What is advertising
Advertising is information that is addressed to an indefinite circle of people and is aimed at attracting attention to the object of advertising, maintaining interest in it and promoting it on the market (Clause 1, Article 3 of the Law of March 13, 2006 No. 38-FZ).
Situation: what does “an indefinite circle of persons” mean in the definition of advertising?
An indefinite circle of people are those recipients of advertising who are unknown in advance.
As a general requirement, advertising information is addressed to an indefinite number of persons (Clause 1, Article 3 of Law No. 38-FZ of March 13, 2006). This means that advertising:
- cannot be created for specific consumers of a particular product;
- should not mention specific citizens or organizations whose perception it is aimed at.
This interpretation of the concept of “an indefinite circle of persons” is set out in the letter of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of Russia dated April 5, 2007 No. ATs/4624 (brought to the attention of the tax inspectorates by the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 25, 2007 No. ШТ-6-03/348).
The object of advertising can be:
- product;
- a means of individualizing an organization or product;
- manufacturer or seller of goods;
- results of intellectual activity;
- event.
Such a list is established by paragraph 2 of Article 3 of the Law of March 13, 2006 No. 38-FZ.
At the same time, the results of intellectual activity and means of individualization of the organization include:
- trademarks;
- service marks;
- brand names;
- industrial designs;
- inventions;
- computer programs, databases.
This conclusion follows from Article 1225 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The method, form and means of advertising distribution can be any (Clause 1, Article 3 of the Law of March 13, 2006 No. 38-FZ).
Examples of advertising include:
- commercial on television or radio;
- advertising events for film and video services;
- information about the company posted on someone else’s website (banner);
- advertisements in the media;
- information on billboards, vehicles, and stop points;
- advertising on stands, billboards in the metro (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 16, 2008 No. 03-03-06/1/588);
- goods or finished products that are displayed in display cases, in sample rooms and showrooms, at exhibitions, expositions, fairs;
- addressless mailing of catalogs of goods by mail (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 3, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/688);
- incentive lotteries not based on risk (letter of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated April 7, 2014 No. D09i-451. Brought to the attention of tax inspectorates by letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 21, 2014 No. ED-4-2/7598).
Situation: will the information on the sign be advertising?
Answer: no, it won't. Provided that the information on the sign is not related to a specific product.
The provisions of the law on advertising do not apply to information that must be communicated to the consumer by law (subparagraph 2, 5, paragraph 2, article 2 of the Law of March 13, 2006 No. 38-FZ).
For example, the seller of goods is required to indicate the following information on the sign:
- name of company;
- its location;
- operating mode.
This is stated in paragraph 1 of Article 9 of the Law of February 7, 1992 No. 2300-1.
In this case, the sign is not advertising, but informational in nature.
A similar point of view is reflected in the information letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 1998 No. 37, letter of the FAS Russia dated March 16, 2006 No. AK/3512.
If the information on a sign is related to a specific product or causes buyers to associate it with it, then such a sign will be advertising (see, for example, paragraph 2 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated October 8, 2012 No. 58, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated April 23, 2013 No. A56-46534/2012).
Situation: will the information on the product packaging be advertising?
Answer: no, it won't.
The provisions of the law on advertising do not apply to information that must be communicated to the consumer by law (subparagraph 2, 5, paragraph 2, article 2 of the Law of March 13, 2006 No. 38-FZ).
Legislation obliges the seller (performer) to provide the consumer with reliable information that is necessary for the correct selection of goods, work, or services. Such information includes information about the product, its manufacturer, consumer properties, rules and conditions for the effective and safe use of the items sold. This information may be indicated on the label, marking or packaging of the product (Article 10 of the Law of February 7, 1992 No. 2300-1). Therefore, the mandatory information on the packaging will not constitute advertising.
Situation: can sending SMS messages with information about products be considered advertising? This service is provided by the telecom operator.
Answer: yes, you can. Sending SMS messages with information about products is nothing more than advertising.
After all, advertising is information that, in particular, is addressed to an indefinite number of people. Moreover, advertising can be distributed in any way, in any form and using any means. This is stated in paragraph 1 of Article 3 of the Law of March 13, 2006 No. 38-FZ.
In general, advertising can be distributed by telephone only with the prior consent of the subscriber. The advertiser, that is, the telecom operator, must obtain such consent. It turns out that he knows the specific addressee of the message.
But the advertising organization in this case cannot know in advance which of the potential clients the operator will send messages to. In addition, sending a message to a specific subscriber number does not mean that it is possible to recognize the person using this number. This means that the circle of people to whom the operator will send SMS will not be determined for the advertiser.
In this case, the sending of SMS messages through a telecom operator has the right to be recognized as advertising by the advertising organization.
Similar conclusions follow from Article 18 of the Law of March 13, 2006 No. 38-FZ and indirectly confirmed in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 28, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/45479.
Value added tax
Tax consequences for VAT will vary depending on whether the company has entered into an agreement for advertising placement with a resident of the Russian Federation or with a non-resident of the Russian Federation.
The social network is a non-resident and does not have a permanent representative office in the Russian Federation. Foreign companies that provide services electronically are required to pay VAT (“Google tax”). This rule is in effect from January 1, 2021 (Article 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, introduced by Federal Law dated July 3, 2016 No. 244-FZ).
Services in electronic form are advertising on the Internet, including using computer programs and databases operating on the Internet, as well as the provision of advertising space on the Internet (clause 1 of Article 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The provision of services in electronic form is also recognized as:
- searching the Internet and providing the customer with information about potential buyers;
- ensuring (maintaining) a commercial or personal presence on the Internet, supporting electronic resources for website users;
- posting offers for the purchase or sale of goods (works, services) on the Internet.
If a Russian resident company purchases services in electronic form from a non-resident company, it acts as a tax agent for the payment of VAT (clause 1 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The company must transfer VAT to the budget simultaneously with the payment of funds to the non-resident counterparty (paragraph 2, paragraph 4, article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Together with the payment slip for the transfer of funds, you must provide the bank with an order to pay the tax, otherwise the bank will not accept it (paragraph 3, paragraph 4, article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/09/12 No. 03-07-08/33).
If the agreement with a foreign organization does not provide for the withholding of VAT when paying income to the seller, then the buyer will have to pay VAT at his own expense. After transferring VAT to the budget, the organization has the right to accept the tax as a deduction (clause 3 of Article 171, clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, it does not matter whether the Russian company paid the tax at its own expense or at the expense of a non-resident (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/04/10 No. 03-07-08/32).
The Russian Ministry of Finance explains that the income of a foreign person from the provision of services on the territory of the Russian Federation must be determined as the cost of such services, increased by VAT, payable by the tax agent. If a foreign entity does not include VAT payable to the budget in the cost of services, then the Russian organization independently determines the tax base. That is, it increases the cost of services by the amount of VAT and pays tax to the budget at its own expense.
The tax base is determined in a special manner if the contract does not provide for tax withholding (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 09/08/11 No. 03-07-08/276). The cost of advertising services specified in the contract must be increased by the amount of VAT at a rate of 10 or 18 percent. Based on this cost, it is necessary to determine the amount of VAT at the calculated rate. To transfer VAT at the expense of a non-resident, you can ask him to include a corresponding clause in the contract. A non-resident of the Russian Federation does not issue the buyer an invoice for the provision of advertising services, so it is better to issue it yourself. This will avoid claims regarding the acceptance of VAT for VAT deduction. In the document, you should highlight the VAT amount and make the note “Payment for a supplier who is a non-resident of the Russian Federation for advertising services.”
The invoice must be drawn up in two copies. The first of them should be recorded in the invoice journal on the day the funds are transferred to the foreign company and filed with the sales book. The second copy should be recorded in the journal of invoices received and filed with the purchase ledger.
The social network is a resident or has a permanent representative office of the Russian Federation. On the territory of the Russian Federation, the sale of services is recognized as subject to VAT (subclause 1, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Advertising services are not on the list of transactions not subject to taxation, therefore VAT charged by the counterparty for services for placing advertising information on social network pages is subject to deduction in the general manner (clause 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
________________________________________________________________________________________________
Is it profitable to enter into an agreement for advertising services on social networks on behalf of an individual?
In order for a company to advertise on social networks, it needs to collect a large amount of documents. Especially if the seller of services is a non-resident of the Russian Federation. Advertising on social networks is often hidden. Sometimes, companies entrust their employees to conduct relationships with contractors as individuals. The employee pays for advertising on the social network with a personal bank card. The company then reimburses the employee for these expenses by paying a bonus.
From a tax planning point of view, this option of advertising on a social network is unprofitable for a company. The taxpayer must fix the procedure for paying bonuses to employees in the wage regulations or other local regulations. This is necessary in order to take into account the bonus as part of labor costs (clause 2 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The award must be justified and documented (clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In the case of a refund, the employee will have to draw up an order each time, which must reflect the reasons for the bonus.
The company must withhold personal income tax at a rate of 13 percent on each premium. Incentive payments are also subject to insurance premiums. The general tariff for employers on contributions for 2017 is 30 percent. The tariff for contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for injuries is from 0.2 to 8.5 percent. Thus, costs for an advertising campaign on social networks will increase by more than 43 percent.
________________________________________________________________________________________________
Accounting
Advertising expenses are included in expenses for ordinary activities. This follows from paragraphs 5 and 7 of PBU 10/99. Such expenses must be documented (Part 1, Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). Since advertising is recognized as disseminated information, documentary confirmation requires not only the ordering of the advertisement itself, but also its actual distribution (Clause 1, Article 3 of Law No. 38-FZ of March 13, 2006).
Confirmation of advertising distribution, in particular, may be:
- reports from advertising distributors on the work done, for example, on the number of leaflets distributed;
- on-air certificates from television and radio stations;
- metro certificates regarding the provision of advertising services.
Similar conclusions are contained in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 6, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/467, dated June 22, 2012 No. 03-03-06/2/71.
Advertising costs should be reflected in account 44 “Sales expenses” (Instructions for the chart of accounts). It is advisable to open a corresponding “Advertising Expenses” subaccount for this account.
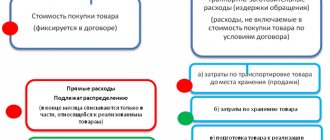
Classification of advertising costs
Advertising costs are the costs of distributing in any form, on any medium, information about a company, brand, product or service, which is intended for an unlimited number of consumers and is aimed at generating and maintaining interest in the object of advertising.
To draw up an optimal advertising budget, it is necessary to clearly determine how much money will be spent on what and how much profit it will bring to the company. In this case, you can use the indicator as a share of advertising costs. This is the ratio of the amount of advertising costs to the profit that it brought.
Advertising costs are a fairly significant cost item for any enterprise, but it is not possible to do without them.
Why do we need a standard for advertising expenses?
An organization can spend significant amounts on advertising; management decides which ones, taking into account the effectiveness of management decisions made in this regard and the financial capabilities of the organization. Since advertising is not only information, but also a business activity, it is reflected in appropriate accounting and is subject to taxation.
For this purpose, spending on advertising is usually divided into two types:
- normalized – those that are recognized as such only in accordance with certain criteria;
- non-standardized - unconditionally taken into account as advertising expenses, without limitation for tax purposes.
This division determines what amount of costs a company can take into account when determining the base for income tax: within limited limits or in full.
Advertising placed by a third party
When placing advertisements through third-party organizations, reflect the cost of their services on account 44. To do this, make the following entry:
Debit 44 subaccount “Advertising expenses” Credit 60
– the cost of advertising services is reflected based on the report of the advertising distributor.
If the advertising placement is advanced several months in advance, then consider the prepayment as an advance payment:
Debit 60 subaccount “Settlements for advances issued” Credit 51 (50)
– paid for advertising placement.
Based on the advertising distributor's report, recognize advertising expenses as current expenses, and offset the advance:
Debit 44 subaccount “Advertising expenses” Credit 60
– the cost of advertising placement by a third party is reflected;
Debit 60 Credit 60 subaccount “Settlements for advances issued”
– the advance payment issued to pay for advertising placement services is credited.
Fixed advertising budget
Before deciding how much money to allocate for advertising expenses, you need to analyze your competitors. To do this, select the closest companies similar to your company and see where they are advertised. Type their name on the Internet and you will see sites where they advertise.
At the initial stage, a certain amount of money is allocated for the promotion of goods and services, which the entrepreneur can afford.
In conditions of high competition and low purchasing power, entrepreneurs are forced to invest heavily in advertising their business.
The organization advertises independently
An organization can independently distribute advertising products. Purchased or manufactured promotional materials, for example, stationery with the organization’s logo, brochures, catalogs, should be reflected on account 10 at actual costs. Keep analytical records separately for each type of advertising product. To do this, open the “Advertising Materials” subaccount for account 10.
Reflect the receipt of promotional products as follows:
Debit 10 subaccount “Advertising materials” Credit 60;
– materials intended for distribution for advertising purposes have been taken into account.
After distributing the materials, charge their cost to account 44:
Debit 44 subaccount “Advertising expenses” Credit 10 subaccount “Advertising materials”
– the cost of advertising materials is written off based on the act of their expenditure.
When distributing (for example, at exhibitions, demonstrations) for advertising purposes goods that were originally intended to be sold, reflect their cost on account 41 subaccount “Goods handed over for advertising purposes.” And after distributing the samples, based on the report of the advertising distributor, write off the cost of the distributed goods as expenses - to the debit of account 44 of the “Advertising expenses” subaccount.
Similarly, reflect in accounting the finished products transferred for advertising purposes.
Why do you need to know RRR (share of advertising costs)
For a developing company, it is important to constantly monitor DRR. Due to the fact that there is no direct relationship between an increase in advertising spending and income received, a middle ground can be found.
For example, you spent 100 thousand on advertising new products. This gave 2 million in income. Next, you spend 200 thousand on the same advertising, but receive only 2.2 million in income.
We conclude that increasing advertising costs does not have a good effect; income has increased slightly.
It is more profitable to continue spending 100 thousand rubles, and spend the other 100 thousand rubles on advertising another product.
Accounting for advertising structures
The costs of creating or purchasing an advertising structure (for example, a stand, a billboard) form the initial cost of this structure. Depending on the period of use and the limit on the value of property recognized as an object of fixed assets established by the accounting policy, take into account the advertising design:
- on account 10 “Materials” as materials;
- on account 01 “Fixed assets” as an object of fixed assets (clause 5 of PBU 6/01).
Amounts recorded on account 10 can be written off at once at the time the advertising structure is put into operation:
Debit 44 subaccount “Advertising expenses” Credit 10 subaccount “Advertising materials”
– the costs of the advertising structure were written off.
Write off the cost of an advertising structure recognized as an object of fixed assets through depreciation:
Debit 44 subaccount “Advertising expenses” Credit 02
– depreciation has been accrued on the advertising structure.
Regardless of the type of advertising, write off the amounts accumulated per month on account 44 to the cost of sales as commercial expenses (clause 9 of PBU 10/99). To do this, make the following entry in accounting:
Debit 90-2 Credit 44 subaccount “Advertising expenses”
– advertising expenses are written off as cost of sales.
Recognition of expenses for basic assets
LLC expenses can be taken into account under the general taxation system in two ways.
The first of these is the accrual method, which in practice is often called “shipment-based” accounting. ( Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). This is the most common accounting option as it can be used by all organizations without restrictions.
With the accrual method, costs are taken into account in the period in which they are incurred, regardless of the transfer of money.
The second method is the cash method, or “on payment” accounting. On the contrary, it depends on the movement of money , because Expenses are recognized in the period in which actual payment is made.
However, the cash method is not available to all LLCs. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, only those companies that:
- over the past 4 quarters, they received revenue of no more than 1 million rubles. in each;
- do not belong to credit institutions;
- do not engage in hydrocarbon production;
- are not controlling persons of foreign companies.
The difference between the two cost recognition methods is easy to understand using the example of payroll accounting.
Example
The employee's salary accrued for October amounted to 50 thousand rubles. At the same time, an advance payment in the amount of 20 thousand rubles. paid in October, and the final payment (30 thousand rubles) - in November. When using the accrual method, all 50 thousand rubles. will be included in the company's expenses for October. And with the cash method in October, only 20 thousand rubles will be written off as expenses, and the remaining 30 thousand rubles. will be included in November costs.
Results
Advertising expenses can be taken into account in full when calculating profits if they are included in the list from clause 4 of Art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If there are no advertising costs incurred, they are taken into account in an amount equal to 1% of revenue.
In accounting, advertising costs are written off in full. If the amount of standardized costs is more than 1% of revenue, temporary differences arise between tax and accounting accounting.
Sources
- https://www.audit-it.ru/terms/taxation/reklamnye_raskhody.html
- https://www.audit-it.ru/terms/accounting/raskhody_na_reklamu.html
- https://assistentus.ru/buhuchet/normirovannye-rashody-na-reklamu/
- https://prof-bk.ru/skolko-deneg-tratit-na-reklamu/
- https://spravochnick.ru/reklama_i_pr/reklama/rashody_organizacii_na_reklamu/
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/nalog_na_pribyl/rashody_nalog_na_pribyl/nalog_na_pribyl_normiruemye_i_nenormiruemye_rashody_na_reklamu/
- https://www.klerk.ru/buh/articles/505030/
- https://e-kontur.ru/enquiry/52
- https://www.MoeDelo.org/club/article-knowledge/kakie-rashody-mozhno-uchest-pri-osno
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/nalog_na_pribyl/rashody_nalog_na_pribyl/poryadok_ucheta_rashodov_na_reklamu_v_buhgalterskom_uchete/
- https://buhland.ru/uchet-rasxodov-na-reklamu/
- https://buh-aktiv.ru/rashody-na-reklamu-raspoznat-i-uchest/
Distribution of promotional products and VAT
Organizations resorting to measures to promote their goods, works or services on the market in the format of distributing advertising materials, it is important to remember one point. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in letters dated October 23, 2014 No. 03-07-11/53626, dated July 16, 2012 No. 03-07-07/64 draws attention to: only gratuitous delivery of brochures and catalogs for advertising purposes is exempt from VAT, regardless of their cost acquisitions. For all other products transferred for advertising purposes that have a material form, be it mugs, calendars with a company logo, etc., the rule applies: if the cost is 1 pc. handouts exceed 100 rubles; in case of transfer, VAT must be charged in accordance with the generally established procedure.
IMPORTANT! Since 2015, when calculating VAT for payment, you can take into account the full amount of input VAT on advertising expenses, without taking into account whether these expenses are regulated or not.
Building a system of advertising expenses
At the initial stage, you need to decide which system you will use. You can select one or more systems that are most common.
Product platforms of large aggregators (there are many of them, we will list only a few of them):
- Yandex.Market - audience of 20 million people;
- Tiu.ru - audience of 10 million people;
- Avito.ru - audience of 25 million people;
- wikimart.ru;
- goods.ru;
- torg.mail.ru
You can register on sites and place your products on a small budget.
It is important to always know how much and where you spend money in order to understand what profit it brings.
Analyze and change platforms to understand which one worked better and brought you more sales.