Which legal acts regulate the filling out of the account balance sheet
Historically, the term “ turnover balance sheet ” was not fixed in the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation - in fact, it is used unofficially.
However, the corresponding document is widely used in practice. The use of balance sheets is indirectly predetermined by the provisions of Art. 10 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ. This regulation provides that:
- information reflected in primary documents must be registered and accumulated in accounting registers (Clause 1, Article 10 of Law No. 402-FZ);
- the structure of the accounting register must contain a grouping of accounting objects, as well as the monetary value of the corresponding objects;
- the forms of the corresponding registers for private economic entities are approved by management, for state ones - by budgetary legal acts.
The fact that the balance sheet is used as an accounting register can be associated, first of all, with the legal tradition that was formed in the Soviet Union.
Thus, in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the USSR and the Central Statistical Office of the USSR dated February 20, 1981 No. 35, it is recommended to use just the same turnover statements as accounting registers - for main, synthetic accounts, as well as sub-accounts.
Another significant factor predetermining the use of turnover by modern enterprises is the publication by the Ministry of Finance of Russia of Order No. 119n dated December 28, 2001, by which the department approved methodological guidelines regarding the accounting of inventories of Russian enterprises. The provisions of this legal regulation use 2 concepts:
- turnover sheet - a source that records the amounts of income and expenses that correlate with the movement of goods or materials in the warehouse, balances at the beginning and end of the reporting month, as well as the corresponding amounts in synthetic accounts and sub-accounts;
- balance sheet - a document that generally corresponds to the turnover sheet, but it does not record the receipt and consumption of goods or materials.
Due to the availability of these legal regulations, as well as in the course of document management practices in the business and accounting community of the Russian Federation, more or less generally accepted formats of balance sheets gradually became widespread, the structure of which we will consider further.
There is another significant factor for the compilation of turnover by Russian enterprises. The Federal Tax Service quite often requests them during inspections - both during traditional interaction with taxpayers, and as part of innovative methods of communication with companies, such as tax monitoring.
In particular, clause 8 of the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 05/07/2015 No. ММВ-7-15/184 states that the regulations for information interaction between the taxpayer and the Federal Tax Service should fix the obligation of the former to submit balance sheets to the Federal Tax Service as part of tax monitoring .
Is the fine for failure to submit SALT to the tax authorities legal? The answer to this question, supported by arguments from law enforcement practice, can be found in ConsultantPlus:
If you do not yet have access to the legal system, a trial of full access to the system is available for free.
Express check
The final stage of preparatory activities for submitting reports is the launch of the “Express check of accounting” .
With its help we will check:
- compliance with accounting policies;
- conducting cash transactions;
- analysis of the state of accounting.
After performing an express check, the program displays a report on its results, which reflects the number of errors detected.
Next, a report is generated with detailed information about each detected error with correction tips (Fig. 6). If necessary, from the report you can go to the primary documents and correct them.
What does a balance sheet look like (structure example)
The Soviet legacy and modern business practices have led to the emergence of 3 main types of balance sheets:
- compiled from a set of values in synthetic accounts;
- compiled according to analytical accounts;
- combined, combining the previous types of whorls.
Statements on a set of synthetic accounts compiled by different enterprises will generally be very similar to each other, since the list of relevant accounts is approved by law.
In turn, filling out SALT for analytical accounts in each organization may differ in very specific nuances. Let's consider what a typical structure of a balance sheet for analytical accounts might look like.
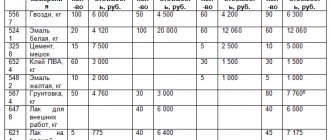
A typical balance sheet for an active or passive account consists of 7 columns:
- name of a specific account (sub-account);
- debit and credit balance at the beginning of the reporting period;
- turnover within the reporting period by debit and credit;
- debit and credit balance at the end of the reporting period.
Depending on which account the balance sheet reflects - active or passive, an increase in assets is recorded in the “Debit” columns and a decrease in them in the “Credit” columns (for active accounts) or, conversely, a decrease in liabilities in the “Debit” and an increase in those in the “Credit” columns (for passive accounts).
You can check whether you are preparing your accounting registers correctly using the Typical Situation from ConsultantPlus. Study the material by getting trial access to the K+ system for free.
How a beginner can understand accounting
Not all accounting rules are regulated by regulations. Most operations are based on primary accounting documents: acts, certificates, invoices, checks, orders, etc. For primary documents, unified forms and recommended samples are provided. The form of the unified document is approved by the relevant instructions and can only be changed by entering additional details . A list of most of these forms with design examples can be found at this link.
How do unified documents differ from ordinary documents?
Ordinary documents can be modified taking into account the specifics of the enterprise or filled out in any form. Unified forms cannot be changed. This is regulated by Federal Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011, which came into force on January 1, 2013, and Russian Government Decree No. 835 dated July 8, 1996. The forms of primary documents are included in the “Album of unified forms of primary documents”, agreed upon by the Ministry of Finance and approved by the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation. The latest amendments to Law 402-FZ were made on May 23, 2016 on the basis of Federal Law No. 149-FZ. Changes have affected the activities of accounting departments of state organizations.
Correct accounting in an organization begins with studying regulatory documents
Where are the SALT fills?
You can download a sample of filling out the balance sheet on our website using the link below. Our experts have prepared for you an example of filling out a statement in Word format, reflecting transactions on account 60 (“Settlements with suppliers and contractors”).
This turnover sheet reflects the following sequence of business transactions:
1. The company transferred to its counterparty an advance payment for goods under a contract in the amount of 100,000 rubles. and reflected this operation as an increase in assets in the debit of active subaccount 60.1. Posting: Dt 60.1 Kt 51 for 100,000 rubles.
2. The counterparty delivered goods to the company under a contract in the amount of 150,000 rubles, and this operation is reflected as an increase in liability in the credit of passive subaccount 60.2. Wiring: Dt 41 Kt 60.2 for RUB 150,000.
3. The company partially pays the counterparty for the goods, and we reflect this transaction as a decrease in liabilities by 100,000 rubles. in the debit of the passive subaccount 60.2 and as a decrease in assets in the credit of subaccount 60.1. Posting: Dt 60.2 Kt 60.1 for 100,000 rubles.
4. As a result, the company owes the counterparty 50,000 rubles, and we record this in the credit of the passive subaccount 60.2, in the credit of the active-passive account 60 as a whole, and also in the final line - as of the end of the reporting period.
Similar statements can be compiled for any accounting account.
My own director
If your business is unthinkable without deferred payment, then we are forced to upset you.
It is impossible to do without certain costs and measures. Especially if you do not use additional tools to protect against the risk of non-payment, such as a bank guarantee, accounts receivable insurance or factoring. The main and most significant risk associated with the delay is the financial losses that the supplier will incur in the event of a long delay or non-payment for the goods supplied by him. Of course, there is always a place for force majeure, because it is impossible to predict absolutely all outcomes of the development of the situation. However, each supplier can (and should!) implement measures to minimize risk. If you are categorically against engaging third parties for protection, then you need to carry out certain activities yourself. We have already talked about how you can check the buyer yourself.
And now you have a new buyer who wants a deferment. You checked it in all databases and open sources - good. But how to assess the financial capabilities of the debtor? Isn't he asking for too much delay? Will it be able to “digest” the volume of goods that is requested? This is where financial reporting comes to the rescue.
Where can I download a blank balance sheet form for free?
The balance sheet form is also available to you on our website. You can download it in Excel format, which allows you to make calculations and apply mathematical formulas.
You can get acquainted with the features of compiling turnover for some common accounts in the articles:
- “Features of the balance sheet for account 60”;
- “Features of the balance sheet for account 01.”
The third one is not superfluous
No matter what you read or what you are told, remember that factoring is not a type of loan.
They have different natures, economic prerequisites, risk management mechanisms, etc. When issuing a loan, the bank evaluates the borrower: who he is, how reliable he is, what his strategy is for “conquering” the market, and how he plans to repay the funds. In factoring, despite the fact that the supplier is financed, the return of funds is made by his debtor. Therefore, it depends on the quality of the debtor whether the factoring company will return its money or not. And it doesn’t matter what type of factoring the supplier uses - with or without recourse: in both cases, the risk lies with the buyer. Therefore, for a factoring company, the reporting of the debtor is even more important than the reporting of the client - the supplier. So, what does a factoring company do with debtor reporting? In principle, exactly the same as what we already wrote about above. It’s just that a factoring company (or bank) has many times more statistics and work experience, which allows you to see some signals in the reporting and react to them a little earlier. But the goals, objectives and tools are the same.
Results
The balance sheet is an accounting register, which is an element of the system for collecting and processing information. As a rule, the form is filled out automatically in accounting systems. Using the statement for tax calculation purposes is possible only in special cases. When carrying out transactions that entail different accounting procedures, there is a need to adjust or prepare a new register for tax purposes.
Sources: Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 N 119n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Fixed Assets (Fixed Assets)
It is necessary to check whether all objects have been accepted for accounting. And when disposing of fixed assets, the documents must indicate the reasons and grounds for the disposal of a fixed asset that could still work. It is important to take into account the consequences of further disposal - liquidation, since the residual value of liquidated fixed assets is taken into account as expenses.
For example, the act in form No. OS-4 must state: before liquidation, the OS is disassembled, and the company plans to use its parts and components.
Drawing up balance sheets and posting transactions
The first job that a novice accountant learns is posting transactions and agreements carried out by the company. It is carried out by double entry, in which a debit for one item will necessarily be a credit for another. For example, withdrawing money from a current account and transferring it to the cash desk of an enterprise for the payment of wages to employees is carried out according to section 5: article 51 - current account (credit for the amount withdrawn), 50 - cash register (debit for the same amount). In this way, all transactions are reflected in accounting.
As a result, for any period, the amount of the entire debit must equal the entire credit. This is balance - the ultimate goal of an accountant in a specific period of time. It cannot be otherwise, because money does not just appear and disappear without a trace. But between posting and balance there is a very important intermediate operation - compiling SALT.