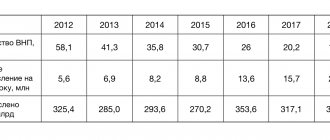
Federal budget taxes
Income tax is a very significant fee for any country, not only Russia.
Due to these payments, the state treasury receives very significant cash injections, which can be compared with revenues from income taxes or VAT. Let’s figure out what level the personal income tax in Russia should be assigned to. The tax system of our country involves three types of taxes: federal, regional and local. Which classification the tax will be assigned to depends on the level of the government agency introducing mandatory payments. According to Article No. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax on labor income is federal. The principle of this classification is based on the fact that personal income tax is a fixed tax, the payment of which is carried out in the same and unchanged way in all settlements of the country without exception.
However, personal income tax does not go entirely to the federal budget. According to the law, only 85% of the total tax funds paid goes to the budget of Russian constituent entities. An exception is made for taxes paid by foreigners who work in Russia under a patent - in this case, the money is credited to the subject budget 100%.
The remaining 15%, according to the Budget Code of Russia, must be credited to local budgets; then they will be distributed depending on the administrative structure of this subject. So, if the subjects have rural settlements divided into municipal districts, the former will receive two percent of the amount, the latter – thirteen percent.
There is no connection between the registration address of individuals and the transfer of personal income tax withheld from wages. However, most often the employer makes the payment based on the territorial affiliation of the company where the employee is employed.
Example. Individual entrepreneurs conducting two or more areas of activity, in one of them will report to the tax office at the place of their registration, in another - to a third-party inspectorate, according to the geolocation where the business is actually carried out. Then the personal income tax for employees will be distributed between different tax inspectorates if the employees are employed in different areas.
All economic entities on the territory of the Russian Federation pay taxes in this group according to the same rules. These rules, as well as any changes made to them for these taxes, are determined only by the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Among federal taxes, special regimes constitute a special category (Section VIII.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Their peculiarity is that when using any special regime, the taxpayer has the right not to pay some other federal, regional and local taxes.
In addition, starting from 2021, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation also regulates the payment of mandatory payments to social funds (Chapter 34). Although the listed insurance premiums, strictly speaking, do not relate to taxes (since they are not gratuitous payments, but assume the receipt of insurance compensation in the future), they can also be conditionally classified as a “federal” group.
Despite their name, not all taxes in this group are credited to the federal budget. Only VAT, water tax, excise taxes (not all, only for certain types of goods) and mineral extraction tax in terms of hydrocarbon raw materials are fully included in it. The rest of the federal taxes are partially, in various proportions, provided for by the Budget Code of the Russian Federation (Chapter.
These types of taxes are not fully regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It defines only the basic principles on which their collection is based (type of tax base, period, terms, range of rates). The exact values of rates, criteria for forming the tax base, as well as benefits are established by specific regions of the Russian Federation or municipalities. Accordingly, individual conditions for these taxes may differ in different regions.
Among the federal, regional and local taxes and fees in force in Russia, one can highlight the trade tax. Its peculiarity is that the code establishes a “territorial” restriction for this mandatory payment. At the moment, only three cities of the Russian Federation can introduce this fee on their territory: Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol (and in practice it has been introduced only in Moscow).
Federal, regional and local taxes represent all levels of the taxation system of the Russian Federation. This means that there is a list of mandatory payments to the government of each level that taxpayers and tax agents need to know.
The federal system of tax payments and fees occupies the supreme position. The main distinctive feature is that it is regulated exclusively by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, established and abolished by it. The transfer of such payments is mandatory throughout the Russian Federation. The full amount transferred by the tax agent or taxpayer goes to the federal budget.
Clause 7 of Art. 12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in 2021 it is established that any other transfers that are not provided for by the specified code cannot be entered into the federal list. The final list of federal taxes is established by numerous articles of the Tax Code of Russia and includes:
- VAT;
- personal income tax;
- income tax;
- for mining;
- water.
However, in addition to the listed mandatory payments, there are other types of monetary contributions to the federal budget, namely:
- National tax;
- excise taxes;
- fee for the use of fauna and water resources.
The procedure for paying tax payments to the federal, regional and local budgets establishes the obligation to indicate the BCC (budget classification code) in the payment order. This detail allows you to correctly attribute the payment and distribute funds exactly to the budget for which they were intended.
Such taxes and fees exist in every subject of the Russian Federation, just as local taxes exist in a separate municipality. The list of types of mandatory payments is established not at the federal, but at the regional and local levels. They may change depending on the decisions of the relevant authorities operating at the level of constituent entities or municipalities. However, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation plays a decisive role in the formation and establishment of the procedure for payment of these taxes. Regional taxes include:
- on the organization's property;
- for gambling business;
- transport.
The list of local tax payments in 2021 includes:
- land;
- on the property of individuals.
The same list includes a trade tax, the procedure for calculation and payment of which is established by Art. 411, 412 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The amount of such payments is determined at the level of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local. For example, the payment rate for the property of a legal entity is regulated by regional authorities, guided by the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The specified rate depends directly on the place of registration of the organization whose property is included in the taxable list.
Most regions of Russia establish payment obligations based on the cadastral value of the property. However, the location to which payments for such property are transferred depends on its location. If the property in question is located at the registration address of the parent organization, then no questions arise. However, if these addresses do not coincide at the level of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, then transfers will be made to the budget of the subject in which the property is actually located.
Regardless of the type of tax payment, the law provides for a special payment procedure. It implies compliance with certain rules. When making payments to the appropriate budgets, in addition to indicating the correct BCC transfers, you must take into account:
- the period for which the transfer takes place. It can be different, including monthly advance payments for some mandatory taxes, for example, on profits;
- compliance with deadlines for reporting and payment of the next amount. For example, income tax is transferred no later than the 28th day of each month following the quarter.
There are other important details for transferring tax payments. For example, income tax belongs to the federal group. Its rate under Article 284 of the Tax Code in 2021 is equal to 20% in the standard case. However, the procedure for its payment implies that it is necessary to create two separate payment orders:
- the first - in the amount of 2% of the calculated amount of tax transfer from the organization's profit. Payment must be made to the federal budget;
- the second - in the amount of the remaining 18% of the organization's total profit. Payment of this part of the profit tax is carried out to the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
It follows that, despite being included in a different group, the majority of the tax on gross profit is transferred to the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation. At the same time, the procedure for paying this mandatory transfer in 2018 by an organization that has a separate division should be established as follows:
- 2% as a general rule, regardless of the location of the OP;
- 18% should be divided between the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in which the head unit and the separate one are located.
Thus, the taxpayer should know which transfers go to which budget level in 2021. Some of them, belonging to a specific group, are divided among several recipients. This is, for example, income tax. You can transfer it correctly using the KBK correctly indicated in the payment order.
Features of the procedure for calculating and paying VAT
The main feature of payment is that the interest is credited at all stages of production of the product. That is, this tax is included in the cost of the initial raw materials from the manufacturer, then the supplier, the seller and, ultimately, the buyer, and each of them must know which budget the rate goes to.
As mentioned above, payment can also be generated after submitting a clarifying document. This information is enshrined in law No. 172 of October 13. 2008.
If, as a result of the audit, an error was found and the tax base was underestimated, before filing the declaration, the payer pays the full amount and penalties for the period of delay.
You need to contact the budgetary institution that indicates the actual location of the companies and where the document is being submitted, that is, in the same locality. Payment is made for a specific period of time for the amount for which the product, service or work was sold, in equal installments until the 20th day of the month following the previous quarter.
Taxation of property of organizations
According to Russian legislation, there are two main objects that are subject to personal income tax. First of all, this is the profit that a resident of Russia receives during the reporting period, regardless of where its source is located - within the country or outside it.
Another object is the profit of non-residents of the country, who, without changing, draw it from Russian sources. In addition to labor income, this includes:
- Money paid for work under an official agreement.
- Income from the sale of your property, shares in organizations, shares, and so on.
- Funds received for the exploitation of the author's rights to intellectual or other property.
- Renting out property located in Russia.
By law, you must independently declare your income:
- Persons conducting private practice (lawyers, private detectives, notaries).
- Persons who received unearned income from the sale or rental of property.
- Citizens whose income is transferred from sources outside the country.
- IP-schniks.
- People who received remuneration from a source that does not have the status of a tax agent.
- Heirs of the authors of inventions, works of science or art, receiving rewards.
- Citizens who have won money in risk-based games (lotteries).
Despite the fact that personal income tax is imposed on any funds that fit the definition of “income,” the Tax Code of Russia includes a specific list of income that is not taxed. Whether this income is received by a resident or non-resident of the country does not matter in this case. The list of such income includes:
- Cash benefits for pregnancy and childbirth, alimony.
- Pension accruals for persons who have reached the legally established age for retirement or who have been recognized as disabled by an examination.
- Compensation for damage to employee health.
- Gifts worth less than 4,000 rubles received by an employee or former employee (pensioner) from the employer.
- Financial assistance in the amount of less than 4,000 rubles received by an employee or former employee (pensioner) from the employer.
- Financial assistance to low-income families whose status is confirmed by the state.
- Payment from the employer's net profit for medical care for its employee or his family members.
- Rewards for blood donors.
- Compensation for damage to employee health.
- Compensation for the cost of vouchers to sanatoriums and other institutions related to the health of citizens (except for tourists).
- Expenses for improving the professional qualifications of an employee.
- Payment for retraining, education or professional training of an employee.
- Scholarships received by students of higher educational institutions.
- Grants for educational or scientific activities.
- Compensation in connection with dismissal, the amount of which is not more than three times the average monthly salary (six times the amount for residents of the Far North).
- Financial assistance to the family of a deceased employee.
- Financial assistance paid to citizens affected by a natural disaster or other emergency situation.
- Funds donated to victims of terrorist attacks.
- Compensation to an employee for the cost of paying interest on a loan for construction or purchase of real estate.
Individuals receiving income (cash) are required to give up part of it in favor of the state budget at a set rate. This alienated part is considered an income tax, which is direct and basic for the entire population of Russia.
The calculation of the amount due for payment to the state treasury is made on the basis of two basic values:
- tax (financial) base;
- tax rate.
Let's talk about these important concepts.
Characteristics of the tax base
For each type of income (object of taxation), such a characteristic as the tax base is used. It is necessary to measure such an object, to express it quantitatively. Essentially, the tax base is the set of incomes on which direct taxes are levied. At the end of each tax period (month, three months, year or other time frame), the tax base is determined.
There is a system - tax accounting, which summarizes data to determine the tax base. Each organization in the status of a tax agent independently creates such an accounting system. This is a necessity established by law. All paying organizations are responsible for the timeliness, reliability and transparency of tax information.
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there are two methods of accounting for the tax base: cash and cumulative. In the first case, actual income that has already been received is taken into account. The accumulative method takes into account not the money itself, but the rights to it. That is, if the organization has not yet received funds, but has the right to receive them, this fact will be taken as income.
In this case, for each form the financial base will be calculated separately, since each type of income has its own rates. The tax base is a value that helps in calculating the amount of income tax. To calculate it, you need to multiply the base by the tax rate.
Tax rates in the Russian Federation
The tax rate is the amount of tax assessments multiplied by the unit used to measure the tax base. This is a mandatory element and the main criterion for calculating any tax established by law.
Table 1. Tax rates in the Russian Federation
| Bid | Meaning |
| 13% | The standard 13% interest rate is levied on the income of individuals, no matter whether it is funds received as wages or money for the sale of an apartment. With the onset of 2015, this rate became valid for the payment of dividends. Please note that the financial basis for dividend deductions is determined separately from other incoming funds that are subject to tax at the standard rate. |
| 9% | 9% is taken from money received in the form of pre-2007 mortgage bonds. The same rate is valid for funds received by the founders of the union managing the mortgage coverage, which were acquired as a result of the purchase of mortgage participation certificates made before 2007. |
| 15% | Non-residents of the Russian Federation, who are individuals who have shares in companies located and operating in Russia, and therefore receive funds here, are subject to a rate of 15% of the amount of income received. |
| 30% | Other income of non-residents not included in the previous paragraph is taxed at 30%. |
| 35% | 35% is withdrawn from cash winnings received by citizens for participating in any kind of event, as well as from the percentage of the bank deposit made. |
One of the elements of regional taxes is a property tax, which is calculated and paid by economic entities, namely legal entities. The object of taxation is property owned by the company. Moreover, the fee is calculated not only from real estate assets (buildings, structures, structures), but also from movable property (machines, equipment, fixed assets).
The maximum tax rate for company property is 2.2%. However, when legislative bodies set regional taxes, officials in some regions approve lower values. Legislators also provide certain benefits for taxpayers.
The frequency of reporting, as well as the deadlines for payment of advance payments and final settlement, is determined by each region independently. That is, for property collection in one region, quarterly transfers to the treasury and submission of settlements to the Federal Tax Service may be provided. And in another subject, organizations pay the budget once a year, and submit a declaration to the Federal Tax Service annually.
General provisions, uniform for application throughout our state, are enshrined in Chapter 30 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. We will tell you how to find out the rules and regulations for a specific region at the end of the article.
You can clarify the tax rates that are fixed for a specific region at the territorial office of the Federal Tax Service. You can also obtain information via the Internet. A special portal developed by tax authorities allows you to determine the key taxation procedure free of charge and without registration. However, the Internet portal does not provide information about the gambling fee.
For information, please follow the link above. Select the type of tax liability, and also determine the tax period for which you need to obtain information. Then you need to select the region you are interested in from the list provided. Click the “Find” button.
The system generates information based on regulations that were adopted by the governments of the regions of Russia regarding tax regulation.
How to reduce the VAT burden for your company
Despite the fact that all business participants are subject to this tax, there are opportunities to reduce the fee or even not pay this percentage at all. Let's consider this point in more detail.
One way to avoid such a percentage is to use a special mode. These include the simplified tax system and UTII. The simplified taxation system is a simplified tax system; it is recommended for representatives of small and medium-sized businesses. UTII stands for unified tax on imputed income. Its peculiarity is considered to be a limited range of areas of activity, for example, passenger transportation. Due to the fact that these regimes already include the payment of all necessary fees, it makes no sense to pay VAT separately to the federal budget level.
The company can take an exemption from transferring for a year. For this, the following conditions are met:
- Location within the Russian Federation.
- No excise duties.
- Revenue for the year is less than 8 million rubles.
The last reduction option represents the hiring of more than 80% of disabled people from the entire state.
We correctly calculate the amount of personal income tax
To avoid imposing a fine for an incorrectly paid amount, it is worth figuring out how to calculate personal income tax. Some will say that the employer does this for most citizens, but at any time you may need to declare income on your own - when you receive winnings, money from the sale or rental of property.
The first step is to quantify the income subject to tax. Next, find out the tax rate for each type of income and calculate the tax base. It was already mentioned above that depending on the type of income, a specific rate is applied, and each rate has its own financial base. The last step, when the named quantities are known, is simple calculations. You need to use the formula specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: multiply the tax base by the tax rate, as a result the total amount of personal income tax will be determined.
Gambling business encumbrance
If a company conducts gambling activities, then it has obligations to the budget to pay a fee for the gambling business. The objects of taxation are:
- Gaming equipment, as well as machines and gaming tables specialized for gaming activities.
- Sweepstakes, bookmakers, betting processing centers with bookmakers.
- Game bets acceptance point.
Since taxes and fees, as well as other payments credited to the treasury of the subject, are recognized as regional, the specifics of taxation are established at the level of a given region. However, there are general rules that apply throughout the country. For example, only two working days are allotted for the procedure for registering a taxable object with the Federal Tax Service.
For this obligation, fixed rates are established, and gradation is provided according to the types of taxable objects. The minimum and maximum values are enshrined in Article 369 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Note that if the region has not established a specific value for the rate, then taxpayers must apply the minimum values.
Formula and example of calculating value added tax
Any taxpayer needs an accountant to carry out the necessary operations and correctly issue invoices and make calculations. But the owner of a particular enterprise will feel more confident if he understands how the scheme for transferring money to state capital works.
To understand the algorithm, let’s present information in the form of formulas and use an example to show how to calculate certain numbers. First, let's take the rate that applies to most goods and was increased from January 1, 2021 - 20%.
As noted earlier, VAT is charged at each stage of production:
- Upon delivery of the original material. For example, a company produces sugar.
- One package of this product costs 50 rubles. The purchasing party must pay an amount of 55 rubles including value added tax.
- When selling the received goods. This package was purchased by a company that is engaged in confectionery activities. From one package two cakes worth 100 rubles were created.
- Upon consumer request. The chain of stores purchased cakes valued at 150 rubles. An ordinary buyer will already pay a price of 165 rubles.
If you buy the same cake, but in a small store, its price will be 330 rubles. Which, of course, becomes unprofitable for the buyer, since 55 rubles are spent on the surcharge; in the form of a percentage, this is 16.6%, which is not true, because sugar belongs to the category of goods eligible for a rate of 10%.
To calculate the VAT amount, you need to know the formula, it looks like this:
VAT= X*20/100, X is a known amount.
For example, if the cost of a product is 100,000, then the premium will be equal to 20,000.
Money calculated and withheld
An employee's income tax goes through two stages before ending up in the government treasury. Every month, at the end of the reporting period, the accounting department accrues personal income tax. The funds will be transferred to the budget later, at the time the employees actually receive their wages. It turns out that in the first order the tax agent calculates (withholds) the amount allocated for the transfer, and in the second order he performs the calculation itself.
The fact of the impossibility of transferring tax funds due to insurmountable reasons is also described in law. If a tax agent company finds itself in this situation, it is obliged to submit to the inspectorate the appropriate papers documenting what is happening as soon as possible.
Personal income tax: document for reporting
Individual entrepreneurs and large companies that are legal entities still hire employees. This means that they are tax agents and must submit to the tax office the necessary documents, which indicate the labor taxes calculated and actually transferred to the state treasury.
Such a certificate in the accounting department is filled out for each employee separately; the basis for the specified data will be the fact that the employee receives wages or other income from the employer.
What happens if you don’t pay personal income tax?
The Russian Tax Code clearly establishes sanctions that will be applied to both the tax agent and the individual in the event that personal income tax is paid late or the transfer of funds to the state treasury is completely ignored.
Thus, tax agents who delay in transferring funds may receive a fine of 20% of the tax amount itself. The state will “charge” the same interest on top if the money is not transferred at all or the calculation is incomplete. Also, arrears and penalties may be withheld from the defaulter.
But there is a nuance - if labor income is paid to employees in kind, it is impossible to collect taxes from them, and delay in tax payment, accordingly, cannot happen either. Another point is that the tax agent did not withhold personal income tax from the employees’ income. In this case, he will also face a fine, but without a penalty.
As for individuals, they may also receive a fine of 20% of the tax amount in case of incomplete payment or non-payment. But the law provides for another penalty for deliberate underestimation of taxable income. If an individual specifically indicates a smaller amount in the declaration, he will be subject to a fine of 40% of the actual amount. The law also exempts individuals from fines in case of late payment. But penalties for personal income tax for late payment will be charged.
By whom, when and to what budget is VAT paid?
So, as it turned out, there are three types of budget revenues:
- Federal (all taxes are mandatory throughout the country).
- Local (organized at the municipal level - land, for the property of individuals).
- Regional (transport, gambling, property of organizations).
The value added tax we are familiar with belongs to the first type, based on this it is clear to which budget the VAT is paid. This means that it is listed everywhere throughout the Russian Federation. Since the total capital is of federal significance, these fees have their own mission: they go towards the improvement of education, medicine, science, culture, social activities, security and defense of the state.
Payers are everyone involved in trade, business, as well as the ordinary consumer. If we turn to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, we will see that it states who exactly needs to pay.
Is personal income tax counted towards other taxes?
We found out that income tax is federal. In this regard, the following questions may arise:
- Is it possible to cover the arrears associated with personal income tax by overpaying another tax, also federal?
- Is it possible to offset the excess of the transferred personal income tax (overpayment) into other missing payments?
If we consider organizations that have the status of tax agents (including individual entrepreneurs), the answers to both questions are negative. We are talking about specific labor income of employees, and personal income tax should be withheld from them. Even if within two to three months the employer makes overpayments or underpayments related to the same person, the tax agent may face fines. The law in this case is adamant - tax is withheld directly when specific money is paid to a specific person.
The above issues are simpler for an individual entrepreneur who pays income tax for himself. Individual entrepreneurs working under the general taxation system also pay VAT (this is also a federal tax), therefore, when submitting a corresponding application to the tax office at their place of residence, they will have the opportunity to make recalculations between these taxes. Such a scheme will help individual entrepreneurs recover overpayments.
Video - Regional and local taxes
Results
The list of taxes that are paid to the federal budget can be seen in the articles of tax legislation. Among them are such large ones as income tax, VAT, and excise taxes. All this significantly replenishes the country's budget.
The regional budget is significantly replenished if there are jobs in the region, factories and factories are functioning, and agriculture is developing.
For the region, this will mean growth both for the subject itself and the standard of living of the working population. The more working citizens engaged in business, the more taxes and contributions are paid, and, accordingly, the budget is replenished.