Minimum wage and sick leave
As for sick leave, a new rule has appeared in 2021 - for a full month, sick leave cannot be less than the minimum wage. This improved the situation of those workers who, for example, had a short insurance period (less than 8 years). Of course, you also need to take into account the rate.
Example:
An employee works at a rate of 0.5. Takes sick leave in 2021 in January from the 11th to the 15th, billing period from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2021. During this time, his earnings amounted to 300,000 rubles. The employee works in an area where the regional coefficient of 15% applies.
We calculate the average earnings:
300 000 / 730 = 410,96.
The minimum wage in 2021 is 12792. We calculate the average daily earnings from the minimum wage:
12792 / 31 = 412,65
It is already obvious that the minimum wage calculation is higher than the average of actual earnings. So we will calculate the benefit from the minimum wage:
412.65 * 0.5 (bet) = 206.33; 206.33 * 5 (sick leave days) = 1031.65; 1031.65 * 1.15 (regional coefficient) = 1186.40
Rice. 1 Example of Calculation from the BukhSoft program
You can right now order free access to the BukhSoft accounting program and index your salary taking into account changes.
Order access to BukhSoft
The minimum wage can also be set in each region. It is determined by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation by regional agreements on the minimum wage. As a rule, the regional minimum wage is equal to or greater than the federal minimum wage. If the region uses regional coefficients, then it must be taken into account that they are not included in the minimum wage and must be calculated in excess of its size.
For example: an employee works in an area equated to the regions of the Far North in a region where a regional coefficient of 15% applies, which means his minimum salary per month must be at least 12792 15% = 14710.80.
Please note that if your sick leave, for example, began in December 2021 and continued in January 2021, then to compare benefits in each individual month you will have to use a different minimum wage - in December it was 12,130, and in January it was already 12,792 rubles.
Note that if an employee was sick, then his earnings in a month not fully worked may be less than the minimum wage. Let's take the data from the previous example about sick leave. The employee was sick from January 11 to January 15, 2021 (5 calendar days, all of them were working days). According to the production calendar, he has 15 working days in January. Let his salary be 18,000 rubles. When calculating salaries for January, the accountant calculated the salary:
18000 / 15 * 5 = 12000 - this is how much employees’ salaries were accrued.
At the same time, there is no violation, because he worked for less than a month.
Similarly, you need to consider the months in which the employee took leave, paid or without pay, absenteeism, etc.
Order access to the BukhSoft accounting program for 2 weeks. All accounting in one program - assistance on accounting, legal and personnel issues.
Order access
Salary is less than the minimum wage
Wages may be less than the minimum wage if the employee works part-time or part-time.
Rostrud also explained this. Officials note that in case of part-time work, remuneration should not be lower than the minimum wage, calculated in proportion to the time worked - depending on output or on other conditions determined by the employment contract (Article 285 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, if an employee has a part-time working day, or if the time actually worked is less than the established norm, then his work is paid in proportion to the time worked. That is, the amount of payment may be lower than the minimum wage. This will not be a violation.
The Federal Tax Service controls the amount of wages
The minimum wage is established, on the one hand, to guarantee workers protection from unreasonable understatement of wages, and on the other hand, to avoid concealment of taxable income and non-payment of personal income tax.
In order to control the amount of remuneration of workers, the Federal Tax Service of Russia has developed control ratios for the calculation in form 6-NDFL (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 17, 2021 No. BS-4-11 / [email protected] ) and the calculation of insurance premiums ( letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 02/07/2020 No. BS-4-11/ [email protected] ).
Control ratios compare the average wage in the calculation provided by the employer with the minimum wage, as well as with the average wage in the region for the relevant industry (according to Rosstat).
If the employer indicates a low salary for employees in the 6-NDFL calculation or in the calculation of insurance contributions, the tax authority sends a request for explanations (clause 3 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The explanations and documents provided by the employer are reviewed by the tax authority. If explanations are not provided, or if, after considering them, the tax authority has reason to assume that the tax base is understated, other tax control measures are determined, including a call to the interdepartmental commission for the legalization of the tax base and the base for insurance premiums in accordance with the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated dated July 25, 2017 No. ED-4-15/ [email protected]
As part of information interaction, information about employers paying low wages to employees is sent by tax authorities to the labor inspectorate and prosecutorial authorities to take measures in accordance with the powers granted.
Thus, the employer can be checked not only at the request of the offended employee, but also after submitting HR reports . A legislative increase in the minimum wage should be a signal to every employer to check personnel documents and employment contracts for compliance with the current level of the minimum wage. making changes to employee documentation, which should undoubtedly affect the actual increase in cash payments to employees.
What is the minimum wage in 2021?
Responsibility for wages below the minimum wage can indeed be extremely burdensome for the employer. Moreover, the risks of underestimating labor compensation for a company may increase given the increase in the minimum wage.
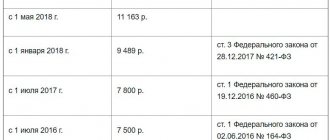
From January 1, 2018, the minimum wage established by law is 9,489 rubles. From May 1, it increased to 11,163 rubles , that is, it was equal to the cost of living in 2021. Subsequently, the minimum wage will be indexed taking into account changes in the dynamics of the cost of living. If the employer is located in a region with difficult climatic conditions, then the minimum wage is increased using the northern coefficient.
Let us note that initially the authorities planned to equate the minimum wage to the subsistence level only in 2019. But the President, during one of his public speeches, said that such an equalization would be carried out from May 1, 2021.
The authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have the right to establish regional minimum wages. The main requirement for them is that they should not be less than the federal one. At the same time, employers have the right to refuse to calculate wages according to the regional minimum wage by writing a statement about this to the regional branch of Rostrud. This must be done within 30 days after the publication of the regional regulatory act establishing the minimum wage in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation. Otherwise, in any case, you will have to calculate your salary taking into account the regional minimum wage.
But the employer, most likely, will not receive any special preferences from such a waiver, since the regions accept the minimum wage, which differs from the federal one, as a rule, only if there are grounds for its increase, taking into account regional climatic characteristics. For example, taking into account the same northern coefficient. And if the employer refuses the regional minimum wage, then, taking into account the federal one, he will have to pay employees a salary of no less than the minimum wage, increased by the coefficient.
As a result, Russian employers may be forced to significantly revise their payroll policies due to increases in the minimum wage. Let us consider in more detail what obligations they are required to fulfill as part of the calculation of compensation for labor, and what penalties are established for failure to fulfill such obligations.
The Criminal Code provides for the following types of punishment:
- Monetary fine: 100,000 - 500,000 rubles in ordinary cases, 200,000 -500,000 in case of serious consequences;
- A fine in the amount of the convicted person’s income for a period of up to 3 years in ordinary cases, or from 1 to 3 years in cases involving grave consequences;
- Forced labor for up to three years (can be applied with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions);
- Restriction of freedom for a period of up to 3 years or for a period of 2 to 5 years (with grave consequences), can also be applied in conjunction with deprivation of the right to work in certain positions.
The guilty person can avoid criminal liability if, within two months from the date of initiation of the criminal case, he pays wages in the required amount and compensates employees for penalties, moral compensation and other payments provided for by law (provided that this offense was committed by him for the first time).
Paying wages less than the minimum wage entails administrative or criminal liability. It is important to understand that both types of liability can apply simultaneously.
What is the relationship between the minimum wage and the employer’s obligations?
An employer, having concluded an employment contract with an employee, does not have the right to pay him a salary below the minimum wage. At the same time, an employee may receive less in person, taking into account personal income tax and other deductions (for example, according to writs of execution). If an employee receives any tax deduction - for example, property tax, then personal income tax is not calculated within the established limits. In this case, the salary is paid at least in the amount of the minimum wage established by law.
Note that the employee’s salary does not necessarily have to correspond to the minimum wage. Compensation for labor no less than the legal minimum can be made up of other components - not counting salary. For example:
- bonus payments;
- compensation payments;
- bonuses for complexity and results of work.
But regardless of the results of work, the total salary should not be less than the minimum wage, even if the salary for the position is much lower than the minimum wage.
Note that the minimum salary established by law is paid only if a person has an employment contract under which he works a standard 8 hours a day and 40 hours a week. If he works, for example, part-time, then his salary is paid proportionally, and its minimum value should not be lower than 50% of the minimum wage.
The same can be said about working at one and a half times the rate - it should be at least 1.5 times the minimum wage.
A fairly similar principle for calculating wages applies if the employment contract stipulates piecework wages. With it, wages depend not on the amount of working time, but on the volume of production and the achievement of some production indicator. As a rule, the target volume of such indicators is fixed in the production rate, and it, in turn, is reflected in the employment contract or annexes to it.
When such a norm is met, the full salary is accrued - not lower than the minimum wage; if it is not met - in proportion to production. That is, perhaps below the minimum wage. And during processing - higher.
The payroll system at an enterprise can be mixed, in which both working time standards and production standards are taken into account. In this case, calculating workers' compensation may be more complex. But the payout, one way or another, should not be less than the minimum wage, despite the complexity of its calculation.
Otherwise, the labor inspectorate will impose hefty fines on the employer.
Employee salaries
The monthly salary of an employee under an employment contract must not be lower than the minimum wage. Depending on where you live, focus on the federal or regional minimum wage:
- The federal minimum wage is 11,163 rubles from May 1.
- Some regions set their own minimum wage - higher than the federal minimum wage. In that case, use it.
Here are examples of several regions with their own minimum wage:
- Moscow - 18,742 rubles,
- Moscow region - 14,200 rubles,
- St. Petersburg - 17 thousand rubles,
- Leningrad region - 11,400 rubles.
In the article we wrote about the minimum wage in several more regions.
What if the employee is hired under a GPC agreement?
Then you can pay him any amount you agree on. The size of the minimum wage does not affect this.
Who monitors the salary?
Labor inspection and tax. An employee can contact the labor inspectorate and complain about a low salary. This is a reason for an unscheduled inspection. There are also scheduled inspections: the list of those who will be inspected this year is on the Rostrud website in the “For Employers” section “Information and Services”.
The tax office receives reports from you on personal income tax and insurance contributions, so it knows the size of employees’ salaries. If he notices that the salary is below the minimum wage, he will ask for clarification.
Penalty for wages below the minimum wage:
- from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles for individual entrepreneurs,
- from 30 to 50 thousand rubles for LLC.
When can you pay less than the minimum wage?
- The employee works part time. For example, for a part-time job—that’s 4 hours a day—you can pay half the minimum wage.
- The salary before personal income tax is higher than the minimum wage, but the employee receives less. For example, if you indicate a salary of 12,000 rubles in the employment contract, the employee will receive 10,440 rubles, the rest of the amount is personal income tax. Since the salary under the contract is higher than the minimum wage, this is legal.
Are regional coefficients included in the minimum wage?
Regional coefficient is a salary supplement for workers in the Far North and equivalent areas.
The regional coefficient is calculated on top of the salary, which must not be lower than the minimum wage.
For example, in the Sverdlovsk region the Ural coefficient is charged - 15%. That is, the minimum salary of an employee should be: 11,163 rubles + 15% = 12,838 rubles.
How to increase your salary
If you pay employees less than 11,163 rubles or the minimum wage in your region, increase it from May 1.
- Compose an order in any form.
- Make changes to your staffing schedule.
- Sign an additional agreement to the employment contract with the employee.
What will happen to the employer for paying wages below the minimum wage?
When paying wages below the minimum wage, the employer as a legal entity may be fined:
- for the first violation - in the amount of 30-50 thousand rubles;
- in case of repeated violation - in the amount of 50-70 thousand rubles.
The fine for wages below the minimum wage is calculated per employee. That is, if the salary was underestimated, relatively speaking, for the entire staff of an organization of 100 people, then the sanctions, obviously, can reach millions of rubles.
At the same time, certain sanctions may be applied to the director, namely:
- a fine of 1000-5000 rubles for the first violation, 10-20 thousand rubles for a repeated violation;
- deprivation of the right to hold office for 1-3 years.
Please note that the same sanctions apply to an employer with the status of an individual entrepreneur as to a director.