What is considered the object of taxation on the simplified tax system
The current law assumes that the simplified taxation system in 2021 for individual entrepreneurs and LLCs, depending on the characteristics of the activity, will be divided into two types.
According to the Tax Code, the tax can be calculated based on a base formed only from income, or a base consisting of income reduced by expenses incurred.
In each of these cases, business entities will be required to generate a declaration once a year, and pay the tax throughout the year in advance installments.
By Income
The system for calculating taxes of the simplified tax system of 6 percent in 2021 for LLCs and entrepreneurs establishes that the amount of tax must be determined based on the amount of funds received at the cash desk and into the bank account, which are income for the entity. The current law sets the tax calculation rate for this system at 6%. But the authorities operating in the regions are given the right to reduce it in certain cases.
A business entity must record all receipts in a special journal, which is called a book of income and expenses. In this case, information is entered in the journal only in the section intended for incoming income, and the part for expenses is not filled out.
The simplified tax system of 6 percent in 2021 for individual entrepreneurs and organizations is the most optimal for small businesses. It is beneficial if the amount of costs is less than 70% of incoming income.
Income minus expenses
The simplified taxation system in 2021 for LLCs and entrepreneurs determines that in the case of using the “Income reduced by expenses” system, the base also includes cash receipts and bank accounts, but they must additionally be reduced by the amount of expenses incurred during this period . The latter must be paid to suppliers, and also be included in the closed list established by the Tax Code.
When calculating the amount of tax payable, a rate of 15% must be used. However, regional authorities can also change it at will - the law allows you to reduce the rate down to 0% both for the entire system and for specific areas of activity.
A special feature of this system is the fact that the tax will have to be paid even if the business entity has a tax period with a loss. In this case, it is important that he has receipts that are recognized as income.
Then it is necessary to calculate and pay a payment, which is called the minimum tax according to the simplified tax system, income minus expenses. Its rate is 1% of the entire income for a given period.
When applying this system, a business entity must also use a journal - a ledger of income and expenses.
However, now it is necessary to fill out both parts, both income and expenses. Attention: for business entities that are engaged in production and have a serious cost component, the use of this system is more profitable.
Features of taxation on the simplified tax system
When using the simplification, a business entity has the opportunity not only to significantly reduce the amount of tax payments, but also to replace several taxes with a single one.
Let's consider what taxes need to be paid, and from which the subject will be exempt:
| Must be paid if simplified payment is used | Exempt from payment when using simplification |
| Single tax, which is calculated when using a simplified tax | – |
| VAT, but only if the subject acts as an agent or accrues VAT on its own initiative | VAT |
| – | Income tax |
| Property tax, but only for those objects that are recorded at cadastral value | Property tax |
| Personal income tax | Personal income tax for individual entrepreneurs regarding types of activities under a simplified regime |
| Transport tax (when there is a base) | – |
| Land tax (when there is a base) | – |
| Water tax (when there is a base) | – |
In addition, for some types of activities reduced rates for payment of social contributions are established. Also, for some types of insurance (usually health insurance and social insurance), 0% rates apply. At this point in time, this reduction is valid until the end of 2018.
When not to use simplification
The law establishes several criteria under which an entity cannot use the simplified system. Thus, a company will not be able to switch to a simplified system if its founders include another company, and its share is 25% or more.
In addition, it is impossible to start using the simplified tax system when a company has branches and representative offices.
Important: types of activities that cannot be performed while on a simplified regime are also defined. These include pawnshops, insurance or lending activities, gambling, production of excise goods and others.
Finally, you cannot be on simplified employment if you do not meet the criteria specified in the Tax Code (number of employees, amount of income, etc.).
Which object to choose
The notification must indicate the selected object of taxation, the residual value of the fixed assets and the amount of income as of October 1, 2021.
Selecting a taxable object is the most important procedure for an organization. As a rule, the “income” object is more profitable if the company’s expenses are not so significant. If the costs are significant and at the same time it will be possible to reduce the base for the simplified tax system (remember that the list of “simplified” expenses is closed - Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), then it is more profitable to use the “income-expense simplification”.
The approximate benefit can be calculated by comparing the tax bases and rates of two simplified taxation system objects, from which it follows: if a company’s expenses are less than 60 percent of its income, it is better to choose the “income” object. If more, then there is an alternative option.
However, for a more accurate calculation, you should take into account a number of other factors, including what single tax rates are set for 2018, depending on the type of activity and category of taxpayer in your region. And only after a detailed analysis, record your choice in a notification.
What if the notification has already been submitted, but a little later the company decides to change the initially selected object of taxation? Then the company can (up to the above-mentioned deadline) submit to the Federal Tax Service a new notification with a different object of taxation, attaching a letter stating that the original one is canceled (letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 14, 2015 No. 03-11-11/58878 and dated January 16, 2015 No. 03-11-06/2/813). If the deadline (in our case - 01/09/2018) is missed, then the company will be able to change the object only from the beginning of the new tax period, that is, from 2019. It will not be possible to do this during 2021 (clause 2 of Article 346.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation for Moscow dated 05/07/2009 No. 20-18/2/ [email protected] ).
In practice, there are cases when an organization actually applies a taxation object that is not specified in the notification. The Federal Tax Service will probably consider this unlawful and will recalculate the company’s tax liabilities with all the ensuing consequences. And the judges will most likely agree with the fiscals. For example, in the Resolution of the Sixth AAS dated 01.10.2014 No. 06AP-5107/2014 it is noted: the transition to a simplified regime, the choice of an object of taxation, despite its voluntary nature, is carried out by the payer not arbitrarily, but in compliance with the conditions and procedures clearly specified in Chapter. 26.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. And if an organization, in violation of the established procedure, actually changed the simplified tax system object, it will have to answer for it.
The procedure for switching to the simplified tax system
The law specifies several ways to begin using the simplified tax regime.
When registering an LLC or individual entrepreneur
If a future business entity is only collecting all the necessary documents for registering an individual entrepreneur or opening an LLC, then he can submit an application to start using the simplified regime in a general package.
In this situation, along with forms confirming completion of the registration procedure, he will also be given a notice of application of the simplified tax system.
Attention: if at the time of opening a business there are still doubts about choosing a system, then this can be done within 30 days from the moment you receive the forms for registering an LLC or individual entrepreneur.
Transition from other modes
The Tax Code allows existing business entities to change the current tax regime to a simplified system.
But such a step is allowed only from January 1 of the calendar year. Therefore, in order to make the transition, you must complete and submit an application to the tax authority before December 31 of the current year. In it, the business entity indicates that it meets the criteria defined in the Tax Code for the application of the simplified tax system. The latter are calculated based on October 1 of the current year.
So, in order to start applying the simplified regime from January 1, 2019, it is necessary that as of October 1, 2021, the income received does not exceed 112.5 million rubles.
Another opportunity to start using a simplified version is not provided for by law.
How to submit a notification to the Federal Tax Service
The notification can be submitted to the inspectorate (either or):
- on paper (the recommended form is approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated November 2, 2012 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] ). Let us note that the company has the right to submit a notification in any form, taking into account the requirements of Art. Code 346.13;
- in electronic form (format approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated November 16, 2012 No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected] ).
Let us pay attention to some features of filling out the notification form recommended by the fiscal authorities by an organization switching to the simplified tax system from the general tax regime. In the “Taxpayer Identification” field, enter “3”, and in the line “Switches to a simplified taxation system” - “1”. And do not forget that the amount of income for 9 months of this year is shown without VAT.
A dash is placed in empty lines of the notification. The document is signed by the head of the company and certified by its seal (if any).
In general, the form, consisting of only one page, is quite easy to fill out. There shouldn't be any difficulties with it.
The notification can be submitted to the Federal Tax Service in person, through an authorized representative, or sent by registered mail. In the first and second cases, the filing date will be the day the document is received by the secretariat or inspection office. In the latter - the day indicated on the postmark.
Please note that if the notification is submitted through a representative of the company, its lower field reflects the name of the document confirming the authority of this person. This document (a copy of it) should be attached to the notification.
Tax and reporting period
The concepts of what is considered a tax period and what is a reporting period are enshrined in the Tax Code.
Taxable period
For simplicity, the tax period is taken as a calendar year. It is at the end of this period of time that the business entity must make the final tax calculation. Moreover, several reporting periods are included in one tax period.
If a business entity violates the rules for applying the simplified regime, the tax period for it will take less than a year.
Attention: information in the tax return is indicated in cumulative form from the beginning of the tax period.
Reporting period
The following time periods are established as reporting periods: 1st quarter, six months, 9 months. Upon completion of each of them, the advance payment according to the simplified tax system must be calculated.
Taxes and reporting on the simplified tax system
Tax payment procedure
Tax Returns
Tax payments to the budget must be made by transferring advance payments. Next, at the end of the calendar year, you must make a full tax calculation and pay the remaining amount.
The dates before which the advance amounts must be transferred are determined in the Tax Code. It establishes that this must be done before the 25th day of the month following the end of the next quarter.
Thus, the advance payment must be made before the following dates:
- For the 1st quarter - until April 25;
- Six months before July 25;
- 9 months before October 25th.
But the day of payment of the final payment differs for entrepreneurs and firms. Companies do this first - they need to transfer the tax by March 31, following the reporting period. Then it’s the turn of entrepreneurs - they send taxes to the budget by April 30.
Attention: if the specified deadlines are violated, then the business entity will be subject to liability as specified in the Tax Code.
Taxes and reporting on a simplified system for individual entrepreneurs
For an individual entrepreneur, the number of tax payments and mandatory reports will depend on whether he has hired employees.
In the case where the individual entrepreneur did not hire employees and operates alone:
- Single tax due to the application of simplification.
- Deductions for compulsory types of insurance for yourself;
- Personal property tax;
- If there are appropriate bases - land, transport taxes;
- VAT, if the subject makes allocations in some shipping documents;
- If the legislation of the region provides for the payment of a trade tax.
If the individual entrepreneur hired at least one person:
- Personal income tax on employee remuneration
- Deductions for compulsory types of insurance for payments in favor of individuals.
Individual entrepreneurs without employees send the following reports:
- Single tax declaration due to the application of the simplified tax system (annually).
- VAT declaration (quarterly when this tax is highlighted in the shipping documents).
- Declarations on transport, land, water taxes (quarterly).
- Statistical reporting to the extent required by law.
If the individual entrepreneur has employees, then you also need to register:
- 2 personal income tax (annually).
- 6 personal income tax (quarterly).
- Calculation of insurance premiums (quarterly).
- Payroll in form 4FSS (quarterly).
- SZV-M report (monthly).
- SZV-experience report (annually).
- Information on the average number of employees.
Taxes and reporting on a simplified system for LLC
When applying the simplified tax system, a legal entity must make the following mandatory payments:
- Single tax due to the application of simplification.
- Personal income tax on remuneration of employees and other individuals engaged under civil contracts.
- Deductions for compulsory types of insurance for payments in favor of individuals.
- Property tax (if the region is based on its cadastral value).
- If appropriate bases are available - land, transport and water taxes.
- VAT, if the subject makes allocations in some shipping documents.
- If the legislation of the region provides for the payment of a trade tax.
Also, a legal entity must submit the following reports to the simplified tax system:
- Single tax declaration due to the application of the simplified tax system (annually).
- 2 personal income tax (annually).
- 6 personal income tax (quarterly).
- VAT declaration (quarterly when this tax is highlighted in the shipping documents).
- Declarations on transport, land, water taxes (quarterly).
- Calculation of insurance premiums (quarterly).
- Payroll in form 4FSS (quarterly).
- SZV-M report (monthly).
- SZV-experience report (annually).
- Information on the average number of employees.
- Statistical reporting to the extent required by law.
- Small businesses submit accounting reports in a simplified form (balance sheet, profit and loss statement, report on the intended use of funds). For all other companies, reporting must be submitted in full.
We notify tax authorities
To switch to the simplified tax system starting next year, an organization must submit a notification to the Federal Tax Service at its location no later than December 31 of the current year. However, December 31, 2021 falls on a day off - Sunday. This means, according to clause 7 of Art. 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the deadline for filing a notification is postponed to the 1st working day of the next year - 01/09/2018. The validity of this conclusion is confirmed by the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 11, 2012 No. 03-11-06/3/70.
It is necessary to report a change in the special regime, since companies that did not promptly notify the tax authorities about the transition to the “simplified system” do not have the right to apply it (clause 19, paragraph 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 13, 2013 No. 03-11- 11/66). The fairness of this is illustrated by the latest verdict of the highest arbitrators - Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of September 29, 2017 No. 309-KG17-13365. Let's look at it in a little more detail.
A citizen who registered as an individual entrepreneur conscientiously applied the simplified tax system: submitted a declaration and transferred the tax to the budget. However, in the middle of the year, the fiscal authorities demanded a VAT return from him, and until it was submitted, they blocked the businessman’s bank account. The reason is that the individual entrepreneur did not submit a notification about the transition to the special regime before December 31 of the previous year, therefore, he does not have the right to the “simplified” regime.
It is interesting that the court of first instance supported the entrepreneur, pointing out that he actually applied the simplified tax system in the absence of objections from inspectors, which means that the requirement to work under the general regime is illegal. However, all subsequent authorities, including the RF Armed Forces, sided with the controllers, referring to the clear prescription of the norm of paragraphs. 19 clause 3 art. 346.12 of the Code. The same fact that a businessman submitted a simplified taxation system declaration, and the inspection accepted it, without any comments, does not indicate approval of the use of the “simplified tax” by the fiscal authorities. After all, the Federal Tax Service does not have the right to refuse to accept a declaration submitted by the payer (Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A similar point of view was expressed by the RF Supreme Court earlier (Determination No. 307-KG16-11322 dated September 20, 2016). The AS of the Moscow District also agrees with her (resolutions dated May 2, 2017 No. F05-3020/2017, dated April 27, 2016 No. F05-4624/2016). Detailed arguments in favor of the considered position can also be found in the Resolution of the AS of the West Siberian District dated December 10, 2014 No. F04-11632/2014.
It is important that in this case there is no need to submit other documents to the inspectorate besides the notification. The auditors also do not have the right to demand any additional information from the organization.
And one more thing - enterprises already operating under the simplified regime do not need to notify tax authorities about continuing to use it next year. This is exactly what the servants of Themis believe (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated September 19, 2007, September 24, 2007 No. KA-A40/9540-07).
Please note that the transition to the simplified tax system during the year is impossible, including due to the emergence of new types of business activities for the company (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 21, 2014 No. 03-11-11/18274).
Minimum tax according to the simplified tax system: income minus expenses (1%)
Tax legislation establishes the obligation of a business entity using the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”, when receiving insignificant income or with negative performance indicators, to calculate and pay the minimum tax, which is 1% of the amount of income received.
The minimum tax must be calculated based on the results for the reporting year.
It is always necessary to calculate the minimum tax, even if the profit is received by a company or individual entrepreneur. This calculated amount is compared with the estimated tax amount. Anything more must be transferred to the budget.
Attention: if the minimum tax is lower than the calculated tax according to the simplified tax system, then you need to transfer a single tax, calculated from the difference in income received and expenses incurred. Otherwise, you need to pay the minimum - 1%.
Previously, the minimum tax and the single tax under the simplified tax system of 15% had different BCCs, and business entities had to send letters to the tax office about the offset. Currently, these payments are united by one KBK and inspectors at the Federal Tax Service independently make offsets based on these declarations.
Tax reduction due to contributions to the Pension Fund and compulsory medical insurance (according to the 6% and 15% systems)
LLC and individual entrepreneur with employees
Legislation establishes the right of organizations and entrepreneurs acting as employers to take into account, when determining tax under the simplified tax system, the amount of contributions calculated and transferred to the budget for their employees.
However, the amount that can be taken as a deduction depends on the type of simplified tax system used:
- If a business entity applies the simplified tax system of 6 percent, then it has the right to reduce the amount of calculated tax by 50%, but no more. Individual entrepreneurs are given the opportunity to use as a deduction not only contributions for employees, but fixed contributions to extra-budgetary funds transferred by them to themselves.
- When the simplified tax system is used for income minus expenses, then all payments transferred to the budget can be taken into account as expenses, thereby reducing the tax base for the single tax.
Attention: you can take into account social contributions that were transferred to the budget in the current period. What is important here is the fact of payment, and not the period for which it was made.
Individual entrepreneur without employees
When an entrepreneur does not involve hired personnel in his activities, the law gives him the right to reduce the amount of tax by the entire amount of compulsory insurance contributions paid to extra-budgetary funds.
At the same time, the provisions of the regulations make it possible to reduce taxes not only by the amount of the above contributions, but also by the amount of contributions that the subject pays to the Pension Fund in the amount of 1% from the excess of income of 300,000 rubles.
There is a rule according to which contributions can be deducted only if the business entity actually paid them in the period under review. If in this period contributions were paid not only for the reporting period, you can claim a deduction for the full amount of the payment made.
Therefore, individual entrepreneurs under this system have the right to choose - pay payments immediately and claim a deduction in full, or transfer money in quarterly or monthly installments and set them to be reduced in installments.
A selection of schemes that allow you to retain the right to use simplification
WITH
special tax regimes, in particular the simplified tax system, are very beneficial for tax planning purposes. That is why the norms of the Tax Code regulating the use of special regimes contain many restrictions designed to prevent abuse. In particular, the possibility of applying simplification depends on the nature of the organization’s activities, cost and quantitative indicators of its activities. Taxpayers naturally try to resist these restrictions. Both by completely legal methods and by using “gray” schemes.
Replacing revenue with a loan will allow you to bypass the income limit
What are the savings? Allows the company to bypass the limit on the amount of income received. When using this scheme, the seller using the simplified tax system receives money immediately, that is, there is no need to wait for the next tax period.
How the scheme works. The main limitation when using the simplified tax system is the amount of income received. A taxpayer can remain in this special regime if, at the end of the year, his income in 2014 did not exceed 64.02 million rubles (clause 4.1 of Article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 13, 2014 No. 03-11-06/2/248 ). The easiest way to get around this restriction is to ask buyers or customers to pay for goods, works, and services sold to them later, that is, next year. This method is used when the threat of exceeding the revenue limit arose at the very end of the tax period. At the same time, this method is the most disadvantageous of all the others. Because the simplifier needs to negotiate with buyers, and the seller will receive the money later, if he receives it at all. In addition, due to the transfer of payments, an excess of the limit may occur in the next year. Therefore, this solution to the problem is only temporary.
A slightly improved version of this scheme is to conclude a loan agreement with the buyer instead of paying for goods, work, or services. That is, the simplifier receives part of the money from buyers not as revenue, but under a loan agreement (see diagram 1). Moreover, borrowed funds are not recognized as income (subclause 1, clause 1.1, article 346.15, subclause 10, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and, accordingly, their receipt does not lead to exceeding the limit. In the next tax period, counter homogeneous claims are offset (Article 410 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) for a monetary loan and for payment for goods, work, and services. It is at the moment of signing the deed that the buyer extinguishes his obligation to the seller. In addition, the borrower (supplier under the simplified tax system) can repay the loan to the lender (buyer) by transferring compensation (Article 409 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The transfer of property as compensation is recognized as a sale (Clause 1, Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Income from the sale of property is taken into account as part of the tax base when calculating the single tax on the date of signing the documents for its transfer (clause 1 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Scheme 1, Replacement of sales proceeds with a loan
Security measures. The main disadvantage of this method of understating the income base is the need to obtain the buyer’s consent to enter into a loan agreement. In addition, such contracts are often interest-bearing. Moreover, companies balancing on the brink of the restrictions established for the simplified tax system attract close attention from inspectors. Therefore, to minimize risks, it is worth stocking up on a business goal that will justify the meaning of receiving funds under a loan agreement.
Fragmentation of a business allows you to retain the right to a special regime
What are the savings? Splitting turnover allows the simplifier not to exceed the established income limit.
How the scheme works. The most common scheme that allows you to retain the right to use simplification at sufficiently large turnover is the division of the business. To do this, business owners register a group of controlled simplified companies. As a rule, as each organization reaches the revenue limit, contractual relations with real counterparties are re-registered to newly created legal entities (see Diagram 2). The number of simplified taxation system entities in this scheme varies based on the expected annual revenue that will be received by all companies in the group. At the same time, the annual turnover of each simplified employee should not exceed 64.02 million rubles (in 2014), and preferably 60–60.8 million rubles, so as not to come close to the limit, that is, closer than 5 percent.
Scheme 2. Fragmentation in order to preserve the right to the simplified tax system
Security measures. To minimize tax risks, it is necessary that all subjects of the simplified tax system be formally independent from the point of view of any legislation - tax, antimonopoly, civil. In this case, it is desirable that there be a minimum number of signs of even indirect affiliation. Since the inspectors consider the tax benefit obtained as a result of fragmentation to be unjustified. In this case, the taxpayer with his controlled organizations can be recognized as a single legal entity on the OSNO with a corresponding recalculation of taxes (decrees of the federal arbitration courts of the Ural district dated October 15, 2012 No. F09-9633/12, West Siberian district dated January 29, 2013 No. A03-12357/2011) .
It is advisable not to successively replace one organization with another as the revenue limit is reached, but to immediately introduce the required number of legal entities into the business. In practice, it is recommended to split the revolutions into a reasonable number of simplifications. Usually these are 4–8 organizations, in extreme cases 10. If, as part of a single business, dozens of simplified entities operate, even if they are not interconnected, the scheme will still become much more noticeable to tax authorities. And it will be easier for inspectors to prove that this is an illegal tax scheme. In the event of any fragmentation, it is advisable to stock up on a convincing business goal for the existing business structure. A business goal not related to reducing the tax burden can be, for example, diversifying the risks of different business projects, preparing a business for sale in parts, franchising, as well as restructuring a company, including the liquidation of non-core assets, the creation of a new business on their basis .
You can also bypass the revenue limit using an intermediary agreement
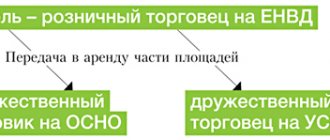
What are the savings? Allows you to bypass the limit on the amount of income received. Since revenue is not all the money coming from the sale of goods, but only a small part of it - the intermediary’s remuneration (see Diagram 3).
Scheme 3. Replacement of sales revenue with intermediary remuneration
How the scheme works. The company turns from a seller into an intermediary (agent, commission agent), acting on its own behalf, but at the expense of one or more principals (committees). Then the proceeds are not all the funds received from the sale of goods, works, services, but only part of them - remuneration from the provision of intermediary services (clause 1 of Article 346.15, clause 1 of Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax base for the single tax also includes other income of the intermediary - the amount of additional benefit, payment for del credere (Articles 991, 1001 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The intermediary's remuneration can be anything, as small as desired, for example 0.1 percent of the principal's revenue. This will allow turnover of tens of billions of rubles per year through the simplified process. The principal who accounts for the bulk of the revenue may be a third-party company on OSNO. True, the agent’s remuneration is not subject to VAT (clause 2 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), so the principal will not be able to deduct the tax. However, the amount of remuneration may be minimal, for example the same 0.1 percent of turnover, so the loss is small. The principals can be several companies using the simplified tax system or even individual entrepreneurs using the patent system (Chapter 26.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and in the case of transport services, also UTII.
Security measures. In this situation, as with business splitting, the turnover is divided, but the principals are represented by one agent to external counterparties, which is much more convenient. That is, externally the crushing is not noticeable. In addition, a foreign company can become the principal. In this case, a simplified Russian company will be an agent of a foreign principal for the sale (or, conversely, purchase) of goods in Russia. This scheme will reduce income taxes in relation to export-import activities, and even in relation to domestic trade.
One of the options for preserving the right to the simplified tax system using an intermediary agreement is the so-called method of separation of relations (see diagram 4). In this case, the company sells goods, works, and services on a common system with a minimum markup (101 thousand rubles). Thus, the amount of income tax and VAT payable by an organization on the general system will be insignificant. The buyer pays the rest of the real cost of goods, works, services to one or more entities of the simplified tax system (19 thousand rubles). The subject of the contract with the simplifier may be just intermediary services, in relation to equipment - installation or commissioning work. In general, these can be any services that suit the buyer. As a result of this division of contractual relations, the main part of the company’s income on the common system is transferred to several subjects of the simplified tax system and is taxed at rates of 6 or 15 percent (Article 346.20 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, simplifiers are not VAT payers. If the entire business had to be transferred to the subjects of the simplified tax system, then not a few, but many simplifications would be needed. In the example given - more than six times more (120 thousand / 19 thousand). In addition, the buyer would not have received VAT deduction on the entire purchase price, and in the described situation - only on 19 thousand rubles.
Scheme 4. Separation of contractual relations
Let us note that the participation of a simplifier in a simple partnership (Chapter 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) will allow one to bypass the revenue limit of 64.02 million rubles. At the same time, participants in joint activities use a simplified form with the object “income minus expenses” (clause 3 of article 346.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Any activity can be carried out within the framework of a simple partnership agreement, for example trade, services, production, construction. The participant’s income is the profit distributed to him, which may be significantly less than the revenue. At the same time, it is precisely the part of the profit due to each of the partners that should not exceed the established limit (clause 3 of article 278, clause 1 of article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is noteworthy that even through two comrades on the simplified tax system (and there can be as many of them as possible) you want more!) you can run a large business with multi-billion dollar turnover.
Manipulations with the number of personnel allow you to maintain the right to the simplified tax system
What are the savings? Allows the simplifier to bypass the restriction on the average number of employees.
How the scheme works. If the actual number of employees for the tax (reporting) period exceeds 100 people (subclause 15, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), then most often the excess part of the employees is registered in a friendly organization. That is, the same splitting scheme works as described above for income with all its risks and nuances.
One option for splitting staff is outsourcing. In this case, some of the employees are immediately registered to work in a friendly organization. In this case, the outsourcer will provide the simplifier with services corresponding to his type of activity. Another option for splitting staff is outstaffing. At the same time, a company using the simplified tax system fires some of its employees and places them on staff with a friendly simplified recruitment agency, or better yet, immediately hires them there. Next, the personnel center provides the simplified worker, who is trying to stay on the simplified tax system, with personnel for rent (see diagram 5). Please note that due to negative judicial practice, it is better not to use outstaffing when implementing this scheme. In addition, from 2021, Federal Law No. 116-FZ of 05.05.14 comes into force, which directly prohibits the use of agency labor.
Scheme 5. Maintaining the right to the simplified tax system by leasing personnel
Security measures. The easiest way to get around the limitation on the number of employees is to re-register some of the employees as part-time workers or register them as external part-time workers. In this case, the average number of employees is determined in proportion to the time they worked (subparagraph “d”, paragraph 79, subparagraph “a”, paragraph 80, paragraph 81.3, 82 instructions, approved by Rosstat order No. 428 dated October 28, 2013). In addition, you can additionally conclude civil contracts with individual full-time employees. When calculating the average number, such employees are not taken into account (subparagraph “b”, paragraph 80, paragraph 3, paragraph 83 of the instructions, approved by Rosstat order No. 428 dated October 28, 2013). However, this option of preserving the right to the simplified tax system is quite risky. Since, most likely, employees will actually work for the company on the simplified tax system full time. At the same time, through questioning of personnel, inspectors can easily confirm this fact.
There are several ways to bypass the limitation on the cost of fixed assets
What are the savings? Will allow you not to exceed the limit on the residual value of fixed assets.
How the scheme works. The company cannot apply the simplification if the residual value of fixed assets exceeds 100 million rubles (subclause 16, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To maintain the right to a special regime, an organization can revaluate fixed assets downward (clause 15 of PBU 6/01, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n). The basis for a revaluation may be, for example, an expert opinion of an independent appraiser (clause 43 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n). However, in the future such revaluation will have to be carried out annually.
A company can also get rid of excess fixed assets through inventory. That is, according to the results of the inventory, “lose” part of the fixed assets. At the same time, failed or obsolete objects can be written off. It may be necessary to sell part of the company's assets, but it is more expedient to remove excess fixed assets from the organization's balance sheet in a tax-free or low-tax manner. For example, transfer to the authorized capital of a friendly company, contribute property to a simple partnership, transfer objects to a legal successor through reorganization in the form of a spin-off.
In addition, the simplifier can transfer part of the fixed assets to conservation. Let us remind you that if fixed assets are transferred to conservation for a period exceeding three months, then such objects are not recognized as depreciable property (paragraph 3, paragraph 3, article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And accordingly they are excluded from the composition of fixed assets.
However, most often in practice this method of getting rid of excess fixed assets is used as asset splitting. This method works by analogy with the schemes described above associated with the division of turnover and personnel. In this case, the excess portion of fixed assets is transferred to the ownership of a friendly company. In the future, the simplifier can lease this property from a friendly counterparty or enter into a leasing agreement with him. Such property is not included in the calculation of the limit, even if it is listed on the simplifier’s balance sheet under the leasing agreement (see Diagram 6).
Scheme 6. Transfer of assets to a friendly organization
Combining the simplified tax system with other tax regimes
An economic entity can carry out several types of activities at once. Some of them may be on the simplified tax system, and some on other preferential systems.
It is allowed to combine simplification with systems such as UTII and PSN. That is, the subject generally applies the simplified tax system, but for a certain type of activity is a UTII payer or has acquired a patent.
The main requirement when implementing a combination of modes is the organization and maintenance of separate records of the company’s performance indicators, as well as the property used. This must be done to avoid double taxation. When UTII or a patent is closed for this type of activity, a simplification should be applied in the future.
What to choose - simplified or OSNO, if the company’s indicators comply with the conditions of the simplified tax system?
The transition to the simplified tax system is voluntary. This means that even if all the conditions of the simplified tax system are met, the organization (or individual entrepreneur) can remain on OSNO. The following materials will help you determine the pros and cons of each tax system and make the right choice:
- “What is the difference between the simplified tax system and the OSNO? What is more profitable?";
- “What are the features of combining OSNO and simplified tax system?”;
- “STS and OSN are not compatible.”
And about how to correctly pay taxes when switching from the simplified tax system to the OSNO, read the publication “The Ministry of Finance reminded about the rules for “switching off” from the simplified tax system.”