For days on a business trip, the employee is paid the average salary and daily allowance for each calendar day of the business trip. Many expected that from January 1, 2021, the daily allowance would be abolished. But that did not happen.
According to paragraph 3, part 1, article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if an employee is sent on a business trip, the employer is obliged to reimburse him for additional expenses associated with living outside his place of permanent residence, that is, daily allowances. Accordingly, from January 1, 2021, employers, as before, are required to pay daily allowances.
| Attention! The organization determines the amount of daily allowance independently, fixing its amount in the local regulations of the organization, for example, in Regulations on business trips. There are maximum amounts of daily allowance that are not subject to personal income tax (paragraph 12, paragraph 3, article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In particular, daily allowance in Russia is 700 rubles , abroad - 2500 rubles. That is, if an organization sets daily allowances in Russia in the amount of 1000 rubles, then from 300 rubles (1000 - 700) the employer should withhold personal income tax |
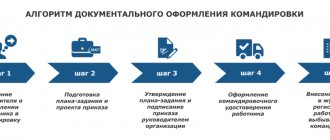
Procedure for paying daily allowances to employees
Daily allowances are reimbursed to the employee for each day while he is on a business trip. Weekends and non-working holidays, as well as days on the road, including forced stops along the way, are also paid. For example, an employee went on a business trip on Sunday and returned the following week on Saturday. Per diems for Saturday and Sunday are paid.
Daily allowances for one-day business trips within Russia are not paid (but the employer has the right to provide compensation in the local regulations of the organization in lieu of daily allowances for such trips). Read more about daily allowances for one-day business trips later in this article.
Travel expenses: changes in accounting for exchange rate differences
In accordance with the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation, the definition of “per diem” includes several main groups of costs, in particular:
| Accommodation in another locality | What is directly related to renting housing? |
| Eating in canteens or purchasing groceries | In shops and supermarkets |
| Fare payment | In public transport |
| Organizing a business lunch directly with partners | Including attending various events planned to increase the level of mutual understanding and the general prevailing situation |
| Other costs | Which are accompanied by the performance of the official duties assigned to the employee |
Often in practice there are awkward situations in which it is difficult to figure out what exactly can be considered a daily requirement and what is unnecessary.
The given list of expenses, according to the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, is closed. Based on this, any employee expenses not related to renting housing, travel to and from the business trip, and exceeding the amount of daily payments established by the agreement are not reimbursed.
For example, the employer is not obliged to pay for the employee’s trips by taxi or other transport to the place of business travel, the employee’s visits to entertainment venues, or telephone conversations not related to work activities. However, the law does not prohibit the employer from paying any expenses of an employee on a business trip if an agreement has been concluded to this effect.
The duration of a business trip can be from one day until the employee completes the assigned task. Existing regulatory documents today do not in any way limit the duration of a business trip. In this case, the first day of a business trip is the day of departure outside the employer’s territory until 00.00 local time. The last day of a business trip is the day of return before 00.00 local time. That is, if an employee left on November 5 at 11 p.m. and returned on November 7 at one in the morning, then the duration of the business trip is assumed to be 3 days.
- Loan revaluation and income tax 1,080
- Transactions on a foreign currency account in the bank statement and in the organization’s accounting: there are 2 differences 1,690
- Exchange differences: various options in December 2020 4,603
- Exchange differences in tax accounting 1.478
When revaluing an advance payment issued to a posted employee, exchange rate differences arise. The article describes what changes have occurred in their accounting in connection with the adoption of Decree No. 504*.
______________
* Decree of the President of the Republic of Belarus dated December 31, 2019 No. 504 “On exchange rate differences” (hereinafter referred to as Decree No. 504).
When do exchange differences arise when issuing an advance to a posted employee?
The employer is obliged to give the posted worker an advance and (or) ensure the availability of funds in the account to which the bank payment card is issued, in Belarusian rubles and (or) foreign currency, as well as reimburse the following expenses (part one, clause 5 of Regulation No. 176*) :
- on travel to and from the business trip;
- for renting residential premises;
- for accommodation outside the place of residence (daily allowance);
- other expenses incurred by a posted employee with the permission or knowledge of the employer.
______________
* Regulations on the procedure and amount of reimbursement of expenses, guarantees and compensation for business trips, approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated March 19, 2019 No. 176 (as amended on September 4, 2019; hereinafter referred to as Regulation No. 176).
The basis for issuing an advance is an order (instruction) of the employer (clause 4 of Regulation No. 176).
For reference: the legislation does not define the period for issuing an advance . The employer must do this within a reasonable time frame, allowing the employee to make the necessary expenses before the start of the business trip.
An employee returning from a business trip must report on the amounts of money spent. To do this, he draws up an advance report with attached documents confirming expenses (clauses 90 and 91 of Instruction No. 117*).
______________
* Instructions on the procedures for conducting cash transactions and cash settlements, approved by Resolution of the Board of the National Bank of the Republic of Belarus dated March 19, 2019 No. 117, which entered into force on June 1, 2019 (hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 117).
For reference: the deadline for submitting an advance report to the accounting department is 15 working days from the date of return from a business trip, excluding the day of arrival .
Money not spent on a business trip, as well as money spent but not agreed upon by the employer for reimbursement, must be returned by the employee no later than 15 working days from the date of return from the business trip, excluding the day of arrival (clause 90 of Instruction No. 117).
The employee deposits the unspent amount of money into the organization's cash desk or into its current account if the advance was given to the employee in cash or by transfer to a personal card or was withdrawn by him from a corporate card. When making non-cash payments using a corporate card, the amount of money not spent by the employee remains in the employer’s account (parts one – three, clause 93 of Instruction No. 117).
For reference: when an employee uses his own funds (an overexpenditure on travel expenses occurs), the employer is obliged to no later than 30 calendar days from the date of submission of the advance report (clause 7 of Regulation No. 176).
Daily allowance in 2021 in Russia and abroad
The company has the right to decide for itself how much to pay employees per business trip day (Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The amount of daily allowance for business trips must be fixed in the internal documents of the organization, for example, in the Regulations on Business Travel .
Accountants know about 700 and 2,500 rubles - if the daily allowance does not exceed these amounts, then you will not have to pay personal income tax on these amounts. Therefore, for convenience, some companies introduce daily allowance amounts of 700 and 2,500 rubles, so as not to withhold personal income tax from these amounts. But this does not mean at all that an organization can set the daily allowance for employees at 700 and 2500 rubles and not a ruble more or less. You can, for example, set a daily allowance of at least 4,000 rubles for each day of a business trip in Russia, but then you will have to withhold personal income tax from 3,300 rubles (4,000 rubles – 700 rubles = 3,300 rubles)
Please note that the organization determines the amount of daily allowance independently, fixing its amount in the local regulations of the organization, for example, in the Regulations on Business Travel. There are maximum amounts of daily allowance that are not subject to personal income tax (paragraph 12, paragraph 3, article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In particular, the daily allowance in Russia is 700 rubles, abroad - 2500 rubles. That is, if an organization sets daily allowances in Russia in the amount of 1000 rubles, then from 300 rubles (1000 - 700) the employer should withhold personal income tax
| As a general rule, daily allowances paid to an employee are not subject to personal income tax if their amount does not exceed: 700 rubles — for each day of a business trip in Russia; 2,500 rubles - for each day when traveling abroad. Conclusion: as such, there is no daily allowance limit for commercial organizations. There are only amounts that are not subject to personal income tax (700 and 2500 rubles). So how much per diem should you pay? — decide for your organization yourself (fix the decision in internal documents). |
Insurance premiums
When calculating contributions for compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance and contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases, daily allowances are not taken into account if they:
- provided for by current legislation;
- are paid within the limits established in accordance with current legislation.
The organization’s obligation to pay daily allowances is provided for in Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The same article obliges employers to establish the procedure and amount (standards) of daily allowances in a collective agreement or other internal documents.
Thus, daily allowances in the amount provided for by internal documents are exempt from insurance premiums. Contributions must be calculated on daily allowances that exceed the established norms.
An exception to this rule is payments to crew members of foreign ships in lieu of daily allowances. Insurance premiums are charged on such amounts, regardless of whether they are provided for by the internal documents of the organization or not (sub-clause “and” clause 2, part 1, part 2, article 9 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ, sub-clause 2 clause 1 article 20.2 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ).
How to calculate business trip days for which you need to pay daily allowance
How to determine the number of days for which daily allowance must be paid? For example, if an employee goes on a business trip in a personal and company car, then you can count the days using a memo. The employee must submit such a note when he returns from a business trip, along with documents confirming the use of transport to travel to the place of business trip and back (waybill (for example, in form No. 3), invoices, receipts, cash receipts, other documents confirming the route transport). In other cases, determine the number of days for which daily allowance must be paid using travel documents:
Necessary documents for payment for a work trip
As soon as the business trip ends, the employee who was away must provide management with all receipts confirming the fact of spending government money.
If documentary evidence of the waste invested in the trip is made public, then all amounts will be reimbursed in full. It is advisable to keep all receipts in order to avoid additional questions about where this or that amount was spent.
The main documents that are required after the official “travel” include:
- a round-trip ticket, where the cost is clearly stated;
- daily expenses receipts;
- cost of travel accommodation;
- receipts from all public vehicles;
If during a business trip an employee makes personal expenses and also goes beyond the daily limit established by the enterprise, then such expenses are not paid by the management.
One day business trip
By law, there is no minimum travel period established. A trip on behalf of the employer can be a one-day trip. We arrange such a trip as a multi-day business trip (we issue an order, put the appropriate mark on the time sheet: “K” or “06”).
Afterwards the employee reports for the trip. The employer reimburses him for expenses, for example, travel expenses, as well as other agreed amounts. Is there a daily allowance? By law, daily allowances are not paid for “mini-trips” around Russia. Leaving an employee completely without money, even on a one-day business trip, is not the best idea, even if it is legal. How can you get out of the situation?
Payments for one-day business trips instead of daily allowances
The employer, at its own decision, can pay the employee a certain amount instead of daily allowance.
| Conclusion: daily allowance for one-day business trips in 2016: abroad - in the amount of 50% of the daily allowance for business trips abroadinstalled in your company's local documents; in Russia - in general, they are not paid, but you can set the payment to the employee yourself. |
Personal income tax on daily allowances for one-day business trips
Previously, the situation with the taxation of daily allowances and reimbursement of other expenses for one-day business trips was controversial. Today we can say with confidence that the situation has stabilized and the general trend is as follows: payments for one-day business trips are not subject to personal income tax. However, the positions of different departments differ:
Opinion of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation: compensation for documented expenses associated with a one-day business trip (for example, food expenses) may not be subject to personal income tax in full. If there is nothing to support such expenses, then they are exempt from tax up to 700 rubles. for domestic Russian business trips and 2500 rubles. during a one-day business trip abroad (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 1, 2013 No. 03-04-07/6189).
Opinion of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation: money paid to an employee (called daily allowance) is not such by virtue of the definition contained in labor legislation, however, based on its focus and economic content, it can be recognized as reimbursement of other expenses associated with a business trip, made with the permission or knowledge of the employer , and therefore are not income (economic benefit) of an employee subject to personal income tax (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated September 11, 2012 No. 4357/12).
Registration of a business trip: documents, expenses, postings in 2021
The amount of daily allowance for business trips in budgetary institutions in the Russian Federation in 2020 is calculated taking into account some features. They are described in detail in the norms of Russian legislation. Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
(Saint Petersburg)
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
It is extremely important to know exactly how much is charged in the case of daily travel expenses in 2021 and what is specified in Russian legislation about this.
A considerable number of hired employees are often forced to go on business trips not only within the country but also abroad.
Moreover, without exception, all costs that are directly related to such trips are forced to be borne by the employer.
To be able to eliminate the possibility of misunderstandings, such employees must know the rules of the law.
A business trip means a trip by a company worker, which is considered a forced measure at the request of the employer and only for work purposes - according to Article 166 of the Labor Code of Russia.
It must be remembered that the absence of a worker is not considered a business trip if he returned from it on the day of departure. From this we can talk about the presence of certain time periods.
What exactly is meant by daily allowance and travel allowance? Many citizens are confident that these concepts are no different from each other.
Of course, a worker who has been sent on a business trip must receive funds for accommodation, travel and other related expenses.
At the same time, the employer provides the worker not only with travel allowances, but also with daily allowances.
They mean funds that are aimed at additional needs that are not directly related to:
- accommodation - payment for housing;
- payment for travel;
- and other expenses.
After an employee returns from a business trip, he must compile a report. Documentation that can verify the use of accountable funds received must be attached.
These in 2021 are generally considered to include:
| Documentary confirmation of rental premises | In particular, you can provide a receipt, a hotel invoice, or a signed rental agreement. In any case, the document must indicate the number of days of stay and the cost of living per day |
| Documentary confirmation of payment for travel to the place of performance of the official task and back | These include tickets, boarding passes, receipts for bedding on the train, and so on. |
| Documentary evidence of the use of taxi services | Tickets, properly prepared receipts, checks, etc. |
| A memo duly prepared by the hired worker with a check attached. | If a personal vehicle was involved |
| Generated memo | Regarding the fact that the worker is not able to provide documentary evidence of the expenditure of funds, for example, due to loss |
| Documentary evidence of other expenses | For example, a receipt for the use of a storage locker, payment for telephone services, etc. |
At the same time, you need to remember that daily allowances for business trips do not need to be documented in 2020.
Issues directly related to the process of calculating travel allowances are explained in detail in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 729.
This regulatory document also establishes a fixed amount of transfers directly related to costs for traveling within Russia. As of 2021, for employees of budgetary institutions the amount is 100 rubles.
In order to calculate daily payments in the case of business trips abroad, you should refer to the norms of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 812.
The relevant Regulations to the specified regulatory act reflect the procedure for transferring funds on an individual basis, depending on the foreign state.
Report on daily allowance for a business trip
Upon returning from a business trip, the employee must submit to the employer within three working days:
- an advance report on the amounts spent in connection with the business trip;
- final payment for the cash advance issued to him before leaving for a business trip for travel expenses (clause 26 of the Business Travel Regulations No. 749).
| Important: as part of the advance document, the employee is not required to report either daily allowances within Russia, or daily allowances outside the Russian Federation, or for one-day or any other business trips. There are no supporting documents for daily allowance. The employer pays a daily allowance of x rubles, the employee spends it at his own discretion. |
Travel expenses under the simplified tax system: a large accountant's guide
The employer compensates the travel costs of a posted employee in the following cases:
- travel to and from the place of business;
- movement between different settlements within a business trip;
- movement to the place of business from the airport, station, pier and back if they are located outside the populated area.
An employee sent on a business trip can use any type of transport except taxi. But the institution may establish restrictions or recommendations in local regulations on the choice of transport.
Renting housing includes renting a home or hotel room. Housing rental expenses are reimbursed to the employee for each day of business travel (including non-working holidays and weekends), as well as in case of temporary disability. Days when the employee was in hospital treatment are not subject to compensation (clause 25 of Resolution No. 749). If free housing is provided, rental costs will not be reimbursed.
Upon returning from a business trip, the employee must account for the advance of funds received or receive compensation for expenses incurred. An advance report (form according to OKUD 0504505) serves as such a document. The report is provided within three days after returning from a business trip. The period for provision can also be the day on which the advance was issued.
The employee must also provide the following documents:
- for travel - supporting documents are tickets, checks, receipts, electronic receipts;
- for rental of residential premises - a receipt from a hotel or a rental agreement for residential premises;
- for other expenses - checks, sales receipts, receipts, invoices and other documents;
- daily allowance - no special document is required; you can confirm the number of days using tickets.
Travel expenses must be reflected in the following accounting accounts (Instruction 157n):
- daily allowances - subaccount 0 208 12 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for other non-social payments to personnel in cash”;
- compensation for the use of personal transport on a business trip - subaccount 0 208 22 00 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment for transport services”;
- accommodation and travel - subaccount 0 208 26 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment for other works and services.”
Account 0 208 00 000 “Settlements with accountable persons” is used with the indication of KOSGU (clause 21 of Instruction No. 157n, clauses 13.6, 14.6 Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 29, 2021 N 209n)
- 567 “Increase in other receivables for settlements with individuals”;
- 667 “Reduction of other receivables for settlements with individuals.”
To reflect in the accounting records of a state institution, the following subarticles of KOSGU are applied:
- 212 (“Other non-social payments to staff in cash”) – daily allowance;
- 222 (“Transport services”) – compensation for the use of personal transport;
- 226 (“Other work, services”) – payment for travel, rental of living quarters, and other expenses.