Enterprises that have received the right to independently decide the issue of wages in the conditions of the formation of a market economy use different systems and models for this purpose. There is no data bank with best practices for organizing salaries.
For this reason, a large proportion of companies use the traditional tariff system in practice. What kind of system this is, its regulatory standards, pros and cons, we will consider further.
Asking is faster than reading! Write your question using the form (below), and within an hour a specialist in the field will call you back to provide a free consultation.
What is salary
First of all, let's figure out what salary is. The concept of “wages” is enshrined in the labor legislation of the Russian Federation. In simple words, wages are payment for the work of employees.
Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) states that wages are remuneration for an employee’s work depending on his qualifications, the complexity of the work itself, including compensation payments.
Based on the legislative definition, you can find out what salary depends on:
- employee qualifications;
- the nature of the activity being carried out; quality of work;
- allowances, compensation, incentives.
Salary consists of the established remuneration (salary) and compensation and incentive payments (allowances, bonuses, bonuses for length of service, etc.)
Nuances of summarized accounting: question - answer
Above we examined the general rules for maintaining summarized records of working time and their payment. Now let’s briefly answer the questions that most often arise when using CS in practice.
How to pay for night hours if they fall on a shift?
Night hours (and this, remember, is the time from 22.00 to 6.00) must be taken into account separately and paid additionally - according to the rules established for payment for work at night. This article explains exactly how.
What if the shifts fall on weekends or holidays?
Shift workers have their own days off. Therefore, the general rules about increased pay for work on days off do not apply here. But there are some nuances when it comes to changing holidays. Read about them in this article.
What to do if, at the end of the accounting period, there is a rework?
Overtime based on the results of the accounting period is overtime. For them, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also has its own rules, which also apply to shift workers. Read about these rules here.
What to do if an employee has not worked the entire accounting period?
If an employee did not fully work the accounting period (for example, was sick, was on vacation, quit), a reduced standard is calculated for him. To do this, the missed time is subtracted from the general norm. If this truncated standard is exceeded at the end of the period, overtime is paid; if, on the contrary, less time was worked, the work is paid upon the fact. The employee is not required to work hours/days missed for valid reasons.
The main differences between salary and salary
Citizens often perceive official salary as synonymous with wages. Although both of these definitions refer to the wage fund and are its components, they are completely different concepts. The official salary is a fixed amount of remuneration, which is established for the performance of labor activities in a worked calendar month. Salary is the final payment to the employee, which includes additional types of payments.
What is the difference between salary and salary:
- No additional payments, bonuses or allowances;
- The size is fixed in the individual employment contract;
- Changing the size is not allowed without the consent of the employee;
- It is permissible to set the minimum wage below the minimum wage if the total amount does not fall below the minimum wage.
Salary is included in the salary structure
The need for summarized accounting
The Labor Code establishes that a person must work in production no more than 40 hours a week. But with a shift work schedule, it is very difficult to fulfill such a requirement. One week may include more working hours, another less. Then overtime occurs, which is a violation of the law, since working more than the established time is allowed only in exceptional cases to eliminate the consequences of disasters.
In special cases, the head of an enterprise can involve employees in additional work:
- to complete certain types of work not completed during working hours;
- for urgent repairs of equipment necessary for the work of the rest of the team;
- in the absence of a shift worker at work, when stopping work is impossible.
In order to officially formalize overtime, you need to prepare an order, obtain the written consent of the employee himself, and coordinate the issue with the trade union. Next, you should keep track of processing time and pay for it separately.
Otherwise, the head of the enterprise faces big trouble in the form of charges of non-compliance with labor laws and penalties.
To engage in such work, it is necessary to increase the number of management staff on a weekly basis, which leads to unplanned costs.
To avoid breaking the law, cumulative accounting of hours worked, summed up in one period, is used. In this case, the time worked is considered a cumulative total in one accounting period.
If in one week the time worked is more than 40 hours, then in another it is necessary to provide for less work. In order to generally meet the established standard for the accounting period.
There are two ways to calculate your hourly rate. Which one to use for work, enterprises can decide independently, taking into account the advantages and disadvantages of each method. In this case, you need to build on the period selected for summing up working time.
Important! Before calculating wages by the hour, the accountant must find out what period is accepted for summing up working time in the regulatory documents of the enterprise. Typically, this issue is reflected in the wage provisions and collective agreement. And in the employment contract concluded with a citizen when applying for a job, the tariff rate for calculating wages must be indicated.
An example of determining an indicator can be done in two versions for different accounting periods. Calculating the hourly tariff rate separately for the month and year will clearly show which method is best to use in accounting for the enterprise.
Monthly calculation
Using this method, the rate is calculated for each month separately. To determine its size, you need to divide the salary (monthly rate) established for the employee by the number of working days according to the standard for a specific month. The standard can be viewed in the production calendar.
Let's consider an example when an employee's salary is 32,000 rubles. According to the norm for May 2021, 160 hours have been approved. The hourly tariff rate will be 200 rubles. If you make the same calculation for the month of March, the result will be different.
Important
The March norm is 175 hours, the hourly tariff rate is 182.86 rubles. With this method of payment, in the case when all days are worked according to the approved schedule, a salary in the amount of salary will be accrued for the month, despite the different number of working days.
But if you need to pay for overtime, then with the same hours in different months of the year, it will add up to different amounts.
Annual calculation
Totaling your work hours over the course of a year may seem more complicated. For this calculation method, it is necessary to determine the average monthly hours by dividing the annual working hours by 12 months. For 2021, the standard working time has been set at 1,973 hours, therefore, the average monthly rate will be 164.42 hours.
The hourly rate can be calculated by dividing the salary (monthly rate) by the average monthly hours. To make the example more clear, we use the same salary of 32,000 rubles, at which the tariff rate per hour will be 194.62 rubles. This calculated figure will remain constant throughout the year and will apply to any additional payments and compensation.
The employer, when approving the method for calculating the hourly rate at the enterprise, must proceed from the production schedule. Some factories only work during day shifts, while others do not stop production at night. There are employers who introduce rest hours during shifts.
It should be taken into account that for certain professions the legislation establishes special requirements. An example of such a profession is a vehicle driver. A monthly schedule should always be drawn up for him, regardless of the approved procedure for recording time worked.
An exception is allowed only for enterprises engaged in seasonal transportation. It is allowed to determine the hourly tariff rate based on semi-annual standards.
If shifts start working every other day, it is better to use an annual accounting period, as it allows you to avoid overtime.
Pay systems
Remuneration systems - a method of calculating funds, rules for remuneration of an employee, which include: the remuneration itself for work activity, incentive payments, various types of compensation.
Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that wages are set in accordance with the employer’s remuneration system. The employer has the right to choose any suitable payment system, provided that it does not contradict current legislation and labor law standards. The payment method is accepted by the employer depending on the following factors:
- Features of work;
- Employer capabilities;
- The need to motivate employees;
- Working conditions.
Let's look at some of the most common remuneration systems.
Tariff system of remuneration
The tariff system for remunerating employees is the only one enshrined in the Labor Code (Article 143 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Based on the compliance of the remuneration with the employee’s category. What does wages consist of in the tariff system:
- Tariff rate (category correspondence to coefficient);
- Official salary;
- Tariff schedule (list of categories of work);
- Tariff coefficient (the value of the coefficient depends on the rank of the tariff schedule).
The tariff schedule is common at various enterprises. For example, when applying for a job at a state-owned and unitary enterprise, you will find that each position has a corresponding salary. In this case, any differences within the same position between different employees are impossible.
Tariff-free wage system
With a tariff-free system, the amount of payments depends on each specific case. Directly depends on the amount of effort invested and the contribution of the employee himself. Includes various criteria, most often:
- The employee’s contribution to the work process;
- The complexity of the work being performed;
- The volume of tasks completed and their quality (for example, the number of products produced, transactions completed);
- Qualification level of the employee (example: level of education).
The non-tariff system is most often used when work is carried out collectively to take into account the initiative and individual contribution of each employee, which helps to increase motivation.
The tariff-free system most effectively takes into account the interests of the employee and employer
Mixed remuneration system
Already from the name you can understand that this mixed system combines the features of tariff and non-tariff. An employee's salary consists of a fixed and variable part.
- The fixed part includes the salary itself;
- The variable part is a combination of additional payments.
Additional payments can be determined, for example, by the following indicators: employee efficiency ratio; labor productivity; quality of the work result; percentage of revenue.
There are three types of mixed payment system.
- "Floating" salary. Monthly wages directly depend on the results of work activities over the same period. For example, the employee’s fulfillment of the established plan.
- Commission form. An employee’s income depends on the quantity of goods produced and sold. The commission form must include a percentage of sales volume.
- Dealer form. The employee himself ensures sales volumes, invests his funds in the goods purchased from the enterprise and is interested in selling them.
How are tariffs set for paying employees?
Personnel performing basic operations are assigned category I. It increases with the growth of the worker’s professionalism.
The tariff rate is fixed by local acts of the organization, regulations, agreements, and collective agreements. The established payment system for work must fully comply with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and the established rates must comply with the norms of ETKS, EKS, professional standards, and also not contradict state guarantees.
According to Rostrud Letter No. 1111-6-1 dated April 27, 2011, official bodies recommend establishing equal salaries for positions of the same name in the state.
Work of equal value must be paid equally (Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Other payments in excess of the tariff: allowances, incentives and others may vary for employees depending on the following points (Article 132 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- Qualifications;
- Difficulties of activity;
- Amount of labor costs;
- Quality of work.
Employee earnings also increase by the coefficients indicated in the table.
| District groups | coefficient |
| Far North: North-eastern districts Siberia (northern regions) European part (northern regions) | 1,6-2,0 1,4-1,8 1,4-1,5 |
| Areas equated to the regions of the Far North: Far East | 1,4-1,6 1,3-1,4 |
| South of the Far East and Eastern Siberia | 1,2-1,3 |
| European North (except the Far North) | 1,15-1,2 |
| Ural, south Western Siberia | 1,15 |
These coefficients are determined by government bodies by industry and separate areas of organizations.
Example #1. Payroll calculation according to the tariff system of remuneration
Accounting employee M.P. Chernygova earnings are calculated based on the daily tariff rate: 1,200 rubles/day. In addition, she is entitled to a bonus of 2,500 rubles per month. It operates in the Far East with a multiplying factor of 1.5. In August 2021, she worked 18 days out of 22 as scheduled, and was on sick leave for 4 days, the amount of which amounted to 4,054 rubles.
The employee’s earnings for August are equal to: ((1,200*18)+(2,500/22*18))*1.5+4,054=(21,600+2,045.45)*1.5+4,054= 39,522 ,18 rub.
Types of remuneration
What types of wages exist? There are only two types of remuneration: basic salary and additional salary.
- Basic payment. The wage structure is a combination of time worked, volume and quality of work;
- Additional. (Vacation, benefits, preferential payments).
Types of remuneration
Forms of remuneration
If we talk about forms of wages, there are much more of them. Form of payment - a mechanism for calculating remuneration to an employee, including accounting for the amount of work performed. Let's next look at the existing forms of remuneration.
Piecework
Piecework wages occur when a salary is calculated for the amount of work performed by employees, and does not depend on the amount of time for which it was completed. In this case, employees strive for their own improvement in productivity and quality. According to the method of calculating salaries, the following types of payments are distinguished:
- Direct piecework. The main calculation factor is the number of products produced or actions performed, which are multiplied by a certain corresponding price.
- Piecework - premium. Consists of direct piecework payment and bonus payment. The bonus may depend on various factors, for example, on exceeding the plan.
- Piecework – progressive. Exceeding the plan is paid at progressive rates.
- Chord. In the chord form, the complex of work performed is taken into account. As an example: a one-time payment to a construction team for laying tiles completed within five days.
The most common type of piecework wage is direct piecework wage.
Time wages
Time wages are calculated for the amount of time actually worked, where the result of the work itself is not taken into account. It is used in cases where the performance of work by an employee is not standardized or it is difficult to record the actions performed. The following subspecies are distinguished:
- Simple time-based form. It is calculated as the product of the tariff rate for the work performed and the amount of time worked.
- Time-based bonus. It is defined as a simple time-based form with payment of a bonus based on the results of work.
At the same time
When working part-time, an employee can work no more than four hours a day. The payment amount is not lower than the minimum wage if the employee has fulfilled the norm. However, Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 06/05/2018 N 14-0/10/B-4085 established that if the norm is not completed, it is possible to pay less than the established minimum. Labor legislation distinguishes 3 ways of working part-time:
- Based on time worked.
- According to the volume of work performed.
- Under an agreement with a part-time worker.
Any person has the right to official part-time work
In maternity leave
Pay during maternity leave is also called maternity benefits. Thus, the state compensates for lost earnings for those who go on maternity leave. Salaries are paid in full. Salary recipients on maternity leave include:
- Officially employed women;
- Military personnel (contract);
- Full-time students;
- Registered individual entrepreneurs;
- Those dismissed and declared unemployed due to the liquidation of the enterprise;
- Adopted a child.
Pregnant women have increased guarantees of labor rights
The amount of time and amount of payments varies depending on several factors:
- In standard cases, it begins 70 days before birth and 70 days after it.
- Complicated childbirth. Maternity leave is extended by 16 days.
- In case of multiple pregnancy and complicated childbirth, maternity leave lasts 194 days.
In less than a month
For an incomplete month, the employee is calculated in accordance with the established salary and the number of days worked. Weekends and holidays worked by the employee are also taken into account. Weekends or holidays do not replace wages on days when the employee was not present, that is, the calculation occurs separately. In this case, the payment amount may be lower than the established minimum wage.
This type of payment is most typical for students who work part-time. Therefore, wages are calculated for less than a full month.
Calculation of hourly tariff rates using illustrative examples
The tariff rate is a constant component of an employee’s salary, as opposed to a variable component - bonuses, compensation, allowances and additional payments.
Based on the tariff rate (salary), the salary paid to the employee for performing a certain amount of labor duties (labor standards) at a specified time is calculated. This type of payment is fixed and is the minimum guaranteed amount accrued for work. It is fixed as required by law in the employment contract, along with other conditions.
Tariff rates, depending on the time period, are divided into monthly, daily and hourly.
Calculation of the hourly tariff rate is necessary for cumulative recording of working hours.
Moreover, each employee has a work schedule and an hourly rate that he must work within a certain period of time. Schedules and standards are reflected in the production calendar.
Working time in such a schedule is measured in hours, so it is most convenient to calculate the minimum wage for labor exactly per hour.
In the event that an employee has exceeded his quota (worked more hours), it is necessary to calculate the hourly tariff rate and make appropriate additional payments.
If an employer has to pay its employees for overtime hours worked, or work on weekends, or the specifics of its activities are such that a shift schedule is required, a tariff system of remuneration should be used. With this system, various tariff rates are used, including hourly rates.
What is an hourly tariff rate and how it is calculated - this is discussed further in our article.
Tariff rate
According to Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the tariff rate is a fixed amount of remuneration for performing certain work during a unit of time, without taking into account compensation, incentives and social payments to the employee. Tariff rates can be calculated per month, day, or hour.
The monthly tariff rate (or salary) does not depend on the number of working days or hours in a particular month - the salary is always calculated in the amount of the salary if all working days of the month are fully worked. Moreover, it does not matter that there may be more working days in one month than in another, this does not affect the amount of earnings.
Advice
The daily tariff rate is applied if the length of the working day is always the same, but the number of working days in a month differs from the established norms.
[/su_box]
An hourly rate may be needed when calculating payment for hours worked is required, namely:
- to calculate earnings with a shift work schedule and summarized recording of working hours,
- to calculate wages for overtime work,
- for pay for night work,
- to calculate wages on weekends and holidays,
- to pay for work in harmful and dangerous conditions.
The cost of one hour of employee work is usually calculated in one of the following ways:
- The employee's monthly salary is divided by the standard working hours per month indicated in the production calendar.
- First, the average monthly number of working hours is determined: the standard working hours for the year (according to the production calendar) is divided into 12 months. Then, the employee’s monthly salary is divided by the resulting number.
The first calculation option has a significant drawback - the hourly tariff rate will be different in each month. When calculating using the second method, the rate will be the same for any month during the year. Let's look at this with examples.
Calculation method 1
The monthly salary of an employee is 40,000 rubles. The standard working time in March 2021, according to the production calendar, is 175 hours. In fact, he worked 183 hours, that is, overtime is 8 hours (183 - 175).
First, let's calculate the hourly tariff rate in March: 40,000 rubles. : 175 hours = 228.57 rub. at one o'clock.
(228.57 rub. x 2 hours x 1.5) (228.57 rub. x 6 hours x 2) = 3428.55 rub.
The total salary for March will be: 40,000 rubles. RUB 3,428.55 = 43,428.55 rub.
Hourly tariff rate for April: 40,000 rubles. : 160 hours = 250.00 rub. at one o'clock.
(RUB 250.00 x 2 hours x 1.5) (RUB 250.00 x 6 hours x 2) = RUB 3,750.00
Salary for April: 40,000 rubles. RUB 3,750.00 = 43,750.00 rub.
From these examples it is clear that with equal processing, its payment in months with different working hours will be different.
Calculation method 2
Let's take the conditions of the previous example and calculate the employee's salary for March and April depending on the average monthly number of working hours. The annual standard working time in 2021 is 1973.0 hours.
40,000 rub. : (1973.0 hours: 12 months) = 40,000 rub. : 164.4 hours per month = 243.41 rub. at one o'clock.
Processing in March: (243.41 rub. x 2 hours x 1.5) (243.41 rub. x 6 hours x 2) = 3651.15 rub.
Salary for March: 40,000 rubles. 3651.15 rub. = 43,651.15 rub.
note
Processing in April: (243.41 rub. x 2 hours x 1.5) (243.41 rub. x 6 hours x 2) = 3651.15 rub.
Salary for April: 40,000 rubles. 3651.15 rub. = 43,651.15 rub.
This method can be called more fair, since workers’ earnings depend only on the time they actually worked.
What the hourly wage rate should be at an enterprise, how to calculate it - each employer decides independently. Having chosen a method for calculating the tariff rate, you should definitely fix it in the regulations on remuneration.
Chn - standard number of working hours in the reporting month. To understand the principle of calculating hourly wages, it is worth using the above formula to solve a specific problem. For example, an employee’s salary is 27,000 rubles.
per month. In February 2021 there are 18 working days, and in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the duration of the pre-holiday day (February 22) is reduced by 1 hour.
These documents include: Payroll calculation under a time-based wage system. Time worked is kept in the timesheet.
Depending on the tariff applied in the time system, wage calculation will vary slightly.
25874 / 21 * 16 1202*5 = 25723.52 rubles Calculation based on the daily tariff rate Calculated using the following formula: (Daily tariff rate) * (Number of days actually worked).
no more than 36 hours a week - teachers, workers in industries with harmful and dangerous working conditions, etc.
Medical workers, depending on their position and specialty, can have a 24-, 30-, 33-, or 36-hour work week.
Let's consider 2 calculation options: for 40 and 24 hours of work per week. Example 1: 40 hours per week. Let’s say a proofreader at a publishing house works 5 days a week, 8 hours a day.
Salary - 20,000 rubles per month. Number of working hours in 2019
Tariff rates can be calculated per month, day, or hour.
[/su_box]
An hourly tariff rate may be needed when calculating payment for hours worked is required, namely: Hourly tariff rate: how to calculate The cost of one hour of an employee’s work is usually calculated in one of the following ways: The first calculation option has a significant drawback - the hourly tariff rate is in each month will be different.
In this case, you can calculate the employee’s salary using the formula: The amount due to the employee for work in the accounting period. It remains to calculate the hourly tariff rate. However, in many organizations salaries are set for employees.
And changing the wage system is not so easy. But this is not necessary. Knowing the salary, you can calculate the hourly rate by calculation.
But it has a significant drawback.
The tariff rate depends on standard working hours. Moreover, their number in one month may differ significantly from the number in another.
The hourly rate is calculated based on the average monthly number of working hours for the year.
The remaining categories are arranged depending on the increasing complexity of the work and the qualifications required for it (tariff categories), or according to the level of professional training of employees (qualification categories). The complex of all categories leaves the tariff schedule of the enterprise.
In it, each subsequent rank is several times larger than the unit rate (that is, 1 rank) - this indicator reflects the tariff coefficient.
Advice
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! The minimum wage is set by the state, and all other elements of the tariff schedule are adopted separately for each organization and are enshrined in the relevant local acts.
The exception is labor in organizations financed from the state budget, where accruals occur according to the Unified Tariff Schedule (UTS). Knowing the tariff coefficient and the size of the unit rate, you can always calculate the amount of payment due to a specific employee according to the tariff.
Example To understand the meaning of payroll according to the tariff system, it is worth considering one simple example. An employee who has recently been employed at an enterprise has a coefficient of 1, and a foreman who has worked for more than 3 years has a coefficient of 2.
The staff also benefits, receiving the amount they originally expected. The main thing is not to forget about motivating employees in the form of bonuses and incentives in order to increase productivity.
To pay funds due to specialists for work at night and overtime, on public holidays and official weekends, an hourly tariff rate is applied.
It is indispensable for calculating salaries for people who work in shifts in an organization. To determine the indicator, the accountant must use the explanations of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation.
You can make the necessary calculations on a calculator or in the 1C program.
To determine the amount of wages that an employee is entitled to, it is enough to multiply the cost of an hour of his labor by the time actually worked in the reporting period.
Positive and negative aspects of various forms of remuneration
Establishing forms of remuneration allows employees and employers to achieve a balance of interests expressed in wages. Although there are many differences between the types of wages, each has positive and negative sides. When determining the pros and cons, it should be remembered that positive and negative aspects for the employer do not always coincide with the interests of employees and vice versa.
Pros and cons of piecework payment
| pros | Minuses | |
| For employee | The employee is motivated to perform his further work functions; Possibility of earning money with a lack of qualifications; Interested in improving productivity. | Dependence on equipment, other workers, and other factors beyond his control; Uncertainty of wages; |
| For the employer | The employer may not control the amount of labor; No need to pay for time spent ineffectively; High labor productivity. | Lack of team cohesion; "Personnel turnover"; Difficulties in determining individual contribution; |
Table of pros and cons of piecework wages
Pros and cons of time payment
Pros:
- Teamwork cohesion;
- Compensation for actual time spent;
- Guarantee of payment at a certain time.
- Quite an easy way to calculate employees;
- Employees work longer in one place (No turnover);
- The workforce is easier to manage and motivate to work.
Minuses:
- When paying, effort and quality of the result are not taken into account;
- The same amount of remuneration for workers who put different efforts into performing the work;
- The salary is lower than for piecework;
- The employer has to constantly monitor employees;
- Decreased employee productivity;
- Companies spend on employee salaries, regardless of their productivity.
All forms of remuneration have both positive and negative sides
General information
The tariff system of remuneration is represented by a set of regulatory materials, thanks to which the specialists of the enterprise. The following nuances are taken into account:
- working conditions;
- complexity of the work performed;
- personal efforts of an enterprise employee in performing work functions;
- work experience of a company specialist;
- education, worker qualifications;
- features of different industries.
Tariff system of remuneration (components)
What it is
The tariff system of remuneration is a system based on the tariff system of differentiation of salaries of enterprise employees of different categories. It is characterized by an element-by-element approach to assessing the labor contribution of a specialist. The essence of the method is to set a set of parameters for assessing the labor contribution of a worker under the guise of labor cost standards, as well as a set of payment standards.
Guarantee and compensation payments are also established with payment terms. With a tariff payment system, wages are based on estimates of labor contribution, and they depend only to a small extent on the results of the enterprise’s activities.
Kinds
There are two types of tariff systems:
- Traditional , which provides for separate tariff conditions for payment of labor activity (separately for workers, separately for other categories of company employees).
- A system that provides for the unification of tariff conditions for remuneration for work for all company employees based on a common tariff schedule.
The time-based tariff system is divided into the following types:
- Piecework (salary depends on the quantity of products manufactured, work performed);
- Accord (payment is made per unit of product, a certain set of works);
- Time-based bonus (the worker receives additional remuneration);
- A simple time-based system (is remuneration according to the company’s tariff rates, salaries, and the amount of time worked).
Tariff system of remuneration (its types)
Essential elements
The main elements of the remuneration system under consideration are:
- tariff rates, salaries;
- tariff schedules;
- surcharges and allowances;
- tariff and qualification reference books.
Wherein:
- The tariff schedule is represented by a set of tariff categories of work (positions, professions), which are determined taking into account the complexity of the work, the requirements for the qualifications of a specialist through tariff coefficients.
- The tariff category is represented by a value that reflects the complexity of the work and the degree of qualification of the specialist.
- The qualification category is a value that reflects the degree of professional training of a company employee.
- Tariffication of work is the assignment of certain types of labor to tariff categories, qualification categories, taking into account the complexity of the work. The complexity of the work performed by a specialist is determined based on its tariff.
The salary under this remuneration system depends on the complexity of the work performed, conditions, intensity of labor, and the cost of labor on the labor market. The tariff rate is differentiated according to the categories of the tariff schedule. At the same time, differences in the complexity of the work are taken into account; the increase in wages increases from the first to subsequent categories.
Advantages and disadvantages
The tariff system of remuneration should be combined with the introduction of special standards aimed at assessing the labor efficiency and efforts of each specialist of the enterprise. The tariff system of remuneration is considered a very common method of calculating wages for workers of enterprises. Its advantages are:
- Transparency of payments. The worker always knows what kind of work is paid, what additional payments, compensations he will receive;
- The system takes into account the contribution of each specialist to the work and development of the company.
- Availability of a clear amount of additional payments and compensations.
- Accounting for qualifications, professionalism, and length of service of a worker.
- The ability to use numbers from the tariff schedule to calculate salaries. The manager does not need to set the salary himself.
In addition to the positive aspects, there are also disadvantages:
- Little consideration of the quality of work (focus on the qualifications of specialists working at the enterprise).
- The need for management to become familiar with many legislative acts establishing tariff rates and salary amounts. They need to closely monitor every change in legislation.
- Insignificant dependence of bonuses and additional payments on the personal labor contribution of each employee of the company.
- Formation of the salary fund by the head of the enterprise based on the tariff schedule and legislation. The actual results of work and the company's profits are not taken into account.
Regulatory regulation
According to Art. 143 of the Labor Code provides for the possibility of using a tariff system of remuneration. Tariff rates are divided into:
- normal;
- rates for heavy, hazardous work;
- rates for especially harmful, heavy work.
The tariff system of remuneration assumes a relationship between the tariff rate of a company specialist and his qualification level. Working conditions are also taken into account. This manifests itself in the form of various additional payments (additional payment for overtime work, coefficients for working in the difficult conditions of the Far North).
Legal regulation of wages is represented by a combination of the following regulations:
- negotiable _ It is carried out in the following forms: collective-negotiable, individual-negotiable. According to Art. 41 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a collective agreement may include systems, forms, amounts of remuneration, compensation, benefits, taking into account rising prices and inflation. Individual contractual regulation determines the price of labor for a specific specialist. According to Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, remuneration is considered a mandatory condition of the employment agreement;
- centralized _ Tariff rates, minimum wages, official salaries in the public sector, calculation of average earnings, wages in case of deviation from normal working conditions are determined;
- local . Local acts of the enterprise determine the wage system, the size of the tariff salary, rates, allowances, additional payments, increasing wages in conditions deviating from the norm, and the bonus system.
Still looking for an answer? It's easier to ask a lawyer! Write your question using the form (below), and our specialists will quickly prepare the best options for solving your problem and call you back on the day you submit your application. It's free!
What salary calculation formula can be used?
It's time to find out how salaries are paid. To do this, it is first important to understand the mechanism for its calculation.
- Wages and salaries are calculated in accordance with the following formula:
Formula for calculating wages based on salary
At the same time, 13% - personal income tax - is obligatory withheld from the remuneration amount.
- When calculating payment in the tariff system, use the formula:
ZP= TSch (TSdn)* Chf (DNf)
TSch (TSdn) – hourly or daily tariff rate;
Chf (DNf) – hours or days actually worked.
- In piecework payment, the formula is as follows:
ZP = SP * KP
SP – cost of production (per unit);
KP – the amount of products produced by the employee.
Salary calculation for piecework and tariff systems
What you need to know to correctly calculate wages
For correct calculation, you will need accurate data, including from your employment contract:
- The established salary or rate depending on the form of remuneration, which we considered earlier;
- Amounts of allowances (for length of service, qualification category, level of education, irregular working hours, etc.);
- Amounts of bonus payments;
- Other allowances.
What to pay attention to when making your own calculations
Savicheva Olga
Corporate accountant, practicing economist
Ask a Question
If you want to learn how to calculate your income in the form of salary yourself, pay attention to: 1. Availability of an advance (Labor legislation obliges employers to make the accrual twice a month, the amount of the advance changes depending on the change in the amount of the salary); 2. Subtraction of income tax; 3. Application of bonuses, coefficients, and other additional payments; 4. Incorrectly credited amounts are subject to refund/withholding in the next month.
Where is it used and how?
The tariff system of remuneration is very popular in Russia. It is considered quite flexible, which means it can be used in almost every enterprise.
In state-owned companies, the tariff system of remuneration is mandatory. There are special legislative acts that determine tariff rates, schedules, and allowances for civil servants.
A unified tariff schedule exists for the following industries:
- medicine;
- forestry;
- education.
If a budget organization operates in one of these areas, when calculating wages it is guided by the approved tariffs. If the salary is set less than expected, the budgetary institution may be held accountable.
Asking is faster than reading! Submit your question using the form (below) and one of our lawyers will call you back to provide a free consultation.
Factors influencing salary size
Everyone wondered what factors influence the amount of salary. There are such concepts as nominal and real wages. And the first factor influencing the size of the salary is the nominal value - the higher the nominal value, the higher the real salary. Tax rates also affect real wages. The more taxes and the higher their rates, the lower real wages are. Another factor is the price level for services and (or) goods. Real wages fall when prices and tariffs rise.
In addition to the above factors, other factors also influence the size of real wages. Article 132 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation speaks about this; it identifies the factors on which the salary of each employee depends.
Employee qualification
An employee’s qualifications are the ability to perform job duties in a particular area. Article 195.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives the following definition of qualification as the totality of an employee’s education, his skills and abilities, as well as experience in professional activities. The employee’s level of competence must be documented in a legally approved form (certificate, diploma, certificate). The qualification of workers is an entry in the work book about the assignment of a rank.
Difficulty of work
The complexity of the work is inextricably linked with qualifications, since work of a certain complexity can be performed by workers who have the appropriate specialization and professional skills. The complexity of the work includes:
- complexity of work;
- independent nature of work performance;
- additional employee responsibility.
Amount of work
In addition to time-based wages, the amount of work always affects the amount of remuneration. The amount of goods produced, operations performed, exceeding the plan - all this directly affects the amount of wages.
The amount of work performed is the most important criterion for determining the salary amount
Quality of work
Nowadays, in completely different places you can find assessments of the quality of work of an employee or an enterprise as a whole. This was done for several reasons:
- The quality of work is a general indicator of the professional level of the company;
- The level of quality of employee work allows us to effectively build a tariff system of remuneration;
- An overall assessment of the quality of work allows you to attract more clients.
Composition of infants
The minimum wage (minimum wage) determines the amount of earnings, since it is the smallest bar for establishing the size of an employee’s salary, being a means of regulating income. The minimum wage is influenced by the following factors:
- Price level by country;
- Unemployment rate;
- Workers' needs;
- Inflation rates.
The minimum wage is set at the country level and is subject to regular adjustments based on the needs of citizens in each region.
Tariffs in the budget
The wage system in the budget is established by a collective agreement, agreements, and other local acts. They must comply with the laws of the Russian Federation.
Payment in the budget until December 2008 was carried out according to the Unified Tariff Schedule. She acted on the basis of Resolution No. 785 of October 14, 1992.
| Pay grades | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Tariff coefficients | 1,00 | 1,36 | 1,59 | 1,73 | 1,82 | 2,00 | 2,27 | 2,54 | 2,91 |
continuation:
| Pay grades | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| Tariff coefficients | 3,27 | 3,68 | 4,18 | 4,73 | 5,32 | 6,00 | 6,68 | 7,41 | 8,23 |
Each employee, according to the UTS, has his own pay ratio.
The salary (tariff) of the first category must be equal to or exceed the minimum wage (see → table of minimum wages by year). The maximum size of this indicator is unlimited and depends solely on the employer’s finances.
The rates for personnel of the highest ranks are equal to the product of the level 1 rate and the skill coefficient.
Now work is paid in a new way (NSOT), this is enshrined in Resolution No. 583 of 08/05/2008. The principle of payment to public sector employees is based on data from the ETKS and EKS, state guarantees, lists of additional payments and incentives.
The size of the rates is determined in a new way by the manager, taking into account the skill of the employee, the complexity and significance of his work. The amount of earnings excluding additional payments under the NSOT should not be lower than the indicators established in the UTS for similar work.
According to the recommendations of the Russian Federation Commission dated December 25, 2015, employees of identical professional levels and positions should earn the same.
The influence of the regional coefficient on wages
The Labor Code designates the regional coefficient as a mechanism for equalizing the income of workers in different regions. The regional coefficient is established in connection with some features of the region:
- Transport options;
- Ecology of the region;
- Climate;
- Sphere of the enterprise.
Thus, in the Russian Federation, such areas include: the Far East, the East Siberian region (Southern part), the Far North and similar regions.
How to check if your salary is calculated correctly
An employee's salary is determined on the basis of a number of documents. The easiest way is to contact the company's accountant. It is the accountant who checks the correctness of salary payments to eliminate accounting errors. If payments were inflated by mistake and were not discovered within a month, then such payment is not subject to withholding in the next month. And in case of illegal understatement, the manager and the organization may be fined.
Monitoring compliance with labor legislation is carried out by the Federal Service for Labor and Employment.
How is it calculated?
The procedure for calculating wages is determined:
- Employment contract;
- Regulations on bonuses, internal regulations on allowances;
- Working time sheet;
- Compensation Regulations;
- Orders on awards and incentives.
The accrual to your account occurs as follows: initially the salary is credited, and then compensation and incentive payments. Such payments occur in separate transactions.
How to use the calculator
Instructions for using the salary calculator
- Enter the monthly salary amount, number of days worked and month for salary calculation.
- Click "CALCULATE". The result will show the total accrued salary amount, how much of the salary will be personal income tax and the amount of salary minus personal income tax.
Is something not working? Having a problem? Take advantage of feedback
A salary calculator based on salary, including for an incomplete month worked, is a convenient service designed both for officials who calculate wages and for employees themselves who want to check the accuracy of calculations.
Payroll is a series of arithmetic operations that determine how much an employee will receive. In fact, these operations are one of the most important functions of the employer, aimed at fulfilling the employment contract.
Correctness and clarity in the calculation and payment of wages is the primary condition for quiet work and minimizing labor disputes.
We have already said above that the algorithm of the calculator corresponds to the formula TS / DM × RD = ZP.
Accordingly, the calculator contains fields for entering data for each component of the formula, namely:
- field for entering the salary amount established by the employment contract;
- field for entering working days worked during a period of time;
- field for selecting the calendar month and year. You will need to select the desired month from the pop-up window.
Since the calculator also offers year selection, you can be sure that it will not miss a leap year.
After entering all the data, you will need to click the left button of the computer mouse on the “Calculate” button.
The results will appear in the three fields below and will include the amount to be accrued, the tax amount and the amount to be issued.
What are the allowances?
Allowances are payments intended to stimulate employees. Payments of bonuses are carried out so that the employee is more interested in professional development, motivated and better performs his work duties in the future.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for different types of salary bonuses
Bonuses
One type of salary supplement is a bonus. Provided for by the bonus regulations, employment contract or local regulations of the enterprise. For example, a bonus for increasing labor productivity, other achievements in the performance of labor functions.
Incentive payments and salary supplements
Such bonuses include payments that will increase the motivation of employees and encourage them to further effective professional activities.
Additional payments of a compensatory nature
Payments of this nature are those that are designed to compensate the employee for additional expenses, unfavorable working conditions, for work on weekends and holidays, traveling nature, and others.
Additional payments in the tariff system
Additional payments are used to compensate the employee for any losses in salary caused by reasons beyond his control. Bonuses encourage workers to improve their professional qualities and skills.
Some above-tariff payments are fixed in the internal documents of the organization, while others are mandatory and guaranteed by law. For example, payments for an academic degree, northern payments, for movement along a mine shaft, etc. Additional payments can be established by agreement of the parties and enshrined in the employment agreement.
Additional payments can be divided as follows:
| Payment groups | Special nature of the work | Special working conditions |
| Types of surcharges and allowances | Weekends and holidays | Dangerous and harmful conditions |
| Shift work | Intensity of work on the conveyor | |
| Overtime work | Combination of professions, substitution | |
| Dividing a work shift into parts | Night work |
According to Art. 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer has the right to independently establish the types of incentives for employees for the successes they have achieved. Additional payments are fixed in the collective agreement, charter, and regulations on discipline. Allowances for work are stimulating and depend on the business qualities of a particular employee.
How to reduce salary losses during sick leave and vacations
At best, if you are able to work, try to negotiate with your boss about remote work. If you have opened a sick leave, then payment of wages is impossible, since you will be paid sick leave payments. However, upon returning from sick leave, your bosses may, for example, give you a bonus to compensate for your work during your illness.
Remember, if your work experience is less than 1 year, the calculation of sick days will not correspond to your average salary. In practice, for 10 sick days under the specified conditions, you can receive less than 1 thousand rubles.
What about vacation? It is not profitable to take holidays as vacation, since they are not included in the calculation of vacation pay, although they increase your vacation. If you have unused vacation days, then by agreement with your boss you can take days off as vacation. Thus, non-working days will be paid.
Differences in wages in different regions
Salaries by region differ for several reasons:
- Minimum wage (For example, for 2021 the minimum wage in Moscow is 20,589 rubles, and in Sochi 12,298 rubles);
- Real estate prices (The cost of housing and its rent affect salaries in different regions, employers try to raise wages so that the employee has the opportunity to work);
- Working conditions (Example: work on a rotational basis in the north, climatic conditions of the regions, and so on).
Salary depends on the region where you work
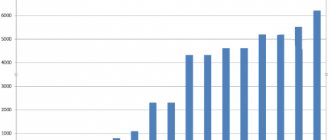
Let's look at average wages in recent years in Russia:
- For 2021, the average salary in Moscow was 135 thousand rubles.
- The average salary in St. Petersburg is 83.5 thousand rubles.
- Chukotka Autonomous Okrug - about 135 thousand rubles, Kirov region - 35.9 thousand rubles.
The highest average salary level in large cities of Russia
How to properly ask for a salary increase
How can you achieve a salary increase? Some simple tips on how to correctly ask for a raise from your boss:
- Get ready! Be confident in yourself and your price. Think about what kind of increase will be discussed, compare whether your salary really lags behind the market average.
- Give reasons why you deserve a raise and not another employee. Demonstrate your importance to the company and convince your boss of this.
- Don't try to blackmail your superiors.
- Showcase your achievements and work results.
- Try to be objective, first of all, to yourself.