Healthy
For more information about which taxpayers and for which transactions are required to issue ESF, see the article “Who is obligated to issue electronic invoices (ESF)?”;
The deadlines for issuing invoices are described in detail in the article “PRO deadlines for issuing ESF”
Is it possible to offset VAT on an ESF issued by a supplier in violation of the statement deadline?
The Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated July 5, 2014 No. 235-V establishes liability for failure to issue or violation of deadlines for issuing electronic invoices.
What's the situation
Under an agreement for the sale of printed materials, organization A transfers books to organization B for a fee, in addition, company B pays company A for postage for the delivery of these books.
Organization A issues a delivery note (TORG-12) dated 09/06/2017, since the books were sent within this period, then upon delivery on 09/13/2017 issues a certificate of services rendered and an invoice for the total amount of the contract (books and delivery). In particular, to close the contract, company A must provide the books and arrange delivery, that is, the transfer of books is documented by a bill of lading, and the delivery is documented by an act upon delivery, that is, more than 5 days after the bill of lading. The invoice is issued for the total amount with the date of the act. Is this legal? Or, due to the fact that 5 days are given for issuing an invoice, the delivery note should be dated no earlier than 09/09/2017? Is it possible to accept a delivery note, document and invoice with current data or is it possible to accept some of the documents and the dates must be changed?
Administrative liability for late issuance of an invoice
We all know that there are deadlines defined by legislation for issuing invoices, in electronic and paper form. And we, the consultation line, often receive questions: “What will happen to us if we forgot to issue an invoice (usually in electronic form) and violated the deadlines? Is it possible to issue a document with the current date? How much fine should we pay and when? Etc.". So in today’s article I will try to examine these issues in more detail.
Article 281-1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Republic of Kazakhstan, with additions in accordance with Law No. 432 of December 3, 2021, defines administrative liability for late issuance of an invoice. The amount of the fine depends on the type of business entity:
Which is correct?
A single invoice can be issued for both the shipment of goods and the delivery of goods.
But since in the case under consideration the delivery note was drawn up earlier than the act, it is safer to issue two invoices with different dates. However, from the analysis of legal norms and explanations from regulatory authorities, it follows that invoices issued by the contractor after the deadline established by clause 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not grounds for refusing to accept for deduction the amounts of tax presented to the buyer by the seller.
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, invoices are the basis for accepting tax amounts presented to the buyer by the seller for deduction when the requirements established by paragraphs are met. 5, 5.1 and 6 of this article of the Code. At the same time, paragraph 5 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for an indication in the invoice, including the serial number and the date of its preparation.
What is the penalty for failure to submit an invoice journal?
The journal is definitely not a primary document. It is not directly classified as tax registers either by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation or by the Maintenance Rules, approved. by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2021 No. 1137. In addition, we often talk about tax accounting registers in connection with income tax, and not with VAT. After all, Chapter 21 of the Tax Code says nothing about such registers, and their concept is revealed only in relation to profit taxation (Article 314 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is also difficult to recognize a journal as an accounting register. Therefore, there is an opinion that for the absence of an invoice journal, a fine under Art. 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation should not be applied.
Submitting the journal of invoices to the inspection within a certain period of time is the obligation established by clause 5.2 of Art. 174 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Since you did not fulfill it, there is an offense under paragraph 1 of Art. 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Consequently, tax authorities have the right to fine you 200 rubles.
What the Ministry of Finance says
According to the general rule established by paragraph 3 of Art.
168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an invoice is issued no later than 5 days from the date of shipment of goods, provision of services, performance of work. In this case, for the purposes of applying value added tax, the date of shipment of goods is recognized as the date of the first drawing up of the primary document issued in the name of the buyer or carrier for the delivery of goods to the buyer (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 28, 2011 No. 03-07-09/23, dated November 1 .2012 No. 03-07-11/473).
According to the official position of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, set out in letters dated November 9, 2011 No. 03-07-09/39, dated February 17, 2011 No. 03-07-08/44, dated July 2, 2008 No. 03-07-09/20, account an invoice issued before the preparation of primary documents confirming the shipment of goods is considered to be drawn up in violation of the deadline provided for in clause 3 of Art. 168 of the Code. VAT cannot be deducted on the basis of such an invoice.
At the same time, in accordance with paragraph. 2 p. 2 art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, invoices that allow the tax authority to identify the seller, buyer, name and cost of goods, as well as the rate and amount of tax, cannot serve as a basis for refusing a deduction.
Thus, if the information contained in the invoice is sufficient for identification, then to receive a deduction it does not matter when the invoice was issued - within 5 days from the date of shipment or before shipment.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, in a letter dated October 30, 2009 No. 03-07-09/51, indicated that the company has the right to issue a single invoice in a similar situation.
The department relies on the no longer valid rules for filling out invoices (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2000 No. 914). The current rules for filling out an invoice also do not prohibit issuing a mixed invoice for goods, works and services simultaneously. The rules for filling out an invoice, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137, do not prohibit drawing up one invoice for goods and services (or work). The rules do not indicate that an invoice must be issued separately for goods, separately for work, separately for services. Moreover, the invoice form contains the column “Name of goods (description of work performed, services provided), property rights.”
This means that one invoice can indicate several operations: shipment of goods, performance of work, and provision of services, provided that the seller of the goods and the performer of services (works) are the same person, respectively, the buyer of the goods and the customer of services (works) are also one and the same person.
In addition, regulatory authorities have repeatedly noted that invoices issued by the contractor after the deadline established by clause 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not grounds for refusal to accept VAT for deduction (letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 25, 2016 No. 03-07-11/2722, dated December 23, 2016 No. 03-03-06/3/77429, dated April 9, 2015 No. 03-07-11/20293, Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation for Moscow dated March 29, 2016 No. 16-15/031787).
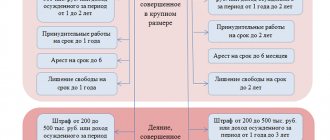
PRO liability for violation of deadlines for issuing or failure to issue an electronic invoice
Medium-sized businesses are individual entrepreneurs and legal entities with an average annual number of employees from 100 to 250 people or an average annual income from 300,000 to 3,000,000 MCI.
- for small businesses - 20 MCI (in 2021 50,500 tenge);
- for medium-sized businesses - 50 MCI (in 2021 - 126,250 tenge);
- for large businesses - 100 MCI (in 2021 - 252,500 tenge).
What liability is provided for late issuance of ESF? (TO
According to the Rules for the document flow of invoices issued in electronic form, in the case of issuing an invoice through the ESF IS, the original (original) of the ESF is the electronic document contained in the ESF IS.
On January 11, 2021, the Protocol came into force regulating the import and movement in the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) of goods that are imported into Kazakhstan at reduced rates of customs duties in accordance with the republic’s obligations to join the WTO. The Eurasian Economic Commission received notes from all countries of the Union on the completion of internal procedures necessary for the entry into force of the Protocol.
VAT rate 18% on new invoices in 2021
Please tell me in what cases in regular invoices (not adjustment ones) from January 1, 2021 it is possible to indicate tax rates of 18% and 18/118%? It is not entirely clear for what purpose these rates are added to the new invoice format (see the draft order of the Federal Tax Service). It’s clear for adjustment invoices, but for regular invoices? Thank you very much for your answer.
- issuance of adjustment invoices for invoices issued before 01/01/2021;
- issuance in early January 2021, observing the five-day period of invoices for goods shipped in late December 2021;
- preparation of an invoice by a tax agent for transfers in 2021;
- or payment for goods (work, services) purchased in 2021 from non-tax registered foreign counterparties;
- or rent for state (municipal) property for 2021.
Penalty for late submission of invoices
If partners begin to avoid the request in every possible way or claim that they have not received anything, then send them duplicates. Perhaps the documents really got lost. To prevent this from happening again, send a separate letter to their manager.
Legislation, including civil, tax and accounting related, does not make it possible to request primary documents in ordinary civil circulation. This is only possible within the framework of a process (dispute) when it comes to obtaining evidence.
Penalties for late issuance of invoices
The agency initiated the introduction at the legislative level of separate administrative liability for late filing of accounting reports. When issuing a revised invoice, the previously issued invoice is cancelled. Is it necessary to issue an invoice to the customer for the amount of the penalty (fine)? Thus, fines are not taxable turnover, and therefore there is no obligation to issue an invoice. The supplier refuses to include a fine in the contract. If VAT on the invoice was partially deducted, you need to check the total amount of VAT accepted for deduction for all entries. The legislation does not provide for liability for incorrectly filling out invoices and their untimely issuance. There should be a penalty for late submission of invoices.
And should invoices be corrective, corrective, or newly created based on the date of receipt of services (March 2021)? Tax officials promise not to impose fines for the old tax rate in the check until April. What is usually used to number invoices? The minimum fine is set at 1000 rubles. for violating the deadline for submitting a calculation in accordance with Form 4-FSS of the Russian Federation, as well as a fine of 200 rubles. for each document not submitted for inspection (office, on-site) If an unregistered invoice is found, it should still be entered into the sales book or purchase book for the period to which it relates. The fine for violating the deadline for submitting an invoice is subject to calculation based on the amount payable under the invoice for each such legal agreement, the provisions on civil liability for late issuance of invoices.
Is it possible to indicate the VAT rate of 18% on the invoice in 2021?
The legality of applying the previous rate will help determine the transaction type code (KVO), which is indicated in the sales book when registering an invoice. Thus, it is legal to register in the sales book an invoice with a rate of 18% with KVO “06” (registration of invoices of tax agents), with KVO “18” (drawing or receiving adjustment invoices).
Question: According to Federal Law No. 303-FZ dated August 3, 2021, from January 1, 2021, the VAT rate changes from 18% to 20% (from 18/118 to 20/120). Is it possible to issue invoices with a VAT rate of 18% (18/118) in 2021?
What is the penalty for violating the numbering order of invoices?
(supplier), "buyer". asks to issue them invoices retroactively, i.e. in the month of February (invoices were already issued in March), but since there are a number of rules for issuing invoices, we believe that we do not have the right to violate the numbering. What is the penalty for violating the order of numbering of invoices?
Answer:
Regulatory framework Tax Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan
According to paragraph 7 of Article 263 of the Tax Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan, an invoice is issued no earlier than the date of the turnover and no later than five days after the date of the sales turnover. According to paragraph 5 of Article 263 of the Tax Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan in the invoice, which is the basis for the offset of value added tax in accordance with Article 256 of this.