Exemption from VAT through the use of special regimes
The best optimization of VAT is not to pay it at all. And there are such options, and there are several of them.
First of all, these are special tax regimes (Article 18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). They allow you to be exempt not only from VAT, but also from income and property taxes. Instead, one “special” tax is paid (different for each special regime), usually at a lower rate.
Most often, businessmen use the simplified taxation system (STS) and the unified tax on imputed income (UTII), because for them there are fewer restrictions on the form of doing business and types of activities.
The Unified Agricultural Tax (USAT) and the patent system (PSN) are used less frequently. The first mode, as is clear from the name, is intended only for agricultural enterprises, and only individual entrepreneurs (IP) can use the patent.
The law also provides for a number of other restrictions for all special regimes: in terms of scale (revenue, number, value of assets), composition of founders and direction of work.
For example, in order to switch to the most common regime - the simplified tax system, revenue for 9 months should be no more than 112.5 million rubles, the number of employees should be no more than 100 people, and the residual value of fixed assets should be no more than 150 million rubles. (Article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If a businessman works in different fields, then it is possible to combine the general taxation regime (OSNO) with special ones, applying them in accordance with the types of activity.
But here it should be taken into account that not all special modes can be combined with OSNO. Simultaneously with the general system, only UTII or PSN (for individual entrepreneurs) can be used.
The simplified tax system and the agricultural tax are not combined with the OSNO; only the entire enterprise (IP) can switch to them if it meets the established criteria.
Sometimes businessmen divide their company into several parts, so that each legal entity (or individual entrepreneur) individually can switch to one or another special regime.
But this method of VAT optimization is quite dangerous. Tax authorities can prove that such “fragmentation” of a business does not make economic sense and its goal is only to reduce the tax burden.
In this case, the entire group will be recognized as a single enterprise operating on OSNO, and the businessman will have to pay additional VAT, income tax and other mandatory payments corresponding to the general system. Naturally, penalties and interest will be assessed.
And if the business is large enough and the amount of arrears exceeds 5 million rubles. for three years, then a criminal case may be initiated under Art. 199 and 199.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Under these articles, a businessman can be fined up to 500 thousand rubles. or imprisoned for up to 6 years.
How to reduce VAT?
So, you are not one of the lucky ones who managed to avoid paying VAT. Then we will try to at least reduce its amount. All of the methods described below are completely legal, but require close attention to detail and proper execution in order to avoid problems with the tax authorities. How to reduce the tax burden?
Reduce your tax amount with benefits
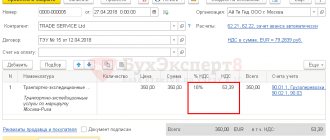
As a general rule, VAT is paid in the amount of 18 percent of the tax base. But in some cases listed in Article 164 of the Tax Code, a 10 percent rate is applied, in particular when selling certain food products, medical goods, periodicals and goods for children, as well as in the case of providing domestic air transportation services.
Make a contribution to the authorized capital of another company
The legislation does not include property contributions to authorized capital as objects of taxation. The following legal VAT reduction scheme is based on this. A company that wants to save on taxation is one of the founders of another legal entity and makes a property contribution, and then leaves the list of participants and takes the cash equivalent of its contribution.
Although the combination looks suspicious from the point of view of tax authorities, the law is not violated in this case, which is confirmed by extensive judicial practice in favor of business entities.
Create a simple partnership
This method is similar to the previous one, but the company does not make a property contribution to the authorized capital of an existing organization, but merges with other companies for temporary cooperation. A simple partnership is created to achieve a specific goal and is not subject to registration with the tax service. After the conclusion of the agreement, the organizations included in the partnership make a contribution in the form of funds or property. After some time, when the goals set for the association are achieved, the agreement is terminated. At the same time, a company that has made a property contribution to the authorized capital can receive money in return without paying VAT.
Exercise your right to deductions
As Article 171 of the Tax Code states, some categories of taxpayers can receive tax deductions, that is, reduce the amount of tax. This right is granted exclusively to companies operating on the general taxation system. To obtain a deduction, it is recommended to enter into agreements for the supply of materials and provision of services with organizations that pay VAT. It is important to correctly document the transactions so that tax authorities do not subsequently deny the deduction due to an error in the company name or identification number.
Since the beginning of 2021, there have been some changes in the application of deductions. Now this procedure cannot be used if a company (IP) purchases a product or service with funds received as a budget investment or subsidy.
In addition, the right to deduct the amount of input VAT if the share of expenses for non-taxable transactions is no more than 5 percent in the current year will be retained only by those business entities that keep separate records of it.
Replace the agreement with an agency agreement
If a standard agreement is replaced by an agency agreement, the seller acts as an agent, and in this case, VAT must be paid only on the amount of his remuneration specified in the agreement. In this scheme, advance payment for goods is made in the form of payment under an agency agreement, which is not subject to taxation. This method requires special attention to paperwork. If the tax authorities manage, using mistakes made when drawing up the agreement, to conclude that this is not an agency agreement, but a supply agreement, a fine cannot be avoided. It is necessary to issue a written order, which will contain specific tasks for the intermediary, and also prepare a report on the agent’s work.
Conclude a commission intermediary agreement
Many trading companies cooperate with business entities that use preferential tax systems (in particular, the simplified tax system) or for other reasons are exempt from VAT. In this case, there is an opportunity to significantly save on this tax. If you enter into a commission agreement with an affiliated company that pays VAT, it will charge tax only on the amount of the commission. The amount of tax that must be paid corresponds to the difference between the VAT that would have been charged upon shipment of the goods and calculated after payment of the goods to the taxpayer supplier. At the same time, when purchasing goods from contractors who are exempt from paying the tax in question, buyers pay value added tax in a significantly smaller amount than when purchasing directly without intermediaries.
Provide discounts to customers
Another way to save on VAT is by providing a trading organization with discounts to its customers on goods that have already been supplied or on services rendered. If this is provided for in advance in the contract, an adjustment invoice is drawn up. The tax base and, accordingly, the VAT itself are reduced by the amount of the discount provided. In this case, the buyer is obligated to restore part of the tax amount accepted for deduction based on the invoice.
Apply for a loan
The Civil Code provides for the possibility of introducing into an agreement on the transfer of funds or other things into the ownership of another person a condition on the provision of a loan, including in the form of installments, deferred payment, prepayment or advance payment. Upon receipt of an advance payment from the counterparty, an invoice is issued for its amount. Thus, the company confirms that it undertakes to pay VAT. However, this can be avoided if you take out an interest-free loan from your buyer in exchange for an advance payment. After receiving the goods, the amounts borrowed are returned and full payment for the delivery is made. In accordance with tax legislation, cash loan transactions are not subject to taxes. This technique should be used if the advance payment and the final payment are made in different tax periods.
It is possible to avoid charges of deliberate attempt to evade VAT, provided that the amounts of the prepayment and the loan do not match. In addition, you should not repay the loan and pay for the shipment of goods on the same day. And one more warning - you should not abuse this method of exempting the deposit from taxation by repeating the technique regularly.
Transfer the bill
You can advance the purchase of goods without having to pay VAT using a bill of exchange. According to the Tax Code, the transfer by the seller of a bill of exchange as a loan is exempt from VAT. By making a tax-deductible payment on the bill, the buyer is actually making an advance payment for the purchased item. It is important that the bill of exchange does not indicate the same date on which delivery of the goods is scheduled. After receiving the purchased product, full payment for it is made and the debt on the bill is repaid.
Agree on a deposit
An advance can be replaced not only with a loan or bill, but also with a deposit. To do this, you must enter into an appropriate agreement with the counterparty. According to the Civil Code, the amount transferred under such an agreement is not considered an advance payment, but a means of securing an obligation. And VAT is not charged on such types of payments.
Fine the buyer
Another way to reduce VAT payable is to apply a fine or penalty to the buyer for violating contractual obligations. To use this technique, when drawing up the contract, it is necessary to provide for the conditions that the buyer could violate, and indicate a fine as a sanction. This could be, for example, a violation of shipment or payment deadlines. The scheme works as follows. The buyer violates his obligations under the contract and pays a fine, which is actually an advance. Tax authorities can force you to pay VAT on the amount of the fine, but practice shows that the courts do not agree with this position and side with entrepreneurs.
Make an advance payment
In some cases, paying an advance may be useful to reduce your tax burden. You can reduce VAT if there is too much of it that the company cannot pay, or there is reason to assume that in the next tax period the amount to be deducted will be quite large. The essence of the method is that the advance payment and delivery of goods are carried out in different tax periods. When using this technique, in most cases no delivery occurs. The seller simply returns the advance to the buyer.
Other VAT exemption options
A businessman can avoid paying VAT and remain within the general tax system. But this is possible only for some special categories:
- Owners of “micro-businesses” with revenues of up to 2 million rubles. per quarter. At the same time, you cannot trade excisable goods (clauses 1, 3 of Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
- Participants of the Skolkovo project (Article 145.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The law also provides for exemption from VAT for certain types of goods and services listed in Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Such preferential categories include, for example:
- Socially significant goods and services (medicine, care for children and disabled people, urban and suburban passenger transport).
- Services in the field of culture and art.
- Financial services (including insurance and banking)
- R&D services.
If a businessman sells both taxable and non-taxable goods (services), then he must keep separate records.
How to get a benefit?
To take advantage of the benefit, a package of documents is sent to the Federal Tax Service by the 20th. For example, if you are planning a transition from October 2021, then by October 20 you send three documents to the Federal Tax Service:
- Notification of transition;
- Extract from the sales book for 3 months (August, September, October);
- Extract from the balance sheet.
The notification is issued in the approved form. The package is reviewed quite quickly, but keep the situation under control. Call the inspector and make sure that they received everything and that the documents were filled out without errors. The tax office will respond with a notification that the transition has been approved.
Work under the new scheme lasts a year, then it needs to be extended. But if revenue for 3 consecutive months becomes more than 2 million, then the company returns to the obligation to pay VAT. You can come back with a new statement and evidence that revenue has returned to previous levels.
After receiving the benefit, the company is exempt from paying VAT and filing a declaration. But you will still have to issue invoices (with a note that without VAT) and keep a sales book. The latter will be requested by the Federal Tax Service during the inspection, so take it seriously.
Preferential rates
A preferential rate of 10% is provided for the following groups of goods and services (clause 2 of article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Food products (except delicacies).
- Children's clothing and school supplies.
- Periodicals (except advertising and erotic).
- Medicines and medical products.
- Domestic air transport.
The “zero” preferential VAT rate is applied primarily for goods sold for export, as well as for international transportation services (clause 1 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It should be noted that the 0% rate is not an exemption from VAT. A businessman must issue invoices, submit declarations and perform other duties provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for the payer of this tax.
The good news for beneficiaries is that the increase in the VAT rate by 2 percentage points from 01/01/2019 did not affect them in any way. Rates of 0% and 10% for the listed groups of goods and services correspond to the 2021 level.
Deferment of advances
As you know, VAT is also paid on advances received. Therefore, if, for example, a supply contract is concluded at the end of the quarter, the seller can agree with the buyer to transfer the advance payment to the beginning of the next tax period. The tax, of course, will still have to be paid, but at the end of the next quarter, i.e. - three months later.
You can “defer” the payment of VAT for a longer period if you use borrowed funds. In this case, the buyer issues a loan to the seller in the amount of the advance. Then, after shipment, the debts on the loan and for the sold products are offset.
Because the issuance of a loan is not subject to VAT, the tax is charged only at the time of sale.
Formally, this scheme complies with the law, but in practice there is a high risk of disputes with tax authorities. It is hardly suitable for use on an ongoing basis, because... inspectors can easily prove that numerous loans and offsets are sham transactions.
But for one-time shipments, you can try to use it if you correctly prepare all the documents justifying the business purpose of this particular calculation scheme.
In addition, with any options for deferring the advance payment, one should not forget about the balance of interests of the seller and the buyer. The fact is that the buyer, when transferring an advance payment, uses the amount of VAT from it for deduction. Therefore, he cannot always agree to postpone the payment deadline or issue a loan.
Is it always necessary to optimize?
Exemption from VAT is not always a plus for a businessman. After all, if the seller does not charge VAT, then the buyer, accordingly, cannot submit the tax for reimbursement.
Therefore, if the main consumers of products or services are large companies, then working without VAT significantly reduces the competitiveness of a businessman. The loss of one or more key customers may result in losses that exceed the savings from the VAT exemption.
This approach also has a downside. Most businessmen act on the market not only as sellers, but also as buyers of goods or services.
Therefore, if you pay VAT, then you must also choose suppliers from among its payers. Purchasing from those who do not allocate VAT is advisable only if they provide a discount from the average market price comparable to the rate of this tax, i.e. 20%.
A situation is possible when a company sells both VAT-taxable and non-VAT-taxable goods and services. In this case, in order not to pay tax on “preferential” sales, you need to keep separate records. But if non-taxable sales constitute an insignificant share of revenue, then the costs of separating accounting may exceed the savings on VAT.
Features of the benefit
Two important points when switching to benefits:
- Buyers and clients cannot deduct VAT from transactions with your company. It doesn't matter if they work in a simplified manner. But if they have OSN, then there may be problems with the profitability of working with you.
- You cannot deduct VAT from incoming invoices during the exemption period and even after it ends.
Not charging or accepting VAT is still more profitable than charging and deducting. Just don't make any mistakes when planning.