Happy owners of apartments, rooms, country houses, garages and outbuildings are required to pay property tax for individuals. From 2021 it is calculated according to new rules. In addition to apartments, residential buildings, country houses and garages, the list of taxable objects will be supplemented with parking spaces registered as property, as well as objects whose construction has not been completed.
In accordance with Chapter 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, from 2021 the formation and calculation of property tax for individuals will be based on the cadastral, and not on the inventory value of the property. It is the one that is as close as possible to the market price.
TAX ON PROPERTY OF ORGANIZATIONS AND OBJECTS OF TAXATION
The property tax of organizations is established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, is put into effect by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and, from the moment of introduction, is required to be paid in the territory of the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
When establishing a tax, the legislative ( representative ) bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation determine:
- tax rate within the limits provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- procedure and deadlines for tax payment.
The laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation may also establish the specifics of determining the tax base of individual real estate objects, tax benefits, the grounds and procedure for their application by taxpayers.
Taxpayers are organizations that have property recognized as an object of taxation. The object of taxation is provided for Russian and foreign organizations.
The object of taxation for Russian organizations is movable and immovable property, recorded on the balance sheet as fixed assets in accordance with the accounting procedure (clause 1 of Article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The objects of taxation include the following property:
- transferred for temporary possession (use, disposal or trust management);
- contributed to joint activities;
- received under a concession agreement.
The object of taxation for foreign organizations depends on whether their activities are carried out on the territory of the Russian Federation through a permanent representative office or not. If the activities of an organization are related to a permanent establishment, then the object of taxation is movable and immovable property (fixed assets), as well as property received under a concession agreement.
For foreign organizations that do not operate through permanent representative offices, the object of taxation is real estate:
- located on the territory of the Russian Federation and owned by a foreign organization;
- received under a concession agreement.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), real estate includes:
- land;
- subsoil areas;
- everything that is directly connected with the earth;
- buildings (structures, unfinished construction projects);
- aircraft and sea vessels, inland navigation vessels, and space objects subject to state registration.
Movable property is considered to be things not related to real estate, including money and securities (Clause 2 of Article 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In accordance with Federal Law No. 202-FZ dated November 29, 2012 “On Amendments to Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation,” from January 1, 2013, movable property registered as fixed assets on January 1, 2013, was not included in the taxation category. Movable property accepted by the taxpayer for registration as fixed assets before this date was the object of taxation and was subject to taxation.
According to the provisions of the Federal Law of November 24, 2014 No. 366-FZ “On Amendments to Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation,” from January 1, 2015, movable property is subject to taxation (with the exception of certain fixed assets).
IT IS IMPORTANT
The objects of taxation are not fixed assets included in the first or second depreciation group in accordance with the Classification of fixed assets approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
The first depreciation group includes fixed assets with a useful life from one year to two years inclusive. This is usually a short-lived property. The second depreciation group includes fixed assets with a useful life of two to three years inclusive (computers, printers, servers, modems, local area network network equipment, industrial and household equipment).
The specified fixed assets have not been subject to taxation since 2015, regardless of when they were registered by the organization.
As for movable fixed assets of the third to tenth depreciation groups acquired in 2015, they are subject to taxation. However, tax relief applies to them (with some exceptions). The corresponding clarifications on this matter are given in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 20, 2015 No. BS-4-11/503 “On the property tax of organizations” (hereinafter referred to as the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. BS-4-11/503). In this case, the benefit applies to movable property registered as fixed assets in 2013 and later.
The benefit does not apply only to movable property registered as a result of:
- reorganization or liquidation of legal entities;
- transfer, including acquisition, of property between persons recognized as interdependent (clause 2 of article 105.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, if an organization received movable property during the reorganization or liquidation of a legal entity, then it has been a payer of property tax since 2015 in the usual manner (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 16, 2015 No. 03-05-05-01/503, 29.12 .2014 No. 03-05-05-01/68233; letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. BS-4-11/503).
Apparently, this norm was introduced into the tax legislation to prevent enterprises from reorganizing or liquidating a legal entity in order to remove movable property from taxation.
NOTE
If an organization has changed its name in connection with bringing its constituent documents into compliance with the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it has the right to use the exemption for movable property, that is, not to pay property tax on movable fixed assets registered in 2013 and later.
A detailed list of benefits for corporate property tax is presented in Art. 381 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Who is obliged to pay and who is not?
Property tax for individuals is levied on holders of ownership rights to property recognized as an object of taxation. Even minors are not exempt from the mandatory payment if they own this or that real estate. Payments for those under 18 years of age are made by guardians or parents until they reach adulthood.
The following are exempt from tax:
- pensioners or persons receiving a pension;
- payers discharged from military service or serving under conscription for military training in other countries where military operations took place;
- payers who are parents or spouses of military personnel who died while performing military duties;
- arts payers who use their premises as a museum, library or other public space;
- payers who own a building, outbuilding, commercial building, the area of which does not exceed 50 sq.m.
What is property tax
Property tax is a payment to the government for the ownership of real estate. You bought an apartment, registered it in your name - now you are the owner and you have real estate. You have to pay for the right to own it. More properties mean more tax liabilities.
Real estate tax is assessed once a year by the Federal Tax Service: in the second half of the year, it charges fees for properties that you owned in the previous reporting period. The Federal Tax Service generates a tax notice - a receipt - indicating what and how much to pay, and sends it to the owner. We have already written where to receive this notification and how to check your debts.
If you have a personal account on the tax website, by default you will not receive any notifications by mail. In order for them to arrive by mail, you need a paper delivery application. After registering in your personal account, you can choose whether to continue receiving paper receipts for debt by mail or refuse.
Tax deductions for property
| Property | Reduction of cadastral value taking into account tax deductions |
| Apartment | 20 sq m area |
| Room | 10 sq m area |
| House | 50 sq m area |
It should be noted that if you own several objects, then a tax deduction is due for each of them. If the property is owned by several people, then the deduction is made for everyone.
Why has the real estate tax for individuals increased since 2021?
From January 1, 2015, amendments were made to the tax legislation of the Russian Federation, to Chapter 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (“Property Tax for Individuals”). If previously homeowners - individuals - paid real estate tax (on owning an apartment), based on its inventory value according to the BTI assessment, then after the changes, the same tax is calculated from the cadastral value of the apartment (Article 402 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And the cadastral value is as close as possible to the real market value of the apartment, and is several times higher than the previous BTI assessment.
Payment of apartment tax for owners occurs once a year - in the current year (until December 1) for the previous year. That is, the tax, for example, for 2021 is paid in the fall of 2021.
The property tax of individuals on an apartment is paid at the location of this apartment, on the basis of a tax notice , which the owner receives by mail from the local Federal Tax Service inspectorate (in paper form), or electronically in the taxpayer’s personal account on the Federal Tax Service website.
Inventory value
The calculation of the inventory value differs from the cadastral calculation. The basis is not the types of real estate, but their inventory and cost. Municipal authorities can vary the level of the tax rate within established limits:
- up to 300 thousand rubles. the value of the property, the rate can be from 0 to 0.1%;
- from 300,001 rub. up to 500 thousand rubles. rate sizes 0.1 – 0.3%;
- from 500,001 rub. and higher size 0.3 - 2%.
If the municipality has not approved the exact rate, then federal fixed rates apply:
- up to 500 thousand rubles. – 0.1%;
- from 500,001 rub. – 0.3%.
We remind you that the inventory value can be applied for 2019 (this is the last period). True, the tax notice will arrive in 2021 or, if the tax service is late in sending it, in 2021, 2022, but not later.
What is subject to tax?
The new list of objects subject to property tax for individuals includes:
- House;
- living space (apartment, room);
- garage, parking place;
- single real estate complex;
- unfinished construction project;
- other buildings, structures, structures, premises.
At the same time, residential buildings located on plots provided for personal subsidiary farming, dacha farming, vegetable gardening, horticulture, and individual housing construction are now classified as residential buildings.
What properties are subject to tax?
Any real estate, except land, owned by a citizen is subject to property tax (land is subject to another - land tax). Most often we are talking about:
- apartments (parts of apartments);
- separate rooms in dormitories;
- residential buildings. These include residential buildings on land for individual housing construction, personal subsidiary plots, gardening, vegetable gardening, as well as parts of such houses;
- unfinished houses designated (according to design documentation) as “residential”;
- outbuildings (baths, sheds, etc.);
- commercial facilities (shops, warehouses, offices, etc.).
Any individual must pay the tax. Even an individual entrepreneur, if he is not in a special simplified tax regime.
TAX BASE FOR PROPERTY TAX OF ORGANIZATIONS
To calculate the property tax of organizations, it is necessary to know the features of the formation of the tax base.
The tax base is defined as the average annual value of property recognized as an object of taxation (unless otherwise provided by Article 375 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In relation to individual real estate objects, the tax base is determined as their cadastral value as of January 1 of the reporting year in accordance with Art. 378.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Tax base as the average annual value of property
If the tax base is the average annual value of property recognized as an object of taxation, then such property is accounted for at its residual value, formed in accordance with the established accounting procedure approved in the accounting policy of the organization.
If the residual value of the property includes a monetary assessment of future future costs associated with this property, the residual value of the specified property is determined without taking into account such costs.
If depreciation is not provided for individual fixed assets, the cost of these objects is determined as the difference between their original cost and the amount of depreciation. Depreciation is calculated according to established depreciation rates for accounting purposes at the end of each tax (reporting) period.
The tax base as the average annual value of property ( AgSt ) is calculated as follows:
CrgSt = (OS1 + OS2 + OS3 + OS4 + … + OS12 + OS13) / (12 + 1), (1)
where OS1, OS2, OS3, ..., OS12 - the residual value of the property as of January 1, February 1, March 1, ..., December 1 of the tax period;
OS13 - residual value of property as of the last date of the tax period (December 31);
12 is the number of months of the tax period.
The residual value of the property does not include the value of the property for which the tax base is determined as the cadastral value.
Let's consider a practical example of calculating the tax base as the average annual value of property.
EXAMPLE 1
In a retail trade organization located on the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, the residual value of property according to accounting data as of the 1st day of each month of the tax period was:
- on January 1 - 200,000 rubles;
- as of February 1 - 190,000 rubles;
- as of March 1 - 180,000 rubles;
- on April 1 - 170,000 rubles;
- on May 1 - 160,000 rubles;
- as of June 1 - 150,000 rubles;
- as of July 1 - 140,000 rubles;
- on August 1 - 130,000 rubles;
- on September 1 - 120,000 rubles;
- on October 1 - 110,000 rubles;
- on November 1 - 100,000 rubles;
- as of December 1 - 90,000 rubles.
The residual value of the property as of the last day of the tax period (December 31) is 80,000 rubles.
Using formula (1), we determine the average annual value of property :
(200 000 + 190 000 + 180 000 + 170 000 + 160 000 + 150 000 + 140 000 + 130 000 + 120 000 + 110 000 + 100 000 + 90 000 + 80 000) / (12 + 1) = 140 000 (rub.).
Based on the results of the reporting period (first quarter, half year, 9 months, calendar year), the average value of property is calculated. Formula for calculating the average value of property for the reporting period ( SrSt ):
SrSt = (OS1 + OS2) / (K + 1), (2)
where OS1 is the residual value of the property as of the 1st day of each month of the reporting period;
OS2 - residual value of property as of the 1st day of the month following the reporting period;
K - number of months of the reporting period.
EXAMPLE 2
Let's use the data from example 1 and calculate the average value of property of a retail trade organization for the reporting period.
Average property value:
- for the first quarter:
(200,000 + 190,000 + 180,000 + 170,000) / (3 + 1) = 185,000 (rub.);
- for the first half of the year:
(200,000 + 190,000 + 180,000 + 170,000 + 160,000 + 150,000 + 140,000) / (6 + 1) = 170,000 (rub.);
- in nine months:
(200,000 + 190,000 + 180,000 + 170,000 + 160,000 + 150,000 + 140,000 + 130,000 + 120,000 + 110,000) / (9 + 1) = 155,000 (rub.).
NOTE
Legislative (representative) bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have the right not to establish tax reporting periods (clause 3 of Article 360 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
To determine advance payments and the amount of corporate property tax , you need to know the tax rate.
The tax rate is established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and cannot exceed 2.2% (provided that the tax base is the average annual value of the property).
It is allowed to establish differentiated tax rates depending on the categories of taxpayers and (or) types of property recognized as an object of taxation.
For certain property objects (public railway tracks, main pipelines, power lines, etc.) reduced tax rates are provided. Until 2013, these types of property belonged to the preferential category of property.
The advance payment at the end of each reporting period is equal to ¼ of the product of the corresponding tax rate and the average value of the property for the reporting period.
EXAMPLE 3
Based on the data in example 2, we calculate advance payments and the amount of property tax.
Advance payments for reporting periods:
- for the first quarter:
1/4 × (185,000 rubles × 2.2% / 100%) = 1017.5 rubles;
- for the first half of the year:
1/4 × (RUB 170,000 × 2.2% / 100%) = RUB 935;
- in nine months:
1/4 × (RUB 155,000 × 2.2% / 100%) = RUB 852.5
Tax amount for the tax period:
140,000 rub. × 2.2% / 100% = 3080 rub .
At the end of the tax period, the difference between the tax amount and advance payments is paid to the budget. It will be 275 rubles. (3080 – 1017.5 – 935 – 852.5).
Cadastral value as a tax base
The tax base for corporate property tax as cadastral value is provided for in Art. 378.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The cadastral value is approved in relation to the following types of real estate recognized as an object of taxation :
- administrative and business centers and shopping centers (complexes), as well as premises in them;
- non-residential premises, which, in accordance with cadastral passports of real estate objects or documents of technical registration (inventory) of real estate objects, provide for the placement of offices, retail facilities, public catering facilities and consumer services;
- real estate objects of foreign organizations that do not operate in Russia through permanent representative offices, as well as real estate objects not related to the activities of these organizations in the Russian Federation through permanent representative offices;
- residential buildings and residential premises that are not taken into account on the balance sheet as fixed assets in the manner established for accounting. These are, as a rule, houses and apartments purchased or built by an organization for resale, that is, those assets that are reflected in account 41 “Goods” and account 43 “Finished products”.
The cadastral value can be used as a tax base under the following conditions:
- the actual use of a building (structure, structure) for business, administrative or commercial purposes. At least 20% of the total area of this building (structure, structure), in accordance with the cadastral passports of the relevant real estate objects or technical registration (inventory) documents of such objects, provides for the placement of offices and related office infrastructure (including centralized reception premises, meeting rooms, office equipment , parking);
- the actual use of a building (structure, structure) for the purpose of locating retail facilities, public catering facilities and (or) consumer service facilities is at least 20% of its total area for the placement of retail facilities, public catering facilities and (or) consumer service facilities.
Cadastral value as a tax base for administrative, business and shopping centers, residential buildings, non-residential and residential premises is possible if two conditions are simultaneously met :
1) in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation at the location of these objects, a regional law has been adopted, which establishes the specifics of determining the tax base based on the cadastral value;
2) the specified objects are included in the regional list of real estate objects, for which the tax base is determined as their cadastral value, approved by the authorized executive body of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
The regional list of real estate is established for a certain year no later than the 1st day of that year and does not change during this period. If during the year objects are identified that were not taken into account in this period, they are included in the list next year (clause 10 of Article 382 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, no new objects are added to this list during the year. This is confirmed by letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 28, 2015 No. BS-4-11/7315.
For such objects, property tax must be calculated in accordance with the generally established procedure - based on the average annual value of the property.
The issue of the tax base in relation to residential buildings and residential premises recorded on the balance sheet of organizations as goods or finished products deserves special attention.
In accordance with the requirements of Federal Law No. 135-FZ dated July 29, 1998 (as amended on July 13, 2015) “On Valuation Activities in the Russian Federation,” state cadastral valuation is carried out in relation to real estate registered in the state cadastre. Based on this law, the tax authorities, in their letter dated April 23, 2015 No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] “On the property tax of organizations,” concluded that houses and residential premises recorded on the organization’s balance sheet as goods or finished products , are subject to taxation at cadastral value if:
- these objects are registered in the state cadastre of real estate;
- there is a corresponding law establishing the calculation of the tax base for these objects.
If the law of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation does not establish the specifics of determining the tax base based on the cadastral value in relation to such real estate, then it is not subject to corporate property tax.
The Ministry of Finance of Russia also gave corresponding clarifications (letters dated 04/08/2015 No. 03-05-05-01/19690 and No. 03-05-05-01/19749).
Considering the cadastral value as a whole as a tax base, the following should be noted.
If the cadastral value has changed during the tax period, then this change is not taken into account for the current and previous tax periods (paragraph 1, clause 15, article 378 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This change is not taken into account in future periods (except in certain cases). Organizational property tax should be calculated based on the new cadastral value, if it is revised:
- due to a technical error made by Rosreestr (cadastral chamber) when maintaining the state real estate cadastre. In this case, the changed cadastral value is taken into account from the beginning of the tax period in which the error was made;
- by decision of the court or commission for the consideration of disputes on the results of determining the cadastral valuation of real estate. In this case, the new cadastral value established by the court or commission is taken into account starting from the tax period in which the application for revision of the cadastral value was submitted, but not earlier than the date of entering information into the state real estate cadastre.
When calculating the tax base based on the cadastral value of an object, the share and period of ownership of such an object are taken into account.
If the cadastral value of the premises owned by the organization has not been determined, but the cadastral value of the building in which it is located has been determined, then the taxpayer calculates the value of the premises independently . In this case, the tax base is calculated as a share of the cadastral value of the building in which the premises are located, corresponding to the share of the premises' area in the total area of the building.
If a taxpayer owns an object during an incomplete tax period, the tax base is calculated taking into account a special coefficient (clause 5 of Article 382 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The coefficient ( K ) is calculated as follows:
K = K1 / K2, (3)
where K1 is the number of full months of ownership of the object;
K2 - the number of months in the tax (reporting) period.
From 01/01/2016, organizations that own real estate objects with the right of economic management must evaluate these objects based on the cadastral value (in 2014–2015, the assessment was made based on the average annual value of the property).
For property included in a mutual investment fund and included in the corresponding regional list, the tax base as cadastral value is applied from 01/01/2015 (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 05/08/2014 No. BS-4-11 / [email protected] “On the property tax of organizations ").
No later than the 1st day of the next tax period for property tax, the approved regional list must be posted on the official website of the authorized executive body of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
Information on the cadastral value of a property included in the regional list can be obtained on the Rosreestr website (www.rosreestr.ru). For tax purposes, official information on the cadastral value of the property or a certificate as of the 1st day of the tax period is desirable.
In 2014, four constituent entities of the Russian Federation adopted the corresponding regional law on the cadastral value of property (Moscow, Moscow, Amur and Kemerovo regions). In 2015, corresponding laws were adopted in another 30 constituent entities of the Russian Federation. However, in four constituent entities of the Russian Federation the regional list was not approved, and in the Ryazan region the law came into force on January 1, 2016.
For the city of Moscow, the list of objects for which tax calculation is based on cadastral value was approved by Moscow Government Decree No. 700-PP dated November 28, 2014 (valid from January 1, 2015).
Property tax rates depend on the tax base . If the tax base is the cadastral value of the property, then the tax rate cannot exceed:
- for the federal city of Moscow: in 2014 - 1.5%, in 2015 - 1.7%, in 2021 and subsequent years - 2.0%;
- for other constituent entities of the Russian Federation: in 2014 - 1%, in 2015 - 1.5%, in 2016 and subsequent years - 2.0%.
ON A NOTE
The Moscow government has revised the tax rates that will be applied when calculating taxes in 2016–2018. at cadastral value. In particular, the previously established rate for 2021 was reduced from 1.5 to 1.3%, for 2021 - from 1.8 to 1.4%, and for 2021 - from 2.0 to 1.5 %.
The specified tax rates are applied with a coefficient of 0.1 in relation to non-residential premises if they simultaneously satisfy the following criteria :
- located in buildings (structures, structures), the tax base for which is determined as their cadastral value;
- are used for the placement of public catering facilities, retail trade facilities, consumer services, for carrying out banking operations for servicing individuals, tourism activities (activities of a tour operator or travel agent to conclude an agreement on the sale of a tourism product with a tourist), activities in the field of performing arts, museum activities, commercial art galleries and/or film exhibition activities;
- located on the ground, first and (or) second floors of buildings (buildings, structures) directly adjacent to pedestrian zones of citywide importance or to streets with heavy pedestrian traffic. The list of pedestrian zones and streets with heavy pedestrian traffic is approved by the Moscow Government.
We will show the calculation of property tax based on the cadastral value of the property using an example.
EXAMPLE 4
As of 01/01/2015, the organization’s balance sheet includes a real estate property - a shopping center building. The cadastral value of the object is 50,000,000 rubles, the tax rate is 1,2 %.
property tax for 2015 will be:
50,000,000 rub. × 1.2% / 100% = 600,000 rub .
Advance payments are the product of the tax rate and one quarter of the cadastral value of the property.
Advance payments for reporting periods:
- for the first quarter:
1/4 × 50,000,000 rub. × 1.2% / 100% = RUB 150,000;
- for the first half of the year:
1/4 × 50,000,000 rub. × 1.2% / 100% = RUB 150,000;
- in nine months:
1/4 × 50,000,000 rub. × 1.2% / 100% = 150,000 rub.
The amount of advance payments for the reporting periods will be:
150,000 rub. × 3 = 450,000 rub .
At the end of the tax period, the organization will pay a tax of 150,000 rubles . (600,000 rub. – 450,000 rub.).
How to find out the cadastral value of your home
Today you can find out the exact cadastral value of your property on the Internet if you know the cadastral number.
If you don’t know the cadastral number , then go to the Rosreestr website in the “Reference information on real estate online” section, enter the address of the apartment, then copy the received GKN (state cadastral number).
When the cadastral number is known, just go to the tax service website. There, fill in the proposed fields (tax year, subject of the Russian Federation, type of real estate, cadastral number), each time clicking “next”. As a result, you will be able to find out the property tax due. In addition, depending on the year and region you are interested in, you will find out whether the cadastral or inventory value is applied. From 2021 (namely, the tax base, not the year for payment), only cadastral calculation is applied.
Other options to find out the cost on the official website of Rosreestr:
- section “Receiving information from the State Tax Committee” - order the receipt of an extract, which will have to wait 5 working days. Remember the order number, because it can be used to track execution;
- section “Public cadastral map” - search by cadastre number, the information obtained can be used as reference information, it has no legal force;
- section “Reference information on real estate objects” - can be found out by one of three conditions: cadastre number, conditional number or property address;
- section “Obtaining information from the state cadastral valuation data fund” - search by cadastral number.
If the unified database contains information about the cadastral value of your real estate, then such information must be provided free of charge within five days from the moment you apply directly to Rosreestr or the MFC for a certificate of cadastral value (if you order a cadastral passport, which, among other things, information and cadastral value, you will have to pay 200 rubles).
What benefits are there?
All existing tax benefits have been retained in the amended law. Thus, the tax will not be levied on disabled people from birth, as well as on disabled people of groups I and II. True, these categories of citizens can take advantage of the preferential right only in relation to one of the objects of each type, that is, in relation to one apartment, one garage, residential building, etc.
Benefits do not apply to:
- objects used in business activities;
- objects worth more than 300 million rubles.
In order to take advantage of the benefit, you must contact the tax authority with a corresponding application. This should be done before January 1 of the year, which is the tax period. If you are late, the tax authority, having finally calculated the amount of due payments, will independently provide the benefit.
What to do if you haven’t received a tax notice about accrued tax?
Owners of real estate and vehicles must report to the Internal Revenue Service if they have not received tax notices.
The absence of a tax receipt indicates that the Federal Tax Service does not have data on real estate and the taxpayer is obliged to provide a report about the property. Such a message is provided one-time until the end of the year following the year of acquisition of the property.
Or this is an omission of the tax service. If subsequent notifications arrive several years in advance, you can pay within a 3-year period. But this does not apply to cases where the owner concealed information about his objects. That is, he did not submit a notice of acquisition of real estate.
Calculation based on cadastral value
To pay real estate taxes, you don't need to calculate anything first. The tax office will calculate everything itself, and the notification will already indicate the total amount for the reporting period. We'll tell you where it comes from so you can check it out. If it doesn’t work out, send a message to the Federal Tax Service.
Now there is a transition period for taxpayers: property taxes are not taken in full, but are multiplied by reduction factors. But first we will show how the full amount is calculated.
When calculating property tax based on the cadastral value, it is reduced by a deduction and multiplied by the tax rate. The tenure period is also important: if it is less than a year, the amount of property tax is proportionally reduced. If you own only part of the property, tax liabilities are divided proportionally between all owners.
N = B × S × KPV × D
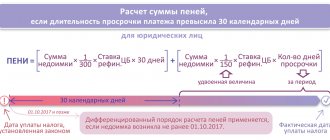
Here N is the amount of property tax, B is the tax base, or the cadastral value of the object after deduction, C is the property tax rate in the region for this object, KPV is the coefficient of the ownership period, D is the size of the ownership share in the object.
To determine the CPV, you need to divide the period of ownership of the property in months by 12. If you bought an apartment before the 15th day inclusive, then this month is considered a full month. If later than this period, the month is not counted.
Art. 408 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: calculation of property tax
The taxpayer bought the apartment on June 20 and sold it on December 20. Then June is not taken into account in the period, but December is. Ownership period: 6 months. CPV is 6/12, that is, 0.5.
You can also see the calculation formula in your personal account on the Federal Tax Service website. It will not necessarily coincide with ours, because we gave an example without taking into account reduction factors. To apply them, the organization first calculates property tax at inventory value. We will tell you how to do this further, but first we will calculate the full property tax according to the cadastre using a real example.
Tax calculation procedure
The tax amount is calculated from the cadastral value established as of January 1 of the current tax period in proportion to the period of ownership.
When calculating tax based on cadastral value, tax deductions are provided (reduction of cadastral value) by the amount of cadastral value:
- 10 sq.m. regarding the room,
- 20 sq.m. regarding the apartment,
- 50 sq. m. in relation to a residential building.
- 1 million rubles - in relation to a single real estate complex with a residential building.
If, when applying tax deductions, the tax base takes a negative value, for the purpose of calculating tax, such a tax base is taken equal to zero.
Correction factors
Due to the fact that the amount of tax calculated from the cadastral value is, as a rule, significantly higher than that calculated from the inventory value, correction factors have been established that are used when calculating the amount of tax:
- 0.2 – when calculating tax for 2015;
- 0.4 - when calculating tax for 2021;
- 0.6 - when calculating tax for 2021;
- 0.8 - when calculating tax for 2021.
Starting from 2021, the correction factor does not apply.
In this case, the tax amount is calculated using the formula:
H = (H1 - H2) x K + H2, where
- N - the amount of tax to be paid;
- N1 - the amount of tax calculated from the cadastral value without taking into account the correction factor;
- N2 - the amount of tax calculated on the basis of the corresponding inventory value of the taxable object;
- K – correction factor.
Calculation example
Let's calculate the tax amount for an apartment with a total area of 70 square meters. m., located in Moscow near the Prospekt Mira metro station with a cadastral value of 6 million rubles. The tax amount for 2014, calculated based on the inventory value, is 950 rubles.
For reference. You can find out the cadastral value of an apartment (residential building) on the Rosreestr website (https://rosreestr.ru/wps/portal/online_request), and then independently calculate the amount of property tax using a calculator.
1. So, the tax deduction is 20 sq.m., that is, the tax base is equal to:
6,000,000 / 70 sq.m. * 20 sq.m. = 1,714,285.71 rubles.
2. The tax rate for this apartment is 0.1%.
(6,000,000 - 1,714,285.71) * 0.1% = 4,285.71 rubles.
3. We apply the tax calculation formula taking into account the correction factor:
H = (H1 - H2) x K + H2
Amount of tax payable for 2015 = (4,285.71-950)*0.2+950 = 1,617.14 rubles.
Amount of tax payable for 2021 = (4,285.71 -950)*0.4+950 = 2,284.28 rubles.
Amount of tax payable for 2021 = (4,285.71 -950)*0.6+950 = 2,951.42 rubles.
Amount of tax payable for 2021 = (4,285.71 -950)*0.8+950 = 3,618.56 rubles.
Amount of tax payable for 2021, 2021 and subsequent years = 4,285.71 rubles.
What will happen in regions that are late with innovations?
Nizhny Novgorod residents will begin paying property taxes according to the new rules in 2021, based on the results of 2015. But this will not be the case in all regions. It is planned to completely switch to the new calculation system within five years, by 2021. If the old principle is still in effect in your region, the tax will be calculated based on the inventory value of the property. To do this, the inventory cost must be multiplied by the rate.
Rates for calculating tax on inventory value
| Property value increased by deflator coefficient | Maximum bet |
| Up to RUB 300,000 inclusive | Up to 01% inclusive |
| Over 300,000 rubles up to 500,000 rubles inclusive | Over 0.1% to 0.3% inclusive |
| Over 500,000 rub. | Over 0.3% up to 2% inclusive |
The rates listed in Chapter 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are set by regional authorities. So far they have not changed, but regional authorities have the right to revise them.
For regions that have not switched to the new taxation system, a special transitional formula has been developed. The tax service will determine the difference between the cadastral and inventory value of the property, and then multiply it by a special coefficient (Article 408 of the new Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The coefficient values will gradually increase over four years as follows: 0.2; 0.4; 0.6 and 0.8.
You can familiarize yourself with the regulatory legal acts on the establishment of tax rates, additional deductions and benefits adopted in a particular region (locality) on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia “Reference information on rates and benefits for property taxes”
Read the next article “How to get a tax deduction when buying real estate?”
How to count?
Chapter 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides basic values that are applied if the tax is calculated at the cadastral value.
Rates for calculating tax on cadastral value
| Property | Maximum bet |
| Residential buildings, apartments, rooms, unfinished housing construction, garages, parking space, outbuildings on land intended for dacha farming | 0,1% |
| Property of shopping or office complexes; property worth more than 300 million rubles | 2% |
| Other objects | 0,5% |
Regional authorities will be able to reduce base rates to 0 percent or increase them, but not more than three times.
An example of calculating tax based on cadastral value:
Owned by Ivanov I.L. there is an apartment of 54 sq. meters. The cadastral value of housing as of January 1, 2015 was 4 million rubles. We reduce the area of the apartment by the amount of the tax deduction:
54 - 20 = 34 sq. meters.
4,000,000 rub. : 54 sq. meters x 34 sq. m = 2,518,519 rub.
It is on this amount that tax will be charged.
We multiply it by the rate and get the amount of payments due from the owner: 2,518,519 × 0.1% = 2,519 rubles.