Excise goods
Excise tax is established, as a rule, for special categories of goods that:
- or they are extremely profitable (gasoline, diesel fuel, natural gas) - in this case, the state, as it were, confiscates part of the profit from the manufacturer;
- or are recognized by the state as undesirable (alcohol, tobacco products) - in this case, excise taxes are established to regulate these types of goods.
Excise goods include:
- cars;
- diesel fuel and gasoline;
- motor oils;
- tobacco products;
- alcoholic products.
The full list of excisable goods can be found in the material “What applies to excisable goods - list 2018?”
How to calculate the amount of excise tax
There are currently three types of bets:
- solid, or as they are often called specific;
- ad valorem;
- combined.
A flat rate is expressed as a fixed amount per unit of production. They are used to determine almost all excisable goods, except tobacco products.
To calculate the amount of excise tax, it is necessary to multiply the corresponding tax rate by the tax base, expressed in physical terms and determined by the volume of excisable products sold.
An example of calculating the amount of excise tax at a fixed rate
The company sold cider in May 2021, which was produced in the amount of 120,000 bottles. The volume of each bottle is 0.5 liters. What is the amount of excise tax that must be paid?
To solve, we first determine the volume that was sold:
Total volume=120,000*0.5=60,000 liters.
Note that the excise tax rate that should be applied is 21 rubles. per liter
After this, you can calculate the amount that should be paid:
Excise tax amount = 60,000*21=1,260,000 rub.
To calculate the ad valorem rate, it is necessary to take a certain percentage of the cost of excisable goods.
The amount of excise tax is determined as the product of the tax base and the ad valorem rate. The base is compiled on the basis of the cost of sold excisable goods, calculated on the basis of prices excluding VAT and excise tax. In Russia, this type of bet is not used.
Excise tax rates for 2021
Excise tax rates for all excisable goods are established in Art. 193 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Let's look at the most common of them:
- Petrol:
- not corresponding to class 5 - the tax rate will be 13,100 rubles. for 1 ton;
- class 5 — 11,213 rub. for 1 ton in the first half of 2021, and 11,892 rubles per 1 ton in the second
For more details, see the material “What is the excise tax on gasoline in 2017?”
- Cars:
- with a power of over 67.5 kW (90 hp) and up to 112.5 kW (150 hp) - the tax rate in 2021 will be 45 rubles. for 0.75 kW (1 hp);
- power over 112.5 kW (150 hp) - 437 rubles. for 0.75 kW (1 hp).
- wine - the tax rate will be 18 rubles. for 1 liter;
- strong alcohol - 523 rub. for 1 liter of anhydrous ethyl alcohol contained in the product.
- cigarettes - the tax rate will be 1,562 rubles. for 1,000 pieces + 14.5% of the estimated cost, calculated based on the maximum retail price, but not less than 2,123 rubles for 1,000 pieces. in the 1st half of 2021 and 1,718 rubles. for 1 thousand pieces + 14.5%, estimated cost, calculated from the maximum retail price, but not less than 2,335 rubles. for 1 thousand units, in the 2nd half of 2021.
Changes in excise taxes 2018
The legislation has introduced a number of clarifications and changes in the rates of some excisable goods. Let's take a closer look at them.
Expanded list of excise-free transactions
Two new subclauses were added to Article 183 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which contains a list of transactions for which excise duty is not provided: 4.1 and 4.2. According to them, from January 2021, in addition to the previously regulated ones, the following operations become non-excise:
- sale of excise goods subject to re-export;
- transfer to the owner or those to whom he indicates, excisable goods that were manufactured according to a toll-to-pay scheme, for the purpose of sale abroad under the re-export procedure.
Changes in excise taxes on distillates
The above law clarified the parameters and operations with such excisable goods as middle distillates . According to subclause 1 of clause 1 of Art. 181 of the new edition of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, they are liquid mixtures of oil and gas processing products. The law specifies the physical and chemical parameters of such distillates:
- the condition of the product is assessed at a temperature of 20ºС and standard atmospheric pressure of 760 mm Hg. Art.;
- the product can be primary or secondary processed;
- excisable hydrocarbons can be produced from oil, gas condensate, oil shale, and associated petroleum gas;
- The density of the products under the specified conditions should not exceed 930 kg/m3.
operations with middle distillates are subject to excise tax :
- receiving;
- purchase of property;
- arrival after processing of raw materials, which were the property of the organization.
The Tax Code clearly outlines the methods for calculating excise duties on this type of goods, as well as the nuances of using the right to a tax deduction for such transactions. In this regard, paragraph 2 of Art. 195, paragraph 4, art. 199, paragraph 2 of Art. 200 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and new clauses were added - clause 25 and clause 26 of Art. 201 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Innovation of evidence
Those entrepreneurs who process middle distillates will have to pay a fee to obtain a registration certificate. This, according to legislators, should help control the accrual and payment of excise taxes. Art. 179.6, new to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, talks about the rules by which such certificates will be issued.
Art. slightly amended. 179.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in terms of clause 1. It regulates the rules for issuing certificates for operations with straight-run gasoline - now they are written out in more detail.
Raising excise rates
An important change affected not only the size of bets. Now the law allows them to be installed only for 6 months, the “border” passes on July 1.
Clause 1 Art. 193 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation increases excise rates on a number of consumer goods, namely:
- tobacco products;
- liquids containing nicotine;
- e-Sigs;
- Cars;
- gasoline and diesel fuel;
- middle distillates;
- alcoholic goods;
- ethanol.
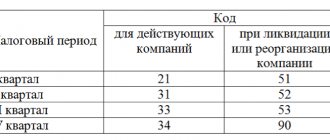
The new bet sizes are shown in the table.
ATTENTION! For cars, not only the rates themselves have changed, but they have been divided into several groups depending on the power of the car’s engine.
Changes in excise rates in 2021
Starting from 01/01/2018 in connection with the entry into force of the Law “On Amendments” dated 11/27/2017 No. 335-FZ in Ch. 22 “Excise Taxes” of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, excise tax rates on gasoline, alcohol, and cars have increased.
Excise tax rates on cars are differentiated and depend on power:
| Automobile | Excise tax rate in 2021 |
| with engine power over 67.5 kW (90 hp) and up to 112.5 kW (150 hp) inclusive | 45 rubles for 0.75 kW (1 hp) |
| with engine power over 112.5 kW (150 hp) and up to 147 kW (200 hp) inclusive | 437 rubles for 0.75 kW (1 hp) |
| with engine power over 147 kW (200 hp) and up to 220 kW (300 hp) inclusive | 714 rubles for 0.75 kW (1 hp) |
| with engine power over 220 kW (300 hp) and up to 294 kW (400 hp) inclusive | 1,218 rubles for 0.75 kW (1 hp) |
| with engine power over 294 kW (400 hp) and up to 367 kW (500 hp) inclusive | 1,260 rubles for 0.75 kW (1 hp) |
| with engine power over 367 kW (500 hp) | 1,302 rubles for 0.75 kW (1 hp) |
Also, new items were added to the list of excisable goods from 01/01/2017:
- electronic nicotine delivery systems,
- liquids for electronic nicotine delivery systems,
- tobacco (tobacco products) intended for consumption by heating.
Application of bets: methods
Excise tax rates for 2021 for each type of excisable goods are established by Article 193 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, options for calculating excise taxes in 2017 may be different. It depends on the form of setting the rate. We provide explanations for the different calculation options.
| 2018 |
| Firm rates |
| The amount of excise duty on excisable goods for which fixed (specific) tax rates are established is calculated as the product of the corresponding tax rate and the tax base calculated in accordance with Articles 187-191 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. |
| Combined bets |
| The amount of excise duty on excisable goods for which combined tax rates have been established (consisting of fixed (specific) and ad valorem (as a percentage) tax rates) is calculated as the amount obtained by adding the excise tax amounts calculated as the product of the fixed (specific) tax rate and the volume of sold (transferred, imported) excisable goods in kind and as a percentage of the maximum retail price of such goods corresponding to the ad valorem (as a percentage) tax rate. |
Results
Excise tax is an indirect tax from which the state budget is formed.
In this regard, excise taxes receive a lot of attention, and excise tax rates are revised every year to “plug holes” in the budget. Therefore, manufacturers producing excisable goods need to very carefully monitor all changes occurring in legislation. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Excise tax as a special type of tax
An indirect tax, which is included in the cost of a certain list of goods, is an excise tax . The following categories must pay it:
- manufacturers of such goods;
- those who import it;
- those who process excisable raw materials.
NOTE! Anyone who resells excisable goods does not pay excise tax separately.
Signs of excise tax:
- collected from all individual entrepreneurs and enterprises throughout the Russian Federation;
- there is no intended purpose (not tied to any budget item);
- calculated and paid by sellers themselves;
- part of the funds goes to the federal budget, part to the regional budget.
Responsibility for non-payment of excise duty
In case of violation of the deadlines for paying excise duty, as well as failure to submit a declaration, the taxpayer faces a fine in the following amounts (122 Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- 20% of the arrears in case of late payment and underpayment;
- 5% of the accrued amount of excise tax in case of failure to submit a declaration, or in case of violation of the reporting deadlines.
Important! The amount of the penalty for failure to file a return will depend on whether the tax was paid on time. If the tax is transferred in full, then the fine for failure to submit a declaration will not exceed 1,000 rubles.
It should also be remembered that if a company must submit a declaration to the Federal Tax Service electronically, but submitted it on paper, the fine will be 200 rubles (119.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How to confirm your right to a tax deduction for excise taxes
Reducing the amount of excise duty payable by using the right to a tax deduction by a refiner of petroleum products is carried out on the basis of the following documents:
- a copy of the registration certificate of the person carrying out operations for refining oil and petroleum products;
- contract for the supply of petroleum raw materials on a property basis;
- agreement for the provision of services for the processing of petroleum raw materials;
- invoices issued by the supplier of petroleum raw materials;
- copies of documents confirming the transfer of petroleum raw materials for processing (invoice for the transfer of raw materials to production, limit cards, etc.). The form of the limit-fence card in form M-8 can be downloaded here ⇒ Limit-fence card;
- copies of documents on the sale of refined petroleum products.
To obtain a tax deduction, the taxpayer is required to provide the above documents along with the tax return within the prescribed period.
Deadlines for paying excise duty and submitting a tax return
It is necessary to pay the excise tax on gasoline and submit a declaration to the tax authority no later than the 25th day of the month following the reporting month. It should be remembered that excise tax on gasoline must be paid at the place of actual production or processing of gasoline (clause 4 of Article 204 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The declaration is submitted to the tax authority at the location of the organization, as well as at the location of each of its separate divisions (clause 5 of Article 204 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Read about the specifics of filling out a gasoline return in the material “Example of filling out an excise tax return .
Concept and elements of excise tax
Excise tax (from the French accise) is one of the types of tax that represents an indirect tax on the sale of a certain type of consumer goods, not related to the receipt of income by the seller. Ultimately, excise tax payers are consumers purchasing goods that are subject to excise duty.
Excise taxes, like VAT, are indirect taxes, since they are also included in the price of goods, but they are levied when carrying out transactions with a certain group of goods that, in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Tax Code), are recognized as excisable. According to the general rule (Article 198 of the Tax Code), a taxpayer carrying out transactions subject to excise taxes is obliged to present the appropriate amount of excise tax for payment to the buyer of these goods.
Payers of excise tax, as well as VAT, are two groups of entities:
- organizations, individual entrepreneurs;
- persons recognized as taxpayers in connection with the movement of goods across the customs border of the Russian Federation.
Excise goods
Article 181 of the Tax Code includes the following groups of goods as excisable goods (subject of taxation)
- ethyl alcohol produced from food or non-food raw materials, including denatured ethyl alcohol, raw alcohol, wine, grape, fruit, cognac, Calvados, whiskey distillates (hereinafter also in this chapter - ethyl alcohol)
- alcohol-containing products (solutions, emulsions, suspensions and other types of products in liquid form) with a volume fraction of ethyl alcohol of more than 9% (with the exceptions specified in subclause 2 of clause 1));
- alcoholic products (vodka, liqueurs, cognacs, wine, fruit wine, liqueur wine, sparkling wine (champagne), wine drinks, beer, drinks made from beer, other drinks with a volume fraction of ethyl alcohol of more than 0.5%, for exclusion of food products in accordance with the list established by the Government of the Russian Federation;
- tobacco products;
- passenger cars;
- motorcycles with engine power over 112.5 kW (150 hp);
- diesel fuel;
- motor oils for diesel and (or) carburetor (injection) engines.
- straight-run gasoline
The object of taxation is transactions on the territory of the Russian Federation with excisable goods listed in Article 182 of the Tax Code.
Tax rates are established by Article 193 of the Tax Code and, depending on the type of excisable goods, are divided into:
- solid (specific), i.e. in absolute amount per unit of measurement (for example, ethyl alcohol - 30 rubles 50 kopecks per 1 liter; cigars - 25 rubles 00 kopecks per 1 piece);
- combined, i.e. hard and ad valorem (as a percentage) (for example, filter cigarettes - 205 rubles 00 kopecks per 1 thousand pieces + 6.5% of the estimated cost, calculated based on the maximum retail price, but not less than 250 rubles 00 kopecks. for 1 thousand pieces).
The tax base is determined separately for each type of excisable goods and depending on the type of taxable transaction.
The tax period is one calendar month.