The procedure for filling out and submitting reports for entrepreneurs under the general regime is established by several chapters of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The greatest number of questions arise when preparing a tax return for individual entrepreneurs for VAT. The legislator established a complex payment mechanism, three rate options and a multi-stage deduction algorithm. In addition, in 2021 there was a transition to an increased rate of 20%. Understanding the system without the help of professional accountants has become even more difficult.
The need to submit a VAT return digitally
Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation regulates the deadlines for submitting a VAT (value added tax) return to the relevant tax authorities. This period is limited to the 25th day of the month following the expired tax period.
Today, the Federal Tax Service accepts VAT returns exclusively in electronic form. In 2021, the right to submit a VAT payment form in paper version is reserved only for agents who are not payers or for some reason are exempt from this obligation. Exceptions are made for persons specified in paragraph 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- carrying out activities in the interests of third parties on the basis of an agency agreement or a commission agreement, which provides for the sale and purchase of services on behalf of the customer;
- carrying out business activities on the basis of a concluded agreement on transport expedition;
- acting as a developer.
If the organization has no employees or their number is small, then no matter what taxation system is applied, there are no exceptions in the form of filing a return for payment of value added tax. If the rules clearly stated in Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are ignored and the VAT declaration is submitted in paper form, then it will not be accepted for consideration. In this case, it will be considered that the document on timely payment of VAT was not submitted, with all the sanctions and consequences arising from this fact.
Should entrepreneurs report VAT?
Not all participants in the turnover are required to submit documents for value added tax. For example, all businessmen who have switched to special taxation systems (USN, PSN, UTII or Unified Agricultural Tax) are exempt from submitting documents.
Agricultural tax entrepreneurs have been recognized as VAT payers since 2019. At the same time, they can take advantage of the exemption under Art. 145 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. You are allowed to submit an application if your revenue for 2018 did not exceed 100 million rubles
The norms of Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are relevant for businessmen who remain in the general regime. The rule on regular submission of information is introduced by Article 174 of the Code. However, the legislator also made exceptions for this category. A VAT return is not submitted in the following cases:
| Item no. | Conditions | Lawyer's comment |
| 1 | Revenue for the previous three-month period did not exceed 2 million rubles | The exemption is provided under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. When determining three months' revenue, value added tax is not taken into account. Only gross income (minus VAT) matters. The definition of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation No. 313-O dated November 10, 2002 established a rule for sellers of excisable products. In general, the rule does not apply to them. Referencing the article is permitted only in relation to transactions that are not related to excise goods. The exemption does not apply to cases of import of goods into Russia (part 4 of paragraph 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
| 2 | Participation in the Skolkovo innovation project for 10 years from the date of acquisition of the corresponding status | The total profit for the grace period should not exceed 1,000,000,000 rubles. The exemption expires once the limit is exceeded. The obligations of a VAT payer arise for the entrepreneur from the beginning of the reporting period in which the limit was exceeded. They lose the right to benefits when leaving the project, as well as when deviating from the chosen direction. Detailed conditions are listed in Article 145.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| 3 | No transactions with VAT, movements on current accounts, cash registers and the provision of a single simplified declaration | Sending EURO is the right, but not the obligation of the taxpayer. The decision to submit this report is made by the entrepreneur |
When answering the question of who reports for VAT, it is worth mentioning special cases. “Special regime officers” who withheld value added tax are required to submit a declaration to the territorial inspection. The reasons for the operation or status will not matter. Such persons are recognized as tax agents (Articles 173 and 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Indirect collection is subject to reflection in reporting and transfer to the budget.
Example. The merchant, using the simplified tax system, mistakenly included the cost of the goods including VAT in the invoice, and the buyer made the payment. In this case, the seller is obliged to transfer the tax to the budget. The corresponding position is enshrined in letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-11-11/48495 dated 08.21.15 and confirmed by judicial practice.
Example. An entrepreneur, using a simplified taxation system, entered into an agreement for the provision of services for the sale of products of a foreign factory. For his work he receives a fixed remuneration. The manufacturer falls under Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and therefore all goods are sold with VAT included. The merchant is required to indicate the tax on invoices and keep records of it in registers. All amounts withheld are subject to transfer to the budget. The plant receives revenue net of VAT.
A special legal status is assigned to FIFA organizations, their subsidiaries, national-level football associations, producers of industry media information, and foreign suppliers involved in the implementation of sporting events. This category of participants in turnover does not pay value added tax and does not submit reports.
In addition, Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes a list of transactions from which VAT is not required to be withheld. The list includes transactions with medical products, medical care, transportation of people, creation of archives, funeral services and more. In fact, VAT payers who apply a 0% rate do not make contributions to the budget. This does not relieve you from the obligation to submit reports.
Representatives of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation have repeatedly explained who should not pay tax. For example, departmental letters have important legal significance:
- on deductions for non-resource exports No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] ;
- on compensation for damages to the contractor No. 03-07-11/70530;
- on the services of tour operators outside the country No. 03-07-08/69685;
- on the sale of club cards of health centers No. 03-07-07/69052.
The legal assessment is greatly influenced by the terms of the transaction. Businessmen should calculate the cost of goods, works and services using zero rates, as well as plan the budget for contracts with the help of qualified lawyers and accountants.
Sanctions for violators
If the procedure for filing a VAT return was not followed (this also includes the case of filing a document in paper form, which was discussed above), the organization will be held accountable. In case of failure to comply with the deadlines for filing a VAT return, according to Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer will be fined. It is 5% of the total amount of tax that has not been paid until the 25th of the current month.
The fine is imposed for each month from the date established by law as the deadline for submitting a document on payment of VAT. It should be borne in mind that the minimum fine cannot be less than 1000 rubles, as well as exceed the 30% limit of the total amount. Since the submission of a VAT return is legitimate only in electronic form, violation of this rule is also subject to penalties, similar to the case when the declaration was not submitted at all.
If the deadlines for filing a VAT reporting document were violated, then, on the basis of Article 15.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, officials of the organization are subject to liability. Punishment includes both a warning and a fine of up to 500 rubles.
A delay in filing a VAT return (this includes attempting to submit it in paper form) for a period exceeding ten working days may also result in sanctions. Tax service employees have the right to suspend any financial transactions with taxpayer accounts, including the circulation of electronic funds. This measure is regulated by Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Important! Since the law makes no difference between filing a value added tax return in paper form and not filing it at all, you should carefully study the rules for filling out the document via the Internet.
Deadlines
The electronic report must be received by the regulatory authority by the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter. Deadlines are strict, and lateness results in monetary penalties.
The taxpayer submits an updated declaration in digital format immediately after discrepancies are discovered. The law does not specify an exact period. If the entrepreneur edits the information before the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter, fines will be avoided (Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Explanations regarding the inspection's request must be submitted no later than 5 working days from the date of receipt of the request.
Formation of VAT returns in digital form
The digital format of the VAT payment document, as well as the necessary attachments, is established by Order of the Federal Tax Service No. ММВ-7-3/ The regulations for submitting a VAT return via the Internet are approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia N BG-3-32/169 dated 04/02/2002.
Sales and purchase books that are generated in CSV, XLSX or older XLS formats must be loaded using operators designed to work with the tax service. All files downloaded in this way will be automatically converted into the universal XML format. The VAT return must be confirmed by an enhanced digital signature in the form established by Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Step-by-step instructions for creating a report
The VAT declaration forms and the format of the explanations are approved by orders of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. MMV-7-3/ [email protected] and No. MMV-7-15/ [email protected] Departmental instructions require that only reliable and complete information be sent to the inspectorate. The basis for filling out the report are accounting registers, as well as primary documentation. Basic requirements are established by Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The legislator obliges entrepreneurs to inform the regulatory authority:
- about all objects subject to VAT;
- about the amount of income and expenses;
- about sources of revenue or other income.
The report must indicate the tax base, the amount of deductions and other information that affects the volume of obligations to the budget. The only appropriate form is electronic. The document must be certified with a qualified digital signature. The number of taxpayers' employees is not taken into account. Paper media cannot be used (Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Note! A change in the VAT rate from 18 to 20% will likely entail a change in the declaration form. However, this has not happened yet. The draft document was published on the portal of regulatory acts. Edits are minor and technical in nature. The order did not come into force.
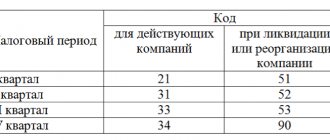
If there were no VAT transactions in the reporting quarter, the documents will still need to be submitted. The zero declaration is filled out according to the same rules as the standard version. The only difference will be the number of sheets:
- Title page;
- first section.
In lines from 030 to 080, the payer should put dashes. An alternative to the zero report is a single simplified declaration (second paragraph of Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is submitted when movements on accounts have completely stopped and there are no transactions subject to VAT.
If an entrepreneur discovers an error, he is obliged to submit updated data to the inspectorate. The adjustment form does not differ from the main declaration form. Features of filling out boil down to reflecting the correct information and putting the report number on the title page.
Additional information may be required by the regulatory authority when conducting a desk audit. In most cases, the reason is discrepancies between the numbers and the control ratios. Sometimes questions arise about the differences between the data of the counterparty and the taxpayer.
Notification of the need for clarification is sent electronically. Inspectors indicate only those points that need confirmation or refutation. The receipt of the prescription must be sent within 6 days. 5 days are allotted for the provision of substantive data. In this case, you must comply with the format requirements (order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. ММВ-7-15 / [email protected] ). Failure to comply with the deadlines may result in blocking of current accounts and a fine.
Important! You can limit yourself to explanations if the adjustment does not change the final indicators. When liabilities are recalculated, an updated declaration is filled out.
Lawyers remind that a desk audit is recognized as the basis for requesting not only clarifications, but also primary documents. The tax office has the right to request accounting registers, invoices and other reports.
Useful information for VAT payers is contained in the letter of the Moscow Regional Office of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. 21-26 / [email protected] dated 12/09/2016. The document is an overview of errors and methods for correcting them.
Tools for preparing reports in electronic form
Obviously, it would be most advisable to submit a VAT return using the program in which it was created. This will eliminate the risk of data corruption or any errors during the process of transferring information from one application to another. That is why there is a need for a tool that will allow you to send VAT data without unnecessary fuss.
Here, first of all, we should mention our own tool with the self-explanatory name “Taxpayer”, which the Federal Tax Service provides on its website. This program is absolutely free, but many may find it inconvenient. For such users, there are many solutions on the market, some of which are distributed under a shareware license, that is, they are shareware.
In practice, this means some restrictions built into the free trial version of the program. These may be limits on the amount of data entered or for the period of the program. Therefore, it makes sense to pay attention to paid products with good technical support, especially since you will have to use them to send a VAT return quite often.
Free VAT submission program from the Federal Tax Service
The official website of the Federal Tax Service provides taxpayers with the opportunity to submit VAT reports absolutely free of charge. Despite the fact that this service does not provide technical support, there is a special “Help” button, upon clicking which the user will be provided with the procedure for each section. This function will greatly simplify filling out the VAT return.
The most significant disadvantage of using software from the Federal Tax Service is the lack of automatic updates. The user will have to independently deal with all possible errors and system failures. Also disappointing is the lack of functionality for testing the declaration before sending it.
Also, in accordance with paragraph 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code and paragraph 3 of Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a VAT return can be submitted using the Federal Tax Service service only if you have an EDS (electronic digital signature) at your disposal. You can purchase it from any center accredited by the Federal Tax Service. Therefore, despite the free nature of the program itself, certain costs for the declaration are inevitable.
What are the consequences of violations?
The absence of a VAT declaration results in fines for the entrepreneur. The control service imposes sanctions taking into account the severity of the offense. Thus, being late in sending a zero declaration is punishable by a penalty of 1 thousand rubles. The basis is Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The fine for failure to submit a report is not collected if the violation is eliminated independently before detection by the inspectorate. In this case, by the time of correction, VAT must be included in the budget along with penalties (clause 3 of Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In other cases, delay is punishable by a penalty of 5% of the unpaid amount. Accruals are made for each month until the final fine reaches 30%.
Reporting methods
You can generate a declaration, as well as explanations for it, in electronic form, as well as send them to the Federal Tax Service, in two ways: direct and representative. The direct method involves the independent conclusion of an agreement between the taxpayer (organization) and the EDI (electronic document management) operator.
In addition to this method, you can resort to the services of intermediary companies that specialize in filing VAT documents. With this scheme, the taxpayer organization acquires the status of a special operator subscriber. She is given access to software for sending tax reports, and a personal digital signature is issued to the manager.
This method presupposes that the organization has a programmer on staff, since it is necessary not only to configure the program, but also to combine it with the accounting program used in the company. You also need to monitor the performance of the system and make regular updates. If you choose to use such a scheme, you will have to make an annual payment to the intermediary company for the services of providing software and for filing a declaration.
A more “advanced” option is to use cloud services. The essence of this service is that to access the software you do not need to install anything on your organization’s computers. All necessary programs are stored in the cloud - on a remote server.
The provider providing the service is responsible for the availability and safety of data. An undoubted advantage of using cloud services for filing a VAT return is their availability from any device connected to the Internet. Also important is the fact that the user has full control over how the declaration is sent, and the possibility of prompt feedback from the tax service.
All of the above concerned the direct method. The representative method is much easier for the taxpayer to implement, but the price comes at the cost of transparency—or rather, the lack of it in monitoring the delivery of reporting documents. The principle of this work is that the delivery of the VAT return is delegated to a company that has all the necessary software.
The services of such companies are usually cheaper than working with an operator. But it should be borne in mind that the tax authorities are not enthusiastic about this scheme for filing a VAT return, since there is no way for them to promptly deliver notifications and demands to the taxpayer organization.
Final check of the declaration
Before sending the VAT return to the tax authority, you should make sure that the filling format is strictly followed, the control ratios are met and all transaction type codes are indicated correctly. This check will save the taxpayer from wasting additional time on providing information clarifying the declaration at the request of the Federal Tax Service.
To carry out such a check, you will need to use special software tools, since the Federal Tax Service online service does not provide a method for testing the correctness of filling out VAT returns. Of the third-party programs designed for verification, we can highlight “Kontur” and “Bukhsoft”, since only they present the verification protocol in the form of decryptions that are understandable to the average person, and not mysterious codes.
Requirements for taxpayers from the Federal Tax Service
In addition to submitting the VAT return directly in electronic form, the taxpayer must:
- Guarantee the receipt of digital notifications of requirements or the provision of any additional documents that will be sent to him by the tax service.
- Send a notification to the tax receipt office in a timely manner, within up to 6 business days, that the digital documents have been accepted.
- Provide, upon request, explanations for the electronically submitted VAT return.
Explanations may be requested by representatives of the tax service if any errors were found in the declaration. The presence of contradictions in the submitted documents or discrepancies between the information provided by the taxpayer and the data available to the tax service may also lead to closer tax control and additional audits.
Sources:
Program "Taxpayer of Legal Entities"
Taxpayer Responsibilities
The procedure for submitting a tax return electronically
Failure to file a tax return
Violation of deadlines for submitting a tax return
Procedure and deadlines for paying taxes to the budget
Suspension of transactions on bank accounts
Approval of the tax return form for value added tax
Tax return, calculations