Cash desk of economic entities
If an enterprise works with cash (receives sums of money from customers, issues them for reporting, receives them from a bank account, issues and accepts cash documents), then its responsibilities include conducting cash transactions. At the same time, cash discipline must be observed in terms of processing transactions, the procedure for issuing and receiving funds, and establishing an acceptable cash limit.
For more complete information, see the article “Cash discipline and responsibility for its violation.”
If the enterprise has the status of a small one or the business is registered as an individual entrepreneur, then cash discipline for such entities is less strict. For example, it is not necessary to approve a cash limit for them, as evidenced by the provisions of clause 2 of the Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014.
For detailed information on the management of cash transactions by entrepreneurs, see the article “What are the features of cash discipline for individual entrepreneurs?”
Legislative regulation
The main provisions and responsibilities for waste management are contained in Federal Law-89. Responsibility for waste disposal lies with the original owner, the organization where it was generated.
Production waste is divided into irrecoverable and returnable. The first are materials with completely lost original useful properties. Their implementation or reuse is not possible. The latter can be used in production or sold for further use.
Is there a list of goods, packaging of goods that are subject to disposal after they lose their consumer properties?
Irrevocable waste is not reflected separately in the balance sheet. These are production (technological) losses, the standard of which is included in the consumption rates of raw materials when calculating the cost of the finished product: shrinkage, volatilization, waste, evaporation. According to the “Basic provisions for calculating the cost of products” clause 27 (approved 20/07/70, valid document), irrecoverable waste is not subject to assessment. This means that the accountant does not need to determine their value and create postings. We can say that indirectly their disposal is paid for by the company itself through the mechanism for calculating production costs. All that is required is their technological accounting.
Returnable waste can be disposed of directly. Federal Law 89 defines waste disposal as its use in the production of products, services, and work. At the same time, for accounting purposes, residues of materials that have retained all their consumer properties and are transferred to other departments and workshops are not recognized as waste (Article 254-6 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What are the standards for recycling waste from the use of goods?
How is account 51 used in accounting?
Account 51 is active. An increase in an account is shown as a debit, and a decrease as a credit. For example: if sales revenue is credited to the company’s account, then debit entries on account 51 will be used, and if services, raw materials or debt to counterparties are paid from the current account, then account 51 entries will be made on credit.
The account balance is debit. It shows the cash balance that belongs to the company at the reporting date. Since monetary resources are the assets of the enterprise, the final account balance is reflected in the balance sheet asset, in particular, in line 1250.
The main document confirming the status of the account is a bank statement.
The balance of account 51 cannot be negative. If the company has no money, then the balance is zero; if it does, then the balance is greater than zero. If the bank has provided an overdraft, then it should be reflected as accounts payable, but not as a positive balance.
Basic Accounting Principles
The main account that appears in settlements with counterparties is account 62 of the same name. It reflects payments for shipped goods and ordered services. The score will be synthetic. In most cases it is active. DT account 62 reflects the formed receivables arising from the shipment of goods, and CT account records the repayment of debt.
Account 62 will be passive when the company received an advance payment under an agreement on services provided. To summarize information about settlements, a subaccount “Advances received” is opened. When shipping products, this wiring is used: DT62 KT90. When the buyer's debt is paid, it will be written off from KT62 to DT50-52.
The company may enter into agreements with customers or counterparties that require prepayment. If a company has received an advance, it must provide settlement documentation for the full cost of products or services. The advance payment is used to reduce the debt of the buyer/counterparty. Accounts payable for advances are repaid after the sale of goods, when the company presents settlement papers to customers. Let's look at the postings that are used when shipping goods:
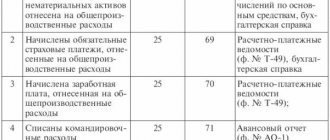
- DT51 KT62. Acceptance of accounts payable.
- DT62 KT90. Repayment of accounts payable.
The amount is indicated for each transaction. For example, this could be the size of the accounts payable.
Need 62 positions
The designated position is necessary so that companies can summarize information about settlements with their customers and customers.
On its credit side, the organization reflects the resulting debt to customers. In turn, the debit part contains information about the buyer’s obligations to the organization.
Analytics for this position is carried out for each invoice that was issued to the customer. If we are talking about mutual settlements through scheduled payments, then analytics should be carried out for each customer.
Receipt of money to the cash register: posting Dt 50 Kt 51 and others
According to the Chart of Accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 34n, account 50 “Cash” is active. In this case, cash receipts are reflected in the debit of account 50.
There may be several sources of replenishing the organization's cash register with funds. One of them is withdrawing money from a bank account. In such cases, the transaction is traditionally recorded by the following entry: Debit 50 Credit 51 .
But there are often situations where time gaps arise between the debiting of cash from one cash source of the company and its capitalization on another. For example, if the collector received funds from the bank at the end of the working day, it may not be possible to post the necessary amounts to the organization's cash desk to account 50 on the same day. In such cases, it is possible to use account 57 “Transfers in transit”:
- Dt 57 Kt 51 - receipt of funds based on a bank receipt to the responsible person (as of the date the cash collector received the cash);
- Dt 50 Kt 57 - posting of received cash to the cash desk (on the date of receipt of cash at the cash desk).
If the operation of withdrawing cash and crediting it to the cash register can be completed within 1 business day, then in accounting it will find a reflection that is already familiar to us: Dt 50 Kt 51.
The return of unused funds to the cash desk by accountable persons is accompanied by the following posting: Debit 50 Credit 71 - recording of unused amounts, balances of funds after the accountant purchases materials and pays for services.
You will find other information about the actions of accountable persons, including when returning funds, in the article “Features of advance reports in accounting.”
If cash comes from customers, then the replenishment of the organization’s cash desk is as follows: Dt 50 Kt 62.
Who can write off overdue receivables?
In tax accounting. Only organizations on OSNO that pay income tax and account for income and expenses on an accrual basis can write off receivables. Individual entrepreneurs on OSNO cannot do this (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated September 4, 2014 N 03-04-05/44287).
Under the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”, only the expenses listed in Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. There are no overdue accounts receivable in this list, so simplifiers cannot write them off in tax accounting (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 13, 2007 No. 03-11-04/2/274).
For the unified agricultural tax, the situation is the same - this type of expense is not on the closed list from clause 2 of Art. 346.5 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
With the simplified tax system “Income” and UTII, expenses do not affect the calculation of the tax base at all. Therefore, everything that we say below about writing off overdue receivables in tax accounting applies only to companies on OSNO.
In accounting. Accounting rules apply to all legal entities, therefore all organizations, regardless of the tax regime, must write off overdue receivables in accounting.
What is it used for?
The account reflects the movement of funds in Russian currency. Debit (Dt) of position 51 reflects transactions accompanied by the receipt of funds to the enterprise's account. For a loan (Kt), transactions are reflected in which funds are written off from an account opened with a credit institution. Funds that were erroneously debited or credited to the account are not reflected in account 51.
Large enterprises and organizations, as a rule, have several accounts with banks. Therefore, analytical accounting for account 51 is maintained for each account. Usually, separate subaccounts are entered for each open account.
The nuances of using subaccounts using the example: Dt 62.1 Kt 62.2
On account 62, analytical accounting should be provided according to the following parameters:
- According to issued invoices.
- For each counterparty.
- By groups of affiliated persons (with whom consolidated reporting should then be prepared).
- By payment characteristics (received prepayments, postpayments).
These tasks are solved, among other things, through the opening of sub-accounts to account 62.
Subaccounts are usually identified by an additional numeric coding of one or two characters added to the main account code. In the original chart of accounts, a unified standard for creating subaccounts for account 62 is not provided. But as a result of the widespread use of computer programs, assigning a subaccount code in practice is approximately the same.
For example:
- Account 62.1 (or 62.01 in most current versions of accounting programs) is assigned to account for postpaid settlements. When the goods have been shipped (services have been provided) but payment has not yet been received. The balance according to 62.1 is debit and means that the buyer (customer) owes the organization for the part of the transaction that it has already completed.
- Account 62.2 (or 62.02) is used to record received payments against future shipments (performance of work, provision of services). The balance is a credit balance and characterizes the size of the organization’s obligations to counterparties who have made prepayments for transactions.
Important to consider! Recommendation from “ConsultantPlus”: Please note: in order to show accounts payable in the balance sheet in the form of the amount of an advance received, you need to subtract account 62 (76) from the credit balance of the analytical account “Advances received” account 62 (76) ... (for more details, see K+). You can get trial access to K+ for free.
Read more about accounting automation in the material “Review of programs for accounting expenses and income of an organization.”
depositing money into a company account
messages: 1,345
messages: 1,177
from an organization, if the authorized (share) capital (fund) of the receiving party consists of more than 50 percent of the contribution (share) of the transferring organization;
(as amended by Federal Law No. 32-FZ dated February 15, 2018)
from an individual, if the authorized (share) capital (fund) of the receiving party consists of more than 50 percent of the contribution (share) of this individual.
in this case, the received property is not recognized as income for tax purposes only if, within one year from the date of its receipt, the specified property (except for cash) is not transferred to third parties;
Postings to account 62 Settlements with buyers and customers using an example
Let's study an example when a product is sold remotely through an online store. Payment for goods purchased through the online store can be made in one of the following ways:
- Bank card (transfer of funds is regulated by law dated June 27, 2011 No. 161-FZ);
- Cash to the courier upon delivery of goods (when selling goods through an online store, OKVED code 52.61.2);
- Through electronic payment systems (regulated by law dated June 27, 2011 No. 161-FZ).
Instructions 50 count
Instructions for using the chart of accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations in accordance with Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000
Account 50 “Cashier” is intended to summarize information about the availability and flow of funds in the organization’s cash desks.
Sub-accounts can be opened for account 50 “Cashier”:
50-1 “Organization cash desk”,
50-2 “Operating cash desk”,
50-3 “Cash documents”, etc.
Subaccount 50-1 “Cash of the organization” records the funds in the cash desk of the organization. When an organization carries out cash transactions with foreign currency, then corresponding sub-accounts must be opened to account 50 “Cash” for separate accounting of the movement of each cash foreign currency.
Subaccount 50-2 “Operating cash desk” takes into account the availability and movement of funds in the cash desks of commodity offices (piers) and operating areas, stopping points, river crossings, ships, ticket and baggage offices of ports (piers), train stations, ticket storage offices, ticket offices post offices, etc. It is opened by organizations (in particular, transport and communications organizations) if necessary.
Subaccount 50-3 Cash documents records postage stamps, state duty stamps, bill stamps, paid air tickets and other cash documents in the organization's cash desk. Cash documents are accounted for on account 50 “Cash” in the amount of actual acquisition costs. Analytical accounting of monetary documents is carried out by their types.
The debit of account 50 “Cash” reflects the receipt of funds and monetary documents at the organization’s cash desk.
The credit of account 50 “Cash” reflects the payment of funds and the issuance of monetary documents from the organization’s cash desk.
Subaccounts
On the credit side of the designated position, the accountant reflects the funds received from the sale of shipped products, as well as advance resources received for goods and services. In this case, the funds received as part of the payment are accounted for in various sub-accounts:
- 01 account – funds received in accordance with the general procedure;
- 02 – advance funds from customers;
- 03 – accounting for bills received.
Accounting for non-cash funds to account 51 – “Current account”
All non-cash payments can be made if you have a current account. It opens in a credit institution, otherwise called a bank. How to open a current account and what documents you need to provide, read this article.
To record the movement of non-cash funds of the organization, 51 accounting accounts are intended.
Is he active or passive?
Analysis of account 51 proves that it is active, it keeps records of the company's assets (non-cash money), and it always has a debit balance. The debit of account 51 is intended to reflect the receipt of non-cash funds (an increase in an asset), and the credit of account 51 is intended to reflect the write-off of non-cash funds (a decrease in an asset).
Currently, an organization is allowed to have several current accounts. Account 51 (download a list of accounts with which account 51 corresponds) can be divided into several analytical ones, each of which will keep records for each individual current account of the enterprise.
The primary document confirming the fact of debiting and receiving non-cash funds is a bank statement, which contains information about all amounts received and debited from the organization’s current account.
Funds are written off on the basis of a payment order, which is drawn up in 2 copies and sent to the bank; one copy is marked by the bank stating that the order has been accepted and returned. When you deposit money from the cash register to your current account, an announcement is issued for a cash contribution.
Typical postings to account 51
Account 51 can correspond with other accounts depending on what needs to be reflected - crediting money or writing it off. Let's look at how postings for business transactions are generated in both cases.
| the name of the operation | Debit | Credit |
| Admission | ||
| Money is credited from the company's cash register | 51 | 50 |
| Partial payment from the buyer has been credited | 51 | 62 |
| A short-term loan with a repayment period of 6 months was received from the bank | 51 | 66 |
| A tax refund was received from the state due to overpayments | 51 | 68 |
| The founders formed the authorized capital | 51 | 75 |
| Received funds included in deferred income are reflected | 51 | 98 |
| Write-off | ||
| To pay an accountable person funds for business needs, money was withdrawn from the current account and credited to the cash register | 50 | 51 |
| Payment has been made against the supplied materials from the supplier | 60 | 51 |
| The short-term loan obligation has been repaid, taking into account accrued interest. | 66, 67 | 51 |
| Salaries of the company's employees have been paid | 70 | 51 |
If, as a result of recording a business transaction, an error was made - the wrong amount was credited or an incorrect payment was written off - then the amounts identified during the audit are subject to reflection on account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”.
Correspondence of account 91 with other accounting accounts
Almost any activity of the organization can become a source of other income and expenses, therefore the number of corresponding accounts is almost equal to the number of accounts in the plan. We have collected all the numbers in a table.
| Only by debit | Only on loan |
| 01 02 03 04 07 08 10 11 14 15 16 19 20 21 23 28 29 58 59 60 63 66 67 68 69 70 71 73 76 79 81 94 98 99 | 07 08 10 11 14 15 20 21 23 28 29 41 43 45 50 51 52 55 57 58 59 60 63 66 67 62 71 73 75 76 79 81 96 98 99 |
Issuance of loans to individuals
The company has the right to issue repayments or assets in non-monetary form to individuals. The latter are the founders, employees or outside citizens.
When drawing up an agreement, the personal data of an individual, passport details, as well as the address of actual residence and the telephone number valid at the time of drawing up the agreement are indicated.
Important! Loans issued by employees can be interest-bearing or interest-free. The decision to issue repayable financial assistance to an employee or founder is made by the company’s management or the meeting of shareholders.
In accounting, two accounts can be used to display interest-bearing loans:
- 58 “Financial investments”.
- 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations.”
The decision on which account will be used to account for interest-bearing loans issued to individuals is made by the company independently. But it must be enshrined in the order on the Accounting Policy for accounting purposes. For interest-free loans, account 73 is always used.