In difficult economic conditions, many employers are forced to reduce the number of jobs. Staff reduction is a special form of dismissal. By law, the employer is obliged not only to pay employees, but also to support them financially during the search for a new job. The total amount of payments is so serious that it can make a hole in the enterprise’s budget. Therefore, it is important to calculate in advance how much it will cost to part with excess staff. Details in our material.
Do I need to justify staff reduction?
Formally, the legislation does not link the decision to reduce staff to any reasons. On the contrary, the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 N 2 “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation” concludes that the employer, for the purpose of effective economic activity and rational property management, independently, under his own responsibility, makes the necessary personnel decisions (selection , placement, dismissal of personnel). The Supreme Court of the Russian Federation bases its arguments on the provisions of Article 8, part 1 of Article 34, parts 1 and 2 of Article 35 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and paragraph two of part one of Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, although the law does not prescribe the existence of any prerequisites for staff reduction, it is still advisable to establish the root cause that served as the basis for making such a decision.
The need to identify the reasons for staff reduction was also pointed out by the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation in its Determination No. 19-B07-34 dated December 3, 2007. In particular, according to the court, the legally significant circumstances of the staff reduction are subject to clarification when considering cases on claims of employees dismissed under clause 2 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The court explained that the employer’s decision to reduce the number of employees and, as a consequence of this, a unilateral change by the employer of the terms of the employment contract in its most acute form, violating the employee’s constitutional right to work - in the form of termination of the employment contract, is unacceptable in an arbitrary manner and must be proven the employer with references to the influence of economic, technical, organizational and other factors on the production process.
Thus, in order to form a future evidence base, it is advisable to initially identify the reasons for the upcoming reduction. The reasons for staff reduction can be different: a change in the owner of the organization, a decrease in production volumes, economic motives, ineffective staff structure, a change in areas of activity, etc.
So, if the employer has decided on the motive for staff reduction, then he can begin the staff reduction procedure, which is expressed in the sequential implementation of the following actions.
You may be interested in: Preparation of a legal opinion Legal Opinion.
Payments on the day of dismissal
The first “package” of payments must be made on the day the employee is dismissed. It includes:
Salary
The employee is paid a salary for the number of days he worked in the month of dismissal, along with the required allowances and bonuses.
Compensation for unused vacation
Each employee who works under an employment contract is entitled to annual paid leave. Unused vacation days do not expire, but accumulate. Upon dismissal, the employer is obliged to pay compensation for these days.
The amount of compensation for dismissal due to reduction is calculated according to a standard algorithm; there are no special nuances. In this article, we will not consider the procedure for calculating compensation.
Severance pay
In general, the amount of severance pay is equal to average monthly earnings.
Separate rules are established for conscripts whose employment contract was concluded for a period of less than 2 months, and seasonal workers. These categories of workers are paid severance pay only for the first two weeks after dismissal.
The benefit amount is calculated as follows:
Severance pay = Average daily earnings * Number of days in the 1st month after dismissal.
Important: when calculating the number of days, not only working days, but also holidays and non-working days are taken into account (Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of November 13, 2019 No. 34-P).
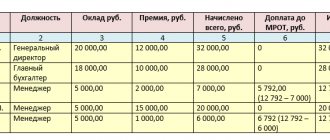
Example: cashier’s salary is 40,000 rubles. On May 17, 2021, the cashier was fired due to staff reduction. Let's calculate the amount of severance pay.
The calculation period for determining the benefit amount includes the months from May 2021 to April 2021 (12 months before the month in which the employee was removed from the workforce).
The cashier's earnings for this period amounted to: 480,000 rubles. (RUB 40,000 * 12 months). During the billing period, the cashier worked 247 days.
Average daily earnings: 1,943.32 rubles/day. (RUB 480,000 / 247 days).
In the 1st month after dismissal (from 05/18/2021 to 06/17/2021) there are 22 working days. June 14 is a holiday, non-working day, we take it into account when calculating.
The severance pay will be: RUB 44,696.36. (RUB 1,943.32/day * 23 days).
Important: the average monthly earnings of an employee who worked the full working hours during the billing period cannot be less than one minimum wage.
So who should not be “redundant”?
An advantage is, of course, good, but some are completely protected from cuts by law. Here the list of people endowed with such immunity is not so long:
- Women who are pregnant or have children under 3 years of age.
- An employee raising a child under 14 years of age alone. And if the child is also disabled, then until he reaches adulthood (18 years old).
- An employee with a large family, while the second parent is unemployed.
- Workers who belong to a trade union. As already described above, they can be fired after agreement with the trade union body.
Involving people in seasonal work: the position of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation enshrines the right of an employer to engage persons in seasonal work by concluding a fixed-term employment contract. Moreover, such an agreement is considered “seasonal”, provided that the nature of the functional responsibilities assigned to the employee directly depends on natural and climatic conditions.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 293 of the Labor Code, the term of a “seasonal” employment contract, as a rule, does not exceed 6 calendar months. The “as usual” clause introduced in Art. 293 of the Labor Code of Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006 implies that a “seasonal” contract can be concluded for a longer period (for example, 8-10 months). But in this case, the employer must comply with the fundamental “principle of seasonality”, namely:
- performance of work under the contract depends on weather conditions;
- During the term of the contract, the employee performs work of the same nature.
For example, an agreement concluded for a period of 10 months, in which during the first 5 months the employee collects crops, and during the next 5 months removes snow, is not legal from the point of view of the Labor Code. In this case, the employer needs to issue 2 fixed-term contracts for a period of 5 months each.
A sample employment contract can be downloaded here ⇒ Employment contract with a seasonal worker.
The concept of pre-emptive right
What exactly is a qualification? And it represents a system of certain ranks in a particular profession. If there is a layoff, the employer will, of course, choose the employee who has a higher rank. Thus, the advantage in staying on the job remains with more valuable employees. However, high qualifications are not the only condition for providing an advantage.
The advantage is provided if:
- The worker is the breadwinner in the family, and besides him there are no other workers.
- There are two or more dependents in the family who are completely financially dependent on the employee.
- A disabled worker from combat operations in defense of the Russian Federation.
- The employee received prof. Illness or injury while working at this enterprise.
- The employee is currently improving his qualifications at the initiative of the employer.
Payments after dismissal
It would seem that the formalities with the employee were settled, the money was given out - goodbye. But it's not that simple. A dismissed employee may receive several more payments from the old employer.
Average earnings while looking for a new job
Such a payment is due to a laid-off employee for the 2nd and 3rd months after dismissal, if he has not found a new job. There is no need to pay anything for the first month, because the employee has already been given severance pay on the day of dismissal.
If the employee was unable to find a job within the 2nd month from the date of layoff, then the former employer compensates him for the period of downtime based on average earnings.
To receive payment, the employee must present a work book that does not contain a record of employment at a new place of work (information about work activity according to the new rules for maintaining electronic work books).
If the employee finds a new job within the 2nd month after the layoff, then he also has the right to receive payment for those days of this month while there was no work.
Let's continue the example: suppose that a cashier who was laid off due to staff reduction will start a new job on July 1, 2021. This means that he has the right to receive benefits from his former employer for the period from 06/18/2021 to 06/30/2021. This period includes 9 working days.
The benefit amount will be: RUB 17,489.88. (RUB 1,943.32/day * 9 days).
And if in the 3rd month after the layoff the dismissed employee was unable to find a job, he can qualify for another payment of average monthly earnings (part of it) from the former employer.
Payment for the 3rd month of unemployment is made only if two conditions are met:
- the employee registered with the employment service within 15 days from the date of dismissal;
- the employee presented the decision of the employment service to maintain average earnings.
The deadline for applying for payment of each average earnings is no later than 15 days from the end of the “unemployed” month (2nd or 3rd).
The employer is obliged to pay the money within 15 days from the date of the former employee’s request.
Workers in the Far North have the right to receive benefits for 4-6 months from the date of layoff.
Instead of payments for the 2nd and 3rd months, the employer can transfer the benefit amount in a lump sum in the amount of twice the average earnings.
Sick leave benefit
If a former employee falls ill, he has the right to demand payment for sick leave from his old employer. But only if the following conditions are met:
- the illness occurred within 30 days from the date of reduction;
- the sick leave was issued for the illness or injury of the former employee himself, and not for caring for a child or infirm relative;
- The former employee has not yet found another job (otherwise paying sick leave is the responsibility of the new employer).
In this case, the employer will pay only three days of sick leave in the amount of 60% of average earnings. In this case, length of service is not taken into account, and average earnings are calculated for the last two years.
Causes and consequences
The main reasons for the reduction include financial difficulties of the enterprise, change of activity, liquidation of the company and its branches. It is financial problems that can be considered the most basic and common reason that forces business managers to resort to such measures.
Currently, this can affect anyone, since the economic situation in the country is unstable and many enterprises are experiencing certain difficulties. Many companies are downsizing because this is the only chance to stay in the market and continue their activities. Let's figure out what happens with this problem.
When staffing is reduced, identical positions or employees of the entire division being reduced are excluded from the staffing table, and not just one employee is dismissed, but everyone who occupies the position that is being eliminated. And if the problem of workforce reduction arises, then the number of employees in a certain position decreases. For example, it is necessary for the enterprise to have 4 mechanics instead of 6.
And then the moment came when the employee was informed that he was being laid off. Every person who faces such a problem has many questions: where to find a job, what to do, but the main question is what payments he is entitled to upon layoff. This issue must be taken seriously, as it has its own characteristics.
How are job offers made?
Within two months after notifying the employee of the layoff, if he has the necessary skills, he can be reassigned to a new position. This is done, of course, only if there are vacancies at the enterprise.
The employee has the right to either agree to the transfer or refuse. The procedure for familiarizing yourself with vacancies is not spelled out verbatim by law, and is organized in each organization individually.
It is advisable to provide a list of available vacancies to employees along with a notice of layoff, and immediately before the dismissal itself, against signature. Also organize a consultation with the HR department so that the employee can familiarize himself with the list of available vacancies at any time. Such measures will help facilitate the reduction procedure.