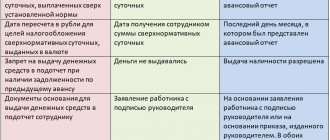
What payments are due to a business traveler?
The definition of a business trip is given in Art. 166 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is indicated that this is a trip to a remote area for a specific period, necessary to resolve a range of issues identified by the hiring company. A specialist goes to another city not of his own free will, so the costs associated with a business trip are borne by the employer.
In Art. 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation indicates what the payment for a business trip made in Russia or abroad consists of. It includes:
- reimbursement of expenses associated with travel to the destination and back (cost of transport tickets);
- compensation for the cost of a booked room, rented room or apartment;
- reimbursement of additional expenses associated with living away from home - daily allowance;
- compensation for other expenses related to the trip and incurred with the consent of the hiring company.
The last category includes expenses for visa support, purchasing an Aeroexpress ticket, taxi or car rental in a foreign city, insurance, communications, etc. These expenses must be confirmed by checks, receipts or BSO.
How travel allowances are paid is determined by the employer in local regulations. He prescribes what amount of daily allowance is due to a specialist sent on a business trip. The law sets the following limits:
- 700 rub. per day – for business trips in Russia;
- 2.5 thousand rubles. – for overseas business trips.
Amounts established within these limits are not subject to personal income tax and insurance premiums are not charged. Income tax is paid on the excess amount and deductions are made to extra-budgetary funds.
The law does not prohibit a company from setting daily allowances below the specified values or making them differentiated depending on the position held by the employee. It all depends on the financial capabilities of the commercial structure and its attitude towards its own staff.
Accrual of travel allowances in 2021
Fare
Of course, the calculator is not able to calculate the costs of a business trip, since the type of transport and class of seat are determined by the employer. It is quite possible that the internal policy of an enterprise or organization does not allow the use of business class.
Transportation costs for civil servants sent on business trips are determined by Decree No. 729 of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 2, 2002.
Payment of other expenses incurred by a business traveler during the performance of official duties while away is subject to the employer’s consent to these expenses and the expediency of these expenses.
How to calculate the amount of the advance before the trip?
The current legislation specifies how business trips are paid. It states that the employee is required to pay an advance before going on a trip. Its amount is calculated based on the following factors:
- approximate cost of travel there and back;
- the amount of daily allowance for the entire planned period of the trip;
- other expected expenses of the specialist.
The advance is paid on the basis of an estimate, which is drawn up by an authorized accounting employee and given to the chief accountant and the head of the company for signature. The issuance of travel allowances before departure can be made on the basis of an application drawn up by the employee himself and containing a calculation of expected expenses.
You can pay the advance in two ways:
- from the cash register in cash (in rubles or foreign currency depending on the country of destination);
- to a specialist’s bank card.
The organization has the right to pay individual employee expenses (for example, the cost of booking a room, plane tickets) from its current account. In this case, it deducts them from the advance amount. Failure to pay travel allowances before departure gives the specialist the legal right not to go anywhere.
Advance calculation example
The employee is sent on a business trip to Perm in the period from 16.06 to 20.06 (five calendar days). He has a hotel booked for 4 nights (room rate is 1,000 rubles per day), which must be paid on the spot. Previously, the organization bought train tickets. The company’s local regulations establish the amount of daily allowance for domestic Russian business trips – 700 rubles. in a day. How to pay for a business trip before the employee departs?
The cost of the hotel will be 1,000* 4 = 4,000 rubles.
The daily allowance will be 700 * 5 = 3,500 rubles.
Tickets have been paid for previously and are therefore not taken into account in the calculation. The amount to be issued before the employee’s departure will be: 4,000 + 3,500 = 7,500 rubles.
Calculation of travel allowances
Funds issued on account to an employee during business trips abroad can be either in Russian rubles or in the currency of the country where the employee is sent. After arrival, recalculation is made at the National Bank rate. There are also a number of nuances when traveling for different periods.
One day business trip
Since the minimum duration of a business trip is not established by law, the employer has the right to send an employee to another locality for one day. If the connection with economic activity is confirmed, such a trip is recognized as a business trip with payment for travel.
The nuances compared to the usual ones are that for a one-day business trip, daily allowances within Russia are not provided, and for an overseas trip - no more than 50% of the amounts established by local documents.
Formally, it turns out that the company cannot pay compensation without being subject to personal income tax and social contributions. The recommendation is to create a clause in internal documents that explains the employee’s lack of economic benefit, thereby avoiding personal income tax. Indirect confirmation in support of this position is the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 1, 2013 No. 03-04-07/6189.
Business trip exceeding daily allowance
An enterprise, by means of an internal administrative document, has the right to standardize the amount of daily allowance, both downward and upward. The specific amount is fixed in the employment contract with the employee and can be differentiated among employees.
For example, an employee left for a business trip on 10/05/2018 at 23.15, and arrived on 10/14/2018 at 00.45, the daily allowance according to the internal regulations is 900 rubles. Then:
- The number of days is 10, since 05.10 and 14.10 are included in the calculation.
- Daily allowance exceeding the limit: (900-700)*10=2000 rubles;
- Personal income tax: 2000*0.13=260 rubles.
In addition to personal income tax, it is necessary to accrue taxes on daily allowances in excess of the limit to social funds except for injuries, and not include them in expenses that form taxable profit.
To fully calculate travel allowances, you need to add documented expenses associated with financial and economic activities.
Rotating business trip
In practice, situations often arise when an employee goes on a business trip in one month and returns in another reporting period. If the trip goes to the next month, how to pay for the business trip, when and in what amount should it be included in expenses? Are there any restrictions on paying an advance? – questions that arise for accountants.
Example
For example, a production worker left on September 28, 2018 for a neighboring locality, and arrived on October 3, 2018 according to the order. He presented a transport ticket dated September 28 for departure in the amount of 1,500 rubles excluding VAT and dated October 3 for entry in the amount of 1,400 rubles, and a hotel bill for the amount of 5,000 rubles. On September 27, 2018, he was given an advance in the amount of 6,000 rubles in cash. The daily allowance is 500 rubles according to the employment contract. The report was submitted on October 4, 2018.
The accounting entries are shown in the table:
| date | Dt | CT | Sum | Operation |
| 27.09.2018 | 71 | 50 | 6000 rub. | An advance was issued for a business trip |
| 04.10.2018 | 20 | 71 | 500*6+1500+1400+5000=10900 rub. | Advance report approved |
| 04.10.2018 | 71 | 50 | 10900-6000=4900 rub. | Final calculation made |
Final payment for business trip
To make final payments to the employer for a business trip, the employee draws up and submits an advance report to the accounting department. He is obliged to do this within three days after arriving back. The form of the document is established by local regulations of the company: it is possible to use the unified AO-1 form or your own sample.
From the report it becomes clear how travel allowances are paid upon the trip. There are two possible outcomes: the employee will be transferred funds for the amount spent in excess of the previously issued advance or they will receive the unspent surplus from him.
The report reflects:
- name of the employer;
- Full name and position of the employee;
- destination;
- the amount of the advance received;
- list of expenses made;
- the amount of surplus (overspend).
The information from the report is documented: the compiler attaches checks, receipts, contracts and other papers, from which the amount of his expenses becomes clear. The transfer of travel allowances to the salary card is made after the submitted form is checked by the accountant and approved by the manager.
If the specialist has not retained supporting documents regarding expenses of a certain type, the question of the possibility of compensation remains at the discretion of the employing company. If she decides to cover these expenses, they will be subject to personal income tax.
How is a business trip paid in 2021: average earnings
In Art. 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that an employee sent on a business trip retains the position held in the company and the average salary (AE). To calculate the amount payable for days on a business trip (C), you must use the formula:
C = SZ* K, where
K – number of days of business trip. When calculating this indicator, the accountant is guided by the company’s work schedule. He adds:
- working days spent at the destination;
- days spent traveling there or back.
For weekends and holidays that fall during the trip, the average salary is not paid in a situation where the employee was on vacation. If these dates were devoted to resolving official issues, the remuneration is calculated in a special manner.
Paying for a business trip based on average earnings involves the following algorithm for calculating it:
NW = W/BH, where:
- Z - the total salary received by the specialist for the billing period - 12 months preceding departure on the trip. For example, if a specialist goes on a business trip in May, the accountant will carry out calculations for the period from May 1 of the previous year to April 30 of the current year.
- K – number of days worked in the billing period.
Payment for business trips in 2021 involves two possible nuances in calculating SZ:
- If a specialist is sent on a business trip in the first month after employment, the SZ is calculated for the period from the first working day to the last date before departure.
- If in the previous 12 months the specialist was on leave for employment or to care for a young child, calculations are made for the year preceding this time.
The “K” indicator includes all days when the specialist was physically present at the service. Dates when the employee was absent for any reason (vacation, time off, temporary disability, business trip, etc.) are not summed up.
To determine wages during a business trip, you need to sum up all the citizen’s income related to work (salary, allowances, bonuses). The calculation does not include social benefits (sick leave benefits), travel allowances, amounts of financial assistance, food allowances, etc.
Average earnings saved while traveling are subject to income tax and insurance contributions. In the 2-NDFL certificate it is reflected using the code “2000”.
Financing activities for sending athletes and coaches to participate in competitions
It can be carried out:
– at the expense of budgetary funds – from government institutions;
- through a subsidy for the implementation of a state (municipal) task, a subsidy for other purposes or funds from income-generating activities - from budgetary and autonomous institutions.
By virtue of Order of the Ministry of Sports and Tourism of the Russian Federation dated November 30, 2010 No. 1298/1 “On approval of the Procedure for determining standard costs for the provision by federal budgetary institutions under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Sports, Tourism and Youth Policy of the Russian Federation, public services (performance of work) and standard costs for maintaining property federal budgetary institutions" at federal institutions subordinate to the Ministry of Sports, the costs of organizing mass cultural and physical culture work are included in the costs directly related to the provision of public services.
According to the Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated June 27, 2011 No. 2070 “On approval of the Procedure for determining standard costs for the provision of public services and standard costs for maintaining the property of federal state institutions of vocational education, in respect of which the functions and powers of the founder are exercised by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation,” the costs of sports and physical culture work at educational institutions of secondary and higher vocational education are included in the standard costs for other general economic needs.
Labor Code: payment for business trips on weekends
Average earnings for weekends and holidays spent on a business trip are paid in two situations:
- If the specialist actually worked on these dates.
- If the specified days include travel time, departure to your destination or return to your hometown.
These dates include the rules on payment of overtime work formulated in Art. 153 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Salary calculations during a business trip are made in one of two options:
- The employee is not given additional rest time and is paid for the day worked at double the rate.
- The employee is given one day off and is paid in the “standard” way: in the amount of one average daily salary.
The company has the right to increase remuneration for overtime work in accordance with the provisions of local regulations. The amount due to the specialist is subject to income tax and contributions. It is shown in the 2-NDFL certificate with the code “2000”.
The procedure for paying for business trips assumes that for weekends and holidays during which the specialist was on vacation, the transfer of average daily earnings is not provided. Employee compensation is limited to per diem.