What are the rates in 2021
The general income tax rate for 2021 is 20% of profits. Of these, in 2021, 2% received the federal budget, 18% received the regional budget. [email protected] came into force , which introduced a new declaration form and changed the procedure for distributing interest between budgets. In 2021, 3% will go to the federal treasury, 17% to the regional treasury.
At the local level, authorities have the right to lower the tax rate, but only in that part that goes to the local budget: 3% is added on top. Local regulations indicate what indicator is used to calculate income tax in the region - not lower than 13.5%. Together with payments going to the federal budget, the lower threshold is now 16.5% (13.5 + 3) - it has increased compared to 2021.
In Moscow, a rate of 13.5% is paid by certain categories of taxpayers who:
- use the labor of disabled people;
- produce cars;
- work in a special economic zone;
- are residents of technopolises and industrial parks.
In St. Petersburg, 13.5% of profits is paid only by residents of the special economic zone who operate on its territory.
In most regions, the rate has been reduced for at least some types of activities.
In addition to the main one, there are special rates. Profit tax at such rates is fully directed to the federal budget.
They are used if you have a certain status or for special types of income:
- 20% is paid by foreign companies without Russian representation, hydrocarbon producers and controlled foreign companies;
- 10% - foreign companies without a representative office in the Russian Federation from income from leasing vehicles and international transportation;
- 13% - local organizations from dividends of foreign and Russian companies and from dividends from shares on depositary receipts;
- 15% - foreign organizations from dividends of Russian companies; all owners of income from state and municipal securities (CB);
- 9% - from interest on municipal securities and other income from paragraphs. 2 clause 4 art. 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- 0% - rate for medical and educational institutions, residents of special economic zones (EZ), participants in regional investment projects, free EZ in Crimea and Sevastopol, residents of the territory of rapid socio-economic development.
What innovations happened in 2018
The rate for the tax levy we are considering in this article has remained unchanged since last year, 2021. It is 20%. As mentioned above, only its distribution between budgets of different levels has changed.
Thus, the federal treasury, which previously claimed only 2% of the required collection, now receives 1% more, therefore, the regional budget has lost this percentage, and instead of 18% today it has only 17%.
In 2021, a widespread assessment of the qualification level of company employees began. Since it was necessary to involve as many enterprises as possible to complete the task, the costs associated with assessing the qualification level were allowed to be included in the list of expenses that can be reduced from the taxable financial base.
To carry out the required assessment, each employee must provide written consent
In addition, such a check cannot be initiated “out of thin air”. So that it can subsequently be included in the list of expenses incurred by the company, it is necessary to provide employees with an employment contract and draw up an agreement for the provision of services aimed at assessing qualifications.
If an employee works in a company without employment, you can conduct a check on him, however, only for your own information, because such costs are prohibited from being included in the list of items that reduce the amount of profit.
Review: Major changes to tax legislation in 2018
Instructions for calculating income tax
Current step-by-step instructions on how to calculate income tax in 2021:
Example: your organization operates on OSN and received an income of 4,500,000 rubles for the calendar year. Expenses amounted to 2,700,000 rubles. Your profit: 4,500,000 – 2,700,000 = 1,800,000 rubles.
Let's look at the calculation of corporate income tax using a formula with tables based on this data:
| Income | 4,500,000 rubles |
| Expenses | 2,700,000 rubles |
| Profit | 1,800,000 rubles |
The contribution is paid on the amount of 1,800,000. See below for an example of how to find income tax.
If the regional rate in your area is basic and equal to 18%, then at the end of the year you will pay the following amounts.
To the local budget:
To the federal budget:
If a reduced rate of 13.5% is applied in the region, then the calculation is as follows.
To the local budget:
To federal:
The example shows that the amount of receipts to the federal budget does not change - 3% of income goes there.
Advance payments
Income tax is paid in advance payments every month or quarter, and then at the end of the year. Transferring advances quarterly in 2021 is allowed to those companies whose sales revenues do not exceed 15 million rubles per quarter over the previous 4 quarters. Other legal entities pay advances monthly. We described how to calculate advances for income tax in a separate article. Quarterly advances are calculated from actual income, and monthly advances are calculated from estimated income (based on data for the previous quarter).
Expenses and income
What is included in income?
Income is your revenue from your main activity (sales, provision of services or performance of work) and from additional sources (bank interest, rental of property). When the tax base for income tax is calculated, income is taken into account without VAT and excise taxes, confirmed by invoices, payment orders, entries in the book of income and expenses, and accounting documents.
What are expenses?
Expenses are confirmed and justified expenses of the company. They may be related to production activities, for example:
- employee salaries;
- cost of raw materials and equipment;
- depreciation.
But there are also those not related to production:
- legal costs;
- difference in exchange rates;
- interest on loans.
What expenses are deducted from income?
Accountants pay close attention to papers that confirm income tax expenses, since reducing income by expenses is allowed only if the following conditions are met:
- it is necessary to justify expenses - to prove economic feasibility;
- prepare primary documents (book of income and expenses, tax documentation).
There is a list of costs that cannot be taken into account when reducing the base.
Subtracted from income:
- commercial, transport, production costs (raw materials, wages, depreciation, rent, services of third-party lawyers, representation expenses);
- interest on debts;
- expenses on advertising (with a limitation - only 1% of sales revenue is written off);
- insurance costs;
- spending on research (to improve products);
- expenses for education and training of personnel;
- expenses for the purchase of databases and computer programs.
What expenses cannot be deducted?
The list of costs that do not reduce income is given in Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- remuneration of members of the board of directors;
- contributions to the authorized capital;
- contributions to the securities reserve;
- payments for exceeding the level of emissions into the environment;
- losses associated with economic activities in the communal, housing and socio-cultural spheres;
- penalties and fines;
- money and property transferred to pay for loans and borrowings;
- fees for notary services above the tariff;
- prepayment for a product or service;
- repayment of loans for employee housing;
- voluntary membership contributions to public funds;
- the amount of revaluation of the Central Bank with a negative difference;
- the cost of property that was given free of charge, transfer costs;
- payment for employee travel to work and home, if it is not provided for by production features and contract;
- pension benefits;
- vouchers for treatment and rest of employees;
- payment for vacations that are not provided for by law, but are specified in the contract with the employee;
- payment for sports and cultural events;
- payments for personal consumption goods purchased for employees;
- the cost of subscriptions to newspapers, magazines and other literature not related to production;
- payment for food for employees, unless this is provided for by law or collective agreement.
Moment of recognition of income and expenses
The moment of recognition is the period in which income or expenses are reflected in income tax accounting. There are two such points, they depend on the method of recognizing income and expenses:
- cash method;
- accrual method.
The company chooses one of the methods and, before December 31 (without waiting for the start of the next tax period), informs the territorial body of the Federal Tax Service about its choice.
When applying methods, firms take into account amounts at different times. Let's look into the nuances.
The cash method assumes that:
- income is taken into account at the time of receipt at the cash desk or in the company's current account, not earlier;
- expenses are taken into account at the time of debiting from the account or paying from the cash register, not earlier;
- When paying tax, amounts are taken into account according to the dates of receipt or write-off.
Accrual method:
- income is taken into account at the time of occurrence (under contracts or payment orders), and not upon direct payment;
- expenses are taken into account at the time of occurrence, and not when funds are written off from accounts;
- When paying tax, amounts are taken into account based on documented dates, even if payment actually occurred later.
Example:
Kolibri LLC issued an invoice for office rent in March, but payment was made only in June. Under the cash method, the accountant of Kolibri LLC reflects the expenses for renting an office in June - upon the transfer of money. In tax accounting, this expense is written off in the second quarter. Under the accrual method, the accountant of Kolibri LLC takes into account rental expenses in March, when the company should have paid it. In tax accounting, this expense is reflected in the first quarter.
All enterprises have the right to use the accrual method, but the use of the cash method is limited:
- Banks are prohibited from using it;
- firms recognize income and expenses in fact only if revenue does not exceed 1 million rubles for each of the last four quarters;
- If, when applying the method, the limit is exceeded, then the company is obliged to switch to the accrual method from the beginning of the current year.
What is the tax base if the company suffers a loss?
According to tax accounting rules, the profit of an organization is not a negative value. Even if there is a loss at the end of the year, the tax base is recognized as zero. The tax in this case is also zero. Tax accounting documents must confirm the correctness of the tax base calculation. It is mandatory to submit a declaration, even if the amount is zero.
The procedure for calculating the rate of return
The rate of profit (Np) is the ratio of profit (P) for a certain period to the advanced funds (AS).
Advanced funds consist of the costs of production of goods and wages for the reporting period.
The result of the ratio should be multiplied by 100%:
Np=(P/AS)x100%
Depending on the field of activity of the enterprise, the profit rate can range from 15 to 50%. With such values, the company has opportunities for growth, and its activities pay for themselves. If the rate of return is less than 15%, the enterprise has problems and its future is unstable, and if it is more than 100%, then you receive excess profits.
When calculating this indicator, it is necessary to carefully select the reporting period - in a number of industries, advanced funds have a turnover of more than one year, therefore, calculating the rate of profit in a shorter period of time can lead to false results.
Calculation
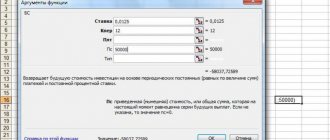
The basic formula for corporate income tax is:
NP = C * B,
Where
- NP - income tax;
- C - rate;
- B is the basis for calculation.
Kolibri LLC produces and sells soft toys. Let's find out the amount of tax that the company will pay for 2021 if:
- The LLC received a bank loan for 500,000 rubles;
- sold toys for 1,200,000 rubles including VAT;
- used raw materials for production worth 350,000 rubles;
- paid wages to workers in the amount of 250,000 rubles;
- insurance premiums amounted to 40,000 rubles;
- carried out depreciation in the amount of 30,000 rubles;
- paid interest on the loan in the amount of 25,000 rubles;
- wants to take into account last year’s loss of 120,000 rubles.
Expenses of Kolibri LLC in 2021:
Since income is calculated without VAT, it will be 1,000,000 rubles at a VAT rate of 20%. And 200,000 rubles is the amount of VAT that the LLC will transfer to the state. Loan amounts are not subject to contributions; they are simply not included in the tax base under paragraphs. 10 p. 1 art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. 500,000 rubles of loan are not considered income.
Then the profit of Kolibri LLC in 2021:
This is income minus expenses and minus last year's loss.
Calculation using the formula:
Of which go to the budget of the Russian Federation:
Goes to the regional budget:
We use the example of Kolibri LLC below to show calculations using an online calculator.
The convenient 1C:BusinessStart application allows you to automatically calculate tax amounts; you do not need to monitor changes in rates, the service is updated automatically, taking into account the latest changes in legislation. The program will warn you about the deadlines for submitting reports and paying taxes, and will tell you what and how to do.
Tax base: income from sales (revenue) and non-operating income
Income can be received by an organization as:
- income from sales (revenue);
- non-operating income.
According to the rules of Ch. 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income is determined not only under OSNO, but also under some special regimes (Articles 346.5, 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Revenue is interpreted in Art. 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as the totality of all receipts in the form of payment for goods sold.
Based on paragraph 1 of Art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, do not apply to income:
- Prepayment. In this case, prepayment includes, for example, the sale of gift cards / certificates (see the definition of the IC of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 2014 No. 305-KG-1498).
- Deposit, deposit.
- Contribution (contribution to the authorized capital), payment of the cost of the contribution and some other types of property provision.
All other property benefits (in the form of money, property or estimated income) are non-operating income (Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). These include:
- rent;
- gratuitous receipts;
- positive exchange rate difference (change in the value of foreign currency values due to changes in the exchange rate);
- penalties of various types;
- debt that has expired or has been forgiven by the creditor;
- benefit in the form of saved interest on loans, etc.
Important! If a settlement agreement was concluded, the amount of claims for which the creditor abandoned the claim is not included in taxable profit if the debtor did not recognize the debt (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated October 22, 2013 No. 3710/13).