To check the actual cash balance in the organization and its compliance with the accounting system data, a cash register inventory . During this procedure, funds are recalculated, the correctness of documents is checked, as well as the established cash norm.
Carrying out an inventory procedure allows the owner or director of the company to monitor cashiers for theft or poor quality work. In case of a tax audit, each organization must have completed and signed cash register inventory reports in the INV-15 form.
Preparation for the procedure
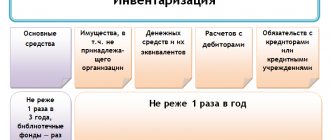
Inventory is an audit of all property that a company or enterprise actually has for the purpose of reporting and auditing all valuables, which include:
- products ready for sale;
- all goods of the enterprise that are in circulation;
- raw materials;
- funds (fixed).
An audit of cash transactions is also carried out at the end of the year, the results are compared with the information that is entered into the accounting records in order to identify deficiencies in property or its surplus. The procedure for conducting operations and methodology in 2021 is regulated by law and the Russian Ministry of Finance.
In order to prepare for the procedure, the company needs to prepare a number of documents, the main ones being:
- order to conduct an audit;
- papers with receipts from persons who are financially responsible in the organization.
To begin with, the manager forms the composition of the commission, which must include the following departments:
- administration and management staff;
- accounting staff;
- department with other employees.
The latter unit may include guards or supervisors, disinterested persons or managers. Persons who bear financial responsibility are never members of the commission, but their presence at the procedure is necessary.
Cash desk audit
A cash audit is an element of internal control in organizations and enterprises of individual entrepreneurs. According to clause 1.11 of the Regulations on the procedure for conducting cash transactions with banknotes and coins of the Bank of Russia on the territory of the Russian Federation, approved. Central Bank of the Russian Federation October 12, 2011 No. 373-P, a legal entity, an individual entrepreneur independently determine the procedure and timing for conducting checks of the actual availability of cash.
At the same time, paragraph 2 of Article 12 of the Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ on accounting for legal entities establishes cases when conducting a cash inventory is mandatory, namely:
— before preparing annual financial statements;
— when changing cashiers;
- when facts of theft or abuse are revealed.
In organizations and enterprises of individual entrepreneurs, as a rule, the cash register is audited monthly - in the morning on the first working day of each month or at the end of the last working day of each month. This guarantees the safety of funds and also disciplines financially responsible persons. In addition, it is periodically necessary to conduct sudden audits of the cash register. An order to conduct such an audit is drawn up immediately before it begins. The initiator of such an order is the manager, or the chief accountant, or the internal auditor. Other persons should not know about the audit before the audit begins.
An individual entrepreneur who runs a cash register himself must also conduct an audit and document its results in documents of standardized forms. He must determine in his decision the frequency of such audits. For example, quarterly, once every six months or only at the end of the year. In this case, this will be sufficient, since the entrepreneur, by virtue of performing the duties of a cashier, daily recalculates cash and checks its availability with the balance in the cash book.
An audit of the cash register is carried out with a complete page-by-sheet recalculation of cash and verification of other valuables in the cash register. The actual availability of cash in the cash register is compared with the book balance, that is, the balance in the cash book. The actual availability of monetary documents, securities, which are stored in the organization's cash desk, is compared with accounting data and the securities accounting book, the monetary documents accounting book.
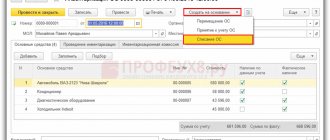
To carry out an audit of the cash register, by order of the manager (individual entrepreneur), a commission is appointed, which draws up an act. The order to conduct an audit is drawn up according to the unified form No. INV-22. The cash inventory report is drawn up according to the unified form No. INV-15. The unified forms were approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of August 18, 1998 No. 88. The procedure for conducting an inventory is established by the Methodological Guidelines for the Inventory of Property and Financial Liabilities, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 13, 1995 No. 49.
If the audit detects a shortage or surplus of valuables in the cash register, the act indicates their amount and the circumstances of their occurrence.
In accounting, organizations make the following entries:
Debit 50.1 Credit 91.1 – surpluses identified by the cash register audit have been capitalized;
Debit 94 Credit 50.1 – a shortage of funds in the cash register was identified;
Debit 73.2 Credit 94 – the shortage identified in the cash register is attributed to the guilty person (cashier).
Procedure and methodology
Once all departments have been formed, the director must issue an order that the audit can begin. The document must necessarily contain the following information:
- grounds for conducting an inspection;
- commission members;
- a list of property that is subject to inspection;
- obligations of participants;
- start date;
- accounting end date.
At the third stage, all persons who are financially responsible must create and submit receipts stating that the valuables attached to them are within the enterprise or are currently used.
An audit of valuables can only be carried out if there is a documentary inventory of the property. During the inspection process, all property is counted, verified, weighed by members of the commission, after which the information is entered into the inventory.
After the 2021 inventory is completely completed, the data obtained can be compared with financial statements; for this purpose, matching statements are used, which should be in any enterprise. The chief accountant compares the information in the statements with accounting information and then draws conclusions.
If during the inspection deviations from the norm were identified, then the authorized person is obliged to create another comparison sheet in two samples at once:
- for a person who assumes financial responsibility;
- for enterprise accounting.
At the end of the audit, the results are compiled in the form of accounting certificates, in order to establish a balance in the property, it is necessary to write off deficiencies, and find the correct and logical use of surpluses.
Any enterprise or company in 2021 can use ready-made forms of documents to conduct transactions or use their own forms and certificates. Ready-made forms (unified forms) are created and regulated in accordance with the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88.
INVENTORY OF CASH IN THE ORGANIZATION'S CASH
Rate this article
The procedure for conducting cash transactions provides for sudden audits of the cash register with a complete recalculation of money and verification of other valuables in the cash register within the time limits established by the head of the enterprise. The audit of the cash register is carried out by the enterprise's inventory commission, appointed by order of the enterprise. Members of the commission, in the presence of the cashier, check the presence of a sheet-by-sheet count of all the money in the cash register, receipts for valuables deposited for storage, securities, checkbooks and strict reporting forms, as well as the maintenance of the cash book and the procedure for storing money.
The procedure for conducting cash inventory is additionally regulated by the Procedure for conducting cash transactions in the Russian Federation, approved by the decision of the Board of Directors of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated September 22, 1993 No. 40 and communicated by the Letter of the Bank of Russia dated October 4, 1993 No. 18.
The organization's cash desk can store cash, monetary documents, forms of securities and strict reporting documents.
Cash is represented by cash.
Monetary documents include: postage stamps, state duty stamps, bill of exchange stamps, vouchers to holiday homes and sanatoriums, air tickets and other documents.
Strict reporting forms are: receipt books, certificate forms, diplomas, various subscriptions, coupons, tickets, forms of shipping documents, etc.
The timing and procedure for conducting an inventory of the cash register and funds stored in current and other bank accounts are established by the head of the organization and are enshrined in the order on accounting policies.
The cashier bears financial responsibility for the safety of all funds and documents available at the organization's cash desk.
An inventory of cash is carried out on the basis of an order (instruction) from the head of the organization by a commission consisting of a representative of the administration, the chief accountant, and the cashier (as the financially responsible person).
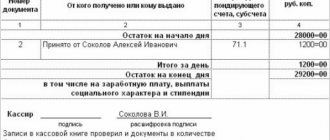
Before checking the availability of cash and other valuables in the cash register, the cashier draws up a final cash report. The report includes all receipts and expenditure documents available at the cash desk, which must comply with the standard unified forms of primary accounting documents.
If at the time of inventory there are open payrolls in the cash register (according to which wages are paid), the amounts paid on such slips are included in the inventory report and are equated to cash. The cashier calculates the amounts paid for each statement and at the end of the statement makes a note about the amount paid.
In practice, to disguise the facts of embezzlement of funds, various types of receipts are often used as accounting documents, which cannot serve as documentary evidence of the expenditure of funds, since they do not correspond to the unified form of an expense cash document and do not contain the signatures of the recipient of the money, the chief accountant and the head of the organization . The violation (embezzlement) is also evidenced by the fact that the documents (invoices, statements, etc.) attached to the cash receipts do not contain the authorization signature of the manager. Amounts for such documents or receipts are not included in the cash balance of the cash register and are considered as a shortage (clause 27 of the Procedure for conducting cash transactions in the Russian Federation).
The chairman of the inventory commission endorses all incoming and outgoing cash orders attached to the cashier’s report, indicating “before inventory on “____” (date).” This report, compiled at the time of inventory, serves the organization’s accounting department as the basis for determining the accounting balances of funds and documents.
The cashier must give a receipt stating that by the beginning of the inventory, all incoming and outgoing documents confirming the movement of funds and documents were submitted to the accounting department or transferred to the commission, and all cash received under his responsibility was capitalized, and the cash that was withdrawn was written off as an expense. This is necessary to prevent the cashier from making statements (after checking the cash register) about the presence of documents that were not included in the latest cash report. The cashier's report is checked to ensure that the accounting balance of funds in the cash register is correctly determined at the time of inventory. This accounting balance is reconciled with the entries in the cash book and in the order journal.
During the cash inventory process, the cash book is checked in the following main areas: the correctness of the cash book; arithmetic control of amounts for receipts and expenses and the correctness of counting the totals of the pages of the book, as well as transferring amounts of cash balances from one page to another; timeliness and documentary validity of entries in the cash book.
When taking inventory of the cash register, it is also necessary to control: compliance with the cash balance limit in the cash register; intended use of funds received from the bank for the purpose specified in the check; presence of facts of non-compliance with the date of the transaction and its reflection in the cash receipt order; validity of entries in cash orders; timely return to the bank of the balance of funds for unpaid wages; the correctness of the documentation of cash documents and their compliance with standard unified forms; presence of facts of the manager and chief accountant signing blank checks and filling them out independently when receiving money from the bank; existence of facts of storage of the checkbook outside the cash register; the legality of cash transactions performed within one transaction; correspondence of accounts to standard transactions for accounting cash transactions.
The actual availability of funds and documents at the cash desk is confirmed by their complete page-by-page recalculation.
When calculating the actual presence of banknotes and other valuables in the cash register, cash, securities and monetary documents are taken into account.
The cashier counts money and other valuables in the presence of members of the inventory commission.
Cash is recalculated for each banknote separately (as a rule, starting with the highest denomination bills and ending with the lowest denomination bills). If there is a significant number of banknotes, it is necessary to draw up an inventory indicating the denomination of the banknotes, their quantity and amount. The inventory is signed by all members of the inventory commission.
Checking the actual availability of securities forms and other forms of strict reporting documents is carried out by names, types, categories of forms (for example, by shares: registered and bearer, preferred and ordinary), taking into account the starting and ending numbers of certain forms, their series and nominal value. Monetary documents and strict reporting forms are accepted for accounting when the inventory result is identified in the amount of actual costs for their acquisition. The accounting balance of funds is determined according to the cash book (cashier's report). To establish the accounting balance of monetary documents and strict reporting forms, information from analytical and synthetic accounting as of the inventory date is used.
To organize the accounting of funds and documents, an active account 50 “Cash” is provided. This account has three subaccounts: 50/1 “Organizational cash register”, 50/2 “Operating cash register”, 50/3 “Cash documents”.
Strict reporting forms are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 006 “Strict reporting forms”.
By comparing actual and accounting balances, the result of the inventory is revealed: surplus or shortage.
According to the new Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n and in accordance with clause 77 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 28, 2000 No. 60n “On methodological recommendations on the procedure for forming indicators financial statements of the organization”, surplus funds in the cash register identified during inventory are subject to capitalization (accepted for accounting) and are reflected in non-operating income. In accounting, actual surpluses of funds and documents are accounted for by the following entry:
Debit 50 “Cash” of subaccount 1 “Cash of the organization” or 3 “Cash documents”
Credit 91 “Other income and expenses” subaccount 1 “Other income”.
If excess strict reporting document forms are identified, they are reflected in the debit of account 006 “Strict reporting forms” in a conditional (nominal) valuation.
If a shortage of funds is detected, entries are made in the debit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables.” For missing funds and documents, the debit of account 94 reflects their actual cost.
For the amount of shortage of funds and documents identified during the inventory, the following entry is made in accounting:
Debit 94
Credit 50 Subaccounts 1 or 3.
The amount of missing strict reporting forms is reflected in the credit of account 006 “Strict reporting forms”. If the shortage of funds and documents is due to the fault of the financially responsible person - the cashier, then its amount is written off in the accounting records by posting:
Debit 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” subaccount 2 “Settlements for compensation of material damage”
Credit 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables.”
Reimbursement of the amount of the shortfall is possible from the cashier’s salary, which is reflected in the following entry:
Debit 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”
Credit to account 73/2 “Calculations for compensation of material damage.”
If the shortage is reimbursed to the organization’s cash desk, then the following entry is made in the accounting records:
Debit 50/1 “Organization cash register”
Credit 73/2 “Calculations for compensation for material damage.”
In the absence of a specific culprit, the amount of cash shortage, previously reflected in the debit of account 94, is included in the non-operating expenses of the organization and written off by correspondence of the accounts:
Debit 91/2 “Other expenses”
Credit account 94
The results of the inventory of cash and documents at the cash desk are documented in the cash inventory act according to form No. INV-15, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 8 8, which provides the cashier’s explanations about the identified violations and the manager’s resolution on further decisions on inventory results. The cash register inventory report is drawn up in two copies (if there is a change of cashier - in triplicate), signed by the inventory commission and the financially responsible person and brought to the attention of the head of the organization. One copy of the act is transferred to the accounting department of the organization, and the second remains with the financially responsible person.
To reflect the results of the inventory of the actual availability of securities and forms of strict reporting documents and to identify quantitative discrepancies between them and the accounting data, an inventory list of securities and forms of strict reporting documents is compiled in form No. INV-16.
To provide the production program with appropriate material resources, enterprises create specialized warehouses for storing basic and auxiliary materials, fuel, spare parts and other materials. In addition to the central factory warehouses, in various structural divisions of the organization there may be storerooms that perform the functions of intermediate warehouses. Each warehouse is assigned a permanent number by order of the enterprise, which is subsequently indicated on all documents related to the operations of this warehouse. Warehouses must be provided with working scales, measuring instruments and measuring containers.
In warehouses (storerooms), material assets are placed in sections, and within them - in groups, types and sizes in stacks, boxes, containers, on racks, shelves, cells, pallets, which ensures their rapid acceptance, release and control over compliance with the actual Availability of established stock standards (limit).
Accounting for materials in a warehouse is carried out by the warehouse manager (storekeeper), who is the financially responsible person who is hired, as a rule, in agreement with the chief accountant of the enterprise. A standard agreement in the prescribed form on full individual financial responsibility is concluded with the storekeeper.
If the organization’s staffing table does not include the position of warehouse manager, then his duties can be assigned to any employee of the organization with his consent and with the mandatory conclusion of an agreement on individual liability. A storekeeper can be released from his position only after a complete inventory of inventory items and their transfer according to an act approved by the head of the enterprise.
For each item number of materials, the storekeeper fills out a material label and attaches it to the place where the materials are stored. The label indicates the name of the materials, item number, unit of measurement, price and limit of availability of materials.
Accounting for the movement and balances of materials is carried out in materials accounting cards. A separate card is opened for each item number, so accounting is called varietal accounting and is carried out only in kind.
The cards are opened in the accounting department or computer installation and the warehouse number, name of the material, brand, grade, profile, size, unit of measurement, item number, registration price and expiration date are written down. After this, the cards are transferred to the warehouse, and the storekeeper fills out the columns for receipt, consumption and balance of materials.
The storekeeper makes entries in the cards on the basis of primary documents (receipt orders, invoice requirements, etc.) on the day of the transactions. After each entry, the remaining materials are displayed. Thanks to this, the warehouse has operational information about the status of material stocks. If the balance of materials is higher or lower than the established stock norm, the warehouse manager is obliged to report this to the supply department.
Keeping records of materials is also allowed in the materials record book, which contains the same details as the materials record cards.
In the context of the functioning of automated control systems and automated warehousing, instead of accounting cards, systematically compiled machine diagrams-statements of movement and balances of materials are used. Based on primary documents, they reflect the same data as in warehouse accounting cards, but unlike them, machine reports are compiled only for warehouses and financially responsible persons. Machine diagrams are used to monitor the movement and condition of materials in the warehouse and operational production management.
Primary documents, after recording their data on accounting cards, are transferred to the accounting department; Limit and withdrawal cards are also transferred here as the limit is used, but no later than the 1st day of the next month. The delivery of documents is documented in a register, which indicates the name and numbers of the documents being submitted.
In workshops with storerooms, as well as in reporting organizations (points, departments, factories), financially responsible persons (heads of points and departments, plant foremen) draw up monthly reports on the balances and movement of materials in the sub-report and submit them to the accounting department. The reports contain information about the balance of materials at the beginning of the month, their receipt, consumption and balance at the end of the month. In the reports of factory foremen, along with the actual consumption of materials, their consumption according to the norm is indicated. The standard consumption of materials is calculated in the accounting department, where, in addition, the taxation of the report is carried out.
When using material reports, there is no need to draw up other documents for the consumption of materials and the accounting of materials in a sub-report is simplified, since reports of financially responsible persons are used as analytical accounting registers.
The following goods are subject to excise taxes: ethyl alcohol from all types of raw materials (except for cognac alcohol), alcohol-containing products with a volume fraction of ethyl alcohol more than 9%, alcoholic products, beer, tobacco products, jewelry, motor gasoline, diesel fuel, motor oils for diesel and (or) carburetor engines, cars and motorcycles with engine power over 112.5 kW (150 hp).
Excise mineral raw materials are oil and stable gas condensate, as well as natural gas.
Rates for certain types of excisable goods are given in Chapter 22 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Part Two).
For natural gas sold on the territory of Russia and member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States, the rate is set at 15% of the cost, for gas; sold outside the territory of Russia - 30% of the cost, for jewelry - 15% of the cost; and for other excisable goods - in rubles for the corresponding unit of measurement.
The procedure for recording excise tax payments is determined by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 12, 1996 No. 96.
To reflect business transactions related to excise taxes in accounting, account 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets”, subaccount “Excise taxes on paid material assets”, and account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, subaccount “Calculations for excise taxes” are used. "
In the debit of account 19 “Value added tax on purchased assets”, subaccount “Excise taxes on paid material assets”, the organization reflects the amounts of excise taxes paid to suppliers for excisable goods used as raw materials for the production of excisable goods, in correspondence with the credit of accounts 60, “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”.
As capitalized materials are written off for production and paid by suppliers, excise tax amounts are written off from the credit of account 19 to the debit of account 68.
For these purposes, separate accounting of excise taxes should be organized both for capitalized and paid acquired material assets, and for unrecorded and unpaid.
The amounts of excise taxes calculated on products sold are reflected in the debit of account 90 “Sales” and the credit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” (with the method of selling products “by shipment”) or the credit of account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” ( using the “on payment” method of selling products). As the products sold are paid for, the debt to the budget for excise taxes is recorded as an accounting entry in the debit of account 76 and the credit of account 68.
- Veshchunova N.L., Fomina L.F. Accounting and taxation. M., 2004.
- Kozlova E.P. Parashutin T.N., Babchenko N.V. Accounting, M., 2004.
- Kondrakov N.P. Accounting. M.: INFRA-M, 2004.
- Kuter M.I. Accounting: basic theory. M., 2003.
- Terekhov A.A. Audit. M., 2004.
Similar articles:
There are no similar articles.
What to do with surpluses and deficiencies in 2019
Carrying out any cash transactions requires compliance with certain auditing and accounting laws. If the audit reveals surpluses, they must be registered as income of the enterprise. This property will be income for both the tax and accounting departments of the company. In the accounting book for the tax office, it is necessary to include the market value of the surplus in the “Income” section.
Accounting accounts provide for the loss of funds, so there is account 94, which displays the company's shortfalls. The value of the lost property must be recorded in the statements, and it must be written off. To complete cash transactions, it is necessary to close the account; 94 the account can be closed in several situations:
- the persons responsible for the shortage have not been found;
- the culprits have been found.
Persons responsible for the loss of property have not been found
In the first option, the cost of the missing property must be included in the “production expenses” column. At the same time, adhere to the principle of natural decrease, which applies to both food and non-food products.
Food products are food products that are used in the process of company operations:
- cottage cheese;
- bread;
- sausage;
- salo.
Non-food products at an enterprise usually include:
- books;
- cups;
- interior items.
For different categories of goods in 2021, different coefficients are provided; they are compiled and regulated by statements and special ministries. The order of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of Russia approved those coefficients that are used in the field of mass trade and public catering. The order of the USSR Ministry of Trade clarifies the norms of coefficients for construction activities.
To complete the cash register, it will be necessary to find acts according to the standards for the property in which shortages were identified. If the size and norms of the shortage meet the standards, then you can safely post and close the account. If this methodology cannot be used (it is impossible to determine the cost or the cost exceeds the norm), then the lost property must be included in the “other expenses” section in 2021.
A tax audit does not provide for situations in which the shortage exceeds the established norms and standards, therefore it is impossible to display such losses in reporting to the inspectorate. The same situation applies to property whose value cannot be determined.
Those responsible for the loss of property have been found
Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that if those responsible for the loss of property are found, then they are the ones who compensate the damage to the enterprise in a strictly fixed reporting form. The procedure for determining the guilty person in 2021 is determined by state regulations, therefore, at any enterprise, users are assigned to each material value - people who are financially responsible for household items and work equipment.
Compensation for damages can come in two forms:
- the cost of the item in balance sheet terms;
- the value of an item in market terms.
If a decision was made to remove the shortfall in market value, then as a result of the transactions, a difference may arise - a premium. This amount must be taken into account with accounting requirements. You need to use account 98, which is called “Deferred income”. In the process of reducing debt, the cost will need to be taken into account in accordance with the “Other income” cash desk.
The book for the tax office in 2021 assumes compensation for all damages; the amount of debt must be recorded in cash procedures on the date of receipt of funds. The amount of damage may be periodically written off from the salary of the employee due to which the material assets were written off. In this case, the procedure for conducting cash transactions is taken into account on the date of withdrawal of part of the loss from the employee’s wages. Inventory and audit are carried out only in strictly state-fixed standards, which are not subject to change. Deviations from the procedure for conducting audit and cash transactions are criminally punishable; the state provides all forms of punishment for non-compliance with the norms and standards of financial reporting of an enterprise. All cash registers of the enterprise must be officially registered, audit and inventory in 2021 are carried out on all accounts of the company.
How often is a cash register inventory carried out?
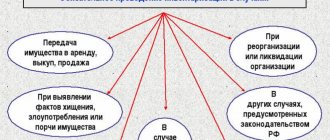
Beginning entrepreneurs are interested in the question of how often a cash register inventory is carried out. It can take place both planned and unscheduled. In the first case, the frequency of inspection is regulated by the company's accounting policy, which can be revised annually. In addition to the planned scenario, there are times when it is necessary to take an inventory of cash:
- if there is more or less money in the cash register than there should be;
- when the cashier (financially responsible person) changes;
- organizational changes, including liquidation of a legal entity;
- force majeure - when an organization suffers damage, for example, as a result of natural disasters;
- the end of the calendar year is also a reason to conduct a cash inventory - the check is carried out on the last working day of December.
The cloud-based trade management service MoySklad will help you quickly establish an organization’s cash register and warehouse accounting, as well as automate retail outlets with a minimum of investment.
Try MySklad