Financial statements: forms 1 and 2 - what are these reports
Data from forms 1 and 2 are the main components of financial statements:
- Form 1 – balance sheet;
- Form 2 – statement of financial results.
Starting with reporting for 2021, all enterprises use accounting forms, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 07/02/10 No. 66n as amended by Department Order No. 61n dated 04/19/2019. In the new edition, in particular:
- OKVED code was replaced by OKVED2;
- There is only one allowed unit of measurement left - thousand rubles. (previously it was possible to indicate data in million rubles);
- OKEY code has been corrected.
What is the balance sheet form for 2020
The form of the current balance sheet form is established by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n. Moreover, from June 1, 2019, the balance sheet form is valid as amended by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated April 19, 2019 No. 61n. The key changes to it (and other reporting) are:
- now reporting can only be prepared in thousand rubles, millions can no longer be used as a unit of measurement;
- OKVED in the header has been replaced by OKVED 2;
- The balance sheet must contain information about the audit organization (auditor).
The auditor mark should only be given to those companies that are subject to mandatory audit. Tax authorities will use it both to impose a fine on the organization itself if it ignored the obligation to undergo an audit, and in order to know from which auditor they can request information on the organization in accordance with Art. 93 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Find out what fines are possible for failure to conduct a mandatory audit or failure to submit an audit report from a typical situation from ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
More significant changes have occurred in Form 2. Read more about them here.
Order 66n offers us two options for the form of the balance sheet:
- complete, contained in Appendix 1;
- simplified, given in Appendix 5.
A simplified form of balance sheet can be used by those legal entities that have the right to maintain simplified accounting (SMEs, non-profit organizations, participants in the Skolkovo project).
Read more about simplified reporting in the materials:
- “Simplified reporting for small businesses”;
- “How to fill out a balance sheet using the simplified tax system.”
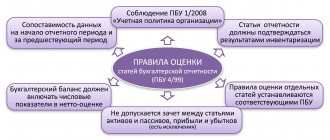
At the same time, organizations retain the right to independently develop a balance sheet form, observing the basic requirements for this document:
- compiling it on the basis of data from accounting accounts in accordance with current accounting regulations;
- completeness and reliability;
- ensuring the required level of detail;
- the ability to reflect data as of not only the reporting date, but also as of the last day of the two previous years;
- the ability to reflect the necessary explanations on specific lines;
- compliance with the order of coding strings in accordance with the requirements of the State Statistics Committee.
For information on the requirements for the balance sheet, read the article “What requirements should accounting records satisfy?” .
Let us remind you that starting from 2013, only the annual balance sheet is mandatory for submission to the Federal Tax Service. It contains reporting data as of December 31 of the last three years (the reporting year and the two previous ones).
If the balance sheet is prepared for any intermediate date using a standard balance sheet form, then the data for this date is reflected in the column that in the annual balance sheet is intended for the last day of the reporting year.
Accounting: forms 1 and 2 - who submits
All organizations maintain accounting records, and entities that maintain simplified accounting can use simplified forms of reporting forms. According to paragraph 4 of Art. 6 of Law No. 402-FZ, such enterprises include:
- small firms (including micro-enterprises) included in the SME register - these include companies with an average staff of up to 100 people. and an annual income of no more than 800 million rubles;
- non-profit organizations (NPOs);
- participants of the Skolkovo project.
Simplified Form 1 and Form 2 of the enterprise imply a generalized grouping of data, which is recommended in Appendix 5 to Order No. 66n. But subjects have the right to develop and use their own forms.
Clause 5 Art. 6 of Law No. 402-FZ provides a list of organizations for which simplified methods of accounting and reporting are not available, incl. These are enterprises whose reporting is subject to mandatory audit, public sector employees, non-profit organizations with the functions of a foreign agent, bar and notary chambers, etc.
Where to find a sample balance sheet form
Where is the balance sheet so as not to make a mistake with the current form? You can download the balance sheet from any legal reference database. Also, the ability to generate financial statements is present in accounting programs, from which, if necessary, you can download a balance sheet.
In addition, you can view the balance sheet form on our website and, if necessary, download it from the link below:
A simplified balance sheet form is also available on our website. Download it from the link below:
Form 1 and 2 of simplified accounting statements: basic principles of preparation
The Ministry of Finance brought to the attention of subjects information on the use of simplified reporting (Message No. PZ-3/2015), according to which:
- Information is disclosed taking into account its significance for the user. Individual significant items can be distinguished from groups in reporting forms.
- Events after the reporting date are recognized where it makes reasonable sense to do so.
- Significant errors of previous years are corrected at the expense of other income and expenses of the past year, without changing the financial result.
Balance sheet 2021: features
By filling out the form, the company itself details the indicators by item, taking into account the level of materiality of each. Financial statements must be submitted to the regulatory authorities (IFTS and statistical departments) in a form that includes line codes. We will present a sample of filling out the balance sheet for 2021 in exactly this form.
The basis for drawing up a balance are accounting registers, for example, a chess sheet, memorial orders, order journals, a balance sheet or a general ledger.
Simplified annual balance sheet in form 1 and form 2: how to fill out
When preparing a balance sheet, indicators record the state of affairs in the organization on a specific date - the end of the year or the last day of business (upon liquidation of the company), as well as on December 31 of each of the previous 2 years.
Here are the main relationships between the lines of the simplified balance sheet and the accounting accounts, the balances of which should be used when filling out the report:
| Balance sheet item | Line code | How to calculate |
| Tangible non-current assets | 1150 | The sum of balances on accounts 01, 03, 07, 08 minus the balance on account 02 |
| Intangible, financial and other non-current assets | 1170 | Account balance 04, 08 (investments in intangible assets), 09, 55 (deposits), 58, 73 (employee loans) minus the reserve on the account. 59 and balance 05 |
| Reserves | 1210 | Balances on accounts 10, 11 (minus the reserve on account 14), 15, 16, 20, 21, 23, 28, 29, 41 (minus account 42, if goods are accounted for with a markup), 43-46, 97 |
| Cash | 1250 | Sum of account balances 50, 51, 52, 55 (excluding deposits), 57 |
| Financial and other current assets | 1230 | The sum of account balances is 19, 55 (minus long-term deposits), 58 (short-term investments minus the reserve of 59), + debit balances 60, 62 (minus reserves for 63), 66-71, 73 (minus long-term loans), 75, 76 |
| Capital and reserves | 1300 | Sum of account balances 80, 82, 83, 84 |
| Long-term borrowed funds | 1410 | Balance of debt on account 67 with a repayment period of at least 1 year (interest is included in line 1510) |
| Other long-term liabilities | 1450 | Account balances 77 and 96 (reserves used for more than 12 months) |
| Short-term borrowed funds | 1510 | Account balance 66, interest on long-term borrowed funds (account 67), and account debt. 67, the maturity of which is less than 1 year left at the reporting date |
| Accounts payable | 1520 | Credit balance of accounts 60, 62, 68-71, 73, 75, 76 |
| Other current liabilities | 1550 | Balances on accounts 86, 96 (short-term reserves) and 98 |
Where can I see an example of filling out a balance?
An example of a balance sheet compiled in both full and simplified form can also be found on our website, for example, in this article.
You can download a sample balance sheet in the new edition with comments on completion from K+ experts in the ConsultantPlus legal reference system. To do this, get a free trial demo access to K+:
An example of a balance sheet would be a form automatically filled out in an accounting program. You just need to remember the need to reconcile the data of such reporting with the balances on the accounting accounts and to comply with other rules for filling out the balance sheet:
- debit and credit balances on balance sheet accounts are shown in detail;
- Fixed assets and intangible assets are reflected at their residual value;
- Inventory and materials are shown at cost less reserves;
- interest on long-term loans refers to short-term debt;
- interest on financial investments is reflected as part of settlements with the counterparty;
- the amount of VAT accrued on advances received may reduce the debt to buyers for these advances.
Read about some of the nuances of drawing up a balance sheet in the material “Drawing up a balance sheet .
For information on options for reflecting VAT on the balance sheet, read the article “How is VAT reflected on the balance sheet?” .
Accounting report: form 1 and 2 - how to fill out a simplified statement of financial results
Form 2 is compiled based on the turnover of the accounts and reflects the summarized indicators for the reporting and preceding years:
| Article form 2 | Line code | How to calculate |
| Revenue (net of VAT and excise taxes) | 2110 | Credit turnover of account 90.1 minus debit turnover 90.3 (VAT) and 90.4 (excise taxes) |
| Expenses for ordinary activities | 2120 | Debit turnover by account. 90.2 (cost of sales) |
| Percentage to be paid | 2330 | Debit turnover 91.2 (in relation to interest on all types of obligations) |
| Other income | 2340 | Loan turnover 91.1 |
| other expenses | 2350 | Debit turnover 91.2 (except interest) |
| Income tax | 2410 | Account loan turnover 68 (accrual according to the declaration) |
| Profit Loss) | 2400 | Calculation by lines: 2110 – 2120 – 2330 + 2340 – 2350 – 2410 |
Balance sheet of an enterprise: completed example 2021
A sample of drawing up a balance sheet based on accounting data grouped in the balance sheet of Crocus LLC. To simplify the problem, let’s assume that the company was organized in 2021 and is preparing a balance sheet for 2021 for the first time. The 2017 balance sheet form, a sample of which is presented, involves considering the results of the company’s work for the reporting, last and previous years. In our example, information for 2021:
Account number Balance D/t K/t 01 825 000 02 443 000 04 8700 05 3000 08 32 000 10 50 000 19 10 000 41-2 575 000 41-3 33 000 42 120 000 44 12 500 50 10 000 51 92 000 52 7800 58 5000 60 265 000 62 15 000 66 75 000 68 57 000 69 12 000 70 30 000 71 1900 76 40 000 80 620 900 82 8000 84 75 000 In accordance with the instructions for filling out the form indicated above, we will fill out the balance sheet for 2021 based on the accounting data.
Form 1 and 2 of financial statements: example
The small enterprise Pekar LLC produces bakery and confectionery products. As of December 31, 2021, according to the accounting accounts, the enterprise draws up simplified Form 1 and Form 2:
| Index | Accounting data | Amount, thousand rubles | Form 1 and 2 line codes | Total per line, thousand rubles. |
| Equipment | Debit balance 01 | 1150 | 1150 | 794 (1150 – 356) |
| Accumulated depreciation | Loan balance 02 | 356 | ||
| Cost of a registered trademark (depreciation is calculated without using account 05) | Debit balance 04 | 100 | 1170 | 100 |
| Raw materials | Debit balance 10 | 214 | 1210 | 229 (214 + 15) |
| Finished products | Debit balance 41 | 15 | ||
| Cash in hand | Balance debit 50 | 17 | 1250 | 1002 (17 + 985) |
| Funds in the current account | Balance debit 51 | 985 | ||
| Buyers' debts | Debit balance 62 | 576 | 1230 | 576 |
| Authorized capital | Balance credit 80 | 980 | 1300 | 980 |
| Long-term loan | Loan balance 67 minus interest | 752 | 1410 | 752 |
| Loan with a repayment period of 6 months and interest on it | Loan balance 66 | 321 | 1510 | 396 (321 + 75) |
| Interest on long-term loan | Loan balance 67 (interest) | 75 | ||
| Debt to suppliers | Credit balance 60 | 573 | 1520 | 573 |
| Revenue | Credit turnover 90.1 | 2389 | 2110 | 2078 (2389 — 311) |
| VAT | Debit turnover 90.3 | 311 | ||
| Cost price | Debit turnover for 90.2 in correspondence with 20, 23 | 1256 | 2120 | 1472 (1256 + 216) |
| Business expenses | Debit turnover for 90.2 in correspondence with 44 | 216 | ||
| Interest on loans and borrowings | Debit turnover 91.2 (based on interest paid) | 89 | 2330 | 89 |
| Income from equipment rental | Loan turnover 91.1 | 60 | 2340 | 60 |
| Payment of mandatory payments | Turnover by debit 91.2 (taxes) | 98 | 2350 | 98 |
| Profit tax accrued | Credit turnover at 68 | 102 | 2410 | 102 |
At the end of 2021, the profit of Pekar LLC was (line 2400):
2078 – 1472 – 89 + 60 – 98 – 102 = 377 thousand rubles.
You can check the correctness of filling out the reports using the control ratios given in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 31, 2019 No. BA-4-1/ [email protected] (as amended on March 10, 2020).
Filling out the 2021 balance sheet according to the lines of the passive part
| Line code | Account balances included | |
| D/t | K/t | |
| Section III | ||
| 1310 | 80 | |
| 1320 | 81 | |
| 1340 | 83 s/account “Additional assessment of fixed assets and intangible assets” | |
| 1350 | 83 (except for additional valuation of fixed assets and intangible assets) | |
| 1360 | 82 | |
| 1370 | 84 | |
| 1300: Total for Section III | sum of section III row values | |
| Section IV | ||
| 1410 | 67 | |
| 1420 | 77 | |
| 1430 | 96 | |
| 1450 | amounts not included in the lines of section IV | |
| 1400: Total for Section IV | sum of rows of section IV | |
| Section V | ||
| 1510 | 66, 67 | |
| 1520 | 60, 62, 68, 69, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76 | |
| 1530 | 98, 86 | |
| 1540 | 96 | |
| 1550 | amounts not included in the previous lines of section V | |
| 1500: Section V total | sum of rows of section V | |
| 1700: Total liabilities | sum of row values of sections III, IV and V | |
If all balance lines are filled out correctly, the final results on lines 1600 and 1700 will be the same.