The receipt of an intangible asset (intangible asset) into an organization is naturally accompanied by its inclusion on the economic balance sheet.
In other words, any property acquired by an enterprise for one reason or another must be properly taken into account. The specifics of this procedure significantly depend on the method (reason) of the object coming into the possession of the copyright holder company. In addition, the fact of the appearance of an intangible asset in an enterprise must be documented, without which accounting of the corresponding object also cannot be carried out.
Why do you need an NFA acceptance certificate?
The document in question was put into circulation by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n - the main regulatory act that approved the use of various unified forms by institutions of the budget system of the Russian Federation.
The act of acceptance and transfer of non-financial assets form 0504101 is used when recording the movement of relevant assets between various legal holders and users:
- as part of the transfer of an asset to the operational management of an institution or economic management;
- as part of the transfer of the NFA to the treasury;
- in the process of repossession of an asset by the owner;
- upon transfer of an asset used to finance the authorized capital;
- during the sale of property of a budget system organization.
Read about what NFA is here.
You can learn about the latest changes in budget accounting and new standards that have been applied since 2021 from the Review from ConsultantPlus. If you do not already have access to this legal system, a full access trial is available for free.
How to accept an intangible asset?
The object is accepted by the enterprise for accounting at its original (primary) cost - this is the indicator that appears in the economic balance sheet.
The primary cost of a property is determined by the totality of costs incurred by the organization that are directly related to its appearance on the balance sheet.
The composition of expenses that form the primary cost of intangible assets is determined by the reason for its occurrence in the enterprise.
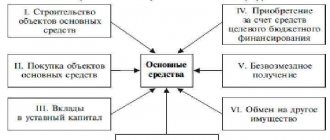
The receipt of an asset by a particular company may be due to the following reasons:
- acquisition (purchase) from a third party;
- creation (development) in-house;
- gratuitous receipt from an external entity;
- exchange for other assets that belonged to the copyright holder enterprise;
- contribution of an intangible asset by the founder (participant) to the authorized capital of the organization.
Documented expenses of the organization directly related to the acquisition/creation or other receipt of objects are recorded first on the debit of account 08 for the subaccount for the acquisition of intangible assets (account 08/5) in correspondence with the credit of cost accounts (98, 76, 75, 70, 60).
The fact of putting an intangible asset into operation is reflected in the debit of account 04, which directly corresponds with the credit of account 08/5, which reflects the acceptance of this asset for accounting.
It is important to note that the recognition of intangible assets and its acceptance for accounting at the enterprise are carried out only if it fully complies with all these requirements:
- The copyright holder organization intends to use this object for its intended purpose for a period exceeding a twelve-month period.
- It is possible to reliably determine (calculate) the value of an acquired or created asset.
- The enterprise does not plan to sell (transfer) this object to a third party. The intangible asset was purposefully acquired by the copyright holder for economic use.
- Exploitation is characterized by the absence of physical expression and is carried out by the organization solely to extract economic benefit (profit, income).
Documenting
The legal aspect of documenting intangible assets is that the organization acquires and takes into account not just any result of intellectual activity, it receives and formalizes the exclusive right to this product.
The facts of acquisition of objects by an enterprise must be confirmed by the preparation and registration of title documents.
The following official documents may serve as such documents:
- license agreement;
- registration certificate;
- an agreement formalizing the transfer/receipt of exclusive rights;
- patent documentation;
- other papers.
The acceptance of intangible assets and its entry into economic activity is documented at the enterprise by drawing up a transfer and acceptance certificate (the established OS-1 form is used).
In order to capitalize an intangible asset for accounting purposes, it is necessary to create and issue a special card for it, designed for analytical accounting of all transactions with this asset.
We are talking about the intangible asset form-1, which reflects data on the receipt of the corresponding object and its further movements (up to disposal or liquidation).
The accounting card must indicate the reasons for a particular action performed at the enterprise in relation to a specific asset. A similar form of intangible asset-1 is drawn up for each intangible asset.
The copyright holder organization can independently develop and apply its own forms (forms) for recording intangible assets, since there are no official instructions (regulations) in this regard yet.
However, one should be guided by the norms of accounting legislation, which prescribe the mandatory presence in accounting documents of the following necessary details:
- lifetime;
- book value;
- regulated depreciation rates;
- dates of acceptance and subsequent disposal;
- other information.
If an enterprise obtains the right to own an intangible asset subject to patent legislation, it is necessary to confirm this authority with a license agreement and registration with the patent service.
This applies, for example, to any invention.
As a rule, taking into account the procedures for the creation (development) or acquisition (purchase) of objects implies the preparation of security documentation regulating the procedure for the lawful operation of such assets.
Sample order for commissioning
The head of the organization-right holder issues an order regulating the acceptance of an intangible asset for accounting.
Typically such an order contains the following details:
- registration number and date of drawing up the order;
- name of the object (brief description);
- the basis (reason) for its receipt by the enterprise (for example, purchase);
- initial cost;
- assignment of a specific inventory number;
- determining the group affiliation of an asset;
- establishment of service life;
- purpose of depreciation method;
- the entity responsible for registering intangible assets.
order to put an intangible asset into operation - word.
Example of an act
The transfer of an object for economic operation is carried out by the enterprise on the basis of an appropriate act, drawn up indicating the following details:
- registration number of the act;
- Date of preparation;
- name of the intangible asset;
- name and details of the title document;
- regulated period of operation;
- correspondence of invoices upon registration;
- date of introduction of the intangible asset into the business process;
- primary cost;
- depreciation rate;
- liquidation value;
- place (division) of direct use.
act on commissioning of an intangible asset - word.
NFA acceptance and transfer certificate form: structure of the document according to order No. 52n and sample filling
The document in question consists of 2 pages.
On the first there are:
- stamps “I approve” - from the sender and recipient of the transferred asset;
- information about the sender and recipient;
- legal basis for the relocation of the NFA;
- information about transferred NFA;
- brief characteristics of objects.
The second page of the document reflects:
- information about received objects;
- Full name, position, signatures of the person who handed over the asset and the person who accepted it;
- information about the documents used to coordinate the transfer of NFA, registration of rights to the object (if these documents were used);
- information about the annexes to the act;
- information about the acceptance of the asset by the commission, the conclusion of the relevant commission, the signatures of its members with a transcript;
- notes on registration of the NFA, on deregistration of the object;
- signatures of the chief accountants - from the institution that sent the NFA and the organization that received the asset;
- signatures of the performers - from the relevant business entities.
You can download the completed act of acceptance and transfer of non-financial assets on our website using the link below:
Postings when purchasing and creating in-house
Accounting for intangible assets is carried out by the enterprise on account 04. The debit of account 04 records the primary value of the intangible asset upon receipt by the organization. However, first all costs associated with the acquisition/creation are accumulated in account 08/5.
If we talk about VAT accounting, today this tax does not apply to exclusive rights to topologies of integrated circuits, know-how, utility models, inventions, databases, and software.
The remaining intangible assets require the allocation and deduction of VAT from expenses that make up the primary cost.
The acquisition of intangible assets is accounted for as follows:
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| The cost of intangible assets is fixed | 08/5 | 76 |
| VAT is deducted from the price | 19 | 76 |
| VAT is sent for deduction | 68 | 19 |
| Fees and duties are included | 08/5 | 76 |
| Fees and duties are paid | 76 | 51 |
| Acceptance of an object for accounting | 04 | 08/5 |
The creation of intangible assets by the organization’s own resources is taken into account as follows:
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Salary to employees | 08/5 | 70 |
| Social charges | 69 | |
| Travel expenses | 71 | |
| Fees, duties | 76 | |
| Contractor services | 60 | |
| Asset depreciation | 02,05 | |
| Materials | 10 | |
| Acceptance for registration | 04 | 08/5 |
Results
The movement of NFA between institutions of the budget system is certified by a special act, which was put into circulation by Order No. 52n. Information about the asset, sender, recipient, as well as persons representing the relevant organizations in one or another status is reflected here.
You can learn more about the specifics of NFA accounting in budgetary institutions from this article.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
conclusions
The receipt of an intangible asset by an enterprise is the starting point for its accounting. Documentation of the acceptance of such assets for accounting is of great importance for their further operation.
It is necessary to ensure that the company has title papers, correctly draw up accounting documents, accurately indicate all mandatory details, and register rights (if necessary).
The specifics of accounting procedures are significantly predetermined by the legal basis for the emergence of intangible assets - creation (development) or acquisition (purchase).
What primary documents are used to account for intangible assets?
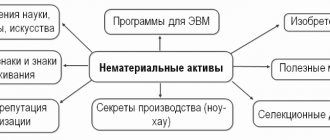
Intangible assets (IMA) are a non-current asset of an organization; it can include licensing rights to the result of intellectual activity, as well as the business name of the organization.
Intangible assets do not have a material structure, but their movement must also be formalized in accordance with the Federal Law “On Accounting”.
This is done through the use of primary accounting documents, including.
What refers to intangible assets
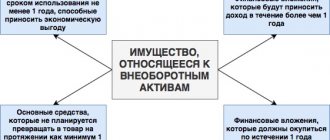
To qualify an object as an intangible asset, the following conditions must be met:
- It will serve the economic benefits of the enterprise;
- Operated in the main production of the enterprise, either for accounting, or for activities aimed at achieving the main goal of the company;
- The company must have confirmation of the right to own the object;
- The useful life of the object is more than 12 months;
- The company does not plan to sell the asset in the coming year;
- The company must be able to establish the initial cost;
- The object must have no material form.
How intangible assets are received by the organization
In the age of innovative technologies, there are especially many intangible assets in companies:
- Software;
- Software licenses;
- All possible defense bases;
- Electronic keys and signatures, etc.
This significantly complicates the accounting of intangible assets, and at the same time encourages you to find out what documents need to be used for accounting in accordance with PBU and the Federal Law of the Russian Federation. Intangible assets can join the organization from suppliers and contractors. According to the Consignment Note, Consignment Note TORG-12.
If software is supplied to an organization, it is important to ensure that rights and licenses are provided, which must be attached to the documents.
If you are simply purchasing a license for a new working year, then you need to check with the responsible employee for how long the purchased license will be valid.
Registration is complicated by the fact that the bulk of software and licenses for software, software for equipment and other intangible assets, as a rule, comes from abroad.
And, accordingly, the value of the asset is stated in the documentation in foreign currency, and this provokes exchange rate differences and revaluation of debt. Therefore, it is especially important to carefully study the contract and primary documentation from the foreign counterparty.
It is important to remember that intangible assets must be registered in Russian currency. On what date the exchange rate should be taken must be specified in the agreement with the counterparty. Accordingly, the initial cost of intangible assets established for registration should be exclusively in rubles.
What primary documents are used to record intangible assets?
The receipt of intangible assets into the organization is carried out using an acceptance certificate for intangible assets. The form is standard, as for fixed assets (form OS-1).
You must specify:
- Title of the document;
- Date of document preparation;
- Name of the enterprise, division of the organization;
- Financially responsible person (MRO).
For analytical accounting, an inventory card for accounting for intangible assets is used in form No. NMA-1. This is a standard form for accounting for an organization’s intangible assets. The card is individual for each intangible object.
A card is opened for each intangible asset after capitalization, the basis is the primary receipt, the act of acceptance and transfer (movement) of an intangible asset form OS-2 or another document. The card specifies the amount of depreciation, which is determined depending on the initial cost of intangible assets and private property assets.
In the section “Brief characteristics of the object of intangible assets,” only the main indicators of the object are indicated. Write-off is carried out according to the act of form OS-4.
The main rule when filling out this form is the need for certification by the signatures of the chief accountant and the head of the organization. The act is filled out in two copies, one copy for the accounting department of the enterprise, the other is transferred to the MOL.
Of course, accounting has long migrated to a computer system and the accounting department fills out all the necessary documentation online. Every day, computer technology is increasingly forcing the accounting habitual for an accountant to be restructured, while simultaneously adding to the list of intangible assets in accounting. But this does not negate the importance of proper accounting, and the need to maintain copies of primary documentation on paper.
Source: //buh-spravka.ru/buhgalterskij-uchet/pervichnyj-uchet-dokumentooborot-arhiv/pervichnye-dokumenty-po-uchetu-nematerialnyh-aktivov.html