For financial and management accounting, one of the key parameters is the cost of production. But it cannot always be easily determined, especially in enterprises where production costs are constantly changing. The cost may be partially “hidden” in variable costs, thereby distorting the overall financial picture. If only direct expenses could be taken into account, how much easier it would be to internal accounting!
With the direct costing system, this is possible, you just need to know the principles and nuances of its application in Russian realities.
What is a direct costing system?
The English expression “Direct Costs” means “direct costs”. This directly reflects the meaning of using this system to calculate the “net” cost of production.
The use of the direct costing method is based on the conscious separation of fixed costs from variable costs, as well as direct costs from indirect ones. The term “ direct costing ” can be used:
- in a narrow sense - as a specific method for calculating the cost of manufactured goods;
- in a broad sense – as a way of organizing management accounting.
Modern Russian legislation does not give the go-ahead for the use of this system at the level of official accounting on a par with accounting and financial, only introducing some of its details into the framework of accounting (and even then, only by the end of the 20th century).
However, its effectiveness and compliance with international market standards has led to its use in management accounting, which is carried out for internal users of the organization. https://youtu.be/https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GGNaddkCBg4
Direct costing system
The American accounting system direct costing literally means direct costs.
There are 2 methods of calculation according to the system:
- Downtime - at direct variable costs;
- Developed - in terms of direct variable and fixed costs.
The main essence of the direct costing accounting system is the generalization of data for the purpose of structuring it and planning future expenses, production costs, and ultimately the profit of the enterprise.
The term can be used not only as the name of a specific calculation method, but also as a description of the system for organizing management accounting at the enterprise as a whole.
From the history
The system owes its origin to the Great Depression in the United States. Until 1928, when it was customary to calculate the cost of any product based on total expenses for it, there was a large number of unsold goods available. In order to adequately evaluate them, it was necessary to redistribute costs to their cost over different accounting periods, for which purpose we conditionally separated direct (variable) expenses and indirect (fixed) expenses, the latter being recognized as “useless”.
In 1936, D. Harris coined the term "direct costing", and in 1953 this method was recognized by the National Association of Accountants and published in detail in their report.
Some experts do not consider the name “direct costing” to be accurate, since inventory costs include not only the cost of materials, but also production costs, which are not constant. Instead of “direct”, they suggest using the prefix “ verible ” (that is, “variable”, thus taking into account not direct, but variable costs).
If we consider the difference between variable costs for the product itself and fixed costs, then the latter can be subtracted from revenue, because they will not change. In this form, the use of this system is called “ margin costing ”.
Distinctive feature of the “direct costing” system
The main point and distinctive feature of the “direct costing” system is the analysis of overhead costs and the formation of a system for direct attribution of costs to costing objects. Subsequently, overhead costs are related to gross profit.
Indirect costs include the following types of expenses:
- works and services directly related to production,
- leasing payments,
- rent,
- information services provided in relation to capital equipment and other costs.
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
If we consider direct costs, then in this case they will be distributed by calculation based on the volume of products that were produced in physical terms. This method can only be used in enterprises producing products of a homogeneous type.
Note 1
Another feature of the direct costing system is the ability to create a multi-stage income report. Using this report, you can track the structure and amount of costs.
If we summarize the information about the direct costing system, then it is:
- provides information on the profitability or unprofitability of production,
- allows you to calculate the critical point of sales volume, *helps optimize the product range,
- helps solve management problems
Key concepts of direct costing
To understand how this system of calculation and cost accounting functions, you need to clarify the essence of the main concepts with which it operates:
- fixed costs - expenses not determined by the volume of output, associated with a particular time period;
- variable costs - amounts, the size of which is determined by the quantity of products; when added to constants, they form total costs;
- marginal income is the “delta” between revenue for goods and variable costs (fixed costs plus profit from production).
How it works
The main goal of using direct costing is to “clean” the cost of fixed costs, reducing it and thus determining the marginal income.
The cost of production will include only variable costs that reflect its quantitative characteristics. In this case, fixed costs do not apply to the cost price, but are immediately allocated to the overall financial result.
Accounting and planning related to production occurs only for variable costs. With the same indicators, the balances of unsold products at the beginning and end of the period, as well as production that was not completed, are taken into account.
Fixed costs are written off from profit with the selected regularity throughout the entire reporting period in which these goods were produced. They are accumulated in a separate accounting account. They are not included in the cost.
NOTE! In the financial report on the results of production, compiled based on the results of applying direct costing, the relationship between profit, costs and output volume will always be traced.
System for calculating product costs based on direct costs (“Direct Costing”)
System for calculating product costs based on direct costs (“Direct Costing”)
The concept of the direct costing system
The name “direct costing,” introduced in 1936 by the American Jonathon Harris, means . ”
The main characteristic of direct costing is the division of costs into fixed and variable depending on changes in production volume. At the same time, only variable costs are included in the cost of products, and fixed costs are immediately included in the financial result .
The cost of finished products is taken into account and planned only in terms of variable costs. Fixed costs are not included in the calculation of the cost of products, i.e. taken into account when calculating the financial result for the reporting period[1].
Variable costs are also used to estimate balances of finished products and work in progress.
The direct costing method is not used for preparing external reporting and calculating taxes. It is used in internal accounting to conduct management analysis and make operational management decisions[2].
At the first stages of using direct costing, in the early 50s of the last century, when calculating the cost of products, only direct costs were taken into account, and indirect costs were written off to the financial result. This is where the name of the method comes from: direct costing system - a system for accounting for direct costs. Subsequently, the direct costing method was somewhat transformed: the cost is often calculated taking into account not only direct variable costs, but also indirect variables .
Direct production (variable) costs from the credit of accounts 10, 70, 69 are collected on the debit of account 20. The variable part of overhead costs is written off from account 25 to account 20. The constant part of overhead costs is not included in the cost of production, but is written off to reduce sales revenue in D 90.2.
Thus, the use of the “direct costing” system involves differentiated accounting of overhead costs :
a) expenses for the maintenance and operation of equipment - the variable part;
b) general production management costs - a constant part.
In this regard, the following subaccounts are distinguished:
– account 25-1 “Variable overhead costs”, subaccount “Costs for the maintenance and operation of machinery and equipment”;
– account 25-2 “Fixed overhead expenses”, subaccount “Overhead production management expenses”.
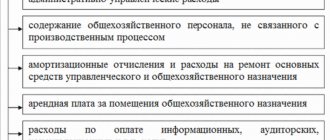
Fixed expenses also include administrative expenses (account 26) and selling expenses (account 44).
At the end of the reporting period, fixed expenses are written off directly to financial results.
The fundamental difference between the “direct costing” system and the method of calculating production costs is in relation to constant general production costs: when calculating production costs they are included in the calculations, but in the “direct costing” system they are excluded.
Basic accounting entries in the direct costing system:
| Contents of a business transaction | Debit | Credit |
| Direct costs are included in the cost of products (works, services) | 20 (23) | 10,69,70,02 |
| Variable overhead costs are included in the cost of products (works, services) (account 25-1) | 20 (23) | 25-1 |
| Fixed general production expenses are written off to financial results (account 25-2) | 90.2 | 25-2 |
| General business expenses are written off to financial results (account 26) | 90.2 | |
| Commercial expenses (account 44) associated with the sale of finished products (work, services) are written off to financial results. | 90.2 |
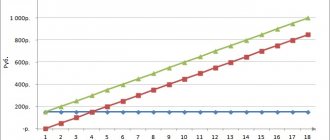
The company's financial results calculated using the direct costing method differ significantly from the results obtained using the full cost method.
Example. The company produced 1,500 units of products during the reporting period. Variable costs for producing a unit of output are 50 rubles. The total amount of fixed costs is 30,000 rubles. Sales volume – 1,000 units of product at a price of 100 rubles. for a unit. There were no inventories of work in progress or finished goods at the beginning of the period. Calculation of cost and financial results using the full and truncated cost method are presented in the table:
| Indicators | Direct costing method | Absorption costing method | ||
| Calculation formula | Value, rub. | Calculation formula | Value, rub. | |
| Revenues from sales | 100 rub. x 1000 units (Price x Sales volume) | 100 000 | 100 rub. x 1000 units (Price x Sales volume) | 100 000 |
| Unit cost | – | 50 rub. + 30,000 rub. / 1500 units (Variable costs per unit + Fixed costs / Production volume) | ||
| Cost of goods sold | 50 rub. x 1,000 units (Variable costs per unit x Sales volume) | 50 000 | 70 rub. x 1000 units (Unit cost x Sales volume) | 70 000 |
| Marginal income | 100,000 rub. — 50,000 rub. (Revenue from sales - Cost of products sold) | 50 000 | – | – |
| Fixed costs | – | 30 000 | – | – |
| Operating profit | 50,000 rub. — 30,000 rub. (Marginal profit - Fixed costs) | 20 000 | 100,000 rub. — 70,000 rub. (Revenue from sales - Cost of products sold) | 30 000 |
As can be seen from the example, the result of financial activities in the case of using different methods for calculating costs will be different due to the fact that at the end of the reporting period the company had a stock of finished products in the amount of 500 units . In other words, if the level of inventory at the end of the year increases, then the financial result determined on the basis of full cost will be higher than if it was calculated using truncated cost. If the inventory level decreases, the picture will be the opposite: when using truncated cost, the profit will be higher.
Construction of the “Report on financial results” in the “direct costing” system
The chosen calculation method affects not only the cost of production, but also the form of the financial results statement
.
The income statement prepared using the marginal approach distinguishes between the fixed and variable portions of costs. marginal income indicator is necessarily formed .
Report on financial results in the direct costing system[3]:
| Indicators | Sum |
| Revenues from sales | 100 000 |
| Variable portion of cost of goods sold | 50 000 |
| Marginal income (line 1-line 2) | 50 000 |
| Fixed costs (administrative and commercial) | 30 000 |
| Operating profit (line 3 – line 4) | 20 000 |
In the report compiled based on the results of calculating the full cost, the marginal income indicator is not calculated.
Statement of financial results in the full cost calculation system:
| Indicators | Sum |
| Revenues from sales | 100 000 |
| Cost of goods sold | 70 000 |
| Profit (page 1 – page 2) | 30 000 |
The future of direct costing
Several years ago, the CBA company, together with the Association of Controllers of Russia, conducted a survey of more than one hundred Russian companies. These were representatives of large, medium and small businesses. The main question asked during the study: “Do you use a direct costing system?”
As it turned out, from 40 to 90% of Russian companies use direct costing in their management practice. The brilliant statistics are somewhat overshadowed by the fact that this application is either purely formal or very limited in nature.
One of the key problems is that the “owners” of the management accounting system – financial economists – are not always interested in the wishes of their non-financial colleagues, and the latter are not always ready to clearly voice their needs. The main reason for such managerial apathy, in all likelihood, is that managers are not yet accustomed to looking at their activities and the activities of the units entrusted to them through the prism of efficiency, when the results obtained must be compared with the costs of achieving them.
Currently, unfortunately, not all potential opportunities of direct costing are used. Of course, if the company’s activities have not yet encountered a situation in which it would be necessary to apply data on limited costs, then it would be absurd to blame the company’s managers for ignoring direct costing. It is possible that when such a situation arises, its capabilities will be fully revealed.
For example, a company is embarking on a restructuring path. It is expected, among other things, to evaluate the activities of auxiliary units. It is possible that its result may be a decision to liquidate some divisions and transfer the corresponding functions to outsourcing.
Of course, in such a situation, both the own costs of the auxiliary units and the cost of the internal services they provide will certainly be taken into account. And to calculate these indicators, you cannot do without the principles of direct costing.
Code structure
The cost code consists of seven characters. Let's consider code 008-02-05 “Other fuels and lubricants”. The first three digits (008) are the code of the cost group “Maintenance of fixed assets”, the next two (02) are the code of the subgroup “Fuel and fuels and lubricants”, the last (05) are the serial number within the subgroup. Thus, we can unambiguously draw a conclusion about which group and subgroup this type of cost belongs to.
Cost center codes are formed according to the following principle. The first three digits are the workshop code. For example, 020 01-03, where the shop code 020 “Shaped foundry shop - FLC” 01 indicates that these are the main production areas of the shop, 03 is the serial number of the section within the shop (in this case, the iron smelting section).
System for calculating product costs based on direct costs (“Direct Costing”)
What does the IS operation and maintenance department do? Responsible for the safety of data (copying schedules, copying, etc.)…
WHAT HAPPENS IN ADULT LIFE? If you are still connected to your mother in the wrong way, you are avoiding separation and independent adult existence...
Conflicts in family life. How can I change this? It is rare that a marriage and relationship exists without conflict and tension. Everyone goes through this...
What to do if there is no reciprocity? And now let's come down from heaven to earth. Have you landed? Let's continue the conversation...
Didn't find what you were looking for? Use Google search on the site:
Two options for direct costing accounting
In domestic practice, two variations of the management accounting system are used, which are based on the direct costing method.
- Simple direct costing provides for separate accounting of financial and management accounting. In this case, only direct variable costs are taken into account when determining the cost.
- Developed direct costing combines cash and production accounting, including in the calculations not only direct, but also indirect variable costs.
Direct costing: general concepts
Direct costing is a theory of management accounting, the essence of which is to divide costs into fixed and variable.
Direct costing originated in the 20th century in the mid-30s. DirectCosts translated from English are direct or fixed costs. And according to the direct costing theory, fixed costs are defined as payments for each reporting period in the same amount.
The costs that arise during the production process are variable costs, which means their size will depend on the scale of production. The more the scale increases every month, the more the fixed costs increase. However, their list remains unchanged.
The accounting system itself, direct costing, comes in two types: simple and developed.
- In simple accounting, only direct variable costs are considered.
- And when developed, indirectly variable costs are also taken into account.
The direct costing system is also attractive because it can help you find the relationship between production, costs and profits.
In turn, this relationship helps to track which product brings more profit and which does not pay off at all.
Cost of direct costing
Direct costing is a method that refers to the types of reduced cost accounting. The essence of reduced cost is that it calculates how many costs were spent on a specific product. The remaining costs are written off as a period expense to reduce profits in the period in which they were incurred.
Cost accounting using direct costing consists of a symbiosis, taking into account several elements at once:
- Costs , first of all, and their types;
- stage ;
- Cost bearer;
- Cost carrier results;
- Results of the period.
Direct costing system
When using a direct costing system at an enterprise, the calculation and management of costs, overheads, and fixed costs is greatly simplified.
The thing is that their total volume accumulates in separate accounts, thanks to which it is possible to track their impact on the amount of profit.
Accordingly, such information not only facilitates the work of the accounting department, but also helps the company’s top managers quickly and with minimal risks solve operational problems and plan the further development of product policy, pricing and other components.
In addition, such information is also useful for the marketing department, because on its basis it is possible to formulate an assortment policy, and, therefore, an advertising strategy.
Based on it, the sales department can make forecasts about sales and plan the volume of sales of a particular product, and therefore predict the volume of purchases of components and spare parts.
Thanks to the direct costing accounting system, the company can differentiate costs, which allows for more accurate control and accounting of spent funds, which allows assessing the profitability of the industry and making prompt decisions in the event of crisis indicators or market changes.
The direct costing accounting system does not provide complete information about the cost of product units due to the division of costs into different accounts, however, many companies have already adapted to this type of accounting.
In any case, the direct costing system has found its place in domestic accounting.
Management accounting system
If we talk about the management accounting system as a whole, we can conclude that it is always characterized by 4 criteria, namely:
- The goals that the company sets for itself.
- Information flow takes into account both primary and secondary.
- The means and sacrifices one can make to achieve a goal.
- System components and their symbiosis.
Of course, information, and only primary information, always plays a key role in management accounting.
The organization's primary information is taken into account thanks to double entry in the company's accounts. The set of such accounts is determined by the working chart of accounts of the organization and demonstrates the composition of the database.
Direct costing costs
Accounting for company costs is an integral part of direct costing.
All company costs when using direct costing are divided into:
Moreover, depending on the type of direct costing, they can also be:
- variable - the amount of such costs depends on production.
- constant - costs whose nominal size represents a constant unit each period of time.
In order to accurately divide all costs into variable and constant, methods such as:
- analysis .
- high and low points (also called the absolute increment method, or minimax);
- least squares;
- technological regulation;
- correlations;
Application of Direct Costing
Most often, direct costing is used in enterprises abroad. In our country, it’s worth thinking about which enterprises can implement a direct costing accounting system. And the point here is not that Russian enterprises are zealous defenders of their homeland.
The point here is the complexity of accounting for costs and accumulating them in different accounts.
But you should not miss the point that the use of direct costing significantly reduces the time and effort for accounting, and as an addition is analytical information data, which, by the way, is very necessary in any enterprise.
It is precisely for these advantages that companies introduce direct costing as management accounting.
Another feature of using such an accounting system is the formation of an independent cost system.
This is where it gets more difficult. It is this part of management accounting that is not being implemented. After all, only large and large holdings with serious turnover can do this.
To resolve once and for all the issue of implementing a particular accounting system, it is necessary to analyze:
- financial capabilities of the company.
- foreign policy of the enterprise.
- OPF and form of ownership.
- Goals and objectives of the enterprise.
- Degree of technical equipment.
- Type of taxation.
- competence .
Direct costing in accounting
So, based on all of the above, we can conclude that direct costing is a management accounting system, which, in addition to the fact that it includes data on the recalculation and calculation of costs, this system allows you to draw conclusions about planning and control of future and present costs, calculate profitability of goods and so on.
Today, Russian manufacturing companies are faced with the difficulty of symbiosis of financial and production accounting. The thing is that the tasks and goals of these two components are different from each other.
Today there are several accounting options:
- Formation of separate accounting in the accounts of financial and production accounting.
- Integration of financial and production accounting.
- Duplication of accounting.
Any of these options is perfect for analyzing the financial situation of a company. Moreover, information about the relationship between production, profit and cost will tell us about the profitability of a particular production.
About the pros and cons
First of all, it is necessary to highlight the advantages of this type of accounting:
- Ease of determining cost.
- analysis .
- The principles of this type are perfectly combined with other types of accounting.
- Pricing , built on the direct costing database, is considered one of the most effective and flexible.
- Assessment of profitability for each unit of goods produced.
- Possibility of building a break-even point.
- Simplification of product cost accounting.
- Based on the obtained accounting data, you can build a sales plan.
However, along with strong arguments in favor of direct costing, there are also several negative points:
- It is very difficult to correlate costs by type , that is, in other words, every company has the concept of mixed costs, and because of this, where to classify this or that unit of cost depends on a lot, including the results of calculation, and, therefore, analysis.
- Generating external environmental
- Collecting information on the size of the total cost will take a lot of time, if in principle such a calculation is possible.
Elements of cost calculation
As part of the application of direct costing, it is necessary to calculate the “true” cost of manufactured products. It includes the following cost accounting elements:
- depending on the type of spending;
- accounting at the place where expenses are generated;
- cost carriers (accounting for the cost of each individual unit of production);
- accounting of costs for a particular period.
IMPORTANT! These components are taken into account for both variable and fixed costs. Most of them do not change, but some may differ slightly depending on how fully they are included in the cost price.
the main problem
A serious difficulty that may arise when applying this system is associated with the ambiguity of cost differentiation. Fixed in some cases, in others the costs may turn out to be variable. Enterprises usually do not have corresponding provisions that would unambiguously declare such a division. Costs are classified as constant or variable based on a number of assumptions, which may turn out to be erroneous. Therefore, you should periodically review the principles of cost sharing, as well as calculate marginal profit (for individual types of production and for the organization as a whole).
Advantages of use
The use of this system not only brings domestic companies closer to world market standards, but also opens up a number of additional prospects for increasing the efficiency of accounting and management:
- the ability to profitably combine production volume and price of finished products;
- effective management of pricing or dumping policies;
- improving the range of manufactured goods;
- convenience of calculating the company’s “break-even point” - that is, reaching “zero”, full cost recovery;
- the ability to quickly reorient production depending on changing market realities;
- assessment of reserves for fixed costs at the existing profitability of production;
- in-depth study of the organization’s work using statistical methods, for example, correlation analysis, etc.
The most important advantage of direct costing as a management system is its high efficiency in making operational decisions.