Small businesses in Russia enjoy special benefits intended only for them. The state is trying to reduce the tax and administrative burden of small businesses, receiving in return an increase in employment and a decrease in social tension. What does the definition of “small businesses” mean and who belongs to them in 2021?
A small business entity is a Russian commercial organization or individual entrepreneur that aims to make a profit. Also included in this category are:
- peasant (farm) farms;
- production and agricultural cooperatives;
- business partnerships.
A non-profit organization, as well as a unitary municipal or state institution is not a small business entity.
Small and medium enterprises criteria 2018
It should be said right away that until 2021, the same rules for classifying companies as small and medium-sized were in effect, but in 2021, slightly different ones apply. This is due to the amendments adopted to Federal Law 209. And such amendments are related to the fact that previously the main criterion, and perhaps the only one, was the amount of revenue from the sale of goods or services. According to Federal Law 209, the criteria for classification as small enterprises are different, and they include three main components.
The components by which enterprises are assessed:
- This is the number of personnel who work at the enterprise;
- The amount of total income from business activities, that is, not just revenue from sales is assessed, but income from all areas of activity: operating, investment and financial;
- Distribution of parts of the authorized capital between shareholders and owners.
It is also important to know that small businesses are divided into two categories: microenterprise and small business enterprise. Depending on the size and amount of income, a company may fall into one or another segment.
So what's changed? Nothing has changed in such a direction as the number of employees. As it was established that a micro-enterprise should employ no more than 15 people, it remains so. As for small businesses, it is allowed to employ up to 100 people.
But in other matters, changes have occurred. For example, the amount of total income from business activities should not exceed 120 million rubles in a micro-enterprise (previously this amount was 60 million rubles), and in a small enterprise no more than 800 million rubles (previously it was 400 million rubles). By the way, please note that the total amount of income is taken into account without VAT, and not with its amount.
I would like to pay special attention to the authorized capital of enterprises claiming to be small businesses. So, there is a limit on the share of authorized capital that can be owned by non-small or medium-sized businesses. Thus, previously it was allowed for up to 29% of the capital to belong to large businesses. Due to the changes, the share in the authorized capital of companies that are not small or medium-sized can now reach up to 49%. If this figure is exceeded, for example, 50%, then the company will not be able to become small. The 2021 small business criteria table is presented below.
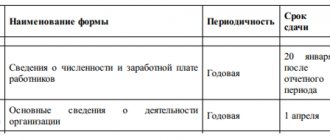
| Type of business | Criteria for classification as small enterprises 2021 | ||
| Number of employees, people | Authorized share in the capital of non-small and non-medium enterprises,% | Amount of income, million | |
| Microenterprise | 15 | 49 | 120 |
| Small business | 100 | 49 | 800 |
Not everyone knows, but in addition to small and large businesses, there are also medium-sized businesses. And in order to have such a status, it is also necessary to meet certain criteria. So such an enterprise should employ no more than 250 people. But regarding the total amount of income from the activities carried out, it should not exceed two billion rubles. The share of the authorized capital must also not exceed 49%.
Considering small and medium-sized businesses, the 2018 criteria, that is, exceptions to the rules. Moreover, such exceptions relate specifically to the share of the authorized capital. So the 49% limit does not apply to the following companies:
- Enterprises working in the direction of innovative development and having government support;
- Enterprises that are included in such a segment of the economy as highly innovative;
- Legal entities that are participants in the Skolkovo project;
- Any companies of national importance that use the achievements of employees in their work (scientific institutes, associations, etc.)
Privileges
Small businesses in Russia enjoy government support in the form of tax and administrative benefits.
For small businesses, there are four special tax payment schemes: the simplified tax system (STS), the unified tax on imputed income (UTI), the patent tax system (PTS) and the unified agricultural tax (UST). If the general taxation scheme implies that a tax of 20% is levied on income, then according to the simplified tax system - 5-15%, according to the Unified Agricultural Tax - 6%. The patent system involves the purchase of a patent, the cost and terms of which are set by regional authorities.
Some small businesses (depending on revenue, type of activity and number of staff) can only enter into fixed-term employment contracts, carry out cash payments without a cash register, and receive various government subsidies.
At the same time, all small businesses have several common benefits:
- the right to keep accounting records in a simplified form;
- 15% share in government procurement;
- the right to receive a state guarantee;
- protection from excessive inspections by state and municipal control.
Some important nuances
The most important question that interests most entrepreneurs is the following: for what period are the results of activities assessed and how quickly the right to small business benefits is lost if one of the criteria is not met?
We answer. Of course, performance results are assessed according to the tax return, as well as according to the company charter.
Regarding the right to benefits for an enterprise that was unable to comply with all requirements during the reporting period. Previously, based on the results of the reporting year, a legal entity lost its small status two years after the reporting period in which such a discrepancy was made. Now this period has been extended and is now three years.
Also, not everyone knows, but there is a special register of small and medium-sized enterprises. Such a register is filled out by tax services, which evaluate such entities according to various criteria. An interesting point is that the owners themselves do nothing to register it as a small business entity. Access to such a register is free. It can be viewed on the Federal Tax Service website, where anyone can, by entering the appropriate details, understand whether there is such a legal entity or an individual. person-entrepreneur in the database or not.
Thus, in order to receive benefits in the form of no funds limit, receiving subsidies from the state, reduced time for inspections, etc., it is necessary to maintain the established limits for a year. Otherwise, you can lose this right in three years.
Similar articles
- Number of small businesses
- Deflator coefficient for 2021 for UTII
- Accounting statements of small businesses 2017
- Simplified balance sheet for simplified tax system 2021 example of filling
- Composition of financial statements 2021 for small businesses
Supervisory holidays
Measures to limit administrative pressure on small businesses began to be taken most actively in Russia in the second half of the 2000s. Thus, on May 17, 2008, shortly after his inauguration, Russian President Dmitry Medvedev signed a decree “On urgent measures to eliminate administrative restrictions in carrying out business activities,” which prohibited inspection of legal entities by state control authorities more often than once every three years (with the exception of tax checks). Dmitry Medvedev’s demand that “law enforcement agencies and all kinds of authorities stop creating nightmares” for business, which he expressed at a meeting on the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the city of Gagarin, Smolensk region on July 31, 2008, became famous.
The public organization “Support of Russia” has repeatedly made a proposal to reduce the number of inspections of small businesses.
On December 4, 2014, Russian President Vladimir Putin proposed introducing supervisory holidays for small businesses. “If an enterprise has acquired a reliable reputation and has had no significant complaints for three years, then for the next three years scheduled inspections within the framework of state and municipal control should not be carried out at all. Of course, we are not talking about emergency cases when there is a threat to the health and lives of people,” the head of state emphasized then. The task of developing regulations for the introduction of supervisory holidays was entrusted to the government of the Russian Federation.
On July 13, 2015, the President of the Russian Federation signed amendments to the legislation developed by the government introducing supervisory holidays for small businesses for the period from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2021. They concern only non-tax audits. According to the established regime, the Ministry of Emergency Situations or Rospotrebnadzor can inspect small businesses only with the sanction of the prosecutor’s office, based on a complaint or having evidence of violations.
On August 17, 2021, the government of the Russian Federation adopted a resolution “On the application of a risk-based approach when organizing certain types of state control (supervision) and amending certain acts.” This document regulates the principles of creating lists for inspection. In particular, if there are no fires at the site, it is allowed to be inspected less frequently. However, such objects as shopping centers are not included in a separate category in the resolution.
In July 2021, the chief state inspector of the Russian Federation for fire supervision, Sergei Kadadov, reported that “the Russian Ministry of Emergency Situations is moving from a system of total control to partnerships with both business and the population.” According to him, in 2021, more than 700 thousand small and medium-sized businesses were removed from the scope of state supervision, and the number of unscheduled inspections was reduced.
Shopping centers - small businesses
The practice of shopping centers being owned or managed by small businesses is widespread in Russian regions. For example, according to Spark-Interfax, small businesses are:
- LLC "Europe-Center" (manages the largest shopping center "Europe" in the Kaliningrad region, area - 60 thousand sq. m), its revenue since 2016 exceeds 800 million rubles, but formally for the supervisory authorities it will remain small for another year enterprise;
- LLC "Management on Svobodny" (owns the shopping center "On Svobodny" in Krasnoyarsk, 37 thousand sq. m);
- LLC "IND-Garnik" (owner of the Tula shopping center "Gostiny Dvor" with an area of 51 thousand sq. m.).
List of advantages of classifying a company as an SME:
- Supervisory 3-year vacation - SMEs should not be subject to scheduled general type inspections by government agencies. But such a relaxation only applies if the company has not been involved in various offenses during the specified period.
- Lack of cash limit - SME firms have the right to operate without the manager’s approval of the cash limit in the cash register. If desired, companies can work with a limit.
- Simplified accounting – the simplified accounting methodology also includes the preparation of simplified financial statements.
- Regional tax incentives – authorities in most regions provide reduced rates for SMEs. For example, this applies to property tax calculated from the cadastral value. The nuances of taxation are specified in the regulations of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for classifying a company as an SME
Organizations are not required to submit any supporting documents or information for inclusion in the SME register. Employees of control bodies, including the Federal Tax Service, automatically classify firms as small or medium-sized businesses. The basis is provided annually by certificates of headcount, tax return data, and information from the Unified Register. Lists of enterprises with SME status are posted on the federal portal of the Federal Tax Service.
The data is updated by tax officials no later than August 10th. The control date is July 1 (Article 6 of Law No. 408-FZ of December 29, 2015). Such a register is open information and is available for viewing by all interested parties. If all the required conditions are met, but the company is not on the list, it is recommended to submit an application to your Federal Tax Service office.
What can you learn from the SME register? In addition to the name of the company and its status, this is the date the company was included in the official register, TIN, and location address. In addition, this is information on the main workers of OKVED and the types of products (services, works). Additionally, this includes data on permits, including licenses, and information on participation in partnerships.