Types of piecework wages
Piece wages are a form of remuneration that is introduced with the aim of stimulating workers to produce a larger volume of production in the allotted time. In this case, the main indicator for calculating an employee’s income is the quantity of products produced (services provided, work performed).
We do not recommend establishing piecework payment in industries that require increased concentration of attention from the employee, since the pursuit of increasing the number of products produced can lead to a large number of defects.
The following types of piecework wages are distinguished:
The employer has the right to approve several remuneration systems at one enterprise for each position, department, etc. For example, for the administration - time-based, for the sales department - commission, for the production department - piece-rate bonus. See also “Time-based wage system is.”
Implementation
To make piecework payments , well-established production accounting is required, as well as compliance with commercial quality. In this case, it is necessary to develop a work evaluation system. We also need conditions for the constant operation of production, which provides regular salaries to employees.
Piecework payment is reflected in documents such as employment agreements, staffing schedules, work acceptance certificates, as well as in the Wage Regulations.
The regulation on remuneration is a regulatory document of the organization , and this document regulates the calculation of salaries, bonuses, additional payments and allowances. When a manager draws up this document, he takes into account the financial capabilities of the enterprise. At the same time, the social guarantees prescribed in the Labor Code are also taken into account.
Here you can read about salary indexation according to the Labor Code.
Direct piecework wage system
It is approved, as a rule, by production employees, for whom work standards can be set. For example, time or production standards.
In this case, earnings are calculated based on the number of products manufactured and the prices set by the employer.
The formula for calculating income is as follows:
The piece rate per unit of production can be determined in several ways, for example:
- multiplying the hourly (daily) tariff rate by the hourly (daily) time standard;
- dividing the hourly (daily) tariff rate by the hourly (daily) time standard.
Example 1
Masterok LLC has established a piecework wage system for workshop employees. For the production of one part, a rate of 1,000 rubles is provided. An employee produced 44 parts in September 2021. His earnings amounted to 44,000 rubles. (44 units × 1,000 rub.)
Such a system encourages the employee to increase the volume of output, but he is not interested in the quality of the parts produced. To motivate employees to produce products without defects, employers are introducing piecework-bonus wages.
Piece-bonus wage system
In this case, in addition to income calculated using direct piece rates, the employer pays a bonus, for example, for reducing defects, exceeding standards, and rational use of raw materials.
The formula for calculation is as follows:
Example 2
Let's continue with the following example, provided that Masterok LLC has set a bonus of 10% of the amount of income for the absence of defects in products. No defects were found in the employee's details. Therefore, he is entitled to a bonus of 4,400 rubles. (44,000 × 10%). And his monthly earnings will be 48,400 rubles. (44,000 + 4,000).
Indirect piecework wage system
This system is used to pay support staff, for example, workers who set up equipment. Their income depends on the output of key workers. This system is used to encourage support staff to provide better services to key workers.
The law does not provide for a single formula for calculating wages under an indirect piecework wage system. The employer can develop and approve its own options.
We'll look at a few possible examples.
At indirect piece rates
The formula for calculation will be as follows:
Example 4
A. M. Grigoriev works at Masterok LLC, who prepares blanks for A. Yu. Semenov for processing manufactured parts. Grigoriev’s daily rate is 1,400 rubles. Semenov’s monthly production rate is 35 parts, but in fact Semenov produced 44 parts.
Grigoriev’s indirect piece rate per shift: 1,400 rubles. / 35 children = 40 rub.
Since Semenov exceeded the plan, Grigoriev’s daily earnings increased:
40 × 44 children. = 1,760 rub.
Grigoriev worked 22 shifts in September. His income was 38,720 rubles. (22 × 1,760 rub.)
Using the average compliance rate
The formula in this case:
Calculation example
If you don’t know how to calculate piecework wages, use our example.
Salaries are calculated using the formula Z=R*number of parts per month.
An employee processes 150 parts per day. The tariff rate is 1,500 rubles. Within a month, 3,000 parts were processed.
The piecework rate can be determined by dividing the tariff rate by the standard rate for the day:
R = 1,500/150 = 10 rubles/piece
This master will receive in a month:
Z = 10 * 3,000 = 30,000 rubles
Vacation pay
According to Article 65 of the Labor Code, all workers are entitled to regular leave every year . At the same time, average earnings must be maintained. Always, with the exception of the use of general accounting of working time, the calculation is based on the average daily earnings.
Taking into account paragraph 5 of the Procedure, such earnings for calculating vacation pay are determined by dividing the salary by the sum of working days or by the number of calendar days.
For piecework wages, vacation pay will be calculated as follows:
- First you need to determine your average daily earnings . This can be done by adding up your earnings for the last three months before your vacation and dividing the resulting figure by three.
- The resulting figure must be divided by 29.4 (the average number of calendar days). The resulting number must now be multiplied by the number of vacation days.
In this article you will learn how many days in advance to write a vacation application.
Chord system of remuneration
As a rule, it is installed for individual teams if it is necessary to reduce the time required to complete the work. Employees are paid for performing a certain set (volume) of work according to a unit assignment, and not individual operations or types of work.
The entire list of works included in the chord task, their volume, time standards (production), prices, total cost and deadline for completing all work are established in advance. Payment is distributed among employees, for example, as follows: based on the time worked by each of them, in accordance with the labor participation rate.
The lump sum wage system can be used for construction work, emergency response, and repair of machinery and equipment.
Example 6
The team consists of 5 people. A contract assignment for the construction of utility premises for Sfera LLC was received in the amount of RUB 250,000. The brigade completed the task in a month. The amount of earnings was distributed in proportion to the time worked:
| Workers | Time worked | Amount to be received (RUB) | Calculation |
| 1 employee | 23 days | 59 895,83 | 250 000 / 96 × 23 |
| 2 employee | 20 days | 52 083,33 | 250 000 / 96 × 20 |
| 3 employee | 25 days | 65 104,17 | 250 000 / 96 × 25 |
| 4 employee | 18 days | 46 875,00 | 250 000 / 96 × 18 |
| 5 employee | 10 days | 26 041,67 | 250 000 / 96 × 10 |
| Total | 96 days | 250 000 |
Employees need to be paid wages at least every half month (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It is prohibited to pay the entire salary amount in one lump sum after completing the work.
With such a system, additional bonuses may be provided. The bonus is paid in accordance with the employer's bonus system (for example, for reducing the deadline for completing a task, subject to high-quality work).
Advantages and disadvantages
None of the material motivation systems used today is ideal and, in addition to positive qualities and results, creates additional negative effects that must be taken into account when using it.
The pros and cons of the piecework-bonus system are presented below in table form.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| 1. High material interest of the employee in the results of work, enhanced by the presence of additional bonuses | 1. In the presence of a complex, branched system of bonuses, it creates the need for rather complex and labor-intensive calculations. |
| 2. Significant reduction in the need for direct control over the employee’s labor behavior | 2. The introduction of the piecework component requires significant preparatory work |
| 3. The piece-rate payment system generates variable company costs, which increase or decrease depending on the volume of activity, which has a positive effect on profit levels | 3. It is advisable to implement only if there is a relatively stable volume of work in the company. |
| 4. Allows you to influence additional parameters of an employee’s work, in addition to pure labor productivity | 4. The premium component requires additional financial costs |
Examples of professions
The use of the piecework part of the piecework-bonus system largely limits the scope of its application. As a rule, this is an activity associated with performing work manually or using mechanization tools with relatively stable volumes of detail.
At the same time, the results of employees’ work should be easily measurable and it can have a direct impact on them. In particular, this is work related to the manufacture of machine parts and mechanisms, in particular, turners, milling operators, machine operators, mechanics, and assemblers.
In addition, a number of positions related to warehouse work also allow the use of a piecework-bonus system: storekeepers, loaders, forklift and stacker drivers.
In part, a piece-rate bonus system can also be considered for the commercial department involved in sales, but you need to understand that in this case it is difficult to ensure the stability of orders, and, accordingly, the employee’s earnings. Consequently, if the market situation worsens, this system will not work in this area.
It is not advisable to use this system in the field of office work, since it is focused on maintaining processes and is poorly linked to the results of the company.
For support workers who indirectly influence the production process (repairmen, adjusters), it is more convenient to use an indirect piecework system.
Commission pay
Such a remuneration system is usually used in relation to workers involved in the sale of goods and services: sales managers, store clerks, advertising and marketing specialists, in order to encourage them to increase sales volume, sell products (work, services) to the maximum volumes.
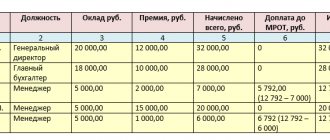
In a commission system of remuneration, earnings are determined as a percentage of sales or revenue received by the organization. At the same time, regardless of the volume of sales or revenue, the monthly earnings of an employee who has fully worked the standard working hours for a given period cannot be lower than the minimum wage (Part 3 of Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
We remind you: from January 1, 2019, the minimum wage is 11,280 rubles. And from 01/01/2020 - 12,130 rubles. Regions have the right to set their own minimum wage, but it cannot be lower than the values given above.
Salary can be calculated in various ways - it can be:
- fixed percentage of revenue;
- salary with additional payment in the form of a fixed percentage of the amount of revenue;
- a fixed percentage of the difference between the sales price and the cost of products (works, services).
Example 7
Sellers at the Severny store are paid 1% of their monthly revenue. In September, the revenue amounted to 2 million rubles. The salary of each seller was 20,000 rubles. (RUB 2,000,000 × 1%).
COMPENSATION PAYMENTS
Compensation payments are designed to compensate for work under conditions that deviate from normal conditions. Compensation payments include:
- payments to employees engaged in heavy work, work with harmful, dangerous and other special working conditions;
- for work in areas with special climatic conditions;
- for work in conditions deviating from normal (overtime, night work, combining professions, expanding service areas, increasing the volume of work or performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee without release from work specified in the employment contract, for working on weekends and non-working holidays days and when performing work in other conditions deviating from normal).
According to Art. 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, remuneration for workers engaged in work with harmful and ( or ) dangerous working conditions is established at an increased rate. The minimum increase in wages for employees engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions is 4% of the tariff rate (salary) established for various types of work with normal working conditions. The specific amounts of wage increases are established by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees.
Remuneration for work in areas with special climatic conditions is made in the manner and amounts not lower than those established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
According to Art. 150 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when an employee with a time wage performs work of various qualifications, his work is paid for work of a higher qualification .
If an employee with piecework wages performs work of various qualifications, his work is paid according to the rates of the work he performs .
IT IS IMPORTANT
In cases where, taking into account the nature of production, workers with piecework wages are entrusted with performing work that is charged below the grades assigned to them, the employer is obliged to pay them the difference between grades.
With the written consent of the employee, he may be assigned to perform, during the working day (shift), along with the work specified in the employment contract, additional work in a different or the same profession (position) for additional pay.
Payment terms are stipulated in Art. 151 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, however, the specific level of additional payment is not regulated, so the enterprise, represented by management, can independently set the amount of additional payment: both in a fixed form and as a percentage of the tariff rate or official salary.
Carrying out the work of a temporarily absent employee (business trip, sick leave, vacation, etc.) and receiving additional payment for performing work additional to the main job responsibilities can not only be temporarily transferred to one person, but also distributed among several employees.
Employees performing the duties of temporarily absent employees are recommended to establish such an additional payment so that in total it does not exceed the level of wages of the temporarily absent employee. Otherwise, the combination becomes economically infeasible.
NOTE
The working time sheet does not keep records of combined positions, therefore, to establish the actual time worked in a combined profession, data is taken from the employee’s main profession.
HR departments should carefully study job descriptions. The instructions may indicate that the deputy head of a department acts as the head of the department during his absence. In this case, additional payments are not mandatory; the final decision on them is made by the head of the enterprise.
EXAMPLE 2
Engineer Ivanov I.I. (salary - 35,000 rubles) for a full working month performed additional work to combine the position of temporarily absent engineer Petrov N.S., whose salary was set at 35,000 rubles.
For performing additional part-time work, Ivanov is given an additional payment of 30% of the official salary of engineer Petrov.
Taking into account the additional payment, Ivanov I. I.’s salary will be:
35,000 rub. + (RUB 35,000 × 30%) = RUB 45,500 .
EXAMPLE 3
Engineer Ivanov I.I. with a fixed salary of 35,000 rubles. Over the course of an incomplete working month, he performed additional work to combine the position of temporarily absent engineer N.S. Petrov with the established salary (RUB 35,000). He was hired to carry out work on the 15th.
For performing additional part-time work, Ivanov is given an additional payment of 30% of the official salary of engineer Petrov.
Additional Information:
- number of working days in a month - 22;
- the number of days actually worked in the combined position is 11 (according to the working time sheet).
Employee Ivanov I.I. will receive the following salary, taking into account additional payments:
35,000 rub. + (35,000 rub. / 22 days × 11 days × 30%) = 40,250 rub .
Overtime pay
Overtime work is paid for the first two hours of work at least one and a half times the rate, for subsequent hours - at least double the rate (Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Specific amounts of payment for overtime work can be established by a collective and labor agreement, and local regulations.
At the request of the employee, overtime work, instead of increased pay, can be compensated by providing additional rest time, but not less than the time worked overtime.
EXAMPLE 4
Mechanic Ivanov S.I. was involved in overtime work due to the temporary absence of another employee. Let's calculate the amount of wages for Ivanov, provided that the hourly tariff rate according to the enterprise tariff schedule for a mechanic is 250 rubles , and the working week is set at 40 hours with an 8-hour working day (Saturday and Sunday are days off). Ivanov S.I. is involved in working overtime for 4 hours twice per calendar month - a total of 8 working overtime hours.
Additional Information:
- number of working days in a month - 22;
- the number of hours actually worked is 184 hours , including 8 hours (data from the time sheet).
Let's calculate the salary of Ivanov S.I.
1. Wages excluding overtime:
(184 hours – 8 hours) × 250 rub. = 44,000 rub .
2. Payment for overtime work (according to the internal regulations of the enterprise and the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: the first two hours - at one and a half times; subsequent ones - at double):
(2 hours × 250 rub. × 1.5) × 2 days. + (2 hours × 250 rub. × 2) × 2 days. = 3500 rub .;
3. Amount to be charged:
44,000 rub. + 3500 rub. = 47,500 rub .
Documentation of wages under the piecework system
To record production and volumes of work performed, you can use unified forms:
- piecework work order,
- statement of work performed,
- route sheet,
- and so on.
The employer has the right to independently develop accounting forms. At the same time, it is important to comply with the requirements for primary documents approved by Art. 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”. The primary must include:
- document's name,
- Date of preparation,
- company name (full name, individual entrepreneur),
- salary calculation,
- sum,
- responsible persons of the organization,
- signatures of responsible persons.
All documents you use must be attached to the enterprise's accounting policies.