The deadline for submitting annual accounting (financial) statements for 2021 is approaching. In what cases is an audit mandatory?
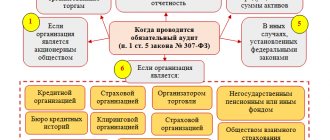
An exhaustive list of grounds for conducting a mandatory audit of the accounting (financial) statements of companies is given in Article 5 of the Federal Law of December 30, 2008 No. 307-FZ “On Auditing Activities” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 307-FZ).
AUDITING SERVICES
Thus, the following are subject to mandatory audit:
- all joint-stock companies without exception (regardless of type - CJSC, OJSC, PJSC and JSC);
- credit, insurance, clearing organizations, mutual insurance companies, organizations that are professional participants in the securities market, funds (non-state pension funds (except for state extra-budgetary funds), mutual funds, AIF);
- companies with revenue from the sale of products (goods, works, services) for the previous reporting year exceeding 400 million rubles (with the exception of state and local government bodies, state and municipal institutions, state unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises, agricultural cooperatives and their unions) or with the amount balance sheet assets at the end of the previous reporting year exceeded 60 million rubles;
- companies whose securities are admitted to organized trading, presenting and (or) publishing summary (consolidated) accounting (financial) statements. Exceptions include bodies of state power and local self-government, state extra-budgetary funds, as well as state and municipal institutions;
- companies in other cases established by federal laws.
For example
, for organizers of gambling, the obligation to conduct an audit is established by clause 12 of Article 6 of the Law of December 29, 2006 No. 244-FZ “On state regulation of activities for the organization and conduct of gambling and on amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation”, for political parties - Federal Law of July 11, 2001 No. 95-FZ “On Political Parties”, for the Russian Science Foundation - Federal Law of November 2, 2013 No. 291-FZ “On the Russian Science Foundation and Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts” RF".
Mandatory audit of accounting (financial) statements for 2018
The list of cases of mandatory audit of accounting (financial) statements for 2021 is given in Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 15, 2019, No. b/n.
Thus, the following are subject to mandatory audit:
- state corporations and companies, state companies (clause 2 of article 7.1 and clause 8 of article 7.2 of the Federal Law of January 12, 1996 No. 7-FZ);
- microfinance companies (clause 4 of article 15 of the Federal Law of July 2, 2010 No. 151-FZ);
- lottery operators (Article 23 of the Federal Law of November 11, 2003 No. 138-FZ);
- organizers of gambling (clause 12 of article 6 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 244-FZ);
- management companies and specialized depositories carrying out activities provided for by Federal Law No. 117-FZ of August 20, 2004 (clause 1 and clause 2 of Article 29 of Law No. 117-FZ);
- housing savings cooperatives (clause 1 of article 54 of the Federal Law of December 30, 2004 No. 215-FZ);
- credit cooperatives, if the number of individuals who are its members exceeds 2,000 people (Clause 1, Article 31 of the Federal Law of July 18, 2009 No. 190-FZ);
- organizations that are self-regulatory organizations (clause 4 of article 12 of the Federal Law of December 1, 2007 No. 315-FZ);
- organizations that are developers that attract funds from participants in shared construction for the construction of apartment buildings and (or) other real estate (except for industrial facilities) (clause 5 of article 3 of the Federal Law of December 30, 2004 No. 214-FZ);
- tour operators operating in the field of outbound tourism (if the total price of the tourist product in the field of outbound tourism for the previous year amounted to more than 400 million rubles) (Article 17.7 of the Federal Law of November 24, 1996 No. 132-FZ);
- other organizations in cases established by Federal laws.
Sphere of influence of the Bank of Russia
- The frequency of control and supervisory activities on the part of the Central Bank in relation to those who audit the SEO will be determined by the Central Bank using a risk-based approach, while according to the law, scheduled inspections by the Central Bank are threatened no more than once a year.
- At the same time, the Central Bank will be able to conduct unscheduled inspections if signs of violations are detected based on the reporting of the audit organization, various complaints and information from the media and other sources.
- The Central Bank will also penetrate into the sphere of conducting qualification exams, in particular, it will establish the procedure for their conduct in agreement with the authorized body
A huge number of other amendments are also being introduced.
- 26 / Jun / 2018
- audit
The status of a small business entity does not always save you from an audit
Let us recall that on June 20, 2021, Order No. 64n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 16, 2016 came into force, changing simplified accounting methods for small and non-profit organizations. This means that small companies will be able to prepare reports for 2021 using simplified forms. A simplified reporting procedure can be used by organizations that are allowed to conduct accounting in a simplified way.
MANDATORY AUDIT
Such organizations include (Article 7 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”):
- small businesses;
- NPO;
- organizations that have received the status of participants in the Skolkovo project.
The criteria by which companies are classified as small businesses are established by Federal Law No. 156-FZ dated June 29, 2015:
- the amount of revenue for the previous year from the sale of goods, works or services (excluding VAT) does not exceed 800 million rubles;
- the average number of employees is no more than 100 people;
- the share of third parties in the authorized capital of the company is no more than 49 percent.
Such small companies can conduct accounting in a simplified way. The indicators of the accounting reporting items also depend on the chosen method of accounting.
But the situation changes dramatically if a small company is subject to mandatory audit. In this case, the company is faced with the need to generate a complete set of financial statements, ensure that differences between accounting and tax accounting are maintained in the accounts (i.e. apply PBU 18/02*, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n), create a reserve for vacation pay (i.e. apply PBU 8/2010, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 13, 2010 No. 167), etc.
Note*
It is possible to refuse to use PBU 18/02 only if a small enterprise has the right to use simplified methods of accounting. And “little ones” who are subject to mandatory audit do not have the right to do this (clause 1, clause 5, article 6 of Law No. 402-FZ).
If a company applies special tax regimes (UTII, simplified tax system, unified agricultural tax), then PBU 18/02 can not be applied, having stated this in the accounting policy.
Usually
, a small enterprise with the organizational and legal form of a joint-stock company is deprived of such simplified benefits (clause 1, clause 1, article 5 of the Federal Law of December 30, 2008 No. 307-FZ “On Auditing Activities”, hereinafter referred to as Law No. 307-FZ ). At the same time, the legislation of the Russian Federation provides for a special procedure for conducting a mandatory audit in a joint-stock company, in the authorized capital of which there is a certain share of state participation (clause 4 of article 5 of Law No. 307-FZ).
The “baby” may have revenues from the sale of products (goods, works, services) for the previous reporting year amounting to more than 400 million rubles, or the amount of balance sheet assets at the end of the previous reporting year - more than 60 million rubles (clause 5, clause 1, art. 5 of Law No. 307-FZ). And in this case, a small enterprise is subject to mandatory audit and you can forget about simplified forms of accounting reporting.
AUDITOR CONSULTATION
Auditing organizations and the Central Bank register
- An audit organization will be able to enter the Central Bank register if it has at least 7 auditors on staff at its main place of work (before January 1, 2023), and after this date - from 12.
- At the same time, at least three full-time employees must meet requirements similar to those for the head of the audit of socially significant organizations (PSO).
- It will no longer be possible to have “bad” auditors among employees.
- A number of other requirements are also introduced: the firm’s audit experience for at least the last three years; absence of violations of independence rules within the same period;
- Cases are also established when an audit firm can be excluded from the register, for example, repeated violations of independence rules over five years.
- It will be established that the audit organization does not have the right to transfer information and documents constituting an audit secret to third parties, or to disclose this information without the prior written consent of the Bank of Russia and the audited entity, except in cases provided for by law.
What if, contrary to the law, the company submits reports using simplified forms?
In the event that the balance sheet and financial results report are presented in simplified forms instead of the generally established (full) forms, or failure to submit certain forms of reports (appendices) may result in the company and its officials being held liable under clause 1 of Article 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Part. 1 Article 15.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
And according to clause 1 of Article 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, failure by the taxpayer to submit documents and (or) other information provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and other acts of legislation on taxes and fees to the tax authorities within the prescribed period entails a fine of 200 rubles for each document not provided.
INITIATIVE AUDIT
Useful with pleasant
Among the individual factors that influenced the market for auditing and consulting services last year, the ranking leaders note demand from the financial sector. In the banking sector, one of the key changes was the transition to IFRS standards in the accounting of credit institutions. “From January 1, 2021, IFRS 9 “Financial Instruments” became mandatory. This standard has generated a wave of demand among credit institutions for the services of auditors and consultants for methodological support of its implementation. This process continued until December 2021,” says Nina Kozlova
, President of the international audit network FinExpertiza.
Alexey Terekhov
, agrees with his colleague : “For banks, the application of new standards has become a difficult task, the implementation of which required changes in a number of business processes in the credit institutions themselves. The qualifications of auditors in applying new accounting standards and the ability to give a professional opinion played an important role when banks chose an audit organization.”
The ranking leaders note stable demand from leasing and factoring companies,” summarizes Klara Valentina Vorobyova
, head of tax consulting practice at MEF PKF.
Among other factors of market growth, it is worth noting the demand for tax consulting services. “In 2021, in our company in the area of tax consulting, three types of services were most in demand: consulting on current issues, project consulting (analysis of tax risks for certain business transactions and tax audits) and accompanying consultations during tax audits, including pre-trial and judicial appeal of decisions of tax authorities. Thus, the surge in activity of client requests for tax consulting at the beginning of 2019 was logically associated with an increase in the VAT rate from 18% to 20% while maintaining the ten percent VAT rate for certain types of goods and services. Also, until February 2021, there was interest in filing special declarations as part of the second stage of the “tax amnesty”; we expect the next wave of requests at the third stage,” says Klara Valentina Vorobyova.
The expanding and deepening digitalization is increasing the interest of large businesses in tax monitoring - when the tax inspector interacts with the taxpayer on an ongoing basis (through remote access to the database of the company being inspected or receiving the relevant information through the EDI operator in electronic form). This replaces on-site and desk tax audits, which are so disliked in companies due to the fact that such audits can simply paralyze the business. “Tax monitoring always replaces audits, plus it provides the opportunity to consult on current issues with tax authorities, which reduces business risks and eliminates uncertainty regarding the tax consequences of the taxpayer’s activities,” adds Nina Kozlova.
Interest in tax monitoring creates a demand for the services of auditors and consultants, since it requires additional adjustment of accounting systems, which, in turn, entails the need for a methodology for organizing the transition to tax monitoring.
How is the fine amount calculated?
When calculating the fine, the full list of documents that the company must submit is taken into account (letters of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated November 16, 2012 No. AS-4-2/19309, Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 23, 2013 No. 03-02-07/2/ 18285).
Thus, as part of the financial statements for 2021, the company must submit:
- balance sheet;
- income statement;
- statement of changes in equity;
- cash flow statement;
- explanations in tabular and text forms.
If the company fails to submit its financial statements on time, the fine will be 1,000 rubles (200 rubles × 5).
If the financial statements are not submitted to Rosstat of the Russian Federation in full, an administrative fine will be charged.
The head of the company faces a fine of 300 to 500 rubles, and the company itself can be fined in the amount of 3,000 to 5,000 rubles (Article 19.7 of the Administrative Code, letter of Rosstat of the Russian Federation dated February 16, 2016 No. 13-13-2/28-SMI) .
AUDIT OF JOINT STOCK COMPANY (JSC)