Mineral extraction tax in the Russian Federation
Editorial Board
Promdevelop editorial team
Mineral extraction tax (mineral extraction tax) must be paid by all enterprises that have the right to use subsoil.
It is regulated by the Tax Code, Chapter 26. All natural resources located on the territory of the country are state property. Therefore, it is impossible to mine them without the knowledge of the government. First, a permit is obtained, after which the entrepreneur is registered as a taxpayer.
mineral extraction tax must be paid by all enterprises involved in this industry. Thanks to him, funds for the use of natural resources are used for the benefit of the population of Russia and the state. They plan to increase the tax, but this may negatively affect the rate of mineral extraction. Failure to pay the appropriate amounts on time will result in a fine. If an organization cannot pay on time, then it is possible to extend the tax payment period, but this requires compelling reasons.
What is mineral extraction tax
What is mineral extraction tax in simple words - this is the main expense item of the oil and gas business. For each ton of extracted products, a certain amount must be paid to the state. All money is sent to the federal budget.
Answering the question, mineral extraction tax - which tax is federal or regional, we can say that the mineral extraction tax is a direct federal tax that is levied on subsoil users. It is the main instrument for taxation of extractive industries.
The general characteristics of the tax on mineral resources show that with its help, funds for the use of natural resources are redistributed and directed to the benefit of citizens and the entire country.
Who is the payer
Which organizations are required to make contributions? Mineral extraction tax (MET for short) must be paid by enterprises that:
- work on sites located on the territory of the country and provided for use by the taxpayer;
- use products obtained from mining waste, if there is a license for extraction;
- extract minerals outside the country in areas leased from other states or under the jurisdiction of Russia.
Taxpayers of mineral extraction tax are all organizations that have received a license and carry out their activities on its basis.
Grounds for registration
By virtue of paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taxpayers are required to register with the tax authorities, if such an obligation is provided for by the Tax Code. Based on paragraph 1 of Art. 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, organizations and individuals are subject to registration with the tax authorities, respectively:
- at the location of the organization;
- at the location of its separate divisions;
- at the place of residence of the individual;
- at the location of their real estate and vehicles;
- on other grounds provided for by the Tax Code. These grounds, in particular, include the presence of an organization or individual entrepreneur in the use of a subsoil plot. According to clauses 1 , 2 of Art. 335 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payers of mineral extraction tax are subject to registration as such:
1) at the location of the subsoil plot provided to the taxpayer for use.
The location of such a site is recognized as the territory of the subject (subjects) of the Russian Federation on which the subsoil plot is located; 2) at the location of the organization (place of residence of the individual). Registration at the location (residence) of the taxpayer is carried out if mining is carried out on a subsoil plot provided to the taxpayer for use, located:
- on the continental shelf of the Russian Federation (includes the seabed and subsoil of underwater areas located outside the territorial sea of the Russian Federation throughout the natural continuation of its land territory to the outer boundary of the underwater edge of the continent);
- in the exclusive economic zone of the Russian Federation. Such a zone is recognized as a maritime area located outside the territorial sea of the Russian Federation and adjacent to it, with a special legal regime established by a special law, international treaties of the Russian Federation and norms of international law;
- outside the territory of the Russian Federation in territories under the jurisdiction of the Russian Federation or leased from foreign states or used on the basis of an international treaty.
Let's figure out under what circumstances it is considered that a subsoil plot has been granted for use. The procedure for using subsoil in the Russian Federation and the relations arising in connection with their use are regulated by the norms of the Law on Subsoil .
Based on Art. 9 of this law, the rights and obligations of the subsoil user arise from the date of state registration of the license to use the subsoil plot. It is a license that is a document certifying the right of its owner to use a subsoil plot within certain boundaries in accordance with the purpose specified in it for a specified period, subject to the owner’s compliance with pre-agreed conditions ( Article 11 of the Subsoil Law ). Consequently, the only criterion for giving an organization or individual entrepreneur the status of a mineral extraction tax payer and the basis for registration as such is the presence of a license to use subsoil. (This is also confirmed by the fact that registration is carried out within 30 calendar days from the date of state registration of the license (permit) for the use of a subsoil plot ( clause 1 of Article 335 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).) Moreover, the need for registration is not affected by the above the license contains the intended purpose of the permitted work. This means that the subsoil user is subject to registration as a mineral extraction tax payer when carrying out any type of subsoil use, including that which does not result in the extraction of mineral resources, which is subject to mineral extraction tax (letters of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 6, 2013 No. GD- 4-3/22016 , Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 10/08/2013 No. 03-06-05-01/41901 ).
Types of subsoil use are listed in Art. 6 of the Law on Subsoil . Subsoil is provided for use:
1) for regional geological study, including:
- regional geological and geophysical work;
- geological survey;
- engineering-geological surveys;
- scientific research, paleontological and other work aimed at the general geological study of the subsoil;
- geological work on forecasting earthquakes and studying volcanic activity, creating and maintaining monitoring of the state of the subsoil, monitoring the regime of groundwater;
- other work carried out without significantly damaging the integrity of the subsoil;
2) for geological study, including the search and assessment of mineral deposits, as well as for geological study and assessment of the suitability of subsoil areas for the construction and operation of underground structures not related to mining;
3) for exploration and extraction of mineral resources, including the use of waste from mining production and related processing industries;
4) for the construction and operation of underground structures not related to mining;
5) for the formation of specially protected geological objects that have scientific, cultural, aesthetic, sanitary, health and other significance (scientific and educational sites, geological reserves, wildlife sanctuaries, natural monuments, caves and other underground cavities);
6) for collecting mineralogical, paleontological and other geological collection materials.
Tax rates for calculating the indicator
All rates are expressed in percentages and rubles. Coefficients are applied to some of them. The rate depends on:
- price fluctuations;
- method and level of difficulty of extraction;
- characteristics of the territory in which the deposit is located;
- price fluctuations on the world market;
- degree of depletion of the deposit.
All coefficients apply to certain types of natural resources. They have a specific meaning or are calculated differentially. The first ones change throughout the year.
The mineral extraction tax rate may be reduced:
- if an entrepreneur is looking for deposits at his own expense (conducting geological exploration of minerals). In this case, the indicator is 30% lower;
- when mining in the Magadan region, the tax is 40% lower. But this does not apply to carbon and common fossils.
Rates expressed as a percentage or ad valorem determine the cost of products obtained from the bowels of the earth. Mineral extraction tax rate and in rubles are specific rates for the amount extracted.
Reference: Ad valorem rates are determined as a percentage of the customs value of goods.
MET rate = R x Kc – Dm
- where R is the base rate of the mineral extraction tax (919 rubles in 2021);
- Kc is a coefficient characterizing the dynamics of world oil prices,
- Dm is an indicator characterizing the characteristics of oil production and determined in the manner established by Art. 342.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (see cost of oil production).
Dm = Kndpi x Kc x (1 – Kv x Kz x Kd x Kdv x Kkan) – Kk,
- Kndpi is equal to 530 - from January 1 to December 31, 2015 inclusive, 559 - for the period from January 1, 2021;
- Kc – coefficient characterizing the dynamics of world oil prices (clause 3 of Article 342 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- CV is a coefficient characterizing the degree of depletion of a specific subsoil area,
- KZ is a coefficient characterizing the amount of reserves of a particular subsoil area,
- KKAN is a coefficient characterizing the production region and the properties of oil,
- CD – coefficient characterizing the degree of complexity of oil production,
- KDV – coefficient characterizing the degree of depletion of a specific hydrocarbon deposit,
- Kk - set equal to 306 for the period from January 1 to December 31, 2021 inclusive, 357 - for the period from January 1 to December 31, 2021 inclusive, 428 - for the period from January 1 to December 31, 2021 inclusive, 0 - from January 1 2021 (source: pravobez.ru).
How to fill out a report
Mineral reporting consists of a title page and eight sections. The general rules for filling out a mineral extraction tax declaration are as follows:
- This is monthly information. Information is provided based on actual performance indicators for each month, and not on an accrual basis for the year.
- Taxpayers report on the use of the resources they actually extract. All other sections are not submitted to the Federal Tax Service.
- Information is sent only for natural resources with a completed production cycle. If on the date of the declaration the mineral is in development, it is not shown in the reporting.
- Mandatory sections to fill out are the title page and section 1 “Amount of tax to be paid to the budget.” The remaining blocks of the declaration are formed only during the actual extraction of a particular resource.
- The pages in the report are numbered in order. If you fill out the form on paper by hand, do not go beyond the margins and do not use a proofreader.
Step-by-step instructions on how to fill out a MET declaration for sand mining for taxpayers:
Step 1. Design the title page. We must indicate:
- TIN, checkpoint;
- correction number (for the primary form set to 0);
- tax authority code and location code;
- tax period (month) and reporting year;
- contact number;
- the number of completed pages in the declaration and the number of pages in accompanying documents;
- FULL NAME. manager or representative of the taxpayer, his signature and date of filling out the report.
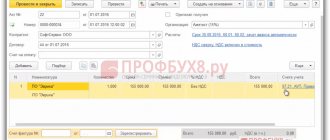
Step 2. Enter information in section 1.
In this part, indicate the budget classification code for paying the tax, the amount of the mineral extraction tax contribution to be transferred and OKTMO at the location of the taxpayer.
IMPORTANT!
The BCC, location identifier and tax amount payable are filled in for each natural resource mined by the taxpayer.
Step 3. Fill out section 3.
This block is not intended for all taxpayers, but only for those organizations that produce oil. Prepare samples of declarations on industrial safety in oil fields for each subsoil site.
Step 4. Enter information in section 3.
In this part, reporting information is provided by gas producers. The production of natural combustible gas and gas condensate is taken into account, with the exception of the production of hydrocarbons in a new offshore field.
Step 5. In section 4, information is provided by hydrocarbon producers in new offshore fields. The license number, name of the deposit and the year of commencement of industrial production are entered.
Step 6. Forming section 5. This section is intended for those who extract the main types of resource. The report must indicate the code of the type of mineral. For our example - construction sand - code 10008 (Appendix No. 2 to Order No. MMV-7-3/827). Here's what else you need to specify:
- KBK for tax payment;
- unit of measure code for the extracted resource;
- tax rate.
Part 5.1 reflects the main characteristics of production - OKTMO, license number, amount of raw materials extracted. Block 5.2 provides tax calculation based on production indicators.
Step 7. We enter information into section 6. It determines the cost of a unit of extracted natural resource at an estimated cost. The taxpayer cites direct and indirect costs for the extraction of all types of raw materials developed by him.
IMPORTANT!
Section 6 is always the same, no matter how many natural resources the organization produces or develops. All expenses are accumulated in this block.
Step 8. Fill out section 7. This block is filled out only by coal miners.
Step 9. We complete filling out the declaration. We reflect the information in section 8. It records the indicators by which the additional tax on the production of dehydrated, desalted and stabilized oil is calculated.
Period, procedure and conditions for collecting payments
Taxpayers must pay a certain amount per calendar month (month – in this case, the tax period). At the end of the month, calculations are made for each type and money is paid to the budget depending on the location of the site.
Payment must be made no later than the 25th day of the month following the expired tax period. The procedure and conditions for payments for the use of subsoil are regulated by the Government of the Russian Federation.
The mineral extraction tax declaration is submitted to the relevant authorities at the location of the enterprise or residence of the individual entrepreneur. The document must be provided in paper or electronic form.
The deadline for paying the mineral extraction tax is determined by Article 344 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but the taxpayer can adjust them legally. It is important not only to make payments on time, but also to report this using a declaration.
According to the mineral extraction tax, the deadline for filing a declaration and payment can be postponed for 3 years in the event that an entrepreneur has serious financial difficulties. But there must be guarantees that he will still pay off the budget.
The KBK MET 2021 for legal entities was approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. The budget classification codes (BCC) also indicate interest, fines and penalties for the mineral extraction tax of the BCC.
Who is required to file mineral extraction tax reports?
Accountable persons are taxpayers extracting mineral resources under a license. As soon as an organization or individual entrepreneur receives a licensing document, it begins to submit monthly mineral extraction tax reports. The obligation to report to regulatory authorities begins from the month in which the extraction of resources actually began (Part 1 of Article 345 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT!
The regulatory documents of the Federal Tax Service indicate whether it is necessary to submit a tax return on mineral extraction tax if the taxpayer has temporarily suspended the extraction of resources - yes, the report must be submitted even if mining activities are suspended (letter of the Federal Tax Service No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] dated 21.08. 2020). While the license for subsoil development is valid, report monthly.
If organizations or individual entrepreneurs are temporarily not engaged in the extraction of mineral resources, they generate zero reporting. Along with the zero mineral extraction tax declaration, a covering letter is submitted explaining the zero indicators in the report.
Tax base for mineral extraction tax
The tax base is:
- The amount of minerals (hereinafter referred to as PI) that were mined. This applies to enterprises engaged in natural gas, oil, gas condensate, except for those extracted from new offshore fields, coal, and multicomponent ores, which are obtained at sites in the Krasnoyarsk Territory.
- Cost of mined PI. If they deal with oil, natural gas, gas condensate in new offshore fields and other useful substances. The cost depends on sales prices, prices excluding subsidies, and the estimated price of products.
Tax base based on current sales prices excluding subsidies
Apply the method of calculating the cost of extracted minerals based on prevailing sales prices without taking into account subsidies if two conditions are met simultaneously:
- the organization receives subsidies from the budget to compensate for the difference between the wholesale price and the estimated cost of the mineral;
- the organization had facts of sales of this mineral during the month for which the mineral extraction tax is calculated, or in the previous month.
This follows from paragraph 2 of Article 340 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If the organization receiving budget subsidies did not sell extracted minerals either in the current or in the previous month, determine the tax base based on the estimated cost of the extracted minerals. This follows from the provisions of paragraph 1 of paragraph 4 of Article 340 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and is confirmed by the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 31, 2014 No. GD-4-3/1631 (the document is posted on the official website of the tax service in the section “Explanations mandatory for use by tax authorities ").
Calculation formulas
The calculation is carried out as follows:
- To find out the cost, you need to multiply the total number of PIs by the unit cost.
- To determine the price per unit of PI, sales revenue is divided by the amount of minerals sold.
- Proceeds from the sale of minerals = price excluding VAT and excise tax - the amount of taxpayer expenses for the delivery of the mineral.
The entrepreneur himself must calculate the tax base. Data is required for each element.
Example for calculating the mineral extraction tax for oil production in 2019
The mineral extraction tax is calculated and paid by taxpayers on a monthly basis. To do this, the Federal Tax Service publishes once a month the data necessary to calculate the mineral extraction tax for oil production. In a message from the Federal Tax Service dated June 18, 2019, the agency notes that the calculation of tax deductions for the period June 2021 should be performed based on the following indicators:
- the average price level for Urals oil on the crude oil markets in June 2021 was $62.37 per barrel;
- The average value of the dollar to ruble exchange rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for all days of the tax period is 64.2314 rubles. for a dollar.
- the value of the Kc coefficient is 11.6576.
Direct and indirect costs
The estimated cost is determined taking into account:
- Direct expenses. They refer to all expenses for wages, the use of funds for production, and the amount of insurance premiums.
- Indirect costs. These are funds spent on repairing equipment, developing natural resources, eliminating fixed assets that are being taken out of service, mothballing and re-mothballing production facilities, and others.
To obtain data on the indicator, it is necessary to select from the total amount of expenses the part that corresponds to the extraction of a certain substance.
Amount of tax deductions
Tax Code of the Russian Federation, mineral extraction tax is calculated in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 343.
The mineral extraction tax formula is as follows:
tax = tax base * tax rate
The calculation must be carried out in compliance with the following rules:
- Each deposit and all types of extracted mineral deposits must be taken into account separately.
- Calculation methods must be enshrined in the payer's accounting policies for the year. You can only change the method at the end of the year.
- Calculation of the mineral extraction tax is carried out taking into account raw materials that have gone through the full technological cycle.
- For some elements, increasing and decreasing coefficients are used.
How to calculate the mineral extraction tax so as not to make a mistake when paying taxes? All changes in calculation rules are displayed on the official tax website.
Example:
Calculation of the mineral extraction tax for sand should be carried out taking into account:
- Relevance rates for sand. It is positioned as a non-metallic raw material.
- The criteria for calculating the base defined in Article 340 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
To obtain the required amount, the first indicator is multiplied by the second.
Also, key indicators in calculating the mineral extraction tax of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are the quantity of goods extracted and sold, delivery costs and VAT amounts. It is also important whether the organization developing and implementing these resources participates in a regional investment project and receives subsidies from the state.
Mineral extraction tax calculation
Calculate the mineral extraction tax monthly separately for each type of mineral (clause 2 of article 343 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Calculate the amount of mineral extraction tax payable to the budget using the formula:
| Mineral extraction tax payable to the budget | = | Tax base (cost of extracted minerals) | × | Tax rate |
This procedure is established by paragraph 1 of Article 343 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Example of mineral extraction tax calculation based on sales prices
Alpha LLC is engaged in the extraction and sale of natural construction sand on the basis of a license.
In September, the organization extracted 28,940 tons of sand and sold:
- 12,000 tons - at a price of 236 rubles/t (including VAT - 36 rubles);
- 14,500 tons - at a price of 330 rubles/t (including VAT - 50 rubles).
The cost of delivering sand to customers in September amounted to 634,100 rubles.
The mineral extraction tax rate for construction sand is 5.5 percent.
The accountant calculated the mineral extraction tax based on the sand sales prices prevailing in September.
The cost of 1 ton of mined sand for calculating the mineral extraction tax was 220 rubles/t (((12,000 t × (236 rubles/t – 36 rubles/t)) + (14,500 t × (330 rubles/t – 50 rubles ./t) – 634,100 rub.) : (12,000 t + 14,500 t)).
The tax base for mineral extraction tax for September is equal to RUB 6,366,800. (220 rub./t × 28,940 t).
The mineral extraction tax payable to the budget for extracted sand at the end of September amounted to: RUB 6,366,800. × 5.5% = 350,174 rub.
An example of calculating the mineral extraction tax on a unique gemstone
In September, Alpha LLC, while mining for precious stones, discovered a diamond weighing 61 carats. The diamond was considered unique. In the same month, the uncut stone was sold at an auction in Moscow for 50,000,000 rubles. (excluding VAT on the basis of subclause 10, clause 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The cost of delivering the stone to the auction amounted to 415,000 rubles. The mineral extraction tax rate on diamonds is 8 percent.
The accountant calculated the mineral extraction tax payable for September for the unique gemstone found: (50,000,000 rubles – 415,000 rubles) × 8% = 3,966,800 rubles.
Tax deduction for oil production
From January 1, 2021, a tax deduction is also provided for oil production in subsoil areas located entirely within the boundaries of the Nizhnevartovsk region of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra, the license for the use of subsoil resources of which was issued before January 1, 2016 and the initial recoverable oil reserves of each of which are 450 million tons or more as of January 1, 2016.
The amount of tax deduction for the tax period is determined in the amount for the named subsoil areas and amounts to 2,917 million rubles. The right to provide this tax deduction is fixed until December 31, 2027.
From January 1 last year, 2 more types of tax deductions were introduced:
- deduction established by Art. 343.3 Tax Code, Russian Federation for the production of natural gas from all types of hydrocarbon deposits produced in a subsoil area located wholly or partially in the Black Sea. This deduction can be used from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2020;
- deduction legalized by Art. 343.4 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when extracting gas condensate from all types of hydrocarbon deposits. This deduction is applied when three points are simultaneously fulfilled:
- the gas condensate produced by the taxpayer organization is sent by it and (or) another organization registered in the Russian Federation, which has the right of ownership and (or) use and (or) disposal in relation to the specified gas condensate, for processing on technological equipment owned by the Russian organization;
- from the gas condensate produced by the taxpayer using technological equipment belonging to a Russian organization, a wide fraction of light hydrocarbons was obtained during its processing;
- the fact of obtaining a wide fraction of light hydrocarbons from gas condensate produced by the taxpayer is documented. Source: hpravobez.ru.
Indirect calculation method
Use the indirect method for determining the amount of extracted mineral resources for the purpose of calculating the mineral extraction tax when the direct method cannot be used. The method consists in determining the amount of extracted minerals by calculation based on the proportion of its content in the extracted mineral raw materials. In this case, the very amount of extracted raw materials is determined by measuring instruments. Such requirements are established in paragraph 2 of Article 339 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Situation: is it possible to apply a 0 percent rate when calculating the mineral extraction tax on standard losses of mineral resources? The organization uses an indirect method to determine the amount of minerals extracted.
Yes, you can.
The mineral extraction tax on standard losses of mineral resources is calculated at a rate of 0 percent (subclause 1, clause 1, article 342 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, Article 342 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not limit the right to apply a zero tax rate depending on the method of determining the amount of extracted mineral resources (direct or indirect). Consequently, an organization using an indirect method for determining the amount of extracted minerals can calculate the mineral extraction tax at a rate of 0 percent in relation to actual losses that do not exceed the standard value.
The legitimacy of this conclusion is confirmed by letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 22, 2007 No. 03-06-06-01/21 and dated February 19, 2007 No. 03-06-06-01/7, as well as arbitration practice (see, for example , determinations of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated December 22, 2008 No. VAS-16551/08 and dated April 10, 2009 No. VAS-3275/09, resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated August 28, 2008 No. KA-A40/7979-08, Ural District dated November 27, 2008 No. F09-6261/08-S3, West Siberian District dated September 17, 2009 No. F04-5633/2009(19823-A75-43)).
How are natural gas and gas condensate producers taxed?
The tax rate is multiplied by the base value of a unit of standard fuel and by a coefficient that characterizes the degree of complexity of extracting combustible natural gas and gas condensate from carbon deposits.
Calculation of the mineral extraction tax on gas condensate is carried out taking into account the established correction factor.
When calculating the tax rate for natural gas, the product of the base rate, the base value of a unit of standard fuel and the production complexity coefficient are summed up with the value of the cost of transporting the fossil fuel.
The estimated price for gas sales outside the territories of the member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States or the Mineral Extraction Tax CDZ for July 2021 is RUB 15,552. per 1000 cubic meters of gas excluding value added tax.
How are precious metals taxed?
The mineral extraction tax for the extraction of alluvial gold and other precious metals from ore, technogenic and alluvial deposits is determined in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on precious metals.
The assessment of the value of extracted precious minerals is carried out depending on the taxpayer’s prices for the sale of chemically pure metal in the corresponding period, excluding VAT, costs of extraction and delivery to the recipient. The mineral extraction tax rate on silver, gold and other metals depends on this.
If prices for the sale of pure precious metal have not been compiled in the tax period, regardless of whether there is a semi-concentrate containing precious metals, calculations are carried out taking into account the prices that were added up in the previous or preceding tax period.
The mineral extraction tax in the diamond mining industry allows you to fully replenish the budget of the regions in which these minerals are mined.
How to calculate the mineral extraction tax on sand: rate
To begin with, we will determine one of the two key indicators for calculating the mineral extraction tax - the rate for sand as a mineral.
Sand, from the point of view of the classification approved in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, can be:
- mining non-metallic raw materials, if it is glass sand (clause 7, article 337 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- non-metallic raw materials, which are used mainly in the construction industry, if it is natural sand or a sand-gravel mixture (clauses 7, 10, article 337 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For both types of raw materials, the rate is set at 5.5% (subclause 4, clause 2, article 342 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is worth noting that if a mineral belonging to the category of common minerals is mined by an individual entrepreneur, and, moreover, for his own consumption, the mineral extraction tax is not paid (subclause 1, clause 2, article 336 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In practice, the most common types of sand found in nature are common minerals. These include, in particular (clause 2.2 of the recommendations approved by order of the Ministry of Natural Resources of the Russian Federation dated 02/07/2003 No. 47-r):
- any types of sand, except for molding sand, used for the production of glass, abrasive, used in the porcelain and earthenware industry, in the production of refractory, cement materials containing a percentage of ore in concentrations of industrial importance;
- sands, represented by sand and gravel rocks.
Thus, if an individual entrepreneur extracts, for example, glass sand for his own needs, which is not a common mineral resource, then he will have to pay the mineral extraction tax for it at the rates indicated above.
AN EXAMPLE of calculating the mineral extraction tax for minerals mined for its own needs, from ConsultantPlus: The organization extracts limestone from which it produces crushed stone. The tax and accounting procedures for production costs are the same. Extraction costs are reflected in the “20-extraction” subaccount and are written off as the limestone is transferred for processing. The balance of the “20-production” subaccount as of September 1…. Get trial demo access to the K+ system and proceed to the calculation example. It's free.
How coal taxation works
A specific rate applies to it. This means that you need to pay for coal in rubles per ton. Rates are set for each type of coal every three months. At the same time, they take into account how coal prices have changed in the territory of the Russian Federation during this period.
Deflator coefficients used earlier are also used. They are identified and published publicly.
The legislation in Article 343.1 of the Tax Code provides for the possibility of reducing the tax if there are expenses that will provide safe conditions for all workers.
The business owner can take this into account when calculating the tax amount or indicate the amount as a tax deduction. He must also independently calculate the amount of the deduction.
Payment upon liquidation
If an organization is liquidated, the obligation to pay the mineral extraction tax is fulfilled by the liquidation commission (Clause 1, Article 49 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It draws up an interim liquidation balance sheet, which reflects all the obligations of the organization. Tax debts are repaid only after the following have been repaid:
– debt to citizens to whom the liquidated organization is liable for causing harm to life or health (for example, the organization must compensate for harm caused to health due to an injury at work);
– debts for payment of royalties, severance pay and salaries to employees;
– debt to pledgees (at the expense of funds from the sale of the pledged item).
This follows from paragraph 3 of Article 49 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Article 64 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
What changes are expected
The mineral extraction tax in 2021 is included in the program of the new tax regime. The government plans to introduce a profit tax (added income tax) for oil companies, which will come into force on January 1, 2019. Currently, the objects of taxation include oil and gas, for which oil companies pay mineral extraction tax.
Before calculating oil royalties, they take into account how much oil prices have changed in the world, whether reserves and production volumes have been depleted.
The approval of the new tax regime has already been carried out by the Government, but the size of the new tax rate has not yet been provided.
Changes in the mineral extraction tax on oil will apply to fields located in Eastern and Western Siberia, some fields in western Siberia that have already been depleted, as well as those fields that benefit from a reduction in export duties.
The Energy Minister claims that this tax will only affect new projects that are being developed by Russian oil companies.
The Ministry of Finance is convinced that if the tax burden on the oil industry is increased, this could negatively affect the rate of mineral extraction in traditional areas.
Rate
Mineral extraction tax rates are set differentially depending on the type of resource, that is, each element has its own percentage. The mineral extraction tax rate for 2021 is divided into two types: percentage expression and in rubles.
Every year the tax rate undergoes changes, and each year the rate increases rather than decreases. But the reduced tariff, benefits and 0% rate make it easier to get busy.
- If the mineral extraction tax tariff on oil in 2021 was 857 rubles per ton, then in 2021 it increased to 919 rubles. At this time, the tariff has not increased further.
- The mineral extraction tax on gold in 2021 is 6%, and the tariff on other precious metals is 6.5%. According to Federal Law No. 41, the amount of tax on precious metals is calculated on the territory of the deposit.
- Gas and natural condensate is measured not only as a percentage, but also in rubles, which makes it more expensive: condensate - 42 rubles. for 1 thousand m3, 35 rubles. - natural fuel.
- The coal coefficient varies greatly between types of resource: the tariff for the extraction of brown coal is 11 rubles. per ton and 47 rubles. costs 1 ton of anthracite. The latter rate has been maintained since 2021.
Privileges
For some organizations, a reduction factor of 0.7 is provided. An enterprise uses it if it meets the requirements:
- before 07/01/2001, a company or individual entrepreneur paid OVMSB, but did not pay this duty for work on developed fields;
- the enterprise searched for and developed new deposits at its own expense, and government subsidies were compensated.
Zero rate
The 0% tariff rate is regulated by Art. 342 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which contains information about natural resources that are not subject to duty. Mineral extraction tax is not paid in the following cases:
- in case of standard losses of obtained fossil raw materials during the work process;
- during the production of sand, associated, natural gas, its condensate, very thick oil;
- during the production of qualified associated tin ores;
- when receiving groundwater that contains minerals;
- when processing residues after the extraction of a natural resource;
- during the extraction of medicinal waters;
- when extracting water for agriculture. needs.
Also in paragraph 21 of Art. 342 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicates specific geographical zones where extraction of natural resources is carried out free of mineral extraction tax.