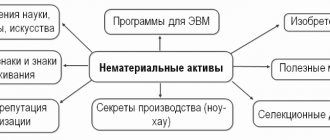
The purpose of creating a homeowners association
An HOA is formed for the effective management of real estate owned by the participants of this association. Owners of housing in apartment buildings most often unite in partnerships, but this is not prohibited for owners of private houses located on neighboring plots.
The HOA is formed for:
- maintaining the property of the owners in proper condition;
- its timely repair;
- creating conditions for comfortable living.
In addition, the partnership is not prohibited from engaging in commercial activities and generating income. This could be small paid repair services for residents of the association, the provision of real estate for rent, advertising, etc.
Sources of partnership funds
Partnership funds can be formed through:
- membership fees, entrance fees, and other similar income;
- subsidies;
- income from the organization's commercial activities.
Money received as membership or other fees does not form the partnership’s income and is used to pay for utilities and maintain housing in proper condition. When carrying out activities and concluding contracts, the HOA must act only in the interests of home owners.
A partnership is not an economic entity created to conduct commercial activities. The list of activities permitted for such organizations is closed and has strict restrictions.
The HOA can carry out:
- maintenance and repair of real estate in the partnership;
- construction of additional real estate;
- provision of premises for rent.
The revenue that goes to the organization’s accounts from this forms special funds. It can be spent in those areas that are provided for by the charter of the partnership.
Accounting statements of the partnership
In accordance with accounting legislation, HOAs are required to generate and submit reports to tax services, the Pension Fund, and statistical authorities. The partnership's financial statements for the year include:
- balance;
- income statement;
- report on the intended use of funds.
The responsibility for accounting and reporting remains with the HOA, even if it does not conduct commercial activities and applies the simplified tax system. In addition to the above forms, the HOA is required to maintain a register of members of the partnership.
Calculation of rent in HOA transactions
The program is designed for comprehensive automation of accounting in the housing and communal services sector: in HOAs, housing cooperatives, PZHEK and management companies. The functionality built into the program allows you to solve the following tasks:
- For residential and non-residential premises, calculate charges for housing and utilities at current rates and tariffs, taking into account benefits, social norms and subsidies;
- Take into account electricity consumption using single-tariff or dual-tariff meters, as well as without meters (according to approved consumption standards);
- Take into account the consumption of services by apartment meters (heat, water, gas and heating);
- Calculate charges based on public service consumption meters;
- Calculate the excess of the maximum level of payment for 1539 PP;
- Calculate ODN in accordance with 354 PP;
- Use special meters: sectional and meters for groups of houses;
- Print receipts for accrued rent, invoices and reconciliation reports;
- Recalculate accruals for previous months, recording the results of recalculation in the receipt for the current month;
- Take into account payments with the possibility of using a cash register or barcoding technology;
- Accept payments from bank statements or electronic payment registers;
- Transfer information about tenants' debt to the bank online;
- Calculate compensation (subsidies) for housing and utilities;
- Make calculations and account for payments under lease agreements;
- Calculate penalties for arrears of rent and major repairs;
- Maintain apartment cards containing information about residents, residential premises, meters and the dates of their verification;
- Generate and transmit data on accruals and payments in the form of accounting entries;
- Interact with GIS housing and communal services;
- Generate and transmit data on beneficiaries to authorized bodies;
- Keep separate records of accruals, payments and penalties for capital repairs since 2014.
We recommend reading: Until what age is a child considered a dependent?
In 1998, Center Bonus developed the first version of a program to automate the accounting of services and the calculation of rent for housing and communal services enterprises. Subsequently, the program was constantly improved and proved itself well at housing and communal services enterprises of the Sverdlovsk region. Today we confidently offer a well-developed, reliable and convenient program “Accounting for services and calculating rent”.
Tax accounting for homeowners associations
Features of accounting under the simplified tax system
In most cases, the HOA prefers a simplified system. The main advantage of the simplification for HOAs is a reduction in insurance premiums (20% rate). The HOA accountant must distinguish between receipts that are classified as income and amounts that do not fall under this definition and, accordingly, under taxation.
The following income does not count as partnership income under the simplified tax system:
- contributions;
- from the owners for the maintenance of the property;
- from the budget for real estate repairs, including capital ones.
According to the charter of the HOA, the main purpose of its creation is the maintenance of common real estate and the provision of utilities to members of the partnership.
Therefore, all funds received by the partnership for such purposes are not included in the income of the organization. It is necessary to take into account that funds received for these purposes from HOA members are not considered income. But funds received for the same purposes from persons who are not members of the partnership are considered income and are subject to taxation.
Cash receipts that are subject to and non-taxable must be accounted for separately. It is also important to ensure separate accounting of expenditures of funds received as targeted revenues. Therefore, the priority areas of work for an HOA accountant include drawing up cost estimates and distribution of costs, organizing analytical accounting of the organization’s costs.
Paying taxes when using the OSNO regime
Homeowners' associations using OSNO are payers of income tax and VAT.
- Income tax. Funds related to targeted financing are exempt from the accrual and payment of this tax. These are amounts received from the owners of housing in the partnership for the repair and maintenance of the HOA premises in proper condition. All income and expenses of the HOA must be taken into account separately. If this condition is not met, then the amounts of targeted financing are subject to taxation in accordance with the generally established procedure. Entry, membership, share fees, donations, and funds in reserve for repairs are not subject to taxation. Tax accounting of amounts received as income in HOAs is no different from accounting in other organizations engaged in commercial activities.
- VAT. HOAs that do not apply special tax regimes are VAT payers. This tax does not apply to targeted funds, the receipt of which is not determined by the commercial activities of the organization. There are VAT benefits for partnerships. The sale of HOA services for the maintenance and repair of premises is not subject to VAT.
Basic rules for accounting in HOAs (nuances)
- receives remuneration for placing advertising on the building, for using the property to provide Internet services, cable television, commercial telephony, etc.;
- leases non-residential premises related to the property;
- provides paid services to residents (for example, minor repairs in apartments).
- provision of utility services to HOAs (cold and hot water supply, sewerage, electricity, gas supply, heating, wastewater disposal, solid waste management) is exempt from VAT (subclause 29, clause 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 4, article 154 Housing Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 03/19/2014 No. 06-05-17/11844, dated 03/05/2013 No. 03-07-14/6462, Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 02/02/2010 No. ШС-17-3/ [email protected] ) , if: the HOA purchases these services from public utility organizations, electricity suppliers, gas supply organizations, organizations providing hot water supply, cold water supply and (or) sanitation;
- the selling price of utilities corresponds to the price of their purchase from resource supply organizations;
- The HOA did not refuse the VAT exemption for these transactions in accordance with clause 5 of Art. 149 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- the provision of services to the HOA for the maintenance and repair of common property in an apartment building is exempt from VAT (subclause 30, clause 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 07/03/2017 No. 03-07-07/41736, dated 06/08/2015 No. 03 -07-07/33108, dated July 15, 2011 No. 03-07-07/34), if: the HOA purchased these services from organizations and individual entrepreneurs directly performing (providing) these works (services);
- the price of sales of work, services for the maintenance of common property and repairs by management companies, HOAs corresponds to the cost of their acquisition;
- The HOA did not refuse the VAT exemption for these transactions in accordance with clause 5 of Art. 149 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- all other receipts of the HOA, except for contributions to the main activities, contain taxable characteristics for profit and VAT - this includes: payments by owners for individual services (for example, apartment renovation), if they are received first by the HOA and then transferred to third-party organizations, actually performing the services;
- other similar cases, including the provision of services to owners by the HOA for an additional fee (in addition to non-taxable mandatory contributions).
We recommend reading: Dacha Amnesty Extended Until Which Year
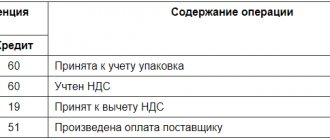
Reflection of transactions on HOA accounts: postings
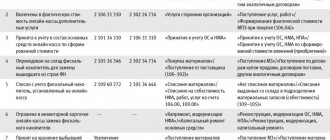
Business transactions in the accounting accounts are reflected as follows:
| Account correspondence | Contents of operation | |
| Debit | Credit | |
| 76 | 86 | Debt of a member of the partnership for contributions |
| 62 | 90 | Debt of a property owner who has not entered into a partnership |
| 26 | 70, 69,02, 10 | Expenses for maintaining HOA property |
| 26 | 68 | Calculation of a single tax under the simplified tax system |
| 26 | 60 | Costs of maintaining the premises of the partnership (services from third party providers) |
| 86, 20 | 26 | Costs have been distributed between HOA members and premises owners who have not joined the partnership |
| 90 | 20 | Expenses for maintaining property that does not belong to HOA members are written off |
| 90 | 51 | Bank expenses |
| 99 | 84 | Reformation of the balance sheet (in the case when the financial result is profit) |
| 84 | 86 | Replenishment of target financing funds from retained earnings |
| 76, 62 | 84 | Claimed loss to be covered |
| 86,20 | 96 | Creation of a repair fund |
Example 1. As a result of the commercial activities of the partnership, a financial result was formed over the year - a profit in the amount of 3,000 rubles. This amount, in accordance with the decision of the HOA members, was spent on landscaping the area in the courtyard of the house. The following entries were made in the accounting records of the partnership:
| Account correspondence | Sum | Contents of operation | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 84 | 86 | 3000 | Profit from commercial activities is included in targeted financing |
| 26 | 60 | 3000 | Costs for landscaping the site (performed by the contractor) |
| 60 | 51 | 3000 | Transferred to the contractor for site improvement work |
| 86 | 26 | 3000 | Write-off of targeted financing funds used for their intended purpose |
| 012 | 3000 | The constructed site has been registered | |
Accounting in HOAs
Disclosure of information Homeowners' associations (TSN) are obliged to disclose information about the main indicators of their financial and economic activities. (Clause 10 of Article 161 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. The forms on which information must be posted are approved by the Ministry of Construction of Russia (Order of the Ministry of Construction of Russia dated December 22, 2014
We recommend reading: Statement of claim for ownership
Housing and communal services organizations (namely, management companies) receive from the Unified Center only summary data on accrual and payment; accordingly, the management company reflects in its accounting only the total debt of citizens for housing and communal services, which is collected by the Unified Center. It turns out that the situation with the organization of accounting in the Management Company is a little unclear, however, for Russia there are plenty of them. Namely: the Criminal Code in accounting reflects the debt of the population only as the debt of the Unified Center for collecting payments. The SRC does not indicate the debt to the management company in its balance sheet, since the funds passing through it are transit. Often, SRCs indicate debt to housing and communal services (MC) only after receiving payments from the population. At the same time, the following entries are made: D-t 50, 51 K-t 76 “Debt to suppliers of housing and communal services” - payments have been received from the population.
Accounting for utility bills
It is necessary to pay attention to the procedure for accounting for utility payments received from the owners of premises when applying the simplified tax system in the partnership. The organization's charter may stipulate its obligation to provide such services to its members and enter into contracts with suppliers on their behalf.
In this case, only the difference between the amount of income from utility bills and their cost is subject to taxation, i.e. remuneration to the partnership for the services of an agent. Payments by those property owners who have not entered into a partnership are subject to taxation in full, unless agency agreements are concluded between them and the HOA .