Issues discussed in the material:
- In what cases should you close an LLC with debts?
- What are the ways to close an LLC with debts?
- What is bankruptcy procedure?
- How much does it cost to close an LLC with debts?
As the organization operates, owners need to make strategic financial decisions from time to time. In some cases, termination or liquidation may be the best option for a company. But how can you close an LLC with debts if your debt to creditors is increasing?
When is it better to close an LLC with debts rather than save it?
A limited liability company (LLC) is a type of commercial organization established by a group of persons, each of whom has their own share in the authorized capital. The responsibilities and obligations of the founders at closing will depend on their participation in the financial activities of the organization.
The company's management is its founders. The annulment process cannot begin without holding a general meeting of founders. Documentation of the minutes of the meeting is a mandatory condition, only after which the adopted agreements come into force. The final decision to close the company is made by the liquidation commission, which is in charge of this process.
Liquidation of an LLC is considered to be the complete cessation of its activities when all business processes of the organization are stopped. However, it is impossible to transfer rights and obligations to third parties.
What is the liquidation of a legal entity with debt to the budget, lenders or other persons? For an organization, this is not only the end of its activities, but also the cessation of the existence of the company, as evidenced by the corresponding marks in the unified state register. Once the company is liquidated, all claims against the legal entity become invalid. It is for this reason that company owners often liquidate LLCs, which allows them to get out of the current unpleasant situation while avoiding negative consequences.
It is possible to terminate the existence of an organization both by order of authorized government services and by the initiative of the owners. In cases where a company cannot fulfill its financial obligations to anyone, it is advisable to initiate bankruptcy proceedings.
Depending on the size of the debt, credit history, the need to prepare additional documents and legal support of the process, the cost and timing of liquidation will be different.
The reasons for the formation of debt may be the following:
- revision of legislation, which entailed negative consequences for the organization;
- the counterparty has not fulfilled its obligations to the organization;
- tough competition in the market;
- wrong management decisions;
- errors in financial planning;
- errors in the management of company assets;
- circumstances of force majeure (force majeure).
When the reasons discussed above arise, the organization may incur debt to the following persons:
- individuals who suffered damage (moral or physical);
- employees of the enterprise who have not been paid wages, vacation pay, benefits, as well as any other legally provided payments;
- state organizations;
- off-budget funds;
- creditors;
- founders;
- other partners and contractors of the company.
From the moment liquidation is initiated, the legal entity is obliged to begin paying off outstanding debts to all listed persons.
Top 3 articles that will be useful to every manager:
- Accounting services for companies: all the subtleties and nuances
- What to choose LLC or individual entrepreneur: pros and cons of different forms of ownership
- How to open a current account for an individual entrepreneur: choosing the best bank
How can you close an LLC with debts depending on the type of debt?
- Debt to the budget
- Debt to the founder
- Debt to counterparties, partners, creditors
Debt to the tax service and extra-budgetary funds (Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund).
Important. If a company has a difficult financial situation, then this is not a reason to refuse to pay mandatory contributions to the state budget and funds (Article 112 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Liquidation of the organization in this case does not exempt from payment of the debt.
Solution. If the debt is small and it is possible to pay it quickly, then this must be done as soon as possible, and then voluntarily liquidate the company.
If the company’s debt is more than 100,000 rubles, and there is no possibility of closing it even after 3 months after the due date, then it is better to initiate bankruptcy proceedings for the company.
The LLC may have a debt to the founder for loans or finances that were invested in the company. In this case, upon liquidation, the owner forgives the debt.
Solution. If voluntary liquidation is carried out, the founder notifies the LLC in writing of debt forgiveness (in accordance with Article 415 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The debt is officially written off.
During the process of closing a company, the tax office does not check accounts payable. If your creditors go to court, the liquidation will be suspended or declared invalid .
Important. If an enterprise has a debt to the bank, the bank will most likely file a claim in court.
Solution. It is better to pay accounts payable before starting the liquidation procedure. In the case when you know for sure that the creditors will not go to court, you can submit documents to close the LLC with debts. After liquidation, the debt will be written off.
In the event that an organization cannot repay a debt and has filed or plans to file a lawsuit, it is necessary to urgently file an insolvency (bankruptcy) claim.
What to do if the debtor is in liquidation
If there is a suspicion that the company may begin the liquidation procedure, it is recommended to periodically check the information on the specified resources - information on each of them is updated every 5 days.
If the liquidation process has begun and the data is officially confirmed, the creditor's actions are as follows:
- within 2 months, but not later, financial demands must be sent to the debtor;
- documents confirming the validity of the requirements must be attached to the application requesting payment of the amount;
- the application is considered by the liquidation commission; the creditor will be informed of the results in writing.
If debt claims are refused, the creditor has the right to go to court. But this also needs to be done quickly while the liquidation process is not completed.
If the creditor did not have time to submit an application within two months, and the liquidation process has already been completed, the issue will have to be resolved in court.
How to close an LLC with debts yourself: algorithm for voluntary liquidation of the company
Voluntary winding up of a company may be considered when you have the ability to pay off your debt. The procedure itself is quite lengthy – it takes about 6 months. The advantage of this solution is that the obligations of the founders regarding the inactive LLC are completely null and void.
If there is money to pay the debt, the best option is voluntary liquidation of the company.
Let's look at the procedure:
- Get your documents in order. When the liquidation of the company begins, regulatory government agencies will check you with passion. Make sure all papers are in order in advance.
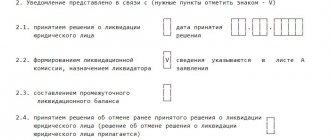
- Organize a board of founders. At such a meeting, you will have to select the composition of the liquidation commission, and document the results of the meeting in the form of minutes.
- Collect the package of documents required for liquidation and submit it to the tax office. The list of such papers includes: applications in forms P-15001 and 15002, completed and notarized; message about the beginning of the liquidation procedure (C-09-04) and minutes of the meeting of founders. The prepared documents must be submitted to the appropriate branch of the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration of the company. The deadline for submitting documents is 3 working days from the moment the decision on liquidation is made.
- Officially notify the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation about the termination of the organization’s existence. A written notice drawn up in free form will be sufficient. It is necessary to place a message containing a description of the procedure and deadlines for submitting claims for creditors in the State Registration Bulletin. Then it is necessary to notify each counterparty (by personal notification) that the liquidation of the organization has begun. Send the notice by registered mail with return receipt requested, then you will have written confirmation that the letter was sent and received.
- Expect verification. Most likely, the tax office will visit you to check the financial statements of your organization for the last 3 years. If they find serious violations, the liquidation will be suspended and the founders will be fined. For this reason, it is worthwhile to make sure in advance (before the liquidation of the LLC is started) that the accounting documents are in perfect order.
- Draw up a liquidation balance sheet. To do this, take an inventory and prepare an interim balance sheet on Form 15003. This document must list a complete list of creditors' claims. Then submit the following set of documents to the tax office: a notarized copy of the interim balance sheet, a receipt for payment of the state duty and confirmation of publication in the Bulletin.
- Obtain certificates of LLC closure. Submit to the tax office all the documents that you collected at the previous stages. The liquidation certificate will be ready in 5 days.
When the due date has passed, create a register of creditors to pay off your debts. You must have evidence that you sent notices to creditors.
Based on the submitted documents, the Federal Tax Service makes an appropriate entry in the state registers. You then satisfy the creditors' financial claims, prepare a closing balance sheet on Form 16001, have it approved and notarized.
Important! All documents on the liquidation of an organization must be bound, numbered and notarized.
Is it possible to collect a debt from a liquidating organization?
It is possible to collect a debt from an organization that is subject to liquidation. But for this you need to meet the deadlines. From the moment the liquidation begins, the creditor has 2 months to file a claim and include the debt in the liquidation balance sheet.
If the creditor fails to do so within the time limits set by law, the issue will have to be resolved in court.
There are several ways to find out that a company will be liquidated:
- through the publication “Bulletin of State Registration”;
- through the “Check yourself and your counterparty” service - it is posted on the official website of the Federal Tax Service;
- requesting information from the Federal Tax Service by contacting them in person;
- through the Unified Federal Register of Information on the Facts of the Activities of Legal Entities.”
Who has the right to close an LLC with debts through bankruptcy proceedings
If you have a debt to someone, creditors can initiate bankruptcy of the organization. The creditor can begin to close the LLC with debts after the court decision in the case to collect the debt from you comes into force. The authorized body representing the interests of the funds, the customs authority, also has the right to launch this procedure if the legal entity is in arrears on mandatory payments after 30 days from the date of entry into force of the decision where the fact of non-payment is established.
To apply to the court to declare a company bankrupt, you can use the services of an authorized representative. Moreover, the legislation clearly states when an organization has the right to do this, and when it is obliged to do it.
Let's look at cases in which an entrepreneur must file an application to declare his company bankrupt in court:
- If there is a risk that the company, having settled with one of the counterparties, will not be able to fully cover obligatory payments, wages, and also fulfill financial obligations to other creditors.
- After the court decision to recover the property of the enterprise has entered into force, and during the execution of this decision, it is clear that the further activities of the company are impossible.
- There are grounds (mentioned above) for declaring the insolvency of a company.
- There are unfulfilled financial obligations (wages, other payments) to the company’s employees (current or former).
The main person during the liquidation procedure (full or simplified) is the arbitration manager. This person is trusted by the organization to handle matters on this issue. It is his professionalism (procedure of action, position taken, etc.) that influences the degree to which the co-founders are brought/not brought to vicarious liability.
An interesting point is that everyone involved in the process has the procedural right to file a petition for an examination to determine whether the bankruptcy procedure is fictitious while the insolvency case is being considered. For an organization, the best option is a simplified bankruptcy procedure.
In the event that the owners of an organization understand that their financial obligations to creditors (counterparties, employees, government bodies) are impossible to fulfill, but do not file a bankruptcy petition in court and mislead new counterparties, they bear legal liability (including criminal liability). ) for such inaction.
In order for the liquidation of an organization to take place with the least losses for you, professionals advise immediately seeking help as soon as signs of insolvency appear, and not delaying until the last minute.
If you apply to the arbitration court in a timely manner, the law will protect the interests of your organization. The court will rule that your application is accepted and the company is declared bankrupt. The accumulated debt to creditors will be written off. Bankruptcy can have unpleasant consequences for an entrepreneur only if he is found guilty of deliberate bankruptcy, as well as of causing damage to the state or business.
If, after the completion of the bankruptcy court case, the owner of the LLC was not brought to criminal liability, then he has the right to create an enterprise, to share participation and corporate rights in any existing business.
The personal property of the founders of such an organizational and legal form as an LLC is protected by law. Personal funds and personal accounts of entrepreneurs can only be used in cases where personal liability is applied in the form of fulfillment of payment obligations.
Do not forget about this risk until you receive a document confirming the liquidation of the legal entity.
What to do if the debt is not paid
If the creditor's claims are legitimate, but the debt is not paid, the following actions may be taken:
- going to court to file a claim regarding unlawful actions of the liquidation commission;
- filing a petition with the court to prohibit the registration of liquidation of the company until the issue of satisfying debt claims is resolved;
- contacting the tax office - you must have with you documents confirming the fact of the debt and refusal to pay it:
- if the company is reorganized, then claims for debt payment can be presented to the successor company;
- if the debtor is an individual entrepreneur, then debts can also be collected from him, but as from an individual;
- if the liquidation has already been completed, but not all the property has been sold, you can go to court to appoint an insolvency administrator. The limitation period is 5 years.
In the latter case, if the court is won, the costs of the arbitration manager can be recovered from the defendant.
Features of the bankruptcy procedure when closing an LLC with debts
The method is long and difficult. To use it, an organization must meet certain criteria:
- there are accounts payable in the amount of more than 300 thousand rubles. and it is expired;
- there are overdue debt obligations, the maturity of which is more than 3 months;
- there are unfulfilled financial obligations to employees (for example, regarding salaries).
Let's consider the 4 stages of the bankruptcy procedure for a company:
- Observation (4–7 months). During this stage, the financial condition of the organization is analyzed, a meeting of creditors is held with a list of their requirements drawn up. A temporary manager is also appointed. He draws up a plan according to which the organization will pay off the debt.
- Financial recovery (no more than two years). At this stage, an action plan is drawn up to restructure the debt by providing installment plans for its payment. If the debt is not repaid at this stage, then proceed to the next stage.
- External management (no more than 24 months). At this stage, an attempt is made to restore the solvency of the company. To achieve this, the functions of the company's management are transferred in full to the arbitration manager, who develops a new strategy for the company and implements specific measures within the framework of the chosen strategy.
- Bankruptcy proceedings (4–6 months). At this stage, the company's assets are sold at auction. The debt to creditors is paid using the proceeds from the sale. In the event that the proceeds do not fully cover the debt, the debt is written off from the company declared bankrupt, and the organization itself is liquidated.
If we talk about the simplified bankruptcy procedure, then first they determine the amount of debt (it should be no more than 100 thousand rubles) and analyze the financial situation of the organization. Then they draw up the liquidation balance sheet of the bankruptcy applicant company.
How to close an LLC with tax debts
Even with a debt to the tax authorities, the founders may decide to liquidate their own company. The debt must be repaid with the organization's finances or property.
Important! If, after conducting an inventory, it turns out that the amount received from the sale of property will not allow repaying the entire debt, a bankruptcy procedure should be carried out instead of liquidation. To do this, the liquidation commission of the LLC applies to the arbitration court with an application and initiates this procedure (clause 4 of article 63 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The liquidation commission has 10 days to file an application with the court (Part 3 of Article 9 of the Federal Law on Bankruptcy). If you know in advance that the liquidation balance sheet will show an outstanding debt, then it is most likely irrational to begin the liquidation procedure.
Important! If an organization falls under the criteria of insolvency of a legal entity (Part 1 of Article 9 of the Federal Law on Bankruptcy), then the bankruptcy application must be submitted by the director of the LLC. Let's look at this aspect in more detail below.
Note!
The tax service can independently initiate bankruptcy proceedings.
This can happen under a combination of the following circumstances:
- there is a tax debt in the amount of more than 300,000 rubles (not taking into account penalties);
- More than 3 months have passed since the presentation of demands for payment of taxes, and the company has still not repaid this debt;
- a court or tax decision has entered into force, on the basis of which tax claims are presented to the company.
How does debt collection work?
The creditor submits an application with supporting documents to the liquidation commission, which is responsible for liquidating the organization. What happens next is:
- the commission reviews the application and enters data into the interim liquidation balance sheet. Even if debt claims are not accepted, data about this must still be entered into the liquidation balance sheet;
- the balance is approved and debt payments begin through the banking institution.
Debt repayment is carried out in the order of priority:
- first of all, payments are made to those persons to whom the organization is responsible for causing harm to health;
- second priority – wage arrears, dismissal benefits and other material obligations to employees;
- third priority – state funds and budget;
- fourth priority – claims of other creditors.
If the funds on the organization’s balance sheet are not enough to satisfy the demands of creditors, then the property is sold to pay off the debt. The creditors' claims are partially satisfied according to the proportion calculated by the liquidation commission.
How to close an LLC with debts to suppliers
In the case when, during the liquidation of an LLC, it becomes clear that it will not be possible to repay the debt using the existing property, the closure of the company is carried out through bankruptcy.
Important! If your company falls under the criteria of insolvency of a legal entity, then not only the tax office, but also counterparties can initiate bankruptcy proceedings.
In the event that a bankruptcy case for a company is initiated at the request of one of the counterparties, other creditors can also write a similar statement and participate in the case.
The director of an insolvent company in any case (even if the insolvency of the LLC is not established during the liquidation process) must file a bankruptcy petition himself.
However, the minimum amount of debt for which such an application can be submitted has not been determined. The presence of the following signs is sufficient:
- the company has several debts that it cannot repay in full;
- a foreclosure was imposed on the assets of the LLC, due to which it was forced to suspend its activities;
- signs of insolvency have been identified. For example, an LLC does not have enough assets to pay off its debt.
In the event that an LLC exhibits all the signs listed above, and it does not declare bankruptcy within one month, the management and founders of the company can be held vicariously liable for the obligations of the LLC. If it is proven that these people are guilty of the bankruptcy of the organization, then they face subsidiary liability.
Conclusion! The procedure for closing an LLC with debts to a counterparty is similar to the procedure for closing a company with debts on taxes and fees.
What is automatic closure of an LLC with debts?
In the event that an organization does not carry out its activities, the liquidation of the company can be carried out by the tax inspectorate unilaterally.
Important . The tax office has the right to close an LLC that does not carry out its activities, but is not obliged to do so. At the same time, the Federal Tax Service may close it only a few years after declaring such a company inactive, or may not close it at all.
An LLC that does not carry out its activities (is inactive) has the following characteristics:
- reporting is not submitted during the year;
- there is no movement on the current account (there are no debits or credits) during the year.
Cases in which an LLC can be forcibly liquidated:
- reporting and declarations are submitted untimely;
- the official location is different from the actual location;
- when opening a company, there were unavoidable gross violations of the law;
- carrying out licensed activities without a license (or permit);
- cases not specified above provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for compulsory liquidation of a legal entity is the same as for the voluntary closure of an LLC:
- A liquidation commission is created. In case of forced closure of a company, a liquidation commission is appointed by the initiator of the procedure.
- Carry out settlements with creditors. At this stage, all issues are dealt with by the liquidator, who has access to the accounts, seals and stamps of the enterprise.
- A liquidation balance sheet is drawn up. Based on this balance sheet, the value of the company's assets is determined.
The consequences of forced liquidation may be as follows:
- Fines. Subsidiary liability arises. For all the time when reporting was not submitted, the owners must pay a fine. It is important to know that this debt is not canceled upon liquidation (clause 3.1 of Article 3 of Federal Law No. 14 “On Limited Liability Companies”, entered into force on June 28, 2017).
- Disqualification. If a company is forced to be liquidated by order of the Federal Tax Service, the owners not only cannot create a new organization for 3 years, but also do not have the right to be co-founders and manage other businesses (Article 23 of Federal Law No. 129 “On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs” ).
If the liquidation of an LLC is carried out voluntarily, the above measures do not apply to the founders.
How to transfer receivables to a single participant during liquidation of a company?
S.A. Tokmina, author of the answer, legal consultant at Askon
QUESTION
The LLC has a single participant (an individual) and is in the process of liquidation. When compiling the interim liquidation balance sheet of the LLC, the liquidator identified accounts receivable in the amount of 27 million rubles, the probability of collection of which is zero, because bankruptcy proceedings have been initiated against the debtor. The amount of the authorized capital of the LLC being liquidated = 10 thousand rubles. The sole participant wants to transfer the rights of claim for this debt to himself in the order of distribution of the property of the liquidated organization.
How to document this?
What documents does he need to present in a bankruptcy case in order to carry out procedural succession?
ANSWER
The legislation does not specify what document should be used to formalize the corresponding decision on the distribution of the remaining property of the liquidated company between the participants (the only participant), including the right to claim receivables.
According to established practice, this transaction is formalized by a transfer and acceptance certificate; all documents confirming the occurrence of receivables are attached to the certificate. The successor must submit all these documents to the arbitration court along with an application for procedural succession in the bankruptcy case.
JUSTIFICATION
The liquidation procedure for a limited liability company is regulated by the provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law No. 14-FZ dated 08.02.1998 “On Limited Liability Companies” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 14-FZ).
The general procedure for distributing the property of a liquidated company between its participants is defined in paragraph 8 of Art. 63 Civil Code of the Russian Federation, art. 58 Law No. 14-FZ. It follows from these norms that the property of the liquidated company remaining after the completion of settlements with creditors is distributed by the liquidation commission among the company's participants. Thus, the decision on the distribution of the property of the liquidated LLC remaining after completion of settlements with creditors is made by the liquidation commission.
At the same time, the legislation does not specify what document should be used to formalize the corresponding decision on the distribution of the remaining property of the liquidated company. Based on established judicial practice, such a document may be:
- act on the distribution of property (for example, the Decision of the Arbitration Court of the Penza Region dated February 28, 2007 in case No. A49-6884/2006-181/12);
- decision of the liquidation commission on the distribution of property (Determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 7, 2011 N VAS-8018/11);
- protocol on the distribution of the remaining property between the participants (Appeal ruling of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Tatarstan dated 08/06/2012 in case No. 33-6976).
The right to claim receivables is a property right and relates to the property of the organization (Article 128 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The transfer of property should be carried out with the execution of a transfer and acceptance certificate, which indicates to whom and what is transferred. The act is signed by all participants of the organization and the liquidation commission. It is necessary to draw up a deed to confirm the fact of transfer of property. At the same time, the act of acceptance and transfer of property of a liquidated enterprise is essentially a transaction of assignment of the right of claim (Resolution of the Tenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated October 15, 2015 No. 10AP-9574/2015 in case No. A41-24635/15).
According to paragraph 3 of Art. 385 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a creditor who has assigned a claim to another person is obliged to transfer to him documents certifying the right (claim) and provide information relevant for the exercise of this right (claim).
Proper fulfillment of the requirements of paragraph 3 of Art. 385 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation will provide all necessary documents confirming the existence of the assigned right (claim) from all previous creditors without exception.
The list of documents to be transferred is not established by law. Documents certifying the right of claim may be acts of delivery and acceptance of goods, works, acts of reconciliation of calculations, copies of sales contracts, invoices, invoices and others. The assignor's obligation to provide confirmation of the transfer of the right of claim will be considered fulfilled from the moment of transfer of any documents that indicate the existence of a right of claim with the new creditor. If this right has been assigned repeatedly, then in this case the supporting documents will be copies of the contracts certified by the assignor organization from which the right of claim originally arose, as well as all assignment agreements and acts (if they were drawn up when transferring the right of claim) certifying the transfer of the right of claim to to the assignor.
The new creditor does not enter into a new independent agreement with the debtor, but enters into an already concluded transaction.
To transfer the rights of a creditor to another person, the consent of the debtor is not required, unless otherwise provided by law or agreement (clause 2 of Article 382 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
It should be noted that resolving the issue of distributing the property of a liquidated company between participants (founders) is possible only after completing settlements with creditors (Article 58 of Law No. 14-FZ) and drawing up the final liquidation balance sheet, which will reflect the remaining property (Article 63 Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, the issue of distribution of property to the company's participants must be resolved before submitting documents to the Federal Tax Service of Russia on the completion of the liquidation process of the company. The liquidation of a legal entity is considered completed, and the legal entity is considered to have ceased to exist after making an entry about this in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities (clause 8 of Article 63 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). After making a record of the liquidation of the company in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, the legal possibility of making a decision on the distribution (transfer) of the remaining property of the company will be lost (Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Moscow District dated January 29, 2016 N F05-18269/2015 in case No. A41-24635/2015, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural district dated May 13, 2013 N F09-1950/13).
However, if bankruptcy proceedings are initiated against the debtor, then it is necessary to follow special rules governing these legal relations.
When establishing the claims of creditors in a bankruptcy case, it is necessary to take into account that in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 126 of the Federal Law of October 26, 2002 N 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” (hereinafter referred to as Law N 127-FZ) from the date of adoption by the arbitration court decisions to declare a debtor bankrupt and to open bankruptcy proceedings, all claims of creditors for monetary obligations, with the exception of current payments and other claims specified in Law No. 127-FZ, can be presented only during bankruptcy proceedings.
The general period for submitting claims, after which the register of creditors' claims must be closed, is determined by paragraph 1 of Article 142 of Law No. 127-FZ and is two months.
The consequence of presenting claims in violation of this deadline, in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 142 of Law No. 127-FZ, is their satisfaction at the expense of the property remaining after satisfaction of the claims of creditors included in the register of creditors’ claims, that is, a decrease in the priority of satisfaction.
Within the meaning of these provisions of Law N 127-FZ, in general, lowering the priority of satisfying creditors’ claims is applied if the possibility of presenting claims within a two-month period objectively existed, but was not implemented in a timely manner by the creditor (Decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated July 24, 2017 N 307-ES17-8691 on case No. A52-1161/2014. Request: On cassation review of judicial acts on the application to include the assignee's claim in the register of creditors' claims. Decision: The transfer of the case to the Judicial Collegium for Economic Disputes of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation was refused, since the court came to the correct conclusion about that on the day the assignor’s right of claim against the debtor arose, the register was closed).
As follows from Part 1 of Article 223 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, insolvency (bankruptcy) cases are considered by the arbitration court according to the rules provided for by the said Code, with the features established by federal laws governing insolvency (bankruptcy) issues.
In accordance with Part 1 of Article 48 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, in cases of the departure of one of the parties in a controversial legal relationship or established by a judicial act of the arbitration court (reorganization of a legal entity, assignment of a claim, transfer of debt, death of a citizen and other cases of change of persons in obligations), the arbitration court replaces this party as its legal successor and indicates this in the judicial act. Succession is possible at any stage of the arbitration process.
Paragraph 1 of Article 61 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the liquidation of a legal entity entails its termination without the transfer of rights and obligations by way of succession to other persons, with the exception of cases provided for by federal law.
At the same time, in accordance with Articles 63 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the liquidation of a legal entity is accompanied by the transfer of ownership of the property of this legal entity to other persons
According to the explanations given in paragraph 23 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated June 22, 2012 N 35 “On some procedural issues related to the consideration of bankruptcy cases,” if the creditor’s claim is confirmed by a judicial act that has entered into legal force and is filed by a person who is a legal successor plaintiff in the relevant case, then such a requirement, within the meaning of paragraph 1 of Article 71 or paragraph 1 of Article 100 of the Bankruptcy Law, must be accompanied by a ruling of the court that made the decision on procedural succession (Article 48 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation). When a creditor's claim is transferred to another person after acceptance of this claim by the court hearing the bankruptcy case, in order for this court to replace the creditor with his legal successor, it is not necessary to first replace him in the case in which a decision confirming the claim was made (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated March 25, 2014 No. F07-10823/2013 in case No. A56-11936/2012. Circumstances: The ruling satisfied the application for procedural succession of the creditor, since as a result of the liquidation of the federal government institution (creditor), the right of claim against the debtor that belonged to it did not cease, but passed to the founder. Decision : Definition left unchanged).
What other ways can you close an LLC with debts?
- Closing through LLC reorganization
- Closing an LLC by merger
- Closing an LLC through sale
- Alternative methods of closing an LLC
Reorganization is a merger, sale, accession to another enterprise, that is, any transformation of the company. To carry out the reorganization, it is necessary to find a suitable legal entity. Liquidating a problematic enterprise in this way may be the simplest and fastest of the proposed options (if the result is positive). It is worth considering that when a company is closed through reorganization, the founders continue to participate in the activities of the organization; they may be subject to fines and held vicariously liable.
If a reorganization is carried out, the owners of the LLC are obliged to inform all interested parties, including creditors, about this. Lenders can protect their interests and insist on suspending the reorganization until the full amount of the debt is paid.
Important! The tax debt also passes to the legal successor of the LLC (Article 50 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). As for fines for non-payment of taxes, only fines imposed by the Federal Tax Service before the completion of the reorganization are transferred to the successor. For example, Resolution 9 of the AAS dated December 1, 2015 No. 09AP-48866/2015 refused to collect a fine from the successor, since this fine was assessed after the completion of the reorganization procedure, while the guilt of the successor was not established, and there were no grounds for holding him accountable.
A merger of several companies involves the liquidation and cessation of activities of all companies participating in this procedure. The newly created company acts as the legal successor.
In this case, a new legal entity is responsible to the creditors, to which all the assets and financial obligations of the closed organization will be transferred.
An LLC with debts can be sold to a third party. This method may be the fastest solution to the founders' problem. The new owner assumes all obligations of the debtor to creditors for a negotiated fee.
You can sell an LLC quite quickly: with proper organization, the sale period is up to 20 days. In this case, the former founders can be completely released from liability.
Important!
The LLC will not be closed either when a stake in it is sold, or in the event of a change in management, since in this case the company remains in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
One of the alternative methods is to change the legal address of the company. You can also change the name of the LLC and the composition of the founders. To do this, it is necessary to organize a meeting of the founders, at which a decision will be made collectively. Then you need to make changes to the statutory documents, pay the state fee and submit an application to the regulatory authorities.
At first glance, alternative methods are quite attractive, but the legality of such actions may raise doubts. In this case, entrepreneurs risk being prosecuted.
To summarize, we can say that if financial difficulties arise, do not look for easy ways, act correctly and comply with legal requirements. Then, having liquidated one company, you will not have any unpleasant consequences, and you can easily create a new business.