How you account for insurance costs depends on which accounting method you use (cash or accrual), as well as the type of insurance. If you use the cash method, then the accounting procedure is the same: expenses are taken into account at a time in the period in which the insurance was paid. If you use the accrual method, you must account for expenses evenly over the term of the insurance contract. At the same time, accounting for expenses for each type of insurance has its own characteristics. For example, in order to take into account the costs of voluntary health insurance, the insurance contract must be concluded for a period of at least a year. And you can include in expenses an amount not exceeding 6% of all labor costs. You can take into account the costs of compulsory property insurance within the established tariff.
How to take into account property insurance costs when calculating income tax
Expenses for property insurance for profit tax purposes are classified as other expenses (Article 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). How you account for them depends on whether you use the cash or accrual accounting method.
If you use the cash method , then take into account the costs of property insurance at a time in the period in which you paid for the insurance. In this case, the validity period of the insurance contract and the procedure for settlement with the insurer do not matter (clause 3 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If you use the accrual method, how you account for property insurance costs depends on the following conditions:
- validity period of the insurance contract (more or less than one reporting period);
- procedure for paying the insurance premium (one-time payment or installments).
If the validity period of the insurance contract is equal to or less than one reporting period, then you can take into account the costs for it at a time in the reporting period when the insurance payment was made (clause 6 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But in practice, such cases are rare, since property insurance is usually carried out for a long period.
More often there are situations when the insurance contract is valid for more than one reporting period.
If the insurance premium is paid as a one-time payment , then you must recognize this expense evenly over the reporting periods in which the insurance contract is valid. To determine the amount of expense that you can account for in each reporting period, divide the insurance premium by the number of calendar days during which the insurance contract is valid and multiply by the number of days the contract is valid in the corresponding reporting period. You will receive an expense amount proportional to the number of calendar days of validity of the insurance contract in the reporting period (clause 6 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An example of accounting for property insurance costs with a one-time payment of the insurance premium
Alpha LLC entered into a property insurance contract. Insurance premium – 100,000 rubles. Payment was made in one payment on December 29, 2017. The contract is valid from January 1 to December 31, 2021.
Reporting periods for income tax – quarter, half year, 9 months.
Alpha LLC will take into account the cost of property insurance when calculating income tax in the following amounts:
for the first quarter RUB 24,657.53. (RUB 100,000 / 365 days x 90 days);
for the half year 49,589.04 rubles. (RUB 100,000 / 365 days x 181 days);
for 9 months RUB 74,794.52. (RUB 100,000 / 365 days x 273 days);
for 2021 100,000 rub. (RUB 100,000 / 365 days x 365 days).
If the insurance premium is paid in installments , then you must determine which part of the payment relates to which insurance period (year, half-year, quarter, month). To avoid disputes with the tax authorities, it is better to stipulate this in the insurance contract.
In this case, you must take into account the costs of each payment evenly in those reporting periods that cover the insurance period for which the payment is transferred. At the same time, in order to determine the amount of expense that you can take into account in each reporting period, divide the payment by the number of calendar days in the insurance period for which the payment is transferred and multiply by the number of days the contract is valid in the corresponding reporting period. You will receive the amount of expense per number of calendar days of validity of the insurance contract in the reporting period (clause 6 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An example of accounting for property insurance costs when paying an insurance premium in installments
Alpha LLC entered into a property insurance contract for 3 years. The insurance premium is paid in installments in three payments of 150,000 rubles. every. The first payment was made on December 29, 2017. The contract is valid from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2021.
The contract states that the first payment applies to property insurance for 2021, the second - to insurance for 2021, the third - to insurance for 2021.
Reporting periods for income tax – quarter, half year, 9 months.
Alpha LLC will take into account the cost of property insurance when calculating income tax for 2021 in the following amounts:
for the first quarter RUB 36,986.30. (RUB 150,000 / 365 days x 90 days);
for the half year 74,383.56 rubles. (RUB 150,000 / 365 days x 181 days);
for 9 months RUB 112,191.78. (RUB 150,000 / 365 days x 273 days);
for 2021 RUB 150,000. (RUB 150,000 / 365 days x 365 days).
How much can you take into account the costs of voluntary property insurance for profit tax purposes?
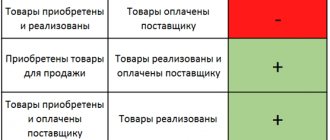
You can take into account the costs of voluntary property insurance in the amount of actual costs. But this applies only to those types of insurance that are listed in Art. 263 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
This type of insurance includes voluntary insurance:
- cargo;
- OS for production purposes;
- inventory;
- means of transport, the costs of which are included in the costs associated with production and sales (for example, comprehensive insurance);
| See also: How to take into account the costs of car insurance under comprehensive insurance in tax accounting |
- other property used by the taxpayer in activities aimed at generating income.
Expenses for voluntary property insurance not mentioned in Art. 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not taken into account when calculating income tax (clause 6 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Payers of insurance premiums
The Tax Code divides all insurance premium payers into two categories:
- Individuals who pay contributions for themselves.
- Persons who pay contributions for other individuals . These are cases when employees are hired and civil contracts are concluded with them (civil agreements, etc.).
Category 1. Individuals who pay contributions for themselves
- IP;
- persons engaged in private practice (lawyers, notaries, etc.);
- self-employed citizens, including individual entrepreneurs, paying professional income tax (PIT).
If insurance premiums are paid by an individual entrepreneur and a person engaged in private practice
Individual entrepreneurs who do not apply NAP and persons engaged in private practice pay insurance premiums in the same manner - according to the approved tariffs:
- the tariff contains a fixed part, the size of which does not depend on the amount of income;
- the contribution rate for compulsory health insurance contains a variable part.
Insurance premium rates for 2021 are determined in Art. 430 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- Mandatory pension insurance - RUB 32,448. in year. This amount is paid if the annual income is not more than 300,000 rubles. If your annual income exceeds this amount, you must pay another 1% on the excess amount. The maximum limit is RUB 259,584. per year, you won’t have to pay any more. In order to achieve this amount, you need to receive income taxable with personal income tax in the amount of 23 million rubles.
- Compulsory medical insurance - RUB 8,426. in year . The payment is fixed and is in no way related to the amount of income received.
- Compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity (for VN and M) - there is no obligation to pay.
To receive payments for VN and M, you can write an application to the FSS and voluntarily pay 4,221.24 rubles. until December 31, 2021. Full payment of this amount will allow you to receive payments from the Social Insurance Fund in 2021 upon the occurrence of an insured event, such as illness.
If insurance premiums are paid by a self-employed citizen
Self-employed citizens are a new category of entrepreneurs using NAP. The professional income tax was introduced by Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018 in 2021 and is valid in 23 regions of the Russian Federation:
- under this system, only one tax is paid at a rate of 4% when receiving income from individuals or 6% when receiving income from legal entities;
- The law gives the right to persons who have switched to NAP not to register as individual entrepreneurs.
Self-employed citizens on NAP are not required to pay insurance premiums. This also applies to persons with individual entrepreneur status. However, they can enter into relations with insurance funds on a voluntary basis.
For more information on how self-employed persons have the right to make voluntary contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, and contributions to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund, read the cheat sheet - download at the end of the article.
There is a cheat sheet at the end of the article
Category 2. Persons who pay individuals
- organizations;
- individual entrepreneurs;
- individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs (Part 1 of Article 419 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Individual entrepreneurs who are payers for themselves can also act as payers for other individuals if they are hired and make payments or under GPC agreements.
Payments and rewards included in the taxable base for insurance premiums
Payments and remunerations of compulsory medical insurance Vn and M Within the framework of labor relations Included in the base (clause 1 of Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) Under civil law contracts, the subject of which is the performance of work, provision of services Included in the base (clause 1 of Article 420 of the Tax Code RF) Not included in the database (clause 2, part 3, article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
- under agreements on the alienation (use under license agreements) of exclusive rights to the results of intellectual activity. In addition to rights to trade names, trademarks and service marks
- under publishing license agreements
- under agreements concluded with users (charged by rights management organizations on a collective basis)
Included in the database (Clause 1, Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) Not included in the database (Clause 2, Part 3, Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) Salary and other payments to prosecutors, investigators, judges Not included in the database (Clause 1, Part 3, Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) Included in the database (Clause 1, Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) Payments to full-time students for work in student groups (included in the established register) Not included in the database (Clause 1, Part 3, Art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) Included in the base (clause 1 of Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) Included in the base if carried out within the framework of labor relations (clause 1 of Article 420 and clause 2 of part 3 of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
There is no need to pay insurance premiums on payments:
- Individual entrepreneurs and persons engaged in private practice (Part 1 of Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), since they pay contributions for themselves.
- self-employed citizens paying NAP. They are generally exempt from the mandatory payment of insurance premiums (Part 1, Article 15 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ).
When making payments to self-employed citizens using the special NAP regime, you should remember that only payments for which a check has been generated in accordance with Art. 14 Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ.
Also do not fall under the NPA and, accordingly, are subject to insurance premiums:
- income received within the framework of labor relations (clause 1, part 2, article 6 of the Federal Law of November 27, 2018 No. 422-FZ);
- payments under GPC agreements, if the customer is a current employer or a person who was the employer of a self-employed person less than two years ago (clause 1, part 2, article 6 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
In order to make sure that the individual to whom the payment is made has the status of an NPA payer, you can:
- Ask this person to generate a certificate of registration as an NPA taxpayer in the “My Tax” mobile application or in the “My Tax” web account.
- You can independently obtain information on the Federal Tax Service website in the service “Check the status of a taxpayer of professional income tax (self-employed).”
Some employers want to save on insurance premiums and transfer their employees to self-employed status by creating a new legal entity for this purpose. Such schemes affect not only the interests of fund budgets, but also the workers themselves. Employers who use such a scheme bear risks. They may be held accountable not only for violating tax laws, but also labor laws.
How to take into account the costs of car insurance under comprehensive insurance in tax accounting
When calculating income tax, take into account the costs of car insurance under comprehensive insurance in the same manner as for voluntary insurance of other property.
The costs of it can be taken into account when calculating income tax only if the costs of maintaining the insured car are included in the costs associated with production and sales (clause 1, clause 1, article 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Since the validity period of a comprehensive insurance agreement is usually longer than one reporting period, expenses for it must be recognized evenly over the term of the agreement (clause 6 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What is meant by comprehensive insurance?
There is no definition of comprehensive insurance in Russian legislation.
In practice, comprehensive insurance means voluntary insurance of a car against the risks of theft and (or) damage.
What are insurance premiums and when did they arise?
Insurance contributions are mandatory payments for compulsory pension insurance, compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity, compulsory medical insurance, collected from organizations and individuals for the purpose of financial security for the implementation of the rights of insured persons to receive insurance coverage for the corresponding type compulsory social insurance (Article 8 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Compulsory social insurance is part of the state system of social protection of the population, the specificity of which is the insurance of working citizens, carried out in accordance with federal law, against possible changes in financial and (or) social status due to reaching retirement age, disability, loss of a breadwinner, illness, injury, accident at work or occupational illness, pregnancy and childbirth, the birth of a child (children), caring for a child under the age of one and a half years and other events established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on compulsory social insurance (Article 1 of the Federal Law No. 165-FZ of July 16, 1999) .
The history of insurance premiums is quite young. The emergence of social insurance was facilitated by the development of the economy and the emergence of labor relations, as a result of which employees began to need social protection. The first mentions of social insurance go back to the 19th century, at which time the Bismar Code of Imperial Laws appeared in Germany.
In Russia, a significant leap in the development of insurance was the abolition of serfdom. At this time, the first law in this area of insurance, “On the mandatory establishment of auxiliary partnerships at state-owned mining plants,” was adopted.
To ensure more progressive economic mechanisms and to regulate pension provision, the Pension Fund was created on December 22, 1990. Even before the formation of the Pension Fund, the budget was replenished from the general wage fund of organizations.
On January 1, 1991, the Social Insurance Fund was created, designed to regulate relations in the field of social insurance of citizens.
On February 24, 1993, the Health Insurance Fund was created to finance medical care.
How are the costs of car insurance under compulsory motor liability insurance reflected in tax accounting?
When calculating your income tax, take into account the costs of compulsory motor liability insurance in the same manner as for property insurance.
At the same time, since compulsory motor liability insurance is a compulsory type of insurance, when calculating income tax, you can take into account the costs of it within the established tariff (clause 2 of Article 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The maximum amounts of MTPL tariffs are established by Directive of the Bank of Russia dated September 19, 2014 N 3384-U.
What is meant by compulsory motor liability insurance?
OSAGO is compulsory civil liability insurance for vehicle owners.
The procedure for insurance under compulsory motor liability insurance is provided for by Federal Law No. 40-FZ of April 25, 2002 “On compulsory insurance of civil liability of vehicle owners.”
An example of reflecting an insurance contract in accounting
The management of the dental clinic “Dent-plus” decided to insure all employees under VHI. Payment for each insurance policy and posting was made in the period from September 28, 2019 to September 30, 2019, the total premium is 38,000 rubles.
It is necessary to write off expenses and make payments in this way at the end of each month until the contract expires.
Who is required to pay insurance premiums
The policyholder who pays wages and other payments in favor of the insured persons is obliged to pay insurance premiums (clause 1 of Article 419 of the Tax Code). The policyholder pays insurance premiums from the organization’s funds, without deducting this amount from the employee’s salary.
In this case, the insurers include:
- organizations;
- individual entrepreneurs;
- individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs.
For example, individual entrepreneurs who have employees on their staff are required to pay insurance premiums from employee payments at generally accepted rates. Please note that in addition to insurance premiums for employees, individual entrepreneurs are required to pay insurance premiums for themselves (clause 2 of Article 419 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Insurance company reporting
Since the activities of insurers are open, they are required to publish their expenses on the official website. If the client does not have the opportunity to view the financial statements of the insurance company online, he can find out about them on the Central Bank website.
Insurance company reporting allows you to find out what financial position the company is in. This is important information for customers. Insurers with an unstable position often delay payments or completely unreasonably refuse to receive insurance compensation.
REFERENCE. Concealing the insurer's reporting, as well as illegally changing the real financial condition of the company, is a violation. Having caught the insurance company in such actions, you can send a complaint to the supervisory authority.