Fixed payments of individual entrepreneurs for themselves in 2021: new terms, kbk and other details
The deadline for payment of the fixed payment to individual entrepreneurs for 2021 is no later than December 31, 2018, according to the requirements of the Tax Code. But since it is a day off, the deadline is postponed to the first working day of 2021. As soon as the Government approves the schedule for postponing holidays and weekends, we will confirm the exact date. Individual entrepreneurs must transfer an additional contribution from income over 300 thousand rubles in 2021 for 2021 no later than 07/02/2018. And for the period 2021 - no later than 07/01/2019.
In 2021, in addition to taxes, individual entrepreneurs also transfer insurance payments for themselves in a fixed amount.
Now the size of the entrepreneurial contribution does not depend on the minimum wage. This applies to contributions to the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, which are transferred to the Federal Tax Service. How to calculate deductions in a new way if income exceeds the limit of 300,000 rubles, in the second change.
Main conclusions
Next, let’s summarize all of the above and tabulate the amounts of insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs “for themselves” from 2021 and focus on the main changes:
| RUR 26,545 – mandatory amount of fixed pension contributions from 2021. From 2021 it will be indexed. |
| 5840 rub. – mandatory amount of fixed medical contributions from 2021. From 2021 it will be indexed. |
| From 2021, the maximum amount of contributions to the Pension Fund budget is 212,360 rubles. |
| From 2021, pension and medical contributions are no longer “tied” to the minimum wage. |
Fixed personal payment for entrepreneurs 2018. Contributions to the Pension Fund
The procedure is such that entrepreneurs are obliged to regularly calculate contributions to the Pension Fund and other funds for themselves (Article 430 of the Tax Code), as well as from all remunerations and cash payments made during the employment relationship in favor of their employees, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 419 NK.
The minimum wage increased from 7800 to 9489 rubles. from 01/01/2018 And starting from the new year 2019, legislators want to equate it to the subsistence level, that is, employers’ payments to the funds increase every year. A fixed payment, even if such an effect is not particularly noticeable so far, is aimed at reducing taxpayer costs. It will be established by decision of the Government in different amounts, with an annual increase.
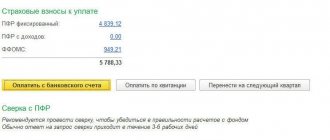
Contributions of individual entrepreneurs to funds for themselves in 2021. amounted to:
RUB 26,545 – compulsory pension insurance; additional contribution from the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation - 1 percent of the amount exceeding the total income of the individual entrepreneur of 300 thousand rubles. in the current year; 5840 rub. - health insurance. The pension fund has established a maximum payment amount per year. Bill No. 274631-7 of the Government of the Russian Federation limits it to 8 times the size of the fixed payment to the Pension Fund, i.e.: 26545.00 x 8 = 212,360 rubles.
Tax Service The recipient of all these payments is the state tax service authority with which the citizen is registered as an individual entrepreneur.
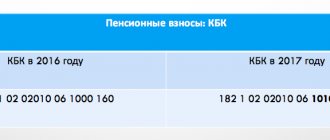
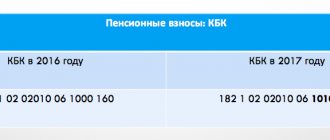
Codes:
182 1 0210 160 - code for transferring compulsory pension insurance (pension) contributions; 182 1 0213 160—KBK for transferring compulsory medical insurance (medical) payments; 182 1 0210 160 – BCC for crediting contributions to the OPS at 1%.
There are more grounds for refusing to accept RSV
Another important change for individual entrepreneurs is related to reporting on insurance premiums. Law 335-FZ expanded the list of cases when the Federal Tax Service can recognize the calculation of insurance premiums as not submitted. This is exactly what tax inspectors will think if errors are found in the indicators listed below or if these data do not converge for each individual and the organization as a whole. These are the indicators:
- total amount of payments to individuals;
- the total amount of payments to individuals within the base for contributions to compulsory pension insurance;
- base for calculating pension contributions according to the additional tariff;
- the amount of pension contributions calculated according to the additional tariff.
These rules came into force at the beginning of the year and apply to 2021 reporting.
Previously, the calculation of insurance premiums was considered not submitted if the total amount of contributions to compulsory health insurance from payments within the base did not coincide with the amount of contributions calculated in relation to each insured person. Now, in addition to this, the reasons listed above have appeared.
If the inspectorate considers that the entrepreneur has not filed the DAM, he will be notified about this. There have been no changes in this part. The notification will be sent in paper or electronic form, depending on how the individual entrepreneur reported. If he manages to make changes within the allotted time, he will be considered to have filed the DAM on time. Let us remind you that the deadlines are 5 days for the electronic form of payment submission and 10 days for the paper form.
Insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs in 2019-2020
Insurance contributions to the funds for the next 2 years have already been fixed: to the Pension Fund in 2021 and 2021. they will be 29,354 and 32,448 rubles, respectively, and according to compulsory medical insurance – 6,884 and 8,426 rubles.
A businessman does not have the right to apply reduced rates when it comes to contributions to himself. This only applies to employees.
For the convenience of fee and tax payers, there are special online calculators (they will help you do the calculations).
Contributions to the Pension Fund in 2021 for individual entrepreneurs without employees, the entrepreneur is obliged to pay for himself in any case: whether he has staff on staff or whether he works alone. The same applies to contributions to compulsory medical insurance. For employees, the calculation scheme remains the same.
If a businessman did not work or did not receive income, or even remained at a loss, then he is still required to pay contributions to all funds.
Calculation of income exceeding 300 thousand rubles for different taxation systems What income is included in the calculation depends entirely on the chosen taxation system.
Changing the income accounting procedure for a preferential insurance rate
The next change for individual entrepreneurs in 2021 concerns entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system with employees . Law 335-FZ introduced clarifications to the list of income that is taken into account when calculating the main type of activity for the application of a preferential rate of insurance premiums. Let us recall that a type of activity is considered the main one if the income from it in the total income exceeds 70%, that is, the following inequality is fulfilled:
Income from activity / total income ≥ 70%
The new edition of the Tax Code states that when determining total income (the denominator in the formula), the following are taken into account:
- income from sales;
- non-operating income;
- income from Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, although they are not taken into account when calculating the base for the single tax under the simplified tax system.
When determining the numerator of the formula, that is, income from activities that give the entrepreneur the right to reduced insurance rates, all income associated with this activity .
Despite the clarification, the problem is not solved. Namely, it has not become clear whether, when determining the numerator of the formula, it is necessary to take into account income not subject to a single tax . Among experts there is an opinion that it is necessary. However, it is possible that inspectors will think differently. This is evidenced by practice, including judicial practice - previously, arbitrators in such disputes usually supported the tax authorities.
Thus, in order not to face claims from the Federal Tax Service, it is safer to take into account income that is not subject to a single tax under the simplified tax system only when calculating total income.
What payments should an individual entrepreneur pay in 2018?
The simplified taxation system of the simplified tax system is divided into two types. But whether the object of taxation is simply “income” or “income minus expenses” did not matter until quite recently. The individual entrepreneur takes into account all of his income corresponding to Article 346.15 of the Tax Code. This is the totality of available sales and non-sales income (articles numbered 249, 250 of the Tax Code). From the amount of revenue that is indicated as a total in the Book that records the income and expenses of the individual entrepreneur, 300 thousand rubles are immediately deducted and 1% is taken.
Formula:
(Income – 300 tr.) x 1% = the amount of the compulsory pension insurance contribution (this calculation now applies only to those who pay taxes simply on income).
However, the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation recognized “income minus expenses” for individual entrepreneurs using the “simplified system” to reduce contributions to themselves - now entrepreneurs have the right to charge a 1% contribution, reducing the amount of income by the amount of expenses. That is, the formula is now:
(Income - expenses - 300 thousand rubles) x 1% = contribution amount for compulsory pension insurance.
UTII. The calculation is made from the amount of imputed income, which is the basis for paying tax, and not from the total amount of revenue. It is convenient to take the annual amount and add it together from the reporting for the Single Tax to the Federal Tax Service (Article 346.29 of the Tax Code). Patent tax system . The potentially probable income for which a patent is issued is the basis for calculating the 1% contribution (Article 346 of the Tax Code). The amount of revenue is also not taken into account. Combination of modes. To calculate the taxable base, you should add together the taxable amounts or income for all regimes used. General system . Entrepreneurs subject to this taxation and paying 13% personal income tax pay a 1% contribution on the income base minus expenses. This decision was made by the Constitutional Court of Russia (resolution No. 27-P dated November 30, 2016) and cannot be appealed.
Personal income tax on wages
Personal income tax must be transferred to the budget by the employer, but at the expense of the employee. That is, the employee receives his salary minus tax.
The standard tax rate is 13% of accrued wages.
Not all payments from an employer to an employee are subject to personal income tax. There are non-taxable amounts; they are listed in Article 217 of the Tax Code. For example, tax is not withheld from government compensation and benefits, financial assistance up to 4 thousand rubles per year, daily allowance up to 700 rubles.
Deadline for transferring personal income tax to the budget:
- from wages - no later than the next day after payment of wages;
- from vacation pay and sick leave - until the end of the month in which the payment was made.
It is impossible to transfer tax before the employee’s income is paid.
By law, the employer must pay wages at least twice a month - the so-called advance and main part. There is no need to withhold personal income tax from the advance, except in cases where the employer pays the advance on the last day of the month.
Example:
The employee's salary is 20 thousand rubles. An advance in the amount of 8 thousand rubles is transferred to him on the 25th of each month, and the rest - on the 10th.
Tax on all wages: 20,000 x 13% = 2,600 rubles.
On the 25th, the employee receives 8 thousand rubles without tax deduction, and from the remaining portion of 12 thousand rubles, the entire tax is withheld, and the employee receives 9,400 rubles.
If an employee has the right to tax deductions, he can bring supporting documents to the employer, and then the employer will calculate the tax not on the entire salary, but on the salary minus such deductions.
All deductions are listed in Articles 218-221 of the Tax Code. Here are the most common ones:
1. For the purchase of housing, land. 2. To pay for education and treatment, for yourself and your children. 3. For children, disabled children. 4. For charitable contributions.
Contribution obligations for individual entrepreneurs with employees
When acquiring hired employees, individual entrepreneurs simultaneously acquire a lot of responsibilities associated with this circumstance:
- the need to monthly calculate and pay insurance premiums from the income of each employee;
- withhold personal income tax from these incomes;
- generate quarterly reports on personal income tax and insurance premiums.
That is, the presence of employees for individual entrepreneurs in terms of contributions for the 3rd quarter obliges not only the calculation and payment of these payments, but also the preparation of reports on them, and submitted to two authorities: the Federal Tax Service and the Social Insurance Fund.
Calculation of contributions from employee income is not only done monthly and individually, but also requires:
- taking into account the existence of a set of reasons for exempting income from assessment of contributions;
- using a special tariff for each type of insurance;
- application, in addition to the main ones, of additional and reduced tariffs if there are grounds for this;
- control over the amount of income accrued to the employee, since for payments to OPS and OSS for disability and maternity insurance, its limits are established, beyond which a different tariff begins to be applied to OPS, and accruals on OSS stop;
- reducing the amount of contributions accrued to OSS (both for disability and maternity, and for injuries) due to expenses incurred for these types of insurance;
- organizing individual accounting of accruals;
- separate payment of amounts intended for each of the funds.
The income limits for 2021 correspond to the following figures:
- for OPS - 1,292,000 rubles;
- for OSS for disability and maternity insurance - 912,000 rubles.
There are no income restrictions for other contributions, and they are calculated on the entire volume of taxable payments to the employee.
The basic tariffs in 2021 are equal (Article 426 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- for OPS - 22%, and for income exceeding the threshold value - 10%;
- for compulsory medical insurance - 5.1%;
- for OSS for disability and maternity insurance - 2.9%.
Individual entrepreneurs who belong to the NSR, in connection with the coronavirus in 2021 (from April 1), can use a 15% tariff instead of the general tariff:
- for OPS - 10%, both from income within the maximum base and above it;
- for compulsory medical insurance - 5%;
- for OSS for disability and maternity insurance - 0%.
Attention! ConsultantPlus warns: Reduced tariffs are used when calculating contributions to compulsory medical insurance, compulsory medical insurance and VNiM for April 2021 and subsequent months of this year. They apply to the part of payments for these months that exceeds for each individual the minimum wage established by federal law as of January 1 of the current year... (for more details, see K+). Trial online access to K+ is free.
The rate applied for injury contributions depends on the type of activity carried out by the employer.
Results
An individual entrepreneur turns out to be a payer of two types of insurance premiums: for himself and for his employees. Contributions for yourself require calculation only if the annual income of an individual entrepreneur exceeds 300 thousand rubles. For lower incomes, their size is fixed. The fixed contribution must be paid during the year to which it relates, which means that there is no requirement for such a transfer after the end of the third quarter. There is no need to submit contribution reports for yourself.
Contributions for employees are calculated and paid monthly, applying special rules to them that determine the basis for calculation, the tariffs used and restrictions that lead to either a change in the tariff value (OSS) or to the cessation of accrual of contributions (OSS for disability and maternity).
Reporting on them is mandatory; it is formed quarterly for two authorities: the tax authority (all contributions, except for “accidents”) and the Social Insurance Fund (injury contributions). You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
An important point is to indicate the correct BCC
A particularly important point is that the correct BCCs have been entered for payment of insurance premiums, since errors in this column will lead to the wrong direction or return of funds.
The main BCCs for insurance premiums for employees are presented in the following table:
| Payment | KBK | ||
| OPS | Compulsory medical insurance | FSS | |
| Contribution | 18210202010061010160 | 18210202101081013160 | 18210202090071010160 |
| Penya | 18210202010062110160 | 18210202101082013160 | 18210202090072110160 |
| Fine | 18210202010063010160 | 18210202101083013160 | 18210202090073010160 |
For more detailed information on various BCCs for insurance premiums, read this material.