Determination of the tax base
The section of the legislation of the Russian Federation devoted to taxation interprets in detail the concept of tax and all its elements. These issues are addressed in Article 8 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A tax is a mandatory fee established by the state for organizations and individuals, which provides for the contribution of a portion of their financial resources intended for the state budget.
Tax base is an element of tax that functions along with others:
- subject and object;
- rate;
- accounting tax period;
- method of accrual;
- features and timing of tax payments;
- possible benefits.
What is the tax base
The tax base characterizes the item subject to taxation in terms of quantity, value, physical properties or other characteristics. In other words, the tax base defines the units in which the object of taxation can be “measured.” the object of taxation is .
The item on which the tax is levied is called its object. It can be represented by various assets and financial amounts, for example:
- income, receipts, profit;
- cost of goods sold;
- payment received for services rendered or work performed;
- total income of an individual;
- own property owned by organizations and citizens;
- hereditary mass;
- vehicles, etc.
NOTE! Most often, the name of the tax reflects precisely its object: “income tax”, “land tax”, etc.
So, we conclude: the item on which tax must be paid is considered an object of taxation, and the tax base is its significant characteristic.
How does the tax base affect the amount of tax?
Any payer is primarily concerned with the question: “Exactly how much will I need to pay?” The concept of the tax base coupled with the application of the tax rate is designed to answer this.
The amount of tax paid is the product of the tax base and the tax rate.
The tax base regulates the units in which the tax is calculated, and the tax rate , in turn, shows what proportion of these units must be allocated to the state. This relationship can be of two types:
- firm - the absolute amount for each unit of the tax base (more often used when calculating taxes, the base of which allows you to assign a fixed amount to each characteristic of the tax base, for example, transport, excise, land taxes);
- interest – one or another percentage of the entire quantitative expression of the tax base is subject to payment.
Types of interest rates
Depending on how the tax percentage is set, interest rates can be of different types:
- proportional - the same percentage is always deducted from the tax base as tax (examples - income tax, VAT);
- progressive - the higher the tax base, the greater the deductible percentage will be, and both the entire base and its individual parts can be taken into account (the modern Russian Tax Code does not apply rates of this type);
- regressive - the lower the tax base, the more the tax percentage will decrease.
Personal taxes
It will not be superfluous for anyone to know how the tax is calculated correctly. Let's look at the most common types of fees.
Transport tax
The procedure for calculating road tax on motor vehicles is determined by Article 362 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and regional laws. In cases where the regional authorities have not established reporting periods for this fee, the tax is calculated and paid for the calendar year. In this case, the annual amount is calculated by multiplying the base by the rate.
The tax base for a vehicle is the horsepower of its engine.
The rate also depends on this indicator. If it is not defined by regional legislation, deductions are calculated at the rates specified in paragraph 1 of Article 361 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The values for passenger cars are given in the table:
| Passenger cars with engine power (per horsepower) | |
| up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 2,5 |
| over 100 hp up to 150 hp (over 73.55 kW to 110.33 kW) inclusive | 3,5 |
| over 150 hp up to 200 hp (over 110.33 kW to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 5 |
| over 200 hp up to 250 hp (over 147.1 kW to 183.9 kW) inclusive | 7,5 |
| over 250 hp (over 183.9 kW) | 15 |
Property tax
For physical For persons, the calculation according to the basic formula (property tax = property value x tax rate) is carried out by the Federal Tax Service. Real estate is taxed according to the cadastral value at the beginning of the year. If it is in common shared ownership, each co-owner pays an amount in proportion to his share.
The tax rate depends on which category the property belongs to. For example, the deduction for residential premises in most cases is 0.1% of the cadastral value. The rates are given in Article 406 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Land tax
Very schematically, the amount of land tax is calculated according to the formula: land tax = (tax rate x tax base). Moreover, the tax rate cannot be more than:
- 0.3% - for agricultural land. purpose, housing plots provided for individual housing construction and personal subsidiary plots;
- 1.5% - for other land holdings. The amount is set by local authorities.
The tax base is the cadastral value of the plot at the beginning of the reporting year. The easiest way to find it out is on the Rosreestr website. In practice, when calculating land tax, both the ownership time coefficient (if it is not equal to a full 12 months in the reporting year) and the increasing coefficient (if the site is planned for housing construction) are often taken into account.
Plots in shared ownership are paid by co-owners in proportion to their share. The tax office calculates the tax for an individual and notifies the payer of this before November 1 of the year following the reporting year.
Below we will consider two questions that are of interest to all categories of taxpayers:
- how to use online tax calculators;
- How is the penalty for late payment calculated?
All this can greatly facilitate the process of independent calculations for you.
Elements that reduce the tax base
Naturally, for the taxpayer, from a financial point of view, it is more profitable for the tax base to be as small as possible, then a smaller amount of taxes will be paid from it. The law allows you to reduce the amount to be multiplied by the tax rate by the following economic values:
- tax deductions – it is allowed not to include categories of amounts specified by law in the taxable amount (these include standard deductions, pension, charitable, “children’s” and some others);
- tax benefits - financial advantages for certain categories established by the Government (lower tax amount, reduction of the tax rate, establishment of a minimum that is not subject to taxation, complete abolition of payment of a particular tax).
So, if we express the tax base as a formula, it will look like this:
NB = SD – V – L
Where:
- NB – tax base;
- B – tax deductions provided for by law and applicable to a given taxpayer;
- L – tax benefits valid for a given tax and category of payers.
A few words about deductions and their impact on the National Bank
Deductions that are prescribed by government agencies or the individual himself are not deducted from the National Bank for personal income tax. Such payments include alimony, credit, utility bills and other services.
What to do with multiple personal income tax rates
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if you have several bets, then the NB is calculated separately for each of them. With equity participation, the NB is determined separately from income, the rate for which is 13%.
Persons exempt from taxation:
- those who received benefits from the state (unemployment, maternity and pregnancy);
- pensioners and those receiving social benefits;
- students;
- who received maternity capital or inheritance.
Personal income tax rate
| 13 % | Rate for residents of the Russian Federation working under employment contracts. This category also includes migrants, employees from the Eurasian Economic Union and highly qualified non-residents. |
| 35 % | For winnings, prize funds received through participation in games, lotteries and other competitions. This category also includes advertising revenue. Only funds over 4 thousand rubles are taxed. |
| 30 % | Rate for non-residents of the Russian Federation. This also applies to other incomes of highly qualified specialists and former migrants. |
How is the personal income tax rate calculated for non-residents who have become residents of the Russian Federation?
As indicated in the table above, rates for residents of the Russian Federation are comparatively lower than for non-residents. However, often the latter receive permanent residence status after six months, in which case it is necessary to recalculate the rate. For accuracy, it is necessary to clearly distinguish between the periods of being in the status of resident and non-resident.
Formula for calculating personal income tax
To get the amount of income tax, you must first subtract tax deductions from the NB (total income), and then multiply the resulting amount by the rate.
For example, for residents of the Russian Federation this formula will look like this:
(Cash income + material benefits + benefits in kind - tax deductions) * 13%.
Domestic principles for calculating the tax base
In modern Russian legislation, the tax base meets the following mandatory requirements.
- All issues related to the method of determining and the procedure for establishing the tax base are regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Each accounting period is reflected in the financial documentation maintained by the taxpayer, and on the basis of these documentary evidence, the quantitative characteristics of the tax base are calculated at the end of each individual period.
- If in the current period an error was found in the calculation of the tax base relating to an already expired period of time, it is necessary to recalculate the tax base of the “erroneous” period.
- If the period in which the error was made cannot be accurately determined, it will be necessary to recalculate the tax base at the present time, that is, in the reporting period.
- The procedure for calculating the tax base is determined by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. Accounting for profits and costs based on business results for the required period reflected in the financial documentation should be kept by:
- individual entrepreneurs;
- organizations;
- tax agents.
- Individual taxpayers take as the basis for calculating the tax base their own profit accounting data, as well as information received from the other party - the counterparty of their activities (organization, other individual).
Methods for accounting for the tax base
Russian tax legislation provides two methods for accounting for the tax base.
- Cash - only those amounts of profits or expenses are taken into account that are actually reflected in certain documentation as received (or incurred) by the tax payer. These may be funds received to the current account, reflected using cash register equipment, etc.
- Cumulative – the moment at which the taxpayer acquired property rights or obligations is taken into account. It does not matter whether the funds were actually received (spent): if the taxpayer has the right to receive them (or the obligation to spend them), the funds are included in the calculation as part of the tax base.
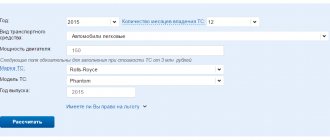
Online calculators for tax calculations
The easiest way to calculate the tax amount is using special online calculators offered by a number of relevant websites. With their help, you can calculate the amount of the most common tax fees.
Such services allow you to simply, remotely and, as a rule, free of charge, insure yourself against possible mistakes in financial relations with the state, and control your calculations or data received in a notification from the tax office.
Naturally, you cannot trust every similar service found on the Internet. It is better to first look for those that are either presented on the official website of the Federal Tax Service or have a long positive history.