At the end of the reporting period, each enterprise or organization summarizes the results of its activities. As a result, net profit or loss is determined. The second option indicates improper organization of the company’s activities, ineffective management and requires careful, in-depth, comprehensive adjustment of processes in the course of further activities. If a company receives a net profit, it can distribute it according to its needs. This affects the further development of the organization. Where can retained earnings be used, and how does this affect the company’s activities? These issues will be discussed further.
What does “retained earnings of an LLC” mean?
Retained (or accumulated) profit is the funds remaining after the enterprise has paid taxes, dividends, fines, and other obligatory payments.
Speaking about this concept, one cannot fail to mention net profit, because they are closely related. So, if a company does not have deferred tax liabilities and there were no dividends accrued during the year, these indicators turn out to be the same in annual reporting. The difference is that net profit is taken into account only in documents for the reporting period, and undistributed profit is also taken into account for the entire period of the LLC’s operation on the market.
Let’s say right away that in accounting and economics, the concepts of retained earnings of an LLC have different uses. For the accountant, we are talking about the result of the work, indicated in the reporting on account 84. In this case, the amount is not actually distributed, since the business owners must decide where the retained profits of the LLC can be sent from March 1 to June 30 of the next year. From an economic point of view, these funds are considered for the past year after the date we named, that is, after all deductions have been made.
There is an opinion that retained and net profit are identical concepts. Indeed, retained earnings are net profits that (as the name suggests) are not divided among the members/shareholders of the LLC. Net profit is that portion of income from sales and non-sales operations that remains in the company after taxes have been paid.
Let us remind you that only the owners have the right to decide where to spend the retained profits of the LLC. This issue is traditionally discussed at the annual meeting of the company's owners, after which the decision is formalized in the form of minutes drawn up based on the results of the general meeting of shareholders.
Typically, these funds are directed to:
- payment of dividends to participants/shareholders;
- repayment of losses;
- replenishment (creation) of reserve capital;
- other goals formulated by shareholders.
Retained earnings on the balance sheet are its liabilities. This indicator represents the actual debt of the company to its owners, because ideally there should be a distribution of retained earnings in the LLC, that is, between the participants of the company, and its investment in the development of the enterprise.
Let us repeat that the company is deprived of the right to dispose of these funds without a corresponding decision of the owners. If we are talking about a loss reflected in line 1370, it also refers to the liability side of the balance sheet. However, it has a negative value, so it is formatted with parentheses.
The new chart of accounts introduced on January 1, 2001 significantly changed the methodology for calculating profits and reflecting them in reporting.
Traditionally, certain types of expenses of a commercial organization were reflected in accounting in one of three ways (1) capitalized, that is, included in the cost of the acquired asset and reflected on the balance sheet (2) charged to the profit and loss account (directly or through the cost of production) (3) written off from net profit, i.e., profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise after paying taxes and other obligatory payments. In this case, there was a confusion of the rights of owners and management personnel, on the one hand, profit belongs to the owners of the enterprise, and management personnel do not have the right to make decisions regarding the directions of its use, on the other hand, writing off part of the expenses at the expense of net profit meant actual intervention management personnel in the process of profit distribution. Such actions led to the infringement of the rights of owners, to a distortion of the financial results for the reporting period (for example, some expenses of the reporting period were written off from retained earnings of previous years), and the inability to calculate indicators of the effectiveness of investments in a given enterprise from the position of its owners. [p.242] The new chart of accounts eliminated the latter scheme (i.e., writing off expenses at the expense of net profit) and thereby brought the accounting methodology in line with the calculation of the financial result to the requirements of the law regarding the rights of the owners of the enterprise. [p.243]
Expenses due to net income [p.277]
Other expenses from net profit [p.278]
Expenses from net profit include various socially oriented payments to encourage the company's personnel, as well as other expenses. In particular, these expenses include F- expenses for material incentives, bonuses, one-time benefits to the organization’s personnel [p.393]
Line 330 reflects current expenses at the expense of net profit, in the absence of residuals of retained earnings from previous years and special-purpose funds. In accounting, they are reflected in the debit of account 88 subaccount “Costs from profits not covered by sources of financing.” [p.104]
A special procedure for reflecting in accounting under the fundless method is expenses at the expense of net profit that are of a capital nature. Profit remaining at the disposal of the organization and aimed at financing capital investments in non-productive areas is reflected in the accounting records as follows [p.106]
It should be noted that recording expenses on account 84 Retained earnings (uncovered losses) at the expense of net profit in the absence of it is not allowed. In this case, expenses should be reflected in the expense accounts for ordinary activities or non-operating, operating expenses. [p.437]
In a joint-stock company, a corporatization fund for employees can also be formed at the expense of net profit. Its funds are spent exclusively on the acquisition of shares of the joint-stock company, sold by its shareholders, for subsequent distribution among the company’s employees. [p.99]
When fixed assets received free of charge are intended for functioning in the non-productive sphere, their cost is attributed to the increase in the social sector fund (88/4). This fund also pays for the costs of delivering such objects (88/4 - 23, 60, 76, 70, 68, 69, 71). In the absence or insufficiency of such sources, expenses for the delivery of non-production objects are made at the expense of net profit (80/3) or profit of previous years (88/2) depending on available sources. [p.49]
In the case when a car or computer equipment is leased from an individual, the costs of their operation (if they are used for the purposes of production and sales of products), as well as the costs of their repair, are subject to inclusion in the cost of production. Passenger cars are not an object of production assets, therefore the costs of fuel and lubricants are not included in the cost price, but are covered by the net profit of the lessee. [p.67]
When a subsidiary (dependent) company is liquidated or one of its participants (founders) leaves, the recorded investments must be returned in accordance with the constituent agreement (agreement). The organization that received the property has the corresponding accounts of material resources and cash debited and the account Long-term financial investments is credited. The excess of the amount received over previously invested property is included in non-operating expenses, the negative difference is written off at the expense of net profit, retained earnings or special funds. [p.106]
According to the chart of accounts, section V of the balance sheet Cash includes account 58 Short-term financial investments. This account is used when investing (investing) funds in income-generating assets for a period of no more than a year, in particular the acquisition of securities, interest-bearing bonds of internal state and local loans, and the provision of loans to other legal entities. The corresponding subaccounts 58/1 Bonds and other securities, 58/2 Deposits, 58/3 Loans provided are opened for the short-term financial investments account. The short-term financial investments account is debited when funds are invested, and the corresponding cash accounts are credited (51, 52). Organizations include dividends received on bonds and securities in the category of income from non-operating activities (51, 52 - 80/3). If securities are stored in a bank branch, the costs of their storage are written off against net profit (80/3 - 51, 52). Organizations pay value added tax on interest received on loans issued. When funds are returned upon expiration of the contract, the short-term financial investment account is credited (closed), and the received cash is credited, accordingly, to the current foreign currency account (debit 51, 52). [p.365]
Expenses for business trips within the limits established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation are included in production costs (20, 23, 25, 26, 29, 43), and the amount of expenses exceeding the established norm is attributed by the organization to net profit (80/3 - 71 ) or by reducing the consumption fund (88/3 - 71). In this case, daily allowances paid to the employee in excess of the established standard, as well as amounts for accommodation that are not documented (there is no hotel account), are subject to income tax in conjunction with wages accrued for the month. The amount of travel expenses included in production costs is not subject to value added tax. In the case when the amount of value added tax is paid, it is reimbursed by the budget within the amount of travel expenses attributed to expenses, and in excess of the established norm, the relevant share of VAT is attributed to net profit or the consumption fund. [p.418]
The rule allowing not to pay UST on payments that do not reduce the taxable profit of the organization has been in effect since the beginning of 2002. Until January 1, 2002, only payments from net profit were not subject to UST. Although the wording of the benefit has changed, it follows from the text of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation that the Unified Tax may not be accrued both for payments from net profit and for payments not taken into account when taxing profits. In other words, when compiling accounting entries on debit, account 84 Retained earnings (uncovered loss), and expense accounts for ordinary activities, and accounts for other expenses can be reflected. [p.177]
Attention We remind you that organizations have the right to use this profit only to accrue taxes and other payments to the budget. The category of other payments includes penalties applied to legal entities for improper fulfillment of obligations for payments to the budget, as well as other sanctions related to violation of current legislation and subject to recovery to the budget from net profit (for example, sanctions for exceeding permissible emissions (discharges) pollutants into the natural environment, etc.). All other expenses and charges that were previously attributed to net profit and reflected in accounting as the debit of account 81 Use of profit, since 2000 can be reflected in account 80 or 88. [p.30]
Please note that, in accordance with the accrual principle used in accounting, a company's expenses associated with ordinary activities can be reflected (written off) as expenses in the current accounting period in which they provided the company with income. However, this does not apply to all expenses, but only those related to generating income, i.e. with the corresponding activities (see Regulations on the composition of costs...). Expenses associated with ordinary activities are not included in net profit, i.e. the enterprise's own funds. In this regard, a careful approach is required to accounting for the enterprise’s expenses for business operations of the reporting year. [p.32]
Let us briefly list some of the problematic issues of determining sources of financing costs exclusive rights for up to a year or exactly one year connecting telephones connecting to the Internet business cards repairing working capital maintaining and updating software products purchasing environmentally friendly water depreciation of cell phones or laptop computers expensive maintenance prestigious furniture or cars, for example, in an audit firm, etc. and so on. If these expenses are not costs, then the question arises about the source of their coverage. Wholesale financing of controversial expenses at the expense of net profit (attributing them to the debit of account 88 Retained earnings (uncovered loss) not only infringes on the interests of shareholders of commercial organizations. This is a violation of the Law on Joint Stock Companies of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ and the Law on Companies with limited liability dated February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ, according to Articles 48 and 28 of which, respectively, the distribution of net profit of organizations is the exclusive competence of the meeting of participants. As a result, the profit of the organization is artificially inflated, which means that the formation of unreliable information is ensured, which, in turn, in turn, it is harmful for both external and internal users of financial information, since it ensures that they make, at a minimum, incorrect decisions.[p.442]
Depreciation of low-value and wear-and-tear items for non-production purposes, accrued at the expense of the organization’s net profit, was moved to the item Administrative expenses 23,358 [p.613]
The general wage fund includes both expenses attributable to the cost of production (goods, works, services) and payments made from net profit [p.281]
Since interest is not paid out of net income, the expense account is debited. [p.189]
A special fund for the corporatization of employees can also be formed in a joint-stock company at the expense of net profit. Its funds are spent exclusively on the acquisition of shares sold by shareholders for subsequent distribution to employees. [p.83]
Financial analysis of bank loan debt includes an analysis of its total size, the presence of overdue and deferred loans, and the timing of the loan. High debt on short-term loans also means large amounts of interest paid to commercial banks. The cost, production and distribution costs may include interest only within the limits of the refinancing rate established by the Central Bank of Russia, increased by three points. Expenses for paying interest in excess of this limit, as well as for deferred and overdue loans, are incurred by the enterprise at the expense of net profit. Expensive credit leads to rising prices and deprives enterprises of the opportunity to use profits for production purposes. [p.155]
The cost of attracting additional capital through the issue of preferred shares is determined taking into account the fixed amount of dividends, which is predetermined for them. This greatly simplifies the process of determining the value of this element of capital, since servicing obligations on preferred shares will largely coincide with servicing obligations on borrowed capital. However, a significant difference in the nature of this service from the standpoint of valuation is that payments for servicing borrowed capital are included in expenses (cost) and are therefore excluded from taxable profit, and dividend payments on preferred shares are made at the expense of the net profit of the enterprise, i.e. . do not have a tax shield.” In addition to paying dividends, the company’s expenses also include issue costs for issuing shares (the so-called placement costs), which amount to a significant amount. [p.418]
Due to the net profit of the enterprise, it becomes possible to increase equity capital. In practice, this opportunity is only partially realized, since irrevocable expenses are made from profits, for example, payment of dividends, bonuses, charitable events, etc. Net profit can be spent on consumption and savings. The increase in the enterprise's equity capital is carried out only at the expense of that part of the net profit that is spent on accumulation, that is, it is added to assets - fixed or working capital, or, in other words, replenishes them. [p.36]
At the same time, in most enterprises, the outflow of funds is also associated with the use of net profit (fines paid from net profit, attributed and paid from net profit, payments to the consumption fund, dividends, etc.). If such expenses occurred, additional adjustment procedures are carried out related to the exclusion of the specified amounts of expenses from net profit. [p.56]
The general wage fund includes both labor costs as part of expenses for ordinary activities, and social payments made from net profit (Fig. 6.2). [p.276]
The costs of paying interest on bonds and dividends on shares are covered from net profit one to three times, due to which the safety of investments in shares and bonds is determined and confidence is created that payment of interest is ensured, and the enterprise has a sufficient margin of safety to ensure payments on securities papers, i.e. on investments. [p.468]
Repair and maintenance of fixed assets for non-production purposes is carried out at the expense of the organization’s net profit (account 81 “Use of profit”) or special-purpose funds (account 88 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”). Actual expenses for the repair of these objects are written off to the debit of account 88 from the credit of material cash and current accounts (10, 60, 69, 70, 76, etc.). [p.90]
Some types of expenses, under certain conditions, are not included in the cost of production, but are reimbursed from the net profit of the organization. Such expenses include [p.176]
Reserve capital is created from net profit, expenses incurred at the expense of net profit are repaid, and deductions are made to accumulation and consumption funds. The composition of expenses incurred at the expense of net profit is determined by the Regulation on the composition of expenses (5). [p.319]
Paid in cash expenses to be written off from net profit from retained earnings and special funds from targeted financing 81-2 8Х 9h [p.154]
Subaccount 81-1 reflects transactions for the accrual of tax payments to the budget from profits (debit of subaccount 81-1, credit of account 68, debit of account 68, credit of account 51), as well as local taxes and fees paid by the enterprise, tax on the resale of cars, computer equipment and personal computers, license fee for the right to trade, fee for the use of local symbols, tax on the construction of industrial facilities in the resort area and others provided for by law. On the debit of subaccount 81-2, the enterprise reflects the write-off of amounts from the net profit of the enterprise (credit to accounts 06, 10. 12, 46, 47, 48, 50, 51, 52, 56, 58, 60, 68, 69, 70, 71, 76, 90, 92, 94, 95) depending on the nature of expenses, deductions to special funds - accumulation funds, social fund, consumption funds (credit to account 88 for the corresponding sub-accounts) and to reserve capital (credit to account 86). As we see, enterprises do not write off these payments and deductions from profits directly as a decrease in financial results. The balance of account 81 shows the amount of payments to the organization from profits during the year. Payments and deductions recorded in account 81 during the year are written off (debit to account 80, credit to account 81) when preparing the annual report. [p.395]
When accounting for the use of net profit, a construction company follows two paths. In the first case, the net profit received is used to create (replenish) special funds, the formation of which is provided for by the constituent documents or the decision of the founders for the coming year. Such special funds formed from net profit include accumulation funds, social sector fund, consumption fund and other similar funds for production development, social development of the team, material incentives). The special funds formed (replenished) at the expense of net profit (debit of subaccount 81-2, credit of account 88 for the corresponding subaccounts) subsequently serve as a source of financing for activities carried out at the expense of net profit, since they represent distributed net profit (debit of account 88, credit accounts 46, 47, 48, 50, 51, 52, 56, 60, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 76, 90, 92, 94, 95) depending on the nature of the expenses. [p.395]
Savings funds. This article shows the unused balance of special-purpose funds at the end of the reporting period, formed from net profit and intended to finance capital works and cover other similar expenses of the organization. [p.420]
Consumption funds. This item shows the unused balance of special-purpose funds at the end of the reporting period, formed from net profit, intended to cover the enterprise’s expenses for the development of the social sphere, rewarding employees and covering other similar expenses. [p.420]
It’s another matter when an organization, as part of optimizing tax payments, wants to choose between the Unified Social Tax and the income tax. It is quite clear that it is more profitable for the payer to save on UST, even if he pays 24% income tax. The most difficult thing in this matter is to decide whether the organization has the right not to reduce taxable profit for those expenses that are provided for in Art. 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Then, for example, bonuses for production results can be withdrawn from the Unified Social Tax, paying them out of net profit. Or the organization is obliged to reduce profits by everything that is required by the code and charge the corresponding unified social tax payments in Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that the taxpayer reduces the income received by the amount of expenses incurred (except for the expenses specified in Article 270 of this Code). Such wording may mean both that the taxpayer is obliged to reduce, and that the taxpayer has the right to such a reduction. For completely understandable reasons, the tax authorities adhere to the term obligated. However, if we take into account the norm of paragraph 7 of Art. 3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation that all irremovable doubts, contradictions and ambiguities in acts of legislation on taxes and fees are interpreted in favor of the taxpayer, then organizations can defend their right to apply benefits under the unified social tax. [p.178]
All other expenses and charges attributable to net profit should be reflected in account 88 Retained earnings. [p.727]
Targeted financing and revenues" (for reimbursement of expenses for the maintenance of cultural and educational institutions and pioneer camps) and other Accounts that record expenses incurred from net profit. [p.320]
How is the retained profit of an LLC formed?
Regardless of whether the result from the sale of products or the provision of services is positive or negative, it is reflected in the active-passive account 90 “Sales”. The debit of the account shows the full cost, VAT and other costs, while the credit shows revenue. The final balance is transferred to account 99 “Profits and losses”.
The following entries must be made in the ledger:
- Dt90Kt99 – profit made;
- Dt99Kt90 – loss received.
The enterprise's operations, including operating and non-operating ones, must be displayed on account 91 “Other income and expenses”. These include:
- Sale and rental of company assets.
- Depreciation and revaluation of non-current assets.
- Transactions with foreign currency.
- Investments in shares of the business of other companies.
- Liquidation and donation of property.
- Income and expenses from transactions with securities.
The following wiring can be used:
- Dt91Kt99 – profit made;
- Dt99Kt91 – loss received.
The procedure for writing off the totals for accounts 90 and 91 is called balance sheet reformation. Let us say right away that by this term many economists understand the direct distribution of accumulated profit from account 84.
Similarly, the balance from accounts 76 “Extraordinary income and expenses” (for example, insurance compensation or losses from natural disasters) and 10 “Materials” (the cost of accepted inventory items unsuitable for use in production) is transferred to account 99.
An LLC's retained earnings may increase if accounting errors are discovered that cause expenses to be overstated. This also happens when dividends are not claimed by shareholders, provided that more than three years have passed from the date of their accrual. And, conversely, if errors were made in the reporting that caused the profit to be overstated, they reduce the accumulated income.
When conducting an economic analysis, we must not forget that retained earnings do not always consist of financial assets represented in cash or stored in a current account, because the markdown of principal amounts increases profit, but does not add money.
At the end of the reporting year, the chief accountant writes off the final balance (profit or loss) from account 99 to account 84 “Retained earnings”.
To do this, the following postings are made:
- Dt99Kt84 – upon receipt of profit;
- Dt84Kt99 – upon receipt of a loss.
Next, account 99 is reset to zero, and no transactions are carried out on it until the onset of the new year. Whereas the score 84 is considered active-passive. Before entering the total of the accumulated profit of an LLC into the report, the amount of income tax is subtracted from it; the latter may subsequently undergo changes.
Why taxable income will not decrease
However, the cassation side sided with the inspection. The company classified the costs of catering as other expenses associated with production and sales (Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To account for such expenses when taxing profits, a company must ensure that one of the following conditions is met:
— expenses are obligatory for the company by virtue of law;
— expenses are inextricably linked with the financial and economic activities of the organization;
— simultaneously with the expenses, the right of ownership to the result of such expenses arose.
According to the employer, catering is part of the measures to ensure normal working conditions in the organization (Article 163 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, food costs in this case can be taken into account when calculating income tax.
Disagreeing with these arguments, the court noted that the organization had equipped a dining area in the dining room, which contained microwave ovens, refrigerators, coolers and tables with chairs. It was these measures that ensured normal working conditions guaranteed by labor legislation. But food expenses are already unnecessary.
In addition, the court found that the organization does not have a collective agreement. But employment contracts do not stipulate that the employer is obliged to organize food for employees and its delivery to the canteen.
An additional argument in favor of the inspection, which worked in court, is that the organization did not keep personalized records of employee food expenses. Accordingly, it was impossible to determine the cost and quantity of products consumed by a particular employee. That is, the disputed costs are not documented.
The cassation court also agreed with the illegality of deducting VAT from the cost of food. The employer does not consume food himself. This means that payment for food products and services for their delivery is not related to production activities.
The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, by Decision dated June 27, 2016 No. 307-KG16-6330, supported the cassation.
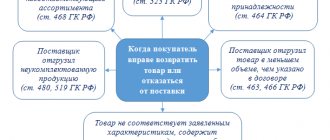
Is retained earnings an asset or a liability?
Retained earnings on the balance sheet are, of course, a liability. The value of this indicator indicates the company’s actual debt to its owners, since ideally this profit should be distributed among the participants and invested in the further development of the business.
In fact, the company cannot dispose of retained earnings without the owners making a decision. The loss reflected in line 1370 is also on the passive side of the balance sheet, only this is a negative value, so the number is placed in parentheses.
“How to read a balance sheet (a practical example)?” will help you better understand balance sheet analysis. .
Retained earnings must be reflected on the balance sheet. ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to do this correctly. To do everything right, get trial access to the system and go to the Tax Guide. It's free.
How to write off retained earnings?
Good afternoon, The procedure for using retained earnings in an LLC reflected in the credit of account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” is established by Federal Law No. 14-FZ dated 02/08/1998. The following areas for the use of net (retained) profit are established by law: - increasing the authorized capital (Article 18 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 N 14-FZ) - payment of dividends (Article 28 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 N 14-FZ) - formation reserve capital (fund) (Clause 1, Article 30 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 N 14-FZ) However, the current legislation establishes the right, and not the obligation, of company participants to decide on the distribution of net profit among themselves and does not limit the company to using net profit funds for purposes not specified in Federal Law No. 14-FZ dated 02/08/1998, subject to a unanimous decision of the general meeting of owners (participants of the company). This means that company participants have the right to refuse to distribute part of the profit in their favor and use it for other purposes. This approach is confirmed by arbitration practice (Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow Region dated 04/19/2005 N KA-A40/2661-05, the Seventeenth AAS dated 06/29/2007 N 17AP-4147/2007-AK, FAS SZO dated 09/20/2013 N A66-15138/2012 ).
Consequently, deductions from net profit are made on the basis of the provisions of the company’s charter, or the decision of the general meeting of the company’s owners. If the owners (participants of the company) made a unanimous decision to use retained earnings from previous years for the development of production, in particular, for the purchase of fixed assets, then this fact is formalized by a decision of the general meeting of owners (participants of the company). In this case, on the date of the founders’ decision on the use of net profit, internal entries are made in account 84: D 84 subaccount “Retained net profit” K 84 subaccount “Net profit subject to distribution” - the amount of net profit aimed at production development (based on decisions of the founders) As of the date of expenses from net profit: D 84 subaccount “Net profit subject to distribution” K 84 subaccount “Use of net profit” - reflects the use of net profit or part of it.
Retained earnings from previous years are not used to increase pay for the organization's employees. Salaries are considered current expenses.
Sincerely, A. Greshkina
Why a company's money is not the property of its owners
Many LLC founders think that the money in the company’s accounts is their personal funds. This is especially true for the sole owners of small companies.
However, according to the law, the property of a legal entity is separate (Article 48 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). This means that all the assets of the company, including cash, belong to the organization itself, and not to its founders. Therefore, even if the company has made a profit, its owners cannot simply transfer the remaining money in the account to themselves.
When withdrawing funds, business owners must pay taxes, and if the salary option is chosen, also insurance premiums.
For non-payment of taxes or fees for any withdrawal option, you will have to pay a fine of 20% of the amount of the arrears, as well as penalties.
What can you spend the retained earnings of an LLC on?
The procedure for distribution of profits is established by the Laws on JSC and LLC. Thus, for accounting purposes, expense items of undistributed funds are specified only in an annotation to account 84 in the Chart of Accounts. There are no other references in accounting to possible ways of using this financial indicator. This means that unallocated funds can be used in such areas as:
- Reserve fund.
By law, JSCs are required to invest net profits in the formation of a reserve fund. Moreover, the size of the latter cannot be less than 5% of the authorized capital of the company. These funds are used to cover losses, repurchase public shares, and repay own bonds.
Unlike joint stock companies, LLCs have the opportunity to create a reserve fund on a voluntary basis. The size of the reserve, the amount of contributions made to it each year and the purposes for which this money can be directed are established by the Charter of the company.
The reserve fund is created by posting:
Debit 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” Credit 82 “Reserve capital”.
It is reflected in the balance sheet in section II “Capital and reserves” on page. As a result, part of the net profit is actually transferred to another item of capital. At the same time, the structure of the balance sheet improves, because the owners are deprived of the right to withdraw funds from the turnover of the enterprise in the amount of the formed fund. In other words, the reserve fund is a kind of financial safety net for the company.
- Dividends.
The amount not spent on the formation of the reserve fund can be used to pay dividends. Let us note that this is the most typical and frequently used method of spending such funds. Retained earnings are reduced when dividends are paid, and when dividends are paid, the company's assets are reduced.
When calculating dividends in accounting, the following entry is used:
Debit 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” Credit 75 “Settlements with founders.”
This entry allows you to reflect the payment of dividends in cash:
Debit 75 “Settlements with founders” Credit 51 “Current accounts”.
If cash issuance is preceded by withdrawal of funds from the current account, the following entry is used:
Debit 75 “Settlements with founders” Credit 50 “Cash”.
Let us note that the law does not prohibit the payment of dividends in both money and property. According to the norms of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, in the second case, VAT must be charged. However, judicial practice knows examples when arbitrators do not recognize the transfer of property through the payment of dividends as a sale, which means that this procedure is not subject to VAT.
Therefore, if a company does not include in the VAT base the value of property transferred as dividend payment, there is a high probability that such a position will have to be defended in court. But is it worth it?
The organization decides to pay dividends in cash, but to do this it will have to sell the property, subject to VAT on its sale, after which funds can be transferred to shareholders. Thus, in the absence of funds, in any case, you will have to pay VAT before making payments to the owners.
Another situation is possible when dividends are goods or fixed assets that are not subject to VAT. In this case, no tax is charged.
The transfer of property to pay off debt on dividend payments is reflected in accounting in accordance with the following standards:
When transferring goods or finished products:
When transferring a fixed asset:
What can you spend retained earnings on and how to reflect this in accounting
At the end of the financial year, many companies need to decide how to spend the net profit received during the reporting period. There are several distribution options, and accordingly, the accounting reflection for each will be different.
Neither the head of the organization, nor especially the accountant, has the right to make a decision on the distribution of net profit. Such a decision can be made exclusively by the general meeting of participants (shareholders). For this reason, it is impossible to automatically summarize the turnover in account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” just to reflect the final figure in the balance sheet, since it is necessary to distinguish:
- retained earnings excluding the decision to pay dividends. This value is shown in the “Income Statement” as net profit and in the balance sheet for the reporting year in the “Capital and Reserves” section;
- retained earnings, taking into account the decision of the founders (participants) to pay dividends, are shown in the organization’s balance sheet in the “Capital and Reserves” section after the meeting of the founders, because this profit can be used in subsequent years to pay dividends to the owners of the organization.
At the same time, we would like to draw your attention to the fact that the distribution of profit based on the results of the year falls into the category of events after the reporting date. And also note that in the reporting period for which the organization must distribute profit, in accounting, both synthetic and analytical, it is shown as retained earnings in the corresponding subaccount of account 84. And already upon the occurrence of an event after the reporting date, i.e. i.e. in the period following the reporting period, in the general order, records are given that reflect this event in accordance with paragraphs. 3, 5, 10 PBU 7/98, i.e. the distribution of this profit is reflected.
GOOD TO KNOW
Profit is determined based on accounting data, not tax data. And all “simplified” people can distribute it, regardless of the object of taxation.
In practice, this also happens when the owners at their meeting decide not to distribute the profit received in the reporting year. In this case, in accounting, a change occurs in the corresponding subaccount of account 84, because retained earnings are formed taking into account the decision of the founders.
Thus, data on account 84 regarding the distribution of profit is formed in the year following the reporting one, taking into account the decision made in the same year on the distribution of profit received based on the results of the previous year, since this is already an event after the reporting date. Well, what if the owners of the company, based on the results of the organization’s activities, decided to direct all the net profit received last year to the development of the organization’s production? In this case, the balance in account 84 remains unchanged, which means that the indicator in line 1370 “Capital and reserves” does not change either.
All retained earnings received can be used to purchase new fixed assets, or the designated amount of retained earnings can be used to create an accumulation fund. Yes, that's not bad. An organization's accountant can reflect the creation of such funds in analytical accounting using the corresponding sub-accounts opened for account 84. In this case, the total value reflected in account 84 will remain unchanged. Note that expenses incurred by the organization aimed at developing production are recognized in the reporting period in which they occurred. In addition, the acquisition of fixed assets by an organization leads to a redistribution of amounts within the balance sheet asset, because the organization in this case decreases the amount of cash, which means the balance on line 1250 of the balance sheet will decrease, but then a fixed asset will appear and the balance on line 1210 of the balance sheet will increase by the same amount. As a result, both the balance sheet asset and capital will remain unchanged.
This raises quite reasonable questions: what are expenses at the expense of profit? For what purposes can it be spent?
These questions can be answered this way: profit is expended only when its value on the balance sheet actually decreases. This happens, for example, when dividends are paid to the owners of the organization at the expense of profits, a bonus can be paid at the expense of profits or material assistance can be provided to employees, and a reserve fund can be created at the expense of retained earnings, the size of the authorized capital can be increased, etc. Such situations have an impact and on reporting indicators.
We pay dividends
In practice, one of the most common ways of distributing profits is the payment of dividends, so let's look at this aspect in more detail. Due to the fact that the outflow of assets in connection with the payment of dividends is not recognized as an expense of the organization for tax purposes, dividends are accrued to participants directly from retained earnings, and therefore from the capital of the organization. In accounting, the following accounting entry is given: Debit account 84 “Retained earnings” Credit 75 “Settlements with founders”.
At the same time, dividends accrued to participants can be paid not only in cash, but also in property. In any case, there will also be a decrease in the corresponding asset of the organization.
So, when dividends are paid in cash, the following entry will be given in accounting:
| Debit | Credit | Operation |
| 75 | 51 | |
| And when paying with property, say, goods, the sale will be shown in accounting, and the following accounting entries will be made: | ||
| 76 | 90.1 "Revenue" | Recognized revenue from the sale of goods transferred to settle the payment of dividends |
| 90.2 “Cost of sales” | 41 | The cost of the goods is written off |
| 75 | 76 | Debt on payment of dividends to participants has been repaid |
We create funds
Let us focus on one more method of distributing profits according to the decision of the founders. This is the creation by an organization of certain funds. Let's name the main ones. Let us say right away that the creation of a reserve fund is the prerogative of joint stock companies. The mandatory creation of this fund is indicated in paragraph 1 of Art. 35 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ “On Joint-Stock Companies”. The law also provides for the size of this fund, which, naturally, must be determined by the company itself, but it must be no less than 5% of the authorized capital, and the amount of annual contributions to this fund should not be less than 5% of the net profit.
As for limited liability companies, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 30 of the Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies” can create a reserve fund in the manner established by the company’s charter and in the amount determined by the organization’s accounting policies.
The reserve fund is created in accounting by posting: Debit to account 84 “Retained earnings” Credit to account 82 “Reserve capital” and is reflected in the balance sheet on line 1370 “Capital and reserves”.
Moreover, all organizations, regardless of their form of ownership, can create other funds designated by the charter of the company. For example, you can create both a dividend fund and a consumption fund to pay bonuses to employees and provide them with financial assistance from retained earnings. It would be a good idea to create a fund to pay off losses from previous years and other funds, although these and other similar funds are not mentioned either in the Law on JSC, or in the Law on LLC, or in the current accounting regulations.
GOOD TO KNOW
The creation of various funds from retained earnings is not mandatory. However, a company can create such if they are established by the charter of the LLC and their size is determined by the accounting policy of the organization. At the same time, we believe that the creation of funds helps maintain order in the distribution and use of the organization’s profits.
Example 1.
Vympel LLC uses the simplified tax system. Based on the results of the organization’s activities in 2013, a loss was received in the amount of 120,000 rubles. In 2014, the company made a profit of 150,000 rubles.
In May 2015, a general meeting of participants was held, at which it was decided to distribute profits in the following order: 120,000 rubles. It was decided to use it to create a reserve fund, which will be used to repay losses from previous years. At the same time, the accounting policy of the organization also determines the size of the reserve fund at 120,000 rubles. Therefore, at the meeting of the founders, it was decided not to accrue or pay dividends to the owners for 2014, but to pay the remaining profit in the amount of 30,000 rubles. do not distribute.
The decision of the founders, i.e., an event after the reporting date, was reflected by the company’s accountant in the following accounting entries for 2015:
| Debit | Credit | Amount (rub.) | Operation |
| 81.1 “Retained earnings” | 82 “Reserve Fund” | 120 000 | A reserve fund of the enterprise was created at the expense of profits |
| 82 “Reserve Fund” | 84.3 “Uncovered loss” | 120 000 | Repayment of losses from previous years using the reserve fund |
| 84.1 "Retained earnings" | 84.2 “Retained earnings” | ||
| The organization's chart of accounts defines: Balance sheet account 84.1 “Retained earnings” without taking into account the decision to pay dividends Balance sheet account 84.2 “Retained earnings” taking into account the decision to pay dividends Balance sheet account 84.3 “Uncovered loss” | |||
As we can see, from the point of view of financial reporting, the creation of a reserve fund leads to a redistribution of amounts within the “Capital and Reserves” section. As a result of such a redistribution of amounts, the structure of the organization’s balance sheet improves, because only retained earnings can be distributed for dividends, including next year, and the reserve fund is inviolable. Moreover, covering losses from the reserve fund makes it possible to show a “break-even” balance, which looks more attractive to investors.
Let us note that the owners’ decision to repay losses from the reserve fund must be disclosed in the notes to the statements in accordance with clause 10 of PBU 7/98.
IMPORTANT IN WORK
It is unlawful to write off in the debit of account 84 such current expenses of the organization as expenses for charity, the purchase of gifts and other events of a cultural, educational and sports nature.
Example 2.
Signal LLC applies the simplified tax system. Based on the results of work for 2014, a net profit of 800,000 rubles was received. In addition, the organization, as of January 1, 2014, had retained earnings from previous years, taking into account the decision to pay dividends in the amount of RUB 1,200,000. In March 2015, a meeting of shareholders was held, at which it was decided to distribute the total amount of retained earnings in the amount of RUB 2,000,000. (RUB 1,200,000 + RUB 800,000) in the following order: to the enterprise development fund - 20%, for payment of dividends - 50%. The remaining profit will be used to create a consumption fund, 20% of which will be used to pay bonuses to employees based on the results of work in 2014, and 10% to pay financial assistance to employees as needed.
At the same time, the amount of the organization’s authorized capital is 200,000 rubles, and the amount of net assets is 1,600,000 rubles.
The credit balance at the beginning of 2014 on account 84.2 amounted to RUB 1,200,000.
In 2014, during the balance sheet reformation, the following entry was made in accounting:
| Debit | Credit | Amount (rub.) | Operation |
| 99 | 84.1 | 800 000 | “Retained earnings” without the founders’ decision to pay dividends |
| In March 2015, in accordance with the decision of the founders following the results of the meeting, the following accounting entries were given: | |||
| 84.2 | 81.1 | 1 200 000 | Profit from previous years accepted for distribution |
| 84.1 | 84.4 | 400,000 rub. = (RUB 2,000,000 x 20%) | Sent to the enterprise development fund |
| 84.1 | 75, 70, 69 | 1,000,000 rub. = (RUB 2,000,000 x 50%) | Dividends accrued to founders* |
| 84.1 | 84.5 | 600,000 rub. = (RUB 2,000,000 x 30%) | Sent to the consumption fund |
| 84.5 | 70, 69 | 120,000 rub. = (RUB 600,000 x 20%) | Bonus payments to the organization's employees were accrued from the consumption fund* |
| * For simplicity of the example, the accrual is shown in total, without individual distribution and without separate accrual of insurance premiums. Personal income tax deductions from accrued amounts of dividends and bonuses are also not shown. When calculating bonuses to employees of an organization at the expense of profits, it is necessary to draw up the following documents: - minutes of the general meeting of founders (participants); — decision of the general meeting of founders (participants) on the expenditure of the consumption fund; — payment of the bonus is made in accordance with the order of the head of the organization. | |||
As a result, after distributing the entire amount of retained earnings in 2015, we have:
- credit balance on account 84.3 – 400,000 rubles. (enterprise development fund);
- credit balance on the account 84.5 – 480,000 rubles. (consumption fund).
As we can see, in the presented example, based on the results of 2013, the available retained earnings were not distributed, because in 2014 the founders held a meeting at which it was decided not to distribute the profits received in 2013. In 2015, a meeting of the founders also took place, and all retained profits available in the organization for this period were distributed. At the same time, the organization had such an opportunity, since the amount of net assets significantly exceeded the amount of the authorized capital, which is important for this.
And one more important nuance. For many years, the issue of the possibility of using retained earnings from previous years to pay dividends has remained controversial, since neither tax nor civil legislation contains restrictions on the payment of dividends from retained earnings of previous years.
Currently, it is possible to enlist tax legislation on this issue. So, in accordance with Art. 43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, retained earnings from previous years can be spent on paying dividends, because “a dividend is any income received by a shareholder (participant) from an organization when distributing profits remaining after taxation.” This position is also consistent with letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 5, 2011 No. ED-4-3/16389, dated April 6, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/235. In addition, such payments must also be provided for in the company’s charter.
GOOD TO KNOW
Funds can be formed from retained earnings only in accounting. The creation and use of funds under the simplified tax system does not in any way affect tax accounting.
Example 3.
Orion LLC uses the simplified tax system. The general meeting of owners, which took place in April 2015, decided to use part of the profit of the reporting year (RUB 150,000) to increase the authorized capital of the organization.
Based on the decision made, changes must be made to the constituent documents. After registering these changes in the prescribed manner, the corresponding entry is given in the accounting records: Debit 84.1 Credit 80 - 150,000 rubles.
Features when paying dividends to foreign participants
Some residents of other countries may have preferential tax rates. Thus, for tax agents in England or Germany the rate is set at 10%, and for residents of Italy it is half as much and is only 5%.
Another important point is the functional aspect of possible double taxation.
Therefore, before paying part of retained earnings or current period income to a foreign participant, it is necessary to clarify whether an international agreement on this issue has been established between the Russian Federation and the resident country.
Increasing the authorized capital of an LLC using retained earnings
If the authorized capital is increased at the expense of the company’s property, its participant does not actually receive funds, goods (work, services) or any other property. Thus, this method of increasing the authorized capital of an LLC does not entail the emergence of income that should be subject to personal income tax.
Let us turn again to judicial practice: there are cases where courts have come to the conclusion that the participants of the company have no income associated with the increase in the nominal value of their shares. This conclusion was considered the only correct one until a company participant exercised any of his property rights, certified by the corresponding share in the authorized capital.
But it is worth noting that this is not the only possible conclusion. According to the position of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, when the authorized capital increases due to retained earnings, an individual receives income at the time of his state registration. These funds should be subject to personal income tax on a general basis (see, for example, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 22, 2017 N 03-04-06/31351).
This position is supported by clause 19 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which provides for non-taxable income representing the difference between the new and original nominal value of a share in the authorized capital, obtained as a result of the revaluation of fixed assets. At the same time, in Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which defines the list of non-taxable personal income tax income, there is no income resulting from an increase in the nominal value of the participant’s share due to retained earnings of previous years.
If an LLC decides to follow the clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, it is considered a tax agent for personal income tax, whose responsibilities include: calculating the amount of personal income tax, withholding it from its income upon actual payment, transferring the corresponding amount to the budget (clauses 1, 2, 4 of Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Since in this case the company does not pay the company member any money in the current year, withholding the calculated amount of personal income tax is impossible. Then, according to paragraph 5 of Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the enterprise must inform the taxpayer and the tax authority at the place of registration in writing about the impossibility of withholding the tax, the amount of the tax itself and the funds from which it was not withheld. This is given until March 1 of the year following the expired tax period in which the corresponding obligations arose. More detailed information on this topic can be obtained in the “Practical manual on personal income tax”.
When increasing the authorized capital of an LLC using funds from retained earnings, an entry is made in accounting to the debit of account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” and the credit of account 80 “Authorized capital” after state registration of changes made to the organization’s Charter. This is required by the instructions for using the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n.
Registration
The employer is obliged to create normal working conditions for employees (Article 163 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), as well as provide sanitary, household and medical services (Article 233 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Article 226 of the Labor Code provides that financing of measures to improve labor conditions and safety by employers (with the exception of state unitary enterprises and federal institutions) is carried out in the amount of at least 0.2% (without setting an upper limit) of the amount of costs for the production of products (works, services) ).
The standard List of measures annually implemented by employers to improve working conditions and labor protection by employers was approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated March 1, 2012 No. 181n.
For the purposes of Chapter 25 “Organizational Income Tax” of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taxpayers have the right to take into account all expenses when forming the tax base for corporate income tax if they meet the criteria specified in paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and provided that such expenses are not listed in the article 270 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The List contains items containing measures to improve working conditions and safety, the cost accounting for which does not raise objections from tax authorities when taxing profits.
In particular, this is paragraph 26, where it is prescribed that when equipping premises for medical care and (or) creating sanitary posts according to established standards, they must be equipped with first aid kits equipped with a set of medicines and preparations for first aid. The organization's expenses for completing such first aid kits can be included in the expenses taken into account when calculating the tax base for corporate income tax, on the basis of subparagraph 7 of paragraph 1 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 3, 2012 No. 03-03-06 /2/112).
The costs of purchasing air conditioners and heaters in order to ensure normal working conditions are also considered justified (clause 15 of the List).
The right to take into account the costs of the purchase and installation of water installations (coolers), provided for in paragraph 18 of the List, is confirmed by the Ministry of Finance in letters dated March 23, 2021 No. 03-03-07/22134, dated July 17, 2021 No. 03-03 -06/1/45286.
The List also contains paragraph 32, which lists activities aimed at developing physical culture and sports in work collectives. Officials do not allow these activities to be taken into account in expenses (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 8, 2021 No. 03-03-06/1/6140):
- compensation to employees for sports activities in clubs and sections;
- organization and conduct of physical education and sports events, including events for the implementation of the All-Russian physical culture and sports complex “Ready for Labor and Defense” (GTO), including remuneration for the labor of methodologists and trainers involved in the implementation of these events;
- organization and conduct of physical culture and health activities (industrial gymnastics, therapeutic physical culture (hereinafter referred to as exercise therapy) with employees who, on the recommendation of the attending physician and based on the results of medical examinations, are indicated for exercise therapy), including remuneration for the labor of methodologists, trainers, medical specialists involved to carry out these activities;
- acquisition, maintenance and renewal of sports equipment;
- construction of new and (or) reconstruction of existing premises and grounds for sports;
- creation and development of physical education and sports clubs, organized for the purpose of mass involvement of citizens in physical education and sports at their place of work.
Paragraph 29 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that expenses not accepted for profit tax purposes include payment by the employer for classes in sports sections, clubs or clubs, visits to cultural, entertainment or physical education (sports) events, payment for goods for personal consumption of employees, as well as other similar expenses made for the benefit of employees. And the key words here are the words “for personal consumption of employees.” That is, these expenses cannot be justified by any “production necessity” or “improvement of working conditions”.
The letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 17, 2021 No. 03-03-06/1/45234 also contains clarifications regarding activities aimed at developing physical culture and sports in work collectives. Here, the justification for prohibiting the accounting of expenses is their spending outside working hours, that is, for the personal purposes of employees. They cannot be associated with production activities, which means that expenses for them cannot be taken into account when calculating income tax.
At the same time, the Ministry of Finance notes, expenses must be economically justified, documented and related to the activities of the taxpayer aimed at generating income (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Expenses for what physical education activities can still be taken into account when calculating income tax? Officials do not answer this question in any letter.
Most likely, this could be industrial gymnastics. Her classes are aimed at restoring working capacity, that is, there is a connection with production activities. How to justify it?
The provisions of Article 109 of the Labor Code stipulate that in certain types of work, workers are provided with special breaks during working hours, determined by the technology and organization of production and labor. The types of these works, the duration and procedure for providing such breaks are established by the internal labor regulations.
Such a special break could be a break for industrial gymnastics. It will be included during working hours, which means it is paid.
Since this is a special break due to production technology, provided for in Article 109 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and local regulations, its payment can be taken into account in tax expenses.
Retained earnings: calculation formula
According to general accounting data, retained earnings are a company's net profit after taxes that can be distributed to the company's owners.
Based on global financial practice, retained earnings (hereinafter referred to as RR) are calculated using the following formula:
NPk = NPn + PE – Div,
Where:
NPk - NP at the end of the reporting year;
NPn - NP at the beginning of the reporting period;
PE - net profit remaining after accrual of income tax;
Div - dividends paid in the reporting year based on the NP of previous years.
If you do not have the NP value, then to calculate the NP you can use the following scheme:
- first calculate profit before tax (to determine it, calculate operating profit, which is defined as the difference between operating income and operating expenses);
- then subtract depreciation and interest costs from operating profit;
- Subtract tax from the resulting profit value.
To find out whether it is possible to see the amount of operating profit in the accounting statements, read the article “Which line is operating profit reflected in the balance sheet?”
Account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”
The result of a company's commercial activities can be either profit (if income exceeds expenses) or loss (in the opposite situation).
To reflect and accumulate data on financial results in accounting, it is customary to use account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss).” This account contains information about the net total amount accumulated by the company at the end of the relevant reporting period. In other words, account 84 reflects not only the net profit (NP) generated in the current period, but along with it also the retained earnings of previous years (NP) or uncovered loss (UN).
ATTENTION! The state of emergency for the past year is shown on line 2400 of the financial results report (hereinafter referred to as the report). The balance of NP or NU minus dividends can be seen in line 1370 of the balance sheet.
In the tax guide from ConsultantPlus you will find step-by-step instructions for filling out line 1370 of the balance sheet. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
How the company’s PE is calculated, see the article “How to calculate net profit (calculation formula)?” .
The amount of NI for previous years is indicated by the credit turnover of account 84. In circumstances where the company received NI in the current year, the company compensates for it from retained earnings remaining from previous years. If the company did not have NP or NU in previous years, the financial result indicated in line 1370 of the balance sheet (taking into account the payment of dividends) will be equal to the PE from the report.
Read about the nuances of reflecting retained earnings in the balance sheet in the material “Retained earnings in the balance sheet (nuances).”
Answers to frequently asked questions
Question No. 1: It is well known that NP may change from one period to another depending on the income received. What else can influence its size?
In fact, there are quite a lot of influencing factors. First of all, these include changes in the size of dividends, net profit, taxes, cost of products sold, as well as administrative expenses.
In practice, a detailed financial analysis is carried out, which shows which factors in a given situation “helped” to make a profit.
Question No. 2 : Are dividends subject to mandatory insurance contributions?
No, they are not taxed, since they are not considered as an employee’s salary. Only income tax is withheld from them.
Accounting entries
The following table shows the accounting entries for dividend accruals from the organization’s undistributed private equity:
| DEBIT | CREDIT | Action |
| 84 | 75 | Formation of a dividend base for participants who are not employees of the company |
| 84 | 70 | Formation of a dividend base for participants who are employees of the company |
| 75 | 68 | Tax Withholding for Non-Employee Participants |
| 70 | 68 | Withholding tax from participants who are employees |
| 75 | 50,51 | Dividends are paid to non-employees |
| 70 | 50,51 | Dividend payments were made to employees |
| 68 | 51 | Personal income tax deduction |
| 75 | 84 | Transfer of unpaid dividend flows to persons who are not employees of the organization into the company's retained earnings |
| 70 | 84 | Transfer of unpaid dividend flows to persons who are employees of the organization into the retained earnings of the company |