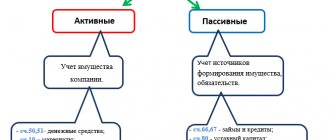
The subject of accounting in banks refers to objects in the form of assets and liabilities, where assets are the funds on which the bank’s business activities are carried out, liabilities are the sources from which the funds are generated.
The bank's assets include:
- The bank's own share of the authorized capital.
- Cash and precious metals.
- Correspondent accounts of a commercial bank with the Bank of Russia and other credit institutions.
- Securities and financial investments.
- Loans provided.
- Deposits and other placed funds.
- Discounted bills.
- Bank property.
- Accounts receivable.
- Bank expenses.
The bank's liabilities include:
- Authorized capital.
- Extra capital.
- Funds.
- Correspondent accounts of commercial banks opened in the bank.
- Loans received.
- Deposits and other funds raised.
- Client funds in settlement, current and other accounts.
- Securities issued by a bank.
- Accounts payable.
- Bank income.
Assets and liabilities are involved in the business operations of a commercial bank:
- settlement;
- cash;
- on attracting and placing funds, namely credit, deposit, interbank;
- for the purchase and sale of securities and precious metals;
- with foreign currency;
- intrabank operations, namely the movement of capital, funds, property.
All operations of a commercial bank are divided into passive and active, i.e. operations to attract and place funds.
The bank's passive operations—operations to raise funds—contain three groups. The first group of passive operations is associated with the formation and development of own funds. The second group of passive operations are short-term and long-term loans provided by one bank to another. This group also includes deposits and borrowed funds from commercial banks. The third group of passive operations - deposit operations - is the main one in banking activities. It reflects the activities of commercial banks as intermediaries in the acquisition of resources on the free market for credit resources.
Active operations of a commercial bank are operations for placing client funds and own funds of a commercial bank.
The accounting method (a set of methods and techniques) is:
- documentation;
- inventory;
- ledger accounts and double entry.
Let us dwell in more detail on the accounting method in commercial banks.
Documentation is written evidence of a business transaction that gives legal force to accounting data. It provides a continuous and continuous reflection of the statutory and economic activities of the bank.
Mandatory details in the documents contain:
- Name of the bank;
- Title of the document;
- numbering;
- date;
- summary of the operation;
- quantitative and monetary expressions of the transaction;
- signatures of the persons responsible for the operation.
The main groups of documents include:
- cash documents (for processing and issuing cash in rubles and foreign currency);
- settlement documents (for payment of client obligations);
- memorial documents (when processing intra-bank transactions).
The accumulation of information on memorial documents is carried out using specialized computer programs.
Here are the main registers for maintaining the accounting records of a commercial bank:
- accounting journal (2 copies): one copy - for the daily balance, the second - for the accounting documents of the day;
- cash registers (2 copies): one copy - for cash documents, the second - for accounting documents of the day (compiled daily);
- statements of balances on first and second order accounts, personal accounts, balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts (compiled daily);
- statement of balances of placed funds;
- turnover sheet for commercial bank accounts in the context of first and second order accounts;
- balance.
The management of a commercial bank organizes internal bank control, which is divided into preliminary and subsequent (before and after drawing up the balance sheet). Preliminary control is carried out according to the control signatures of the performers affixed to the documents. Bank accounting defines a list of documents subject to additional control.
Inventory is a method of checking the availability of material assets, fixed and cash assets, precious metals, claims and obligations. Inventory either confirms accounting data or reveals unaccounted for values and funds, losses, thefts, shortages, and miscalculations. With its help, the safety of any type of property is monitored, and the completeness and accuracy of accounting data is checked. The number of inventories carried out is established by the Bank of Russia and is supplemented individually by each commercial bank independently.
Accounting accounts are registers for grouping and current reflection of information from homogeneous banking transactions. Accounts in accounting are divided into active and passive. They are named according to the parts of the balance sheet and reflect their content. The structure of accounts, regardless of their type, corresponds to the traditional form of accounts in accounting. The amount of each banking transaction is reflected in the accounts twice in accordance with the double entry principle. Reflecting the amount of a banking transaction on the debit of one account and the credit of another account is also called correspondence of accounts or accounting entry.
Information on accounts is divided into analytical and synthetic according to the method of its generalization and grouping. Analytical accounts are maintained in monetary, natural and labor dimensions. Their number and name are established by the bank independently. Analytical accounting involves opening and maintaining personal accounts by type of currency, clients, correspondent banks, types of loans and other characteristics. Each personal account is assigned a name and number, which determines its belonging to the intended purpose of the collected information and to a specific client, subdividing them by purpose and by owner. Personal accounts of analytical accounting are opened for each balance sheet and off-balance sheet account of synthetic accounting. To account for expenses and income of the federal budget, personal accounts are maintained in accordance with budget qualifications.
Personal accounts are registered at the bank in a special book, in which separate sheets are allocated for each account. This book is a classifier of personal accounts opened in banks by enterprises, organizations and institutions. The account designation must indicate:
- its name (in words);
- digital personal account number;
- for loan accounts - the purpose for which the loan was issued, the number of the loan agreement, the interest rate, the digital designation of the credit risk group for which the reserve for possible loan losses is calculated, other data as decided by the bank.
The header of the personal account indicates its number and reference data, and the headers of the personal accounts of individual borrowers indicate a reporting symbol and additional data to monitor the timely repayment of the loan. In personal accounts of analytical accounting for off-balance sheet accounts, the number of the corresponding account and the conventional digital designation of the type of transaction are not indicated. Personal accounts of analytical accounting are printed according to established standard forms, which are included in the unified system of settlement and monetary documents and are the bank's output documents. With automated accounting, personal accounts are printed on roll paper, in compliance with the forms of standard personal account forms.
The following details are common to all forms of personal accounts:
- transaction date;
- number of the document on the basis of which the entry is made;
- Number of correspondent account;
- symbol of the type of operation;
- the amount of debit and credit turnover and the balance amount.
The standard form of the main personal account is shown in Fig.
1. Main personal account form
Client name__
______________________________ Name of the bank____________________________________
Date (period) for which the statement is provided
______ Extract from personal account No. ___________________________ Opening balance ________________________________________ Total turnover _________ Outgoing balance ____________
| date | Document Number | Type of operation | Number of correspondent account | Revolutions | |
| debit | credit | ||||
Total turnover___________ Closing balance_______
Rice. 1
Entries in personal accounts and statements on them are made simultaneously for all documents of the operating day with the withdrawal of the balance amount for the next day, based on the turnover for the day and the balance at the beginning of the day. The date in the personal account is printed once when the first transaction is reflected. When compiling personal accounts, a conventional digital designation of the type of transaction is used. For example, debiting funds according to a payment order or crediting payments, according to a copy of the payment order, is indicated by the number 2, cash payment by check - by the number 3, etc. Information about the movement of funds on a personal account is issued to the bank client in the form of an extract.
Statements from personal accounts issued to bank clients are compiled on electronic computers. To decipher entries in personal accounts for a loan, documents (copies of documents) are attached to the statements, according to which entries in personal accounts were made. These documents are affixed with a stamp, which is used to issue statements, and also indicates the date of their posting to the personal account. When preparing the statement, the responsible executor is obliged to ensure that it fully corresponds to the personal account, as well as the presence of the necessary applications and the correctness of their execution.
Extracts from personal accounts are issued to clients within the time limits established in agreement with the account owner. For accounts that were not valid on the last working day of the month, statements will not be issued on the first day. If there is no movement on the account during the month, clients are sent notifications about the amount of the balance as of the first day. On January 1, all personal accounts must be prepared and statements issued to clients. Based on these statements, clients must provide the bank with written confirmation of their personal account balances at the end of the reporting year.
Analytical accounting registers in credit institutions are:
- personal accounts;
- accounting journals;
- statement of balances on first- and second-order accounts, personal accounts, balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts;
- statement of balances of placed (raised) funds.
It is allowed to maintain analytical accounting of contributions from shareholders, deposits of individuals, bank employees, accounting of fixed assets, inventories, etc., operations important for the bank, according to separate programs with the total amounts reflected on the corresponding accounts in the balance sheet.
Synthetic accounts group analytical accounting data according to certain characteristics. They reflect the state and movement of bank funds and their sources in a generalized form in monetary terms. The number of synthetic accounts is regulated by the Chart of Accounts for accounting in credit institutions of the Russian Federation. Accounts are the basis for filling out reports, balance sheets and are used to analyze bank performance indicators. The main registers of synthetic accounting are daily balances and check sheets. Synthetic accounts are divided into first and second order accounts. First-order accounts have three-digit numbering, second-order accounts have five-digit numbering.
Synthetic accounting registers in credit institutions include:
- daily turnover sheet;
- daily balance.
The daily turnover sheet is compiled for balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts in the prescribed form. Within a month, turnover is shown per day. In addition, on the first day of the month, a turnover sheet for the month is compiled, for quarterly and annual dates - with increasing turnover from the beginning of the year. The daily balance is compiled according to the established form programmatically in the context of second-order balance sheet accounts. When creating reserves for possible losses, balances on active accounts are shown minus the reserve.
Balance sheets and turnover sheets are signed after their consideration by the head of the credit institution, the chief accountant.
The amounts reflected in the analytical accounting accounts must correspond to the amounts reflected in the synthetic accounting accounts. This is achieved by stable software, simultaneous reflection of transactions in interconnected accounting registers.
Before signing the balance sheet, the chief accountant or on his behalf, an accounting employee must verify:
- correspondence of the total balances reflected in the accounting journal with the turnover shown in the turnover sheet;
- correspondence of balances on second-order accounts reflected in the balance sheet with balances shown in the turnover sheet, statement of account balances;
- correspondence of balances on second-order accounts reflected in the statement of account balances with the balances shown in the statement of balances of placed (raised) funds.
A corresponding entry is made in the balance sheet about the inspection performed before the signatures of officials. If a discrepancy is identified, the reasons are determined and measures are taken to eliminate it. If necessary, correction entries are issued. The error is corrected the moment it is discovered. Reprinting of analytical and synthetic accounting materials is not permitted.
In addition to accounting, bank institutions maintain operational records. The latter, as a rule, is not checked by the balance sheet and is maintained directly by operational employees. In an operational manner, first of all, changes in balances in personal accounts that occur in connection with receipts and payments of money are taken into account. Such accounting, maintained during operating hours, allows payments to be made from settlement, current, budget and other accounts only within the limits of available funds. Operational accounting is carried out by counting the amounts of money received and paid, balancing them and displaying the balance for each account. The new account balance received promptly is recorded on documents: in the personal account or in the verification sheet for the previous day.
The chart of accounts for commercial banks and the accounting rules were developed by the Bank of Russia. The rules for its application are based on the following accounting principles:
- Continuity of activity of the credit institution in the future.
- Consistency of accounting rules, ensuring comparability with reports of the previous period.
- Prudence involves a reasonable assessment of assets and liabilities, income and expenses, which allows not to transfer risks that potentially threaten the financial position of the organization to subsequent periods.
- Reflection of income and expenses using the “cash” method, after receipt of income and expenses, except for cases established by the Rules.
- The day of reflection of the transaction provides for the reflection of transactions (receipt of documents) on the day they are performed, unless otherwise provided by regulations of the Bank of Russia.
- Separate and detailed reflection in the accounting of assets and liabilities.
- Continuity of the opening balance according to the balances of balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts at the end of the previous and beginning of the current period.
- The priority of content over form provides for the reflection of transactions in accordance with their economic essence, and not their legal form.
- The unit of measurement provides that assets and liabilities are recorded at their historical cost at the time of acquisition or occurrence.
- Openness provides for a reliable reflection of business transactions that avoids ambiguity in the position of a credit institution.
- Consolidation provides for a consolidated balance sheet and reporting for the credit institution as a whole and daily balance sheets for secondary accounts.
- Non-repetition of data on the balance sheet and off the balance sheet (on off-balance sheet accounts), except in cases provided for by the Rules and regulations of the Bank of Russia.
A chart of accounts is a list of synthetic accounts of the first and second order, sufficient for organizing accounting. It is presented in the form of the following table:
| No. of balance accounts | Name of sections and accounts of the balance sheet | Account attribute | |
| I order | II order | ||
The chart of accounts includes five sections, which look like this:
| Section number | Section name | Account number 1st order |
| A. Balance sheet accounts | ||
| 1 | Capital and funds | 102-107 |
| 2 | Cash and precious metals | 202-204 |
| 3 | Interbank transactions | 301-328 |
| 4 | Customer Transactions | 401-476 |
| 5 | Transactions with securities | 501-525 |
| 6 | Funds and property | 601-614 |
| 7 | Performance results | 701-705 |
| B. Trust Accounts | ||
| These accounts record transactions stipulated by the trust management agreement for resources not owned by the bank. A separate balance sheet is drawn up for these accounts. Active accounts Passive accounts | 801-810 851-855 | |
| B. Off-balance sheet accounts | ||
| 2 3 4 5 6 7 | They take into account valuables and documents accepted for storage, collection, commissions, sources of financing for capital investments, strict reporting forms, and shares. A separate balance sheet is drawn up for these accounts. Unpaid authorized capital of credit institutions Securities Payment transactions and documents Credit and leasing operations Debt written off and taken off balance sheet due to impossibility of collection Corresponding accounts: — for correspondence with passive accounts with double entry — for correspondence with active accounts with double entry | 906 907, 908 909-912 913-915 916-918 99998 99999 |
| D. Urgent operations | ||
| Accounts for recording transactions for purchase/sale transactions of funds in foreign currency, precious metals and securities for which the transaction dates do not coincide with the settlement date. These are memorial accounts that take into account the volume of transactions concluded before the payment is due. When this period occurs, the data will move to balance sheet accounts. A separate balance sheet is drawn up for them. They consist of accounts: - for cash transactions; — forward transactions; — unrealized exchange rate differences Active accounts Passive accounts | 930-940 960-970 | |
| D. Securities accounts | ||
| They are used to record transactions with issue-grade securities accepted from clients for storage or for the implementation of trust management of them. Operations on securities accounts are called depository. A separate balance sheet is drawn up for them: Active accounts Passive accounts | 98000-98035 98040-98090 | |
The chart of accounts contains only active and passive accounts; there are no active-passive accounts. To organize accounting, paired accounts have been introduced: one is active, the other is passive. At the beginning of the operating day, transactions are reflected in the paired account that has a balance. At the end of the operating day, if the account balance changes place, it is transferred to the matching account.
The chart of accounts does not provide for separate reflection of transactions in foreign currency. All transactions are reflected in national currency. Currency codes and ruble equivalent are maintained on personal accounts. Active and passive accounts take into account the time factor for completing settlement transactions and are divided by type of client, taking into account the form of ownership, type of activity and country of origin.
In analytical accounting, the construction of a personal account code is interconnected with the numbering of second-order synthetic accounts in the chart of accounts and is built according to the following principle.
Personal accounts opened for clients in a commercial bank are designated by a twenty-digit code. The first digit is the section number of the chart of accounts. The next two are the account number of the first order (always starting from zero). The fourth and fifth digits are the second-order account number, namely its numbering. For each first-order account, this numbering begins with “01”. The next three digits are the code of the currency or precious metal. The ninth digit is the security key. The next four digits are the branch or division number. The last seven digits for bank clients represent the serial number of the personal account. Similar numbering is used for credit accounts. For income and expense accounts, the first five of the last seven digits are the income statement symbol. The last two are the serial number of the personal account. Free positions when assigning personal account numbers are filled with zeros, which are located in the positions on the left, i.e. numbering is from right to left.
The numbering of trust accounts, off-balance sheet accounts, urgent transaction accounts, and custody accounts is established by the bank independently, taking into account the instructions of the Bank of Russia. In accordance with the plan, the first five digits of the numbering accounts contain the account number of the second order.
The elements of accounting are:
- balance;
- reporting.
The balance sheet as an element of the accounting method is a grouping of information about the resources and funds of the bank, which are distributed in it according to the degree of liquidity. The balance sheet of a commercial bank is compiled daily and reflects the state of the bank's borrowed and own funds, as well as their placement in credit and other operations. According to the balance sheet, the formation and placement of monetary resources is controlled; the state of credit, settlement, cash and other banking operations; correct reflection of transactions in accounting. The balance is drawn up monthly according to Form No. 101.
The reporting covers the statutory activities of the bank, satisfies the information requirements of internal and external users (founders, clients, tax authorities, Bank of Russia) and is divided into reporting at the end of the month and reporting at the end of the quarter. The procedure for compiling, content, and deadlines for submitting current financial statements by commercial banks is determined by the Bank of Russia. Current reporting at the end of the month is submitted to the Main Directorate of the Bank of Russia and contains:
- balance;
- consolidated balance sheet (including balance sheets of branches);
- deciphering the balances of loan debt and non-payments on loans from banks of organizations by industry;
- decoding of individual balance sheet accounts according to the timing of raising and distributing funds;
- decoding of individual balance sheet accounts for economic standards for the activities of a commercial bank;
- list of major creditors;
- decoding of balance sheet accounts;
- calculation of economic standards;
- calculation of the required reserve fund;
- decryption of balance sheet account 30102;
- decoding of balance sheet accounts for correspondent accounts 30109, 30110.
Commercial banks carrying out transactions in foreign currency additionally submit to the Main Directorate of the Bank of Russia a report on the movement of foreign assets and liabilities in freely convertible currencies, as well as in other types of currencies for transactions with non-residents, highlighting countries far and near abroad. In addition to the above forms, banks performing operations in foreign currency submit to the Bank of Russia branch a special report on maintaining an open currency position and a report on the movement of cash foreign currency and payment documents in foreign currency.
To prepare an annual accounting report, banks at the end of the reporting year conduct an inventory of all cash and valuables, fixed assets, household and other materials, and settlements recorded on balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts. Accounts receivable and payable are analyzed, and active measures are taken to repay them. Unrealistic amounts must be written off from the balance sheet and recognized as losses. The loan portfolio is analyzed, and measures are taken to identify unrealistic loan debt, as well as accrued interest on such loans and write them off in the prescribed manner. Similar work is carried out for all other types of assets in order to reflect real and reliable data on assets and liabilities in the annual balance sheet.
Assistance in opening a current account for LLC (Moscow)
A quick opening of a current account for LLCs and individual entrepreneurs in Moscow can be done without any problems. In this case, a person who decides to open a current account for an LLC only needs to choose the most acceptable bank, after which specialists will get down to business. For every legal entity, the question of how to open a current account for an LLC is especially acute, since this process contains a large number of pitfalls, without knowledge of which you can forget about achieving a positive result.
Assistance in opening an LLC current account in Moscow is provided by a large number of companies, but not every one of them is able to do everything correctly. If you need to open a current account for an LLC without any problems, contact experienced specialists who are able to open a current account for an LLC in any bank in the shortest possible time.
Guarantees for long-term obligations
The remuneration for a transaction with a guarantor relates to the period for which the guarantee was issued (clause 1 of Article 378 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). This period may cover more than one reporting (tax) period when the guarantee ensures the fulfillment of the principal's obligations under a long-term agreement aimed at generating income. At the same time, the connection between the warranty expense and the corresponding income of the principal company is indirect. This situation falls under paragraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 272 of the Tax Code.
In the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 11, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/4, a company carrying out the construction of oil and gas complex facilities under a contract for a period of 2 years appears as a principal. Financiers indicated that expenses in the form of fees for the provision of a bank guarantee purchased in order to ensure the fulfillment of obligations under the contract must be taken into account evenly over the period for which it is purchased. A similar conclusion is contained in letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 19, 2012 No. 03-03-06/4/75 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 4, 2013 No. ED-18-3/606. It is noteworthy that in all of the letters listed, not a word is said about the interest nature of expenses.
Closing a current account upon liquidation of an LLC
When liquidating an LLC, it is important to find out in advance how to close a bank account for the LLC. This process is very important, since closing must take place at a strictly defined time. You cannot close the account of an LLC or individual entrepreneur during the liquidation process whenever you want.
First you need to close all debts, pay off creditors, and even after that you cannot close the account. During liquidation, the tax service can check the documentation of an LLC or individual entrepreneur at any time. If closure has already occurred at this time, then you may face fines even during liquidation. That is why closing an LLC or individual entrepreneur account must occur at a strictly defined time and you cannot close it whenever you want. First, all debts are eliminated, then the balance is paid to the founders, and only then the account is closed.
If you are especially concerned about how to close a current account in an LLC bank during liquidation, then just contact the bank where the opening took place. There they will tell you in detail how to close a bank account of an LLC and not violate the terms of liquidation.
Opening an account in the treasury for a legal entity
For a legal entity, there is always the opportunity to open a current account for LLCs and individual entrepreneurs not only in the bank, but also in the treasury. In order to open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur not in a bank, but in the treasury, you need to provide a pre-prepared package of documents to this treasury, after which within five days the legal entity will receive a notification that the account has been opened. If you don’t know what documents you need to provide to the treasury in order to open a current account for an LLC, you can always find them on the organization’s official website.
In addition, in order to open a current account for an LLC not in a bank, but in the treasury, you will need to perform a number of important steps, including preparing a special application filled out in accordance with all the rules. If you make a mistake when drafting it, then you can forget about the desire to open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur not in a bank, but in the treasury, since the treasury simply will not accept an application with errors for consideration.
Accounting
The cost of a bank guarantee includes the cost of the asset for the purpose of purchasing or creating which it was acquired:
DEBIT 76 CREDIT 51
- remuneration was transferred to the bank for issuing a guarantee;
DEBIT 08, 10, 20, 41, etc. CREDIT 76
- a guarantee of payment under a contract or supply agreement was received from the bank.
This is a general rule for the formation of the cost of all inventory items.
Example 2
As security for payment obligations for a real estate transaction in the amount of 10 million rubles, the company presented the seller with a bank guarantee.
The bank's remuneration for the guarantee is three percent of the transaction amount, that is, 300,000 rubles (10,000,000 rubles x 3%), the guarantee period is one month. The principal company did not make the payment within the period stipulated in the purchase and sale agreement. The bank, which repaid the company's obligation to the beneficiary seller, demanded reimbursement of this amount from it. In this situation, the accountant will make entries: DEBIT 76 CREDIT 51
- 300,000 rubles.
– funds were transferred to the guarantor bank for providing a guarantee; DEBIT 08 CREDIT 76
- 300,000 rub.
— warranty costs are included in the initial cost of a non-current asset; DEBIT 08 CREDIT 60
- 10,000,000 rub.
— the property was accepted under the transfer deed (clause 1 of Article 556 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation); DEBIT 01 CREDIT 08
- 10,300,000 rub.
– the fixed asset is accepted for accounting; DEBIT 60 CREDIT 76
- 10,000,000 rub.
– the bank’s recourse claim is recognized; DEBIT 76 CREDIT 51
- 10,000,000 rub. – the obligation to the bank has been repaid.
What if the principal’s expenses turned out to be fruitless? Let's say a company provided a bank guarantee to the organizer of a competition, but lost the competition. In this case, no asset arises. The following expenses should be recognized in accounting:
DEBIT 91-2 CREDIT 76
- expenses that did not produce results were written off.
Opening an account in a foreign bank
If you decide to open an account in a foreign bank, then this will require an even larger package of documents. For each legal entity, opening a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur in a foreign bank is especially beneficial, since the foreign bank provides clients with especially favorable conditions.
This was the case several years ago, but today you can open a current account for an LLC in a domestic bank on the same favorable terms. The only advantage for a legal entity is that opening a current account for an LLC in a foreign bank may be more reliable, since the unstable economic situation in our country can at any time lead to the fact that even the most reliable organization may go bankrupt.
You can open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur in a foreign bank with the help of third-party specialists who know exactly what documents need to be prepared and what needs to be done to open a current account for an LLC or individual entrepreneur without any extra effort.
Urgent opening of a current account
You can open a current account for an LLC, individual entrepreneur or other legal entity either in a few days or in a few months. It all depends on who is in charge of the discovery. If you decide to open a current account for an LLC, individual entrepreneur or other legal entity on your own, you can waste a lot of time without achieving the desired result.
The thing is that only an experienced person who knows all the intricacies of this process can open a current account for an LLC, individual entrepreneur or other legal entity. Otherwise, you can constantly make mistakes, due to which the entire process during which the discovery occurs will be spoiled. That is why it is best to entrust the opening of a current account for an LLC, individual entrepreneur or other legal entity to professionals in their field, such as lawyers, who can handle it in a few days. If you need to urgently open an account for a legal entity, then contact the professionals.
Closing an LLC current account in a bank
Closing a current account is much easier than opening a current account for an LLC, individual entrepreneur or other legal entity. It is enough to contact the bank where the current account is opened for an individual entrepreneur or LLC with a corresponding application, which will be reviewed in the near future.
Unlike those cases when you need to open a current account for an LLC, individual entrepreneur or other legal entity, you can close it yourself, without resorting to the help of specialists. However, it should be understood that even closing can cause difficulties if you do not know all the intricacies of the process.
Unblocking a current account
If the tax office has discovered any violations, it may block the current account until they are eliminated. In this case, you will need to unblock the account, and it is important to complete this urgent matter as quickly as possible. Unblocking is carried out by eliminating all detected violations.
In this case, unlocking will be carried out only if all actions are performed in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Unlocking is a complex process that should be entrusted to professionals. Only in this case can you be sure that the unlocking will be done as it should, after which the account will not be completely closed.
Similar services on the topic
- Registration of a patent for an invention
- Taxation of individual entrepreneurs
- Conducting business intelligence
- Registration with Rosfinmonitoring
- Registration with the Assay Office
- Trademark registration
- Obtaining a duplicate TIN and OGRN
- Extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities/Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs
- Making stamps
- Simplified taxation system
- Obtaining OKVED codes
- Inclusion in the register of microfinance organizations
Regulatory regulation
Banking services can be paid either by order of the client organization (for example, by payment order), or without acceptance - on the basis of an order drawn up by the bank, automatically from the current account (Article 851 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, clauses 9.2, 9.3 Regulations of the Bank of Russia 06/19/2012 N 383-P). The condition for direct debiting of the commission must be enshrined in the contract.
If the bank account agreement specifies a period for the direct debit of the commission, then it cannot be debited at any other time without the client’s consent (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated March 30, 2011 in case No. A56-26518/2010, FAS East Siberian District dated August 25 .2010 in case No. A33-21940/2009).
In the accounting book, bank commissions are reflected according to Dt 91.02 “Other expenses” in the period in which these expenses were incurred (clause 7 of PBU 15/2008, clause 18 of PBU 10/99, chart of accounts 1C).
The NU commission of the bank takes into account:
- as indirect costs (other) - if they are related to production and (or) sales (clause 25, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- as non-operating expenses - in other cases (clause 15, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The amount of the commission is recognized as expenses on the date of its accrual (clause 3, clause 7, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The taxpayer's expenses for paying bank commissions are included in expenses if they are economically justified and documented (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 18, 2017 N 03-03-06/1/1916). In this case, it does not matter whether the expenses incurred are named in the list given in Art. 5 of the Federal Law of December 2, 1990 N 395-1.
As for VAT, many banking services are exempt from this tax (clause 3, clause 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), therefore an invoice for their cost should not be issued (clause 1, clause 3, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, if an invoice with an allocated amount of tax for services exempt from VAT is received from the bank, then the deduction for it will be legal (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 21, 2017 N 03-07-15/38864, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 18 .2014 N GD-4-3/26274).