Source: Journal “Audit and inspection of financial and economic activities of state (municipal) institutions”
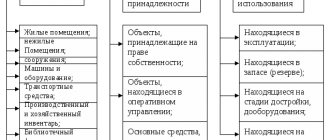
It is difficult to imagine the work of any state (municipal) institution without the use of non-financial assets, which include fixed assets, intangible assets and inventories. We will talk about what violations in accounting and in organizing the safety of such assets are revealed during inspections of the financial and economic activities of state (municipal) institutions in this article.
When checking the accounting of non-financial assets, inspectors compare the compliance of the actual results of the institution’s activities with the requirements:
- Instructions No. 157n;
- Instructions No. 174n (if the audit is carried out in relation to a budgetary institution);
- Instructions No. 162n (if the audit is carried out in relation to a government institution);
- Instructions No. 183n (if the inspection is carried out in relation to an autonomous institution);
- Accounting Law No. 402-FZ (since the period of the audit carried out in 2014 may cover 2013, 2012 and 2011, and this law came into force only on January 1, 2013, then when checking the correctness of the financial and economic activities of the institution in 2011–2012, inspectors are guided by the norms of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ “On Accounting” (hereinafter referred to as the Accounting Law No. 129-FZ);
- other documents.
As the results of the audit show, violations committed by employees of the institution when maintaining accounting records relate to non-compliance with well-known norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation. Often, in the routine of daily affairs, during which complex issues are resolved, the accountant loses sight of the little things, which then do not go unnoticed during the audit. Let us highlight some violations that are quite often committed by accountants of state (municipal) institutions.
Property inventory
Violation. When preparing annual reporting forms or when changing the head of an institution, an inventory of assets and liabilities was not made.
According to the provisions of Art. 11 of the Accounting Law No. 402-FZ, assets and liabilities are subject to inventory. During the inventory, the actual presence of the relevant objects is revealed, which is compared with the data of the accounting registers. The cases, timing and procedure for conducting an inventory, as well as the list of objects subject to inventory, are determined by the economic entity, with the exception of mandatory inventory. Mandatory inventory is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, federal and industry standards. Thus, when conducting an inventory, state (municipal) institutions are guided by the provisions of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 13, 1995 No. 49 “On approval of the Guidelines for the inventory of property and financial obligations” (hereinafter referred to as the Guidelines). Note that Art. 12 of the Accounting Law No. 129-FZ contains the same list of cases when conducting an inventory is mandatory as clause 1.5 of the Methodological Instructions .
According to clause 1.5 of the Methodological Instructions, inventory is carried out without fail in the following cases:
- when transferring the institution’s property for rent, redemption, sale, as well as in cases provided for by law during the transformation of a state or municipal unitary enterprise;
- before drawing up annual financial statements, except for property, the inventory of which was carried out no earlier than October 1 of the reporting year. An inventory of fixed assets can be carried out once every three years, and of library collections - once every five years. In areas located in the Far North and similar areas, inventory of goods, raw materials and materials can be carried out during the period of their smallest balances;
- when changing financially responsible persons (on the day of acceptance and transfer of cases);
- when establishing facts of theft or abuse, as well as damage to valuables;
- in case of natural disasters, fire, accidents or other emergencies caused by extreme conditions;
- during the liquidation (reorganization) of an organization before drawing up a liquidation (separation) balance sheet and in other cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation or regulations of the Ministry of Finance.
Thus, when drawing up annual reporting forms and when changing the head of an institution, an inventory is required.
Violation. By checking the correctness of registration and approval of the results of the inventory of fixed assets, it was established that, in violation of Methodological Instructions No. 173n for a number of objects of non-financial assets, in the inventory lists (matching sheet) for objects of non-financial assets, form 0504087, the columns reflecting the actual availability were not filled in; The correspondence of the actual availability of property with accounting data has not been verified, while the signatures of the members of the inventory commission have been affixed to the documents. Also, in the inventory lists, the composition of the inventory commission does not correspond to the composition specified in the order of the head of the institution, the start and end dates of the inventory are not indicated, the total number of units for the amount is not actually stated, and the results are not summed up. The results of the inventory, as well as the conclusion of the inventory commission, are not documented.
Methodological instructions No. 173n establish that the inventory list (matching sheet) for non-financial asset objects (hereinafter referred to as the inventory list) (f. 0504087) is used to reflect the results of the inventory of non-financial asset objects carried out in the institution. It is drawn up by the institution’s commission for financially responsible persons, indicating the location of the inventory, a receipt from the financially responsible person and reflects:
- name and code of the accounting object;
- inventory number;
- unit of measurement;
- information about the actual availability of the accounting object (price, quantity);
- accounting data (quantity, amount);
- information on inventory results (for shortages and surpluses - quantity and amount).
The inventory list (f. 0504087) is signed by the chairman and all members of the commission of the institution carrying out the inventory.
Thus, the inspectors’ comments are completely justified. The requirement for registration of inventory results is established in clause 4.1 of Methodological Instructions No. 173n . Unfortunately, such a violation can only be corrected by repeating the inventory, during which the inventory records and inventory results will be correctly completed.
Violation. During the inspection, a discrepancy was revealed between the names of fixed assets objects indicated in the inventory list compiled during the previous inventory with the names of the objects of the actually inspected property and their technical characteristics. Repeated inventory showed the presence of unaccounted for objects.
According to the norms of clause 3.3 of Methodological Instructions No. 173n , when identifying objects that have not been registered, as well as objects for which the accounting registers do not contain or contain incorrect data characterizing them, the commission must include in the inventory the correct information and technical indicators for these objects . For example, for buildings - indicate their purpose, the main materials from which they are built, volume (according to external or internal measurements), area (total usable area), number of floors (excluding basements, semi-basements, etc.), year of construction and etc.; along the canals - length, depth and width (along the bottom and surface), artificial structures, materials for fastening the bottom and slopes; for bridges - location, type of materials and main dimensions; on roads - type of road (highway, profiled), length, covering materials, width of the road surface, etc.
The assessment of unaccounted for objects identified by the inventory must be made taking into account market prices, and depreciation is determined based on the actual technical condition of the objects, with information about the assessment and depreciation recorded in the relevant acts. The requirement that unrecorded items of non-financial assets are accepted for accounting at market value, taking into account depreciation, is established by clauses 25 , 44 of Instruction No. 157n .
To correct this violation, the institution should take into account non-financial assets identified during the inventory by control authorities, determining their market value and period of use in the institution. Let us recall that according to the norms of clause 25 of Instruction No. 157n, the current market value is understood as the amount of funds that can be received as a result of the sale of these assets on the date of acceptance for accounting.
The current market value for the purpose of accepting a non-financial asset for accounting is determined on the basis of the price in effect on the date of acceptance for accounting (recording) of the property. Data on the current price must be confirmed by documents, and in cases where documentary confirmation is not possible - by expert means.
When determining the current market value for the purpose of accepting a non-financial asset for accounting purposes, the commission for the receipt and disposal of assets, created in the institution on an ongoing basis, uses: data on prices for similar material assets received in writing from manufacturing organizations; information on the price level available from state statistical bodies, as well as in the media and specialized literature; expert opinions (including experts recruited on a voluntary basis to work in the commission for the receipt and disposal of assets) on the value of individual (similar) objects of non-financial assets.
Inventory numbers
Violation. The audit showed that the institution violated the requirements of paragraph 46 of Instruction No. 157n - some fixed assets did not have inventory numbers, although their affixing was technically possible. According to the norms of this paragraph, each inventory item of real estate, as well as an inventory item of movable property, except for objects worth up to 3,000 rubles. inclusive, and objects of the library collection, regardless of their value, are assigned a unique inventory serial number (hereinafter referred to as the inventory number), regardless of whether the object is in operation, in reserve or under conservation.
The inventory number assigned to the object must be designated by the financially responsible person in the presence of an authorized member of the commission for the receipt and disposal of assets by attaching a token to it, applying paint to the accounting object or in another way that ensures the safety of the marking.
If a fixed asset object is complex (a complex of structurally articulated objects), that is, it includes separate elements (structural objects) that together form a single whole, then each such element (structural object) must be marked with an inventory number assigned to the main means (complex object, complex of structurally articulated objects).
The inventory number assigned to an object of fixed assets is retained by it for the entire period of its presence in the institution.
Inventory numbers of inventory fixed assets that have been removed from the balance sheet are not assigned to newly accepted objects for accounting.
If it is impossible to designate an inventory number on a fixed asset object in cases determined by the requirements of its operation, the inventory number assigned to it is used for accounting purposes and is reflected in the relevant accounting registers without applying it to the fixed asset object.
Placing inventory numbers on those fixed asset objects on which, according to the norms of clause 46 of Instruction No. 157n , they must be present, will eliminate this violation.
Assigning inventory numbers to fixed assets
General approaches to assigning inventory numbers to fixed assets are specified in the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 91n dated 10/13/2003 (as amended on 12/24/2010)) and Instruction No. 157n (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 12/01/2010). According to them:
- the inventory number is unique, that is, there should not be two fixed assets with the same inventory numbers,
- if the object is composite, that is, it consists of elements that make up a single whole, then all parts of the complex fixed asset are allocated one single inventory number,
- inventory numbers must be in order,
- the inventory number does not change when the location of a fixed asset object changes within the same organization,
- once an inventory number is attached to a fixed asset, it remains with it throughout the entire time it is in the organization,
- inventory numbers of fixed assets removed from balance sheet accounting are not assigned to newly accepted fixed assets for accounting,
- For a fixed asset received by an organization under a lease agreement, the same inventory number may be used that was assigned to the fixed asset by the lessor.
We put the number correctly
Typically, inventory numbers are applied directly to the object. However, there are nuances here too. First of all, it is worth specifying where exactly the number is applied. This will greatly simplify the inventory process itself, since the commission will know exactly where to look for the number and will not have to examine the object from all sides in search of the “cherished” numbers. In addition, this approach will improve the aesthetic appearance of the objects - they will look neat even after many years.
For example, you can establish a rule in your organization that the inventory number on machinery and equipment is always applied next to the factory number (easy to find; this place is protected from harmful influences). And on cabinets and bedside tables that have doors - inside, on the upper inner corner of the left door (easy to apply; less likely to be damaged during use and cleaning; visible during any rearrangement). By the same logic, on tables it is better to place the number on the inside of the leg or on the side panel.
Finally, some objects are too small to be numbered. In such cases, the number may not be applied at all, which must be noted on the inventory card. In this case, it is advisable to configure the accounting program in such a way that the accountant can quickly generate a list of such unmarked objects indicating their physical location. This will speed up the inventory process.
Inventory card
Methodological guidelines No. 173n approved a list of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for accounting of fixed assets, including an inventory card for recording a fixed asset object (form 0504031), in the section “Brief individual characteristics of the object”, in which only the main qualitative and quantitative indicators of the main object are recorded, as well as the most important extensions, fixtures and accessories related to it (two or three of the most important quality indicators for this object, excluding duplication of data from the technical documentation available in the organization for this object). As the results of the audit showed, in violation of the specified regulatory document, in some institutions there were cases when the above section was not filled out. In order to eliminate this violation, you should fill out this section of the inventory cards for recording a fixed asset item.
Our email newsletters:
New in legislation for budgetary institutionsAddress: | New in legislation for non-profit organizationsAddress: | New in legislation for government institutionsAddress: |
Budget institutions: financial and economic activitiesAddress: | Non-profit organizations: financial and economic activitiesAddress: | State institutions: financial and economic activitiesAddress: |
Accounting for property received for use
Violation. During the inventory, it was established that the institution contains property belonging to the employees of the institution, as well as property transferred for use under gratuitous use agreements. This property is not taken into account in any way by the institution. The institution violated the norms of paragraph 333 of Instruction No. 157n .
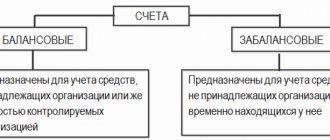
Let us recall that, according to its norms, off-balance sheet account 01 “Property received for use” takes into account objects of movable and immovable property received by the institution for free use, land plots assigned to the institution on the right of permanent (perpetual) use, as well as objects of movable and immovable property received for paid use, except for financial lease, if the property is on the balance sheet of the lessee. In addition, the received real estate is recorded on an off-balance sheet account during the time of registration of state registration of rights to it (until the moment the real estate is accepted for registration).
An object of property received by an institution from the balance sheet holder (owner) of the property is accounted for on an off-balance sheet account on the basis of an acceptance and transfer certificate (another document confirming receipt of the property and (or) the right to use it) at the cost indicated (determined) by the transferring party (owner).
Thus, property owned by employees of the institution, as well as property transferred for free use under an agreement, should be accounted for in off-balance sheet account 01. This violation can be corrected by taking such property into account. The basis document for registering the personal property of employees, as well as for deregistering it from the register, is the employee’s application. In turn, the basis document for accepting for accounting property transferred to an institution for free use is an agreement for the free use of property.
Also, in some institutions, inspectors found a violation of clause 333 of Instruction No. 157n , which resulted in non-acceptance of software products for accounting.
Let's give another example of an institution violating the norms of clause 333 of Instruction No. 157n . Under a license agreement concluded between an institution (Licensee) and an organization (Licensor), a computer program was purchased. According to the subject of the agreement, the Licensee grants the right to use the purchased program. The validity period of the agreement is determined during the validity period of the certificate - the signature key from the moment of signing by the parties. In violation of clause 333, during the validity period of the signature key certificate, the software was not listed in the institution’s accounting records in off-balance sheet account 01 “Property received for use.”
The acceptance of software products for off-balance sheet accounting will eliminate this violation and the inspectors in their act on.
How to correctly assign an inventory number
3459 Page contents The organization of accounting for any company requires strict accounting of fixed assets: the means of labor with the help of which products, work or services are produced.
One of the main mechanisms for monitoring the safety and movement of OSes is the assignment of inventory numbers to them: unique digital and symbol combinations that do not change throughout the entire operational life of the OS. When assigning an inventory number, certain techniques are used that allow you to encode in numbers and symbols all the basic information about each OS.
In addition to the operating system, inventory numbers are assigned to some other objects important for the functioning of the company.
An inventory number is assigned to a property at the time it is accepted for registration.
After this, it acquires the status of an inventory object - a control unit. The number is applied to the object using durable paint, barcode,
Accounting for property accepted for storage
Violation. During the control activities, it was revealed that the institution, in accordance with the custody agreement concluded with the LLC, accepted for storage 17 material assets (equipment for using the Internet). In violation of clause 335 of Instruction No. 157n, the above property was not assigned to off-balance sheet account 02 “Tangible assets accepted for storage.” According to the norms of clause 335, the following material assets are recorded in off-balance sheet account 02 “Material assets accepted for storage”:
- accepted by the institution for storage and processing;
- received (accepted for accounting) by the institution until they become the property of the state and (or) transfer of the specified property to the body exercising the powers of the owner in relation to the specified property (property received as a gift, ownerless property, etc.);
- confiscated in compensation for damage caused, with the exception of material assets that, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, are material evidence and are taken into account separately, material assets seized (detained) by customs authorities and not placed in a temporary storage warehouse of the customs authority.
Thus, property stored in the institution should be taken into account. In this case, the violation will be eliminated.
Inventory accounting
Violation. The institution, in violation of clause 38 of Instruction No. 157n, took into account banners on account 0 105 00 000 “Inventory”. Banners are accepted for accounting as inventory, but should be accounted for as fixed assets. Clause 38 establishes that tangible assets, regardless of their value, with a useful life of more than 12 months, intended for repeated or permanent use on the basis of operational management during the activities of the institution when it performs work, provides services, or exercises state powers (functions) or for management needs, institutions that are in operation, in reserve, on conservation, leased, leased (subleasing) are taken into account as fixed assets. Since the useful life of the banner exceeds 12 months, it must be accounted for as an item of property, plant and equipment. By making corrective entries in accordance with clause 18 of Instruction No. 157n, the institution should transfer banners from inventory items to fixed assets.
Accounting entries reflecting the acceptance of banners for accounting as inventory are reversed and additional entries are made to accept them for accounting as fixed assets. Violation. When checking the correctness of filling out waybills for the UAZ-396255 car, it was found that in some waybills, corrections were made to the speedometer readings by sticking and applying new data on mileage and fuel consumption; Not all waybills are assigned a number. Facts of discrepancies between the data of waybills and the data of the logbook for registering waybills were also established. For example, according to the waybill dated 06/09/2013 No. 350, the speedometer readings at the time of leaving the garage and when returning to the garage were 5,064 km and 5,164 km, respectively; according to the waybill registration log, the same readings were 3,245 km and 3,256 km .
Based on clause 5 of the Order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation dated March 14, 2008 No. AM-23-r “On the introduction into force of methodological recommendations “Consumption standards for fuels and lubricants in road transport” in 2011 in the institution to the basic fuel consumption rate when running in a new car UAZ-396255 a correction factor of 10% was applied. The operating manual for this vehicle sets the running-in standard at 2,500 km. However, in fact, this coefficient was applied when the mileage of the UAZ 396255 was over 2,500 km, which led to the unjustified write-off of fuel and lubricants.
Violation. As it turned out during the inspection according to the certificates of completed work, form KS-2, dismantling of pipelines from water and gas pipes, dismantling of pipelines from cast iron sewer pipes and dismantling of heating radiators by weight were carried out. In accordance with clause 23 of Instruction No. 162n , clause 34 of Instruction No. 174n , clause 34 of Instruction No. 183n , inventories remaining at the disposal of the institution as a result of dismantling and repair work are taken into account and reflected in account 0 105 00 000 " Material reserves."
Material reserves (scrap metal) obtained during the dismantling of heating and water supply systems were not recorded in the accounting accounts. As follows from the explanatory note of the deputy chief accountant, the dismantled radiators and pipes were removed as construction waste by the contractor.
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n “On approval of the Unified Chart of Accounts for public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions and Instructions for its application "
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2010 No. 174n “On approval of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of budgetary institutions and Instructions for its application.”
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 6, 2010 No. 162n “On approval of the Chart of Accounts for Budget Accounting and Instructions for its Application.”
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 23, 2010 No. 183n “On approval of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of autonomous institutions and Instructions for its application.”
- Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”.
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 15, 2010 No. 173n “On approval of forms of primary accounting documents and accounting registers used by public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions and Guidelines for their use."