Financial accounting and accounting are aimed at solving one problem - to take into account the means and results of the organization’s activities and provide complete and reliable information about the state of affairs at the enterprise to owners, managers and regulatory authorities. Both types of accounting have the same essence, meaning, subjects and objects. However, financial and accounting have differences.
Differences between financial and management accounting
Management accounting separated from financial accounting for objective reasons, in particular, under the influence of competition and the tendency to increase the scale of business. It combined partly accounting and partly operational accounting.
How does management accounting differ from financial accounting? The purposes for using management and financial accounting information are significantly different. The main goal of management accounting is to increase the efficiency of the company's business activities. Information reflected in management reporting is usually available only to internal users. The management accounting system is used by managers at various levels in their current work. This information, among other things, is necessary for making operational management decisions both for the company as a whole for a specific period, and for individual segments of activity, processes, products for different periods of time.
Management accounting is regulated according to the vision of the company itself, which increases the efficiency and versatility of the use of financial and commercial information.
Financial accounting and reporting must meet certain standards that are established and controlled by various external institutions: for example, national legislation (RAS), the International Financial Reporting Council (IFRS). Users of financial statements can be not only top managers and founders of the company, but also various creditors, investors, tax authorities, etc. These users are interested in assessing the financial position and financial results of the company (for example, investors and creditors can assess the financial stability, liquidity, creditworthiness of the company), but they do not have the opportunity to request additional reports from the company.
Financial accounting provides clearly reconciled information that is not subject to adjustment when presented in the form of official reports. Government authorities can use the information to check the payment discipline of the organization in the field of taxes and fees. Financial accounting is intended to carry out, first of all, documentation, evaluation, inventory, cost calculation, etc.
Financial and management accounting have a number of differences. The main differences include:
- Periodicity. The reporting deadlines in financial accounting are regulated by external institutions, and in management accounting they depend on the needs of internal users and are established by the company.
- Characteristics of indicators. All information in financial accounting is displayed in monetary terms, and management accounting can operate not only with monetary, but also with other indicators. They can be quantitative, qualitative, probabilistic.
- Objectivity of assessment. In financial accounting, most often, only objective data are used, while in management accounting, along with actual indicators, estimated information is also used.
- Information requirements. In management accounting, special attention is paid to the completeness, efficiency and form of provision of information, in financial accounting - to reliability and compliance with legal requirements and standards.
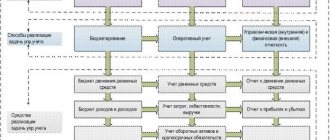
Figure 1. Fragment of the management report “Analysis of operating activities” using the example of the software product “WA: Financier”.
Final conclusions
Despite the above clearly identified differences between financial accounting and accounting, one cannot help but recognize the fact of their close similarity . Most of the information collected by financial accounting is used simultaneously in the management part of accounting. To avoid data duplication, uniform rules for collecting primary information and accounting principles are applied.
Both types of accounting are used as a tool for making clear management decisions and assessing the state of affairs at the enterprise and the correct prospects, which gives the main similarity to financial and accounting accounting.
FinanceComment
The relationship between financial and management accounting
The relationship between management and financial analysis is quite close and they have common tasks:
- ensure the target financial result of the company’s activities;
- identify internal reserves to ensure the financial stability of the company;
- determine the feasibility of business operations;
- exercise control over the availability and movement of inventory and other property;
- determine the feasibility of using resources.
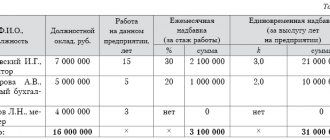
Figure 2. Fragment of financial statements according to IFRS “Statement of Financial Position” using the example of the software product “WA: Financier”.
PBU and IFRS
PBU and IFRS are accounting standards. What is the difference?
PBU is an abbreviation for “Accounting Regulations”. These are Russian accounting standards that regulate the accounting of assets, liabilities or events of economic activity. PBUs are internal documents of Russia, they are adopted by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and are valid for commercial non-banking organizations (for banks and credit organizations, the provisions adopted by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation are used).
Today there are 24 PBUs in force, all of them are mandatory for use when preparing financial statements and maintaining accounting registers.
IFRS is an abbreviation for International Financial Reporting Standards. These standards are adopted by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), located in the UK.
IFRS is mandatory for use in some European countries, as well as for almost all European companies whose securities are traded on the stock exchange.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:accounts.google.comServiceLogin
In Russia there is a program for reforming accounting in accordance with IFRS. By Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 25, 2011 No. 160n, 63 documents were put into effect in our country: the IFRS standards themselves and explanations to them.
Similarities
Both types of reporting have many points in which they are similar:
- Documentation . There is a unified regulatory framework for accounting. Controlled by the international standard IFRS or Russian RAS. It is in these documents that the principles, goals, objectives and frequency are specified. IFRS is aimed at making investment decisions of creditors and investors. Such documentation reflects the actual information and results of the policies being implemented. While RAS is created for regulatory authorities, for example, tax authorities. All accounting is provided in national currency and is primarily necessary for calculating taxes.
- Unity . In both cases, accounting objects are compiled for the organization as a whole. Very often, a large company has branches throughout the country. Less often, companies merge to stay afloat. This happens when one of them is on the verge of bankruptcy. To simplify reporting, all accounting calculations are merged into one document. Because of this, there are two types of reporting for huge corporations: consolidated (if there is a parent and subsidiary); combined (with equal cooperation between departments of the organization).
- Unit . To measure funds, first of all, cost characteristics. Cost, transportation costs, net profit. In addition, labor and natural income are taken into account. Cost, or net costs, is the money spent on the production of a product. Labor includes wages to employees, payment of utilities, storage under certain conditions. Natural – production costs, purchase of raw materials.
- Time . The compilation period is the same in both cases - historical, that is, for the past reporting period. Moreover, all calculations and figures are supported by relevant documents. These include: balance sheet (application on financial costs and results), reports on the intended use of funds. Moreover, the documentation can be submitted in a simplified or regular form. In addition, the document management process is continuous. All monetary transactions must be reflected in the company's accounts.
- Analysis . The economic activities of the enterprise are analyzed based on reports. An orderly system of recording all monetary transactions serves to make management decisions by senior management positions. The more accurately and correctly the organization’s actions are reflected in accounting, the more thoughtful decisions will be made. They contain actions on financial and economic status.
Financial statements
It includes systematization of the property situation in the organization for the accounting period. The regulatory framework is based on the federal law “On the Accounting Law” and the order of the Ministry of Finance “On the Forms of Accounting Reports of Organizations” . According to them, all transactions are carried out in the national currency, that is, in rubles.
The main goal is to summarize the data for the accounting period and present it in a visual form for further monitoring and reference. When compiling it, all divisions and subsidiaries are taken into account. For this purpose, consolidated accounting or combined accounting . This is necessary to understand the completeness of the movements of the organization’s funds in all corners. To compile them, analytical or synthetic accounting is used. The responsible persons are the chief accountant and the manager, whose signatures are used. It is important that the opening and closing balance numbers are the same.
Accounting is tied to a legal entity, but a business can consist of several legal entities
For example, one produces components, the second serves, the third sells. From an accounting point of view, mutual sales between companies of the same business are revenue in one case and expenses in the second. Of course, if this is an unofficial group of companies. And in management accounting, intragroup turnover should not be taken into account when assessing the group’s performance.
Take into account all actual income, expenses and cash flows for management accounting purposes, excluding intragroup turnover!
Financial statements
Every economic entity must introduce it. For this, either Russian standards RAS or international IFRS (IAS) can be used. It is required by the legislation of the Russian Federation, especially in large corporations. Includes three main sections: cash flow, current balance sheet, income statement. Targeted at indirect or external readers. These include investors, creditors, suppliers, buyers, and the country's tax authorities. It is historical in nature. Because it documents completed events of the past. Sometimes the prospects of the organization are considered. All information must be truthful, neutral, material (supported by documents), holistic, consistent, comparable. Also, when submitting it, it is necessary to take into account the reporting period and fill it out correctly.
When do you need a financier
At the very beginning of the business, the owner himself understands all the reports, drawing up a plan and calculating financial risks. A financier is needed when there are more operational tasks. The owner delegates them by hiring a financier. In the future, a financier may grow into a financial director.
A financier is not needed only if at the initial stage the owner himself can correctly calculate the financial model, take into account all the risks and make informed decisions. If not, hire a financier who will save the company from failure right at the start.
An accountant can become a financier and even a financial director. If you urgently need to learn new skills, it is better to take an intensive course. But quickly retraining from an accountant to a financier using lessons from Google or a 15-year-old textbook will not work.
An accountant works with yesterday's data to create today's accounting, and applies only financial data within the framework of financial standards. A financier works with a large amount of data: income and expenses, assets, liabilities, cash gap risks, in order to make forecasts. These forecasts are needed so that the owner sees trends and the business grows rapidly. For example, take out a loan in advance to pay off a key partner or allocate money for a new plant and increase turnover.
What are the differences between an accountant and a financier
| Accountant | Financier |
| Works with history - records deals and operations | Plans for the future - looks at indicators and makes predictions |
| Operates within accounting standards | Focuses on the specifics of the company and its business model |
| Maintains what is there and keeps records | Deals with risks and looks for solutions to improve business performance |
| Works only with financial data | Takes into account all the data to make correct forecasts and take into account everything that affects the business |
The positions of financier and accountant should be divided between two employees. For one person this is a big burden, and for the owner there is a risk of receiving an incorrect report and problems with the tax office. But this does not mean that the owner can delegate everything and not even understand the reports that the financial director brings him.
In order not to lose money and control over the business, entrepreneurs of the new economy must understand and understand all financial indicators, monitor the key ones and objectively evaluate the work of the financial director.
Team: Evgenia Stepanenko / Illustrator. Vlad Anisimov / editor-in-chief.
Financier
A financier manages capital; the main thing for him is business. When a company is young, the main financier is always the owner. But when the company has grown and requires more control and tasks, such as budgeting, automation of work with finances, operational plans, a financier is needed. The financier's responsibilities include:
- analysis of income and expenses;
- planning and control of budget plans;
- forecasts;
- tracking and analysis of the company’s place in the market;
- monitoring the implementation of KPIs.
A financier or financial manager works with documents and collects information about the entire company on a daily basis. For example, it is important for a financier to track production, sales numbers, and promotion strategy. This is necessary to concentrate on indicators that will show where in the business the main potential is to make a profit and increase the scale of the company. When a company already has weight in the market, evaluate the liquidity and investment attractiveness of the company, monitor changes on the stock exchanges.
For example, you went to GreenTech Amsterdam, an international exhibition of horticulture and plant growing technologies, to present your startup. And they became interested in investors who are interested in your unique technology. Your financier will calculate the absolute investment attractiveness of the startup in order to understand how profitable this deal will be.
The financier prepares indicators: liquidity, assets and liabilities and company valuation using various methods. And also, from the work of a financier, analyzes and conclusions, you can make different financial decisions. For example, whether to take out a loan or not if your company has just opened. What if you don’t last and can’t repay the loan? Where and how to invest money, enter into agreements to attract new financial resources.
On the 5th-10th of each month, the financier prepares a management report, which includes important reports for the owner: balance sheet, P&L, Cash Flow. If there are problems or risks, the financier calculates them and offers a solution. For example, you decided that it’s time for your startup to enter the international market, say, Holland. And for this, the financier analyzes how profitable it will be to expand the scale of the enterprise, what kind of loan we need to take if there is not enough equity capital.
A specialist can become a good financier even without 30 years of experience. Modern finance requires immersion in business and a creative approach, knowledge of new systems and programs for work. The financial director is the most often appointed of all top managers to the board of directors, because the profitability of the company depends on his decisions. If you want to improve your skills, understand finances, understand reports and indicators, sign up for a financial planning course from Alena Mysko.
ADVANTAGES
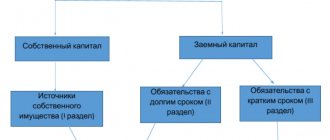
Let's consider the main advantages of management accounting over accounting (see diagram).
Compared to accounting, management accounting is more operational and more detailed. Consequently, it allows you to analyze activities in any context .
Accounting does not provide all the operational information for making management decisions. Assessing the state of affairs at an enterprise based only on accounting data is not enough.
Accounting takes into account documented, already accomplished facts of economic activity. Management accounting can work for the future, make forecasts, and evaluate the effectiveness of a transaction before it is completed.
Management accounting is not limited by legal framework, therefore each organization adapts this accounting to itself, that is, chooses accounting methods that are convenient for it. The accounting methodology must comply with the accounting regulations.
EXAMPLE
As a result of the introduction of a management accounting system , the production facility, which produces interior items, received a tangible economic effect :
- reduction of accounts receivable at the end of the year;
- optimization of accounts payable.
A similar result was achieved through control over accounts receivable, based on online registration of shipments with appropriate payment terms. Monetary discipline was also strengthened due to strict control over the validity of payments.
After the implementation of the management system, payments are made only on the basis of payment documents registered in the system that comply with contractual obligations. This made it possible to eliminate overdue advance payments and introduce limits on the payment of advances for each obligation. Result : advance payments reduced by 15%.
The introduction of management accounting made it possible to effectively manage costs, create an effective mechanism for cost planning, operational accounting tools and control of actual costs in the main production departments. Thanks to this, it can keep operational records of costs in value and physical terms, and generate standard costs for the actual volume of production. In addition, the manufacturing company received additional opportunities when planning capacity utilization and material resources.
Thanks to the implementation of the management system, the company's inventories were reduced by 15 %.