First, let's turn to the provisions of the Labor Code that regulate the payment of wages. Thus, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages are established for an employee by an employment contract in accordance with the remuneration systems that operate at a particular employer, as stated in Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, the Labor Code establishes the payment of wages at least every half month.
The exact dates for payment of wages are not established by law; the Labor Code of the Russian Federation only states that payments must occur no later than 15 calendar days from the end of the period for which wages were accrued. These dates are set by the employer in documents such as: internal labor regulations, collective or labor agreements (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
note
There is no concept of “advance” in labor legislation. This expression is accepted in everyday life, but in essence it is payment for the first half of the month. The algorithm for calculating the advance payment is also not fixed at the legislative level. However, the Ministry of Labor of Russia, in its letter No. 14-1/B-725 dated August 10, 2017, clarifies that in order to calculate and pay the advance for the first half of the month, it must be calculated in proportion to the time worked. In this case, it is necessary to take into account not only the employee’s salary for the time he worked, but also bonuses, which are compensatory and stimulating in nature and the calculation of which does not depend on the assessment of work results at the end of the month.
In my opinion, this method of calculating the advance by the regulatory authorities is absolutely rightly recommended. It is this method that eliminates for the employer the risks of overpaying money to an employee, which arise if the company pays employees a fixed amount of advance, as well as the risk of not being able to withhold personal income tax upon the final calculation of wages for the month.
What is a salary advance?
Each employee receives remuneration for his activities in the organization. This is the meaning of working for hire. Wages are designed to satisfy the needs of the employee and stimulate him to achieve high results.
Salary is a single, holistic concept in which there are two parts:
- Advance (or first part of salary)
- Second part of salary
There is no such thing as an advance in law. Everything an employee earns in a month is wages. It’s just that the issuance occurs in parts, at least two. The first part of the salary is usually called an advance .
The advance is intended to support the employee financially until the main part of the salary is paid.
The advance can be issued either from the company’s cash desk or by transfer through a bank to the employee’s card. Currently, an employer cannot force an employee to open a card account with a specific bank. The employee must choose in which bank he would like to open an account to receive wages.
It should also be remembered that when determining the amount of the advance, incentive payments, bonuses, sick leave and other accruals on top of the salary are not taken into account. The calculation is based on the amount that is guaranteed to be accrued under any circumstances.
Employer method
Despite the recommendations of the Ministry of Labor, many organizations continue to pay an advance as a fixed amount from the employee’s income. In most cases, companies choose one of two options for calculating the advance: the actual amount or a percentage of the salary.
In the first option, when the advance is defined as a fixed amount, the company risks overpaying the employee, because in this case the payment does not depend on whether the employee actually worked or was absent for any reason. There are often cases in which, based on the results of work for a month, the salary turns out to be significantly less than the advance payment, which is recorded in the employer’s regulatory documents. I think more than one employer has encountered this problem, which is why the payment option as a percentage of wages is currently the most widespread among businessmen. According to my observations, the advance percentage is 40%.
Why do companies choose this approach? Since the amounts of the advance and wages should be approximately equal, and personal income tax of 13% is withheld when paying wages and not the advance, it turns out that if you divide the remaining 87% equally, the advance will be exactly 40%. It is better to attribute a larger percentage of the payment to the employee to wages, since after transferring the advance, unforeseen situations may arise: the employee may get sick, take a vacation at his own expense, or quit. Because of such unforeseen situations, questions arise that worry the accountant so much, because he is the one who deals with payroll calculations.
So what to do in the cases listed above, how to apply a fixed advance and at the same time not violate the law and the rights of the employee?
Where are the conditions for issuance established and within what time frame is the advance issued?
Since issues related to the payment of wages are regulated by the state and are considered one of the most important, the enterprise must also create a coherent system in this area.
The procedure and terms for issuing wages must be fixed in the internal documents of the company. As the law states, this must be done in the internal regulations and in one of the agreements - either a collective agreement or a labor agreement. Currently, not many collective agreements are drawn up, so the majority of employers specify the conditions for issuance in employment contracts.
Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the issue of wages and advance payments, among other things. It has been established that wages must be paid at least twice a month, that is, every half month. The advance is issued for the first 15 days of the month. The advance payment period is from the 16th to the 30th (or 31st). Each company sets a specific date independently and enshrines it in its internal documents .
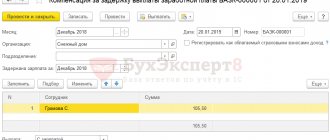
An example of calculating and recording an advance in accounting
At Prodov LLC, the collective agreement provides for a monthly advance payment deadline of the 20th. The salary of employee Drobyazko V.I. is 20,000 rubles. The employment contract also provides for a monthly bonus for professional skill level of 10% of the salary. There are 10 working days for the period from October 1 to October 15. There are a total of 22 working days in October. From October 9 to October 11, Drobyazko V.I. was on leave without pay at his own request. How much should I pay advance payment to V. I. Drobyazko for October?
Solution:
1. Let us determine the amount of the entire salary of V. I. Drobyazko for October:
20,000 + (20,000 × 10%) = 22,000 rub.
2. Let’s calculate the advance for the fully worked half-month:
(22,000 / 22) × 10 = 10,000 rub.
If V.I. Drobyazko had worked the full 10 days required, the advance payment would have amounted to 10,000 rubles.
3. In our case, V.I. Drobyazko was on leave without pay for 3 working days, therefore:
(22,000 / 22) × 7 = 7,000 rub.
On October 20, Drobyazko V.I. will be paid an advance in the amount of 7,000 rubles.
We've figured out how to calculate salary advances. The advance can be issued by the cashier directly from the organization's cash desk, and can also be transferred by the accounting department to the employees' salary accounts in the bank.
Let's look at how advances and salaries are calculated in accounting.
Dt 70 Kt 50 (51) - employees were paid wages for the first half of the month.
The accrual of the advance as part of the salary itself is not reflected in accounting, that is, receivables are formed from the working personnel. It closes at the end of the month after payroll is processed:
Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 29, 44, 91) Kt 70 - monthly wages accrued.
How much can an advance be given?
If you focus on the legislation, then you cannot find the exact amount of the advance in any regulatory act.
Typically, employers have two ways to calculate the amount of an advance to an employee: the amount is set as a fixed percentage or calculated in proportion to the time worked. The second option is more fair and accurate.
| Fixed interest advance | Advance based on actual time worked |
| This is a simplified method. The amount of expected charges for the month is taken, multiplied by a set percentage (usually 40%), the amount of the advance payment for the first half of the month is obtained | Recently, regulatory authorities have recommended using just this method of calculation. The calculation is made in the following way: personal income tax is deducted from the accrued salary amount, the resulting result is divided by the number of working days in a full month and multiplied by the number of days already worked. This method is recommended for all companies. |
How to correctly calculate an advance in 2021?
On August 10, 2017, the Ministry of Labor issued letter No. 14-1/B-725, in which it explained its position regarding what payments should be included in the calculation of the advance payment.
Let's consider the basic rules for calculating advance payments in 2021 according to the opinion of the Ministry of Labor.
Rule No. 1. Advance payments for the first half of the month are made in proportion to the working hours worked in the period from the 1st to the 15th of the current month. That is, if the first half of the month the employee was on sick leave, on vacation or on leave without pay, the advance payment for these periods does not occur.
Rule No. 2. When calculating the advance, you must take into account:
- salary (tariff rate);
- other bonuses for time worked, which do not depend on the assessment of the employee’s performance (for example, for a month, quarter or year): for night work, length of service, for professional level (for example, for the category for teaching and medical staff) and so on .
Rule No. 3. When calculating an advance on wages, the following are not included in the calculation data:
- bonuses based on the results of work activities for a certain period;
- compensatory additional payments, the amount of which can be determined at the end of the month after working hours have been worked out (for example, for overtime work).
These rules also apply to advance payments in 2021.
General rules for payment of wages
There are rules common to all employers that must be followed when paying wages:
- Salaries are paid every half month. The first payment for the current month will be an advance payment
- Specific payment days are established. Wages must be paid at least every 15 days. The enterprise selects a specific payment date and enshrines it in local regulations
- When calculating the advance, the time that the employee worked for half the month is taken into account
- Even if the employee wrote a statement that he does not want to receive an advance, the employer is obliged to issue wages at least every 15 days. Otherwise, it will be a violation of labor laws
The advance amount must be indicated on the pay slip, which is issued to each employee upon payment of the final payment . Thus, the employee can control all accruals for the month.
Also, one should not forget that there is liability for violations when paying an advance. She may be:
- Administrative. Includes fines for both organizations or individual entrepreneurs and individuals
- Disciplinary. Such liability may come in the form of a reprimand, reprimand, or even dismissal.
- Material. If there is a delay in payment, the employer is obliged to pay the amounts due with compensation. Such compensation will be a form of financial liability.
- Criminal. If payments are delayed for a long time, criminal liability arises. This may be the imposition of a fine, which will be many times higher than the fines provided for administrative liability. In addition, an official may be subject to forced labor, imprisonment, or deprived of the right to hold office for up to 3 years.
Results
The advance is the salary for the first half of the current month. Salaries are paid to staff at least 2 times a month. Not all allowances and surcharges are included in the advance payment calculation. The timing of advance payment is reflected in the internal local acts of the enterprise. They must comply with applicable labor standards. According to the general rules, personal income tax and insurance premiums are not paid from the advance payment, however, controversial situations are possible.
Often in various sources you can find a question about the possibility of paying salaries more than 2 times a month.
It would be a mistake to give a negative answer to this question. The Labor Code specifies the minimum amount of salary payments to staff - at least 2 times a month or 1 time every two weeks. But you can pay more often. And this is not a labor violation on the part of the employer. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Advance payment as part of salary
There are several ways to pay an advance for a new employee.
One of them is the payment of an advance as a certain part of the employee’s salary for the month.
Let's imagine that an employee got a job from the beginning of the month, on the 1st. The organization has two dates for payment of wages - the 20th and the 5th. Accordingly, the employee should receive the advance only on the 20th, but this will be a violation of Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with this, the employee may be paid a portion of the salary for the time worked. The employer must choose a specific date that will be earlier than the generally established advance date, but later than the date of payment of the final payment. For example, it could be the number 10.
Accordingly, such a payment for new employees must be fixed in the company’s internal documents. You can write down exactly what date money is paid when you start working in different periods of the month.
Advance to a new employee as an advance payment
Another way to pay an advance for a new employee is prepayment.
Such an advance payment does not fall into the category of wage payments, since it is impossible to fully calculate how much work has been completed and how much time has been spent on it.
In this case, an advance payment is made. It is no secret that some courts consider such payment to be part of the salary.
It is worth keeping in mind that the salary at the end of the month must be paid to the employee, taking into account the prepayment already issued. Such amounts paid should be subject to personal income tax, since they are not part of the salary.
Vacation payments issued in advance
There are situations when vacation pay is paid in advance, but very rarely. Sometimes a new employee may ask for leave as early as the month he starts the job. This situation is possible and the employer sometimes takes such a step. In this case, the amount of such advance vacation pay is collected from subsequent salary payments in an amount not exceeding 20%. This is established by Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
When dismissing an employee who has not returned vacation pay, the employer cannot recover the remaining amount from him. The only way out is to write them off as non-operating expenses after the debt is considered bad.
As you can see, paying an advance is a serious matter, clearly regulated by current legislation. And if there are usually no difficulties with the bulk of employees, then with newly hired employees the story is a little different. In order not to violate current legislation, the employer is forced to pay wages for the first month of work in at least three stages. That is, the first payment to a new employee must be made after two weeks of work. Further payments fall into the general routine and do not raise any questions. All nuances related to the payment of wages must be fixed in the company’s internal documents.