Companies whose main activity is the production of agricultural products pay the unified agricultural tax (USAT) to the budget. In addition to the basic tax, agricultural producers pay income tax, and such enterprises are required to apply a zero rate for this tax. We propose to understand how income tax is paid for agricultural producers who receive income from activities related to the sale of produced products.
The farm must be an agricultural producer
To apply a preferential rate for income tax, an enterprise must meet the criteria of an agricultural producer set out in paragraph 2 or subparagraphs 1 or 1.1 of paragraph 2.1 of Article 346.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
These criteria are provided for enterprises switching to paying a single agricultural tax, but they are also relevant for applying a profit tax rate of 0 percent (clause 1.3 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To obtain the status of an agricultural producer, you must have income from the sale of agricultural, forestry and livestock crop products, including as a result of the cultivation and rearing of fish and other aquatic biological resources, or from catching them. Specific types of such products and biological resources are determined by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 25, 2006 No. 458. In addition, it should be borne in mind that the share of proceeds from the sale of these products and products of their primary processing (including on leased fixed assets) should be in the total amount of income from sales is at least 70 percent.
The fact that in the previous year the enterprise did not belong to the category of agricultural producers does not create obstacles to the application of a preferential rate in the current year. This was noted by the judges in the resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated February 9, 2010 No. 12390/09.
Transition to Unified Agricultural Tax
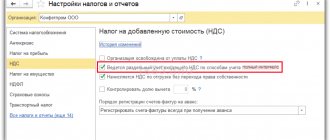
The procedure for switching to a taxation system for agricultural producers is quite standard. The taxpayer must, by December 31 of the current year preceding the year of transition to the unified agricultural tax, submit a corresponding notification on the established form to his tax office. The current form of notification was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 28, 2013 No. ММВ [email protected]
The transition to a single agricultural tax is voluntary. This is a right, but not an obligation of the payer. If a company or individual entrepreneur has just registered with the tax authorities, they can submit an application to switch to the unified agricultural tax within 30 calendar days from the date of registration.
To switch to a taxation system for agricultural producers, it is not enough for a taxpayer to simply have the desire and submit a notification. It must also meet several criteria:
- Proceeds from the sale of agricultural products must be at least 70% of the total income of the payer.
- For fishery companies, as an additional condition for the transition to the Unified Agricultural Tax, the number of personnel is set at no more than 300 people (clause 2.1 of Article 346.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- The goods sold must relate to agricultural products (we indicated earlier what exactly this refers to). A more detailed list of such products can be found in the All-Russian Product Classifier (clause 3 of Article 346.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, companies should be engaged in the production of agricultural goods, and not just resell them.
The following tax regime cannot be applied:
- companies producing excisable products;
- organizations involved in the gambling business;
- budgetary, autonomous and government institutions.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the procedure for switching to the simplified tax system “Submitting a notification of transition to the simplified tax system in 2020–2021.”
When calculating the share, not all income is taken into account
To determine the status, the total revenue from the sale of products, works and services is compared with the revenue from the sale of its own agricultural products and processed products.
Other income is not taken into account when calculating the share. In particular, the income of an agricultural enterprise from the sale of a share in the authorized capital of another company is not taken into account. This was pointed out by financiers in a letter from the Russian Ministry of Finance dated December 3, 2009 No. 03-11-06/1/51. The situation is similar with the implementation of land lease rights. Also, when calculating the share, non-operating income is not taken into account, the list of which is established in Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, income from leasing property (including land plots) for rent (sublease), if such income is not defined by the taxpayer himself as income from sales (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 5, 2012 No. 03-11-06/1/12). Income in the form of interest received under loan agreements, bank accounts, bank deposits, as well as securities (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 24, 2011 No. 03-11-06/1/17) is also not taken into account. Income in the form of gratuitously received property (work, services) or property rights is not taken into account.
A similar conclusion was made for the case when an organization received subsidies from the budget to reimburse costs or lost income in connection with the production (sale) of goods, performance of work, provision of services, including subsidies for one sold dose of bioproducts (letter from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 29 2011 No. 03-11-06/1/10).
Let us note that the lists of income from sales and non-operating income provided for in Articles 249 and 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not exhaustive, as noted in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated April 17, 2007 No. 20-12/035144. It turns out that farms have the right to independently classify in their accounting policies income that is not listed in Articles 249 and 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, defining them as income from sales or non-sales.
Separate records should be maintained
A preferential income tax rate of 0 percent does not apply to all taxable profit, but only to income from activities related to the sale of domestically produced and processed agricultural products.
Therefore, it is necessary to separately determine the tax base for each type of business transaction, the profit from which is taxed at rates other than the general one (clause 2 of Article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To calculate the tax base, the income received by the agricultural enterprise must be reduced by the amount of expenses. In this case, income and expenses must be correlated. That is, income received from such operations can be reduced only by expenses incurred within the framework of these same operations.
Both general business expenses and non-operating expenses are subject to distribution. This is explained by the fact that, in accordance with the requirements of paragraphs 2 and 3 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses, depending on their nature, as well as the operating conditions of the agricultural enterprise, are divided into those related to production and sales (Article 253 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and non-sales (Art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Non-operating expenses that are directly related to the activities of an agricultural producer, subject to corporate income tax at a rate of 0 percent, are taken into account when determining the tax base for this type of activity. If it is not possible to determine whether non-operating expenses belong to a specific type of activity, then such expenses are distributed between them in proportion to the share of the corresponding income in the total volume of all income of the enterprise (clause 1 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 3, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/710).
General business expenses are distributed in a similar way.
Tax reporting
The agricultural tax system gives some tax freedom to single tax payers. Thus, the payer must submit a tax return only based on the results of the tax period (year) by March 31 of the year following the previous one.
If an agricultural enterprise or individual entrepreneur is late in submitting reports, they will be required to pay a fine in the amount of 5–30% of the tax amount, but not less than 1,000 rubles.
For information on the procedure for submitting reports under the simplified tax system, read the article “Procedure for submitting reports under the simplified tax system.”
What income is taxed at a preferential rate?
The income taken into account when determining the status of an agricultural producer and subject to income tax at a rate of 0 percent may not be the same.
For example, according to officials, an agricultural producer has the right to apply a zero rate to non-operating income directly related to the main activity. This is stated in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 8, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/296, dated February 21, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/108.
At the same time, if the receipts have nothing to do with agricultural production, then they should be taxed at a rate of 20 percent (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 23, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/612, dated April 4, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/210). Let us note that this point of view is also supported by the judges (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated April 13, 2012 No. A27-9933/2011).
Procedure for deregistration of unified agricultural tax
In order to deregister as a Unified Agricultural Tax payer, a business entity must inform the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate using a special form about its decision before January 15 of the following year. He can change this regime voluntarily only from the beginning of the year. In this case, you need to use the form provided by law “Notification of refusal to use the Unified Agricultural Tax” form 26.1-3.
Attention: if a company, for one reason or another, completes this activity, then it must also send a message to the Federal Tax Service. To notify the Federal Tax Service, there is a special form “Notification of termination of the activities of the Unified Agricultural Tax” form 26-1-7. The taxpayer must report this within 15 days.
Business entities send a notification of deregistration or refusal to use the unified agricultural tax to the Federal Tax Service at their location - for legal entities, at the place of registration - for individual entrepreneurs.
Tags: Unified Agricultural Tax Tax regimes
If you receive a subsidy
Subsidies received by an enterprise, if they are not related to the activities of an agricultural producer, do not qualify for the benefit.
For example, funds received to compensate for expenses associated with the construction of a road and gas pipeline must be taken into account when forming the tax base, to which the corporate income tax rate of 20 percent is applied (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 23, 2012 No. 03-03-06 /1/611).
But if an enterprise received budget funds under the regional target program “Development of agriculture and regulation of markets for agricultural products, raw materials and food” of a constituent entity of the Federation or for the development of a family livestock farm, then they are taxed at a preferential rate (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 15, 2012 No. No. 03-03-06/1/550).
Subsidies received in order to reimburse costs incurred in the process of eliminating the consequences of damage incurred due to the death of agricultural crops due to abnormal natural conditions for the purchase of mineral fertilizers and diesel fuel are also taxed at a preferential rate (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 27, 2011 No. 03-03-06/1/313).
When the debt is written off
The 0 percent rate does not apply when receiving income from writing off unclaimed accounts payable. This conclusion is contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 23, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/612. In it, officials indicate that in accordance with paragraph 18 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, non-operating income is recognized as the amount of accounts payable (liabilities to creditors) written off due to the expiration of the statute of limitations or for other reasons. In their opinion, these incomes were not received from the sale of produced and processed agricultural products, so they should be taken into account when forming the tax base, to which an income tax rate of 20 percent is applied.
Payment of single tax
The unified agricultural tax is transferred by the taxpayer (clause 5 of Article 346.9 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- before July 25 - advance payment for the 1st half of the year;
- until March 31 of the year following the tax period - the remaining amount of the single tax minus advance payments.
The single tax is transferred to the tax office by bank payment order indicating the necessary budget classification codes and details.
In case of non-payment of the single tax, a fine of 20–40% of the tax amount is provided.
How to take into account fines for late or incomplete payment of taxes (contributions) and fines in connection with violations when submitting reports, find out in ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
What other incomes are not eligible for benefits?
Officials expressed their opinion on the application of a 0 percent rate in relation to income in the form of premiums received by buyers for fulfilling the volume of purchases, interest on placed loans, leasing payments, penalties received under business contracts in a letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 28, 2013 No. 03-03 -06/1/51471.
They indicated that such income is subject to accounting when forming the tax base, to which the corporate income tax rate established by paragraph 1 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (20%) is applied. At the same time, if, due to the terms of the contract, a discount is provided due to a change in the price of the product, the buyer does not receive non-operating income. Financiers came to this conclusion in a letter from the Russian Ministry of Finance dated November 14, 2005 No. 03-03-04/1/354.
Published in the journal “Accounting in Agriculture” No. 3, March 2014.