Every year, in March, the accounting department of any enterprise begins to fill out various reports and draw up a balance sheet for the past reporting period. When drawing up a balance sheet, it is necessary to take into account all the nuances of business activity. In this article you will find instructions for line-by-line filling out the general and simplified balance sheet in 2021, you will be able to download these balance sheet forms and receive information on some nuances related to this topic.
Any business activity is invariably accompanied by the formation of various forms of financial statements. The accuracy and correctness of filling out these forms has a direct impact on the success of doing business. After all, errors in accounting lead to sanctions from regulatory authorities. In this article, you will learn the procedure for filling out the 2021 balance sheet, receive information about who must submit a general and who has a simplified balance sheet, what reporting forms are submitted in 2021, as well as the possibility of Form 1 of the 2021 balance sheet.
Concept, essence and purpose
The balance sheet of a business entity is an important and very first financial document that makes up the reporting accounting documentation generated at the end of each calendar year. This is a generalized reflection of accounting indicators and their economic grouping depending on their purpose.
What is balance needed for and what is its purpose?
The balance sheet compiled by an organization clearly shows the current financial position of the enterprise and characterizes the state of the company's assets and liabilities as of the reporting date.
The use of accounting report data allows you to determine what assets the company has as of a specific date, and also informs the user about what part of these assets is financed from the organization’s own capital, and what share of them is provided by borrowed (raised) funds.
The form of this report is regulated by OKUD 0710001. It is approved by a specific regulatory act - order No. 66n, issued by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation on July 2, 2010.
A balance sheet is a table that includes a set of ordered rows (items) and columns that contain a summary (system) of indicators. In essence, a report is a way of summarizing and grouping information about the activities of an enterprise during the reporting period.
The accounting report consists of two parts - tabular sections:
- assets that reflect information about the structure and valuation of economic property,
- liabilities that contain information about the composition and value terms of the sources of receipt (purchase, formation) of this property.
Assets in the balance sheet are divided into non-current (immobilized) and current (current).
In the structure of balance sheet liabilities, the own funds of an economic entity are distinguished, consisting of its capital and formed reserves, as well as borrowed funds, including both current and long-term obligations of the organization.
All balance sheet figures include information in monetary terms only. It shows assets and liabilities as of 3 dates: December 31 (or, alternatively, another reporting date) of the current reporting year and, accordingly, two years preceding the current year.
This approach to report generation facilitates a visual comparison of balance sheet indicators, which facilitates the study of the dynamics of the company’s economic condition.
An important condition is that the total value of assets must equal the total value of all liabilities reflected in the balance sheet. This equality of results is mandatory when preparing the annual report. The purpose of drawing up a balance sheet is to establish balance.
The balance of assets and liabilities of a business entity is a natural consequence of the fact that the property and liabilities of the organization are reflected (recorded) in accounting using the double entry method on the appropriate accounts.
Accounting statements for 2021:
- financial performance report form 2;
- statement of changes in capital form 3;
- cash flow statement form 4;
- simplified for small businesses.
An explanatory note may be drawn up for the report - how to draw it up and when it is necessary, read here.
To whom does the company report when preparing its annual report?
The government structures (instances) to which the balance sheet and other financial statements should be submitted are clearly stipulated by the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as the legal act 402-FZ, well known as the law on accounting.
We are talking about territorial divisions of the tax service and statistical department operating at the place (address) of official registration of the business entity.
The company's balance sheet must be sent in different copies to both of the above-mentioned authorities within the designated time frame established by current legislation.
In addition, the balance sheet of a particular organization can be compiled for other interested parties - its founders, its management, external investors, financial institutions, and other users.
The procedure for reporting to these entities is not strictly regulated by current regulations.
For what reporting period are reports prepared?
The organization is obliged to form a balance sheet at the end of the calendar year. This report is called the annual report. It consists of all enterprises that maintain accounting records.
In addition, the company has the right to fill out interim balance sheets to verify the correctness of accounting. These reports do not need to be submitted to any structures; they are needed exclusively for the enterprise itself.
When is it submitted to the tax office - deadlines for 2021
The balance sheet compiled based on the results of 2018 is submitted to the territorial divisions of the tax service and statistical department no later than April 1, 2019.
An economic entity can send its annual balance sheet to both official bodies during the first quarter of 2021. This can be done on any day, except holidays/weekends.
It should be noted that current legislation clearly requires the mandatory submission of an annual balance sheet - this procedure is performed once a year.
The accounting policy of an economic entity, orders of management, the will of the founders, and certain provisions of legislation may provide for the formation of interim financial statements compiled monthly, quarterly or six months.
The interim balance is not provided to the tax and statistical authorities.
What is included in the 2019 financial statements?
The specific set of reports depends on the size of your business and whether your company is classified as small or not. In most cases, the set of reports for organizations is as follows:
All report forms are approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n (hereinafter referred to as Order 66n)
- Balance sheet;
- Reports: on financial results, on target cash flows, on changes in capital, on the intended use of funds received;
- Explanations to the balance sheet and income statement. These explanations are presented in a form convenient for you - in tabular or text form.
If your enterprise is classified as a small one, then you can submit reports in a simplified form, filling out only the balance sheet and income statement. If necessary, you can attach explanations to decipher the information contained in the balance sheet or report.
Only small businesses can add explanations at will; all other entrepreneurs do this without fail.
In accordance with clause 5, part 1, art. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Part 2 of Art. 18 of the Federal Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ (as amended on November 4, 2014) (hereinafter referred to as Law 402FZ), all reports must be submitted no later than 3 months after the end of the reporting period (year) . That is, all financial statements for 2021 must be submitted no later than March 31, 2021.
If the internal documents of the enterprise stipulate the obligation to prepare interim reports, you can submit them more often, perhaps once every 3 months or once a month (Part 4 of Article 13 of Law 402FZ). This reporting is provided only to the founders of the enterprise; it does not need to be submitted to the tax office or Rosstat.
Next, you will learn how to fill out the 2021 balance sheet and get a breakdown of the balance sheet items.
Structure, structure and content
As mentioned earlier, a tabular format is provided for the official balance sheet of a business entity. How many sections does the report include?
This table is divided into two main sections – assets and liabilities. In turn, assets include 2 sections, liabilities - 3.
In this case, the main requirement for compilation is: the total value of all assets equals the total value of all liabilities.
What 5 sections does the balance sheet consist of:
- Fixed assets.
- Current assets.
- Capital and reserves.
- Long term duties.
- Short-term liabilities.
The characteristics of the structure and principles of constructing an accounting report are discussed in more detail below.
What does the asset division consist of?
The assets of an economic entity reflect the type structure and book value of the property that is under the control of this entity, used in its activities, and capable of generating future benefits.
The active part of the balance sheet includes data from two sections:
- Fixed assets. This section reflects the structure and valuation of the company's property used by it for a long time (more than twelve months counted from the balance sheet date). The cost of some types of such property is gradually transferred in parts to the financial results of the company (through depreciation).
- Current (current) assets. Their structure changes frequently and significantly (over a period not exceeding twelve months, counted from the balance sheet date), and the cost of certain types of such assets, as a rule, is taken into account one-time in the financial result.
What is included in liabilities?
Liabilities demonstrate the type structure and book value of those sources of financing through which the organization acquires (forms) the above assets. The composition of liabilities is characterized by three main sections:
- Capital and formed reserves of the enterprise. These are the so-called own funds of a business entity, which fully correspond in value to the value of its net assets.
- Long-term obligations of a business entity, clearly reflecting the type structure and valuation of its debt, which has existed for quite a long time. The validity period of such obligations is more than twelve months, counted from the balance sheet date.
- Current (short-term) liabilities demonstrating the structure and valuation of the most dynamic part of the company's balance sheet debt. The structure and valuation of a company's current debts change over a period not exceeding twelve months from the balance sheet date.
Sections and articles with codes and decoding of lines for accounting accounts
Structure in table form:
Instructions for filling out a simplified balance sheet 2021
The simplified balance sheet contains the same indicators as the general one. The only difference is that these indicators have a more aggregated reflection, that is, the indicator with the highest specific weight is reflected in the line.
You can download the simplified balance sheet form here (Appendix No. 5 to Order 66n).
Column “Asset”, row:
- Tangible non-current assets. This reflects the amounts of fixed assets and capital investments in them that have not yet been completed;
- Intangible, financial and other non-current assets. Financial investments with a long-term perspective and intangible assets are reflected. Additionally, it is necessary to reflect the results of developments and research, unfinished investments in them, as well as in intangible assets;
- Inventories. Account balances are reflected, similarly to the usual balance sheet form;
- Cash and cash equivalents. Similar to the usual form of balance sheet;
- Financial and other current assets. Information about other assets is displayed, including accounts receivable and short-term investments of financial assets;
- Balance. The sum of all rows in the Asset column.
Column “Passive”, row:
- Capital and reserves. It is necessary to display the authorized capital (if formed, then additional and reserve), revaluation of fixed intangible assets, uncovered loss (retained earnings). Additionally – shares of the founders (shareholders’ shares), purchased from them for cancellation;
- Long-term borrowed funds. Amounts of long-term loans and credits.
- Short-term borrowed funds. Amounts of short-term loans and credits.
- Accounts payable. Similar to the general balance sheet form;
- Other short-term liabilities. Amounts of short-term debt to creditors that were not included in the previous lines of the “Liability” column;
- Balance. The sum of the rows in the “Passive” column.
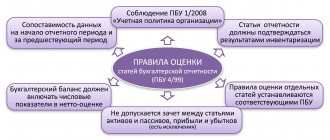
Rules for forming indicators
The basic rules for filling out the annual balance sheet compiled by a business entity are established by specific norms of the current legislation and boil down to strict compliance with the following requirements:
- Compiled on the basis of reliable accounting information.
- Formation of the necessary data in accordance with the norms of generally accepted accounting provisions and the requirements of the accounting policy of the company itself.
- Reliability, accuracy, completeness of the data used.
- If an organization has branches, a single (general) balance sheet is always prepared for the entire company.
- Neutrality of balance sheet data, their correlation with information from previous reporting periods.
- The principle of materiality must be taken into account when highlighting individual items in certain sections of the report under consideration.
- Calendar year is the official reporting period.
- There should be a clear distinction between long-term (more than twelve months) and short-term (less than twelve months) assets/liabilities.
- If accounting provisions do not provide for offset between individual items, it should not be performed.
- Property is assessed at net cost, which implies the deduction of items of a corrective (regulatory) nature.
The information in the annual reporting must be confirmed by the corresponding audit (inventory).
How to fill out in 2021 - the procedure for compiling for an enterprise
The detailing of the above sections of the balance sheet is carried out by breaking them down into individual items. Such detail is associated with the need to identify the main (typical) types of assets/liabilities when forming the corresponding sections of the balance sheet of an economic entity.
The itemized breakdown, often used for preparing official reports, is recommended by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. It has been implemented for quite a long time in the preparation of reporting forms and is used by the vast majority of business entities.
Line-by-line completion of assets and liabilities of the balance sheet at the end of 2021 is carried out in strict accordance with current instructions.
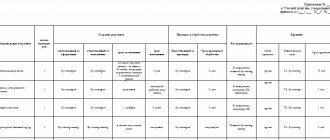
Filling the asset table row by row
The active part of the annual balance sheet is filled out according to the specific form shown in the table below (example).
The table shows how to fill out the items in the assets section, and provides information on which accounts go where:
| ASSETS | |||
| Balance line number | Line name | Information on filling out the line | Accounting accounts to fill out |
| I. Non-current assets: | |||
| 1110 | Intangible assets | Cost of intangible assets minus accumulated depreciation | Debit balance account 04 and 08.5 minus credit balance account 05 |
| 1120 | Research results | Cost results of development and research (R&D) | Account 04 R&D subaccount |
| 1130 | Exploratory intangible assets | Expenses for searching for deposits of an intangible nature (for example, scientific research) | |
| 1140 | Exploratory material assets | Expenses for searching for deposits of an intangible nature (for example, equipment for prospecting work) | |
| 1150 | Fixed assets | Cost of fixed assets minus accumulated depreciation | Debit balance account 01 (07.08) minus credit balance account 02 |
| 1160 | Investments in MC | Investments in material assets that generate income | Balance on account 03 |
| 1170 | Financial investments | Cash investments for a period exceeding 12 months. | The debit balance of accounts is 55.58 minus the credit balance of accounts 59 |
| 1180 | Deferred tax assets | Deferred tax assets | Balance on account 09 |
| 1190 | Other | Non-current assets of other types not included in the first section above | |
| TOTAL for section I | Total amounts for the first section of the balance sheet | ||
| II.Current assets: | |||
| 1210 | Material reserves | Includes the cost of goods, inventories, products | Account debit balance 10,15,20,21,23, 28,29,41,42,43,44,45,97 minus account credit balance 14,42 |
| 1220 | VAT | VAT on purchased values/assets | Debit balance account 19 |
| 1230 | Accounts receivable | Debts of debtors | Account debit balance 60,62,68,69,70, 71,73,75,76 |
| 1240 | Financial investments (without cash equivalents) | Cash investments for a period of less than 12 months. | Debit balance account 58 minus credit balance account 59 |
| 1250 | Money | Cash and cash equivalents | Account debit balance 50,51,52,55,57 |
| 1260 | Other | Current assets of other types not included in the second section above | |
| TOTAL for section II | Total amounts for the second section of the balance sheet | ||
| BALANCE | Total assets | ||
Instructions for liabilities
Instructions for filling out the liabilities of the annual balance sheet:
| LIABILITIES | |||
| Balance line number | Field name | Information on filling out the line | Accounting accounts to fill out |
| III.Capital, reserves: | |||
| 1310 | Authorized capital | Share capital | Loan balance account 80 |
| 1320 | Own shares purchased from holders | The cost of shares that are repurchased from holders | Debit balance account 81 |
| 1340 | Revaluation of the value of non-current assets | The line includes only the result of additional valuation of intangible assets and fixed assets | Balance on loan account 83 in terms of revaluation |
| 1350 | Additional capital (without revaluation) | Extra capital | Loan balance account 83, except for revaluation results |
| 1360 | Reserve capital | Cost of the reserve, if it is formed | Debit balance account 82 |
| 1370 | Undistributed profit (uncovered loss) | You need to fill in the line after the reformation | Balance in account 84, loss is reflected in parentheses (credit balance - profit / debit balance - loss) |
| TOTAL for Section III | Summary data for the third section of the balance sheet | ||
| IV. Long-term liabilities: | |||
| 1410 | Borrowed funds | Loan funds for a period of more than 12 months. | Loan account 67 |
| 1420 | Deferred tax liabilities | Deferred tax liabilities | Loan account 77 |
| 1430 | Estimated liabilities | Liabilities of an estimated nature for a period of more than 12 months. | Loan account 96 |
| 1450 | Other | Other obligations for a period exceeding 12 months. | |
| TOTAL for section IV | Summary data for the fourth section of the balance sheet | ||
| V. Short-term liabilities | |||
| 1510 | Borrowed funds | Loans, loans for a period of up to 12 months. | Loan account 66 |
| 1520 | Accounts payable | Debts of creditors | Account credit balance 60,62,70,71,73, 68,69,75,76 |
| 1530 | revenue of the future periods | Income amounts that relate to future periods | Loan balance account 98 |
| 1540 | Estimated liabilities | Estimated obligations for a period of less than 12 months. | Loan account 96 |
| 1550 | Other | Other obligations for a period of less than 12 months. | |
| TOTAL for section V | Total amounts for the fifth section of the balance sheet | ||
| BALANCE | Total liabilities | ||
Download the free form and completed sample form 1 LLC for 2018
LLC balance sheet for submission in 2021 – excel, word.
Filling out for 2021 – excel.
Instructions for filling out the enterprise balance sheet 2021 with explanation
You can download Form 1 of the general balance sheet here (Appendix No. 1 to Order 66n).
Column “Asset”, section I “Non-current assets”, line:
- Intangible assets = Debit 04 – Credit 05;
- Research and development result = Debit 04;
- Intangible search assets = Debit 08 (subaccount for accounting for expenses for IR costs). The line is filled in only by enterprises using natural resources. The information contained should reflect the costs of resource development;
- Material search assets = Debit 08 (subaccount for accounting for expenses for MP costs). The line is filled in only by enterprises using natural resources. The information contained should reflect the costs of resource development;
- Fixed assets = Debit 01 – Credit 02 + Debit 08 (sub-account for accounting for fixed assets not put into operation);
- Income investments in material assets = Debit 03 – Credit 02 (sub-account for accounting for depreciation of property related to income investments);
- Financial investments = Debit 58 + Debit 55 (sub-account “Deposit accounts”) + Debit 73 (sub-account “Settlements on loans granted”) – Credit 59 (sub-account “Accounting for provisions for long-term financial liabilities”);
- Deferred tax asset = Debit 09;
- Other non-current assets = amounts for non-current assets that were not included in the previous lines of section I;
- Total for section I = the sum of the indicators of the previous lines.
Column “Asset”, section II “Current assets”, line:
- Inventory = Debit 41 – Credit 42 + Debit 15 + Debit 16 – Credit 14 + Debit 97 + sum of debit account balances 10, 11, 43, 45, 20, 21, 23, 29, 44;
- VAT on purchased assets = Debit 19;
- Accounts receivable = Debit 62 + Debit 60 + Debit 68 + Debit 69 + Debit 70 + Debit 71 + Debit 73 (excluding interest-bearing loans) + Debit 75 + Debit 76 – Credit 63;
- Financial investments (excluding cash equivalents) = Debit 58 + Debit 55 (sub-account “Deposit accounts”) + Debit 73 (sub-account “Settlements on loans granted”) – Credit 59;
- Cash and cash equivalents = Debit 50 + Debit 51 + Debit 52 + Debit 55 + Debit 57 – Debit 55 (sub-account “Deposit accounts”);
- Other current assets = amounts for current assets that were not included in the previous lines of section II;
- Total for section II = the sum of the indicators of the previous lines of section II;
- Balance = the sum of the indicators in the lines “Total for Section I” and “Total for Section II”.
Column “Liability”, section III “Capital and reserves”, line:
- Authorized capital = Loan 80;
- Own shares purchased from shareholders = Debit 81;
- Revaluation of non-current assets = Credit 83 (sub-account for the amounts of revaluation of fixed assets and intangible assets);
- Additional capital (without revaluation) = Credit 83 (excluding amounts of additional valuation of fixed assets and intangible assets);
- Reserve capital = Credit 82;
- Retained earnings (uncovered loss) = Credit 84;
- Section III Total = Sum of Section III lines.
Column “Liabilities”, section IV “Long-term liabilities”, line:
- Borrowed funds = Loan 67 (accrued interest with a repayment period of less than 1 year);
- Deferred tax liability = Credit 77;
- Estimated liabilities = Credit 96 (only for liabilities with a useful life of more than 1 year);
- Other liabilities = amounts of long-term debt to creditors that were not included in the previous lines of section IV;
- Section IV Total = the sum of the lines in Section IV.
Column “Liabilities”, section V “Short-term liabilities”, line:
- Borrowed funds = Loan 66 + Loan 67 (accrued interest with a repayment period of more than 1 year);
- Accounts payable = Credit 60 + Credit 62 + Credit 68 + Credit 69 + Credit 70 + Credit 71 + Credit 73 + Credit 75 (short-term debt only) + Credit 76;
- Deferred income = Credit 98 + Credit 86;
- Estimated liabilities = Credit 96 (only liabilities over 1 year);
- Other liabilities = amounts of short-term debt to creditors that were not included in the previous lines of Section V;
- Section V Total = sum of Section V lines;
- Balance = sum of the lines “Total for Section III”, “Total for Section IV”, “Total for Section V”
How to check the correctness of the design?
The reliability of the generated reporting is verified by an external audit, as a result of which it is either confirmed or refuted.
The expert-auditor's opinion is one of the mandatory annexes to the annual balance sheet sent to official structures (instances). However, such an audit is not required for all business entities, but only for those organizations for which the mandatory nature of this procedure is established by current legislation.
Another significant nuance is that the auditor’s opinion on the balance sheet must be provided only to the statistical agency when sending annual reports.
The Tax Service does not yet require an audit opinion when submitting reports for the past 2021.
conclusions
The balance sheet of an economic entity is formed based on the results of 2021 in strict accordance with the norms and rules provided for by law.
Compliance with these requirements is necessary when sending financial statements to official structures.
The balance sheet for 2021 is submitted to the tax/statistical authorities no later than the first day of April 2019. Filling out the reporting form in question is carried out according to the itemized breakdown recommended by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.