From the beginning of 2021, the VAT rate will increase from 18% to 20%. This will be an unpleasant “New Year’s gift” for businessmen who pay VAT. The rate increase will also affect those who are exempt from this tax, for example, those who work in simplified jobs, but are in a contractual relationship with VAT payers.
The introduction of any changes is associated with a transition period. We'll tell you what taxpayers need to pay attention to as January 1, 2021 approaches.
From this article you will learn:
- Who will be affected by the VAT rate increase?
- When to make changes to contracts
- Who will pay for the rate increase?
- What do officials say about changes in the contract price when the VAT rate increases?
- What will the court decide if the transaction partners do not agree?
- How to calculate VAT during the transition period
- When is a correction invoice needed?
Why was it decided to increase the tax?
The current VAT rate of 18% has been in effect since 2004. It is paid by all legal entities at each stage of production and sale of products. Naturally, manufacturers and sellers already include the amount of tax in the price of products, so in the end the tax is paid by the consumer. The need to increase the rate was justified for the general public by A. L. Kudrin, chairman of the joint venture. First of all, this need is associated with a significant drop in oil prices starting in 2014.
The fall led to a significant decrease in federal budget revenues: if in 2014 the price of oil was about $110 per barrel, then in the summer of 2021 it fluctuates around $76, which means a drop of almost a third.
The share of oil in the economic structure is also decreasing. Today, non-resource industries are beginning to develop faster, which reduces the share of revenues from oil sales in the budget. Another reason for the decrease in budget receipts is geopolitical instability and increased costs for the growth of Russian territory.
In order to maintain the same level of spending on social needs: education, medicine, infrastructure, the budget requires additional revenues. The increase from raising the VAT rate should go specifically to them, Anton Siluanov directly stated this.
Are there alternatives to increasing the VAT rate? The government believes that it is undesirable to reduce government spending, which means that as an alternative, only even more painful and unpopular measures can be proposed, such as increasing income taxes, canceling benefits and benefits, ceasing support for private businesses, or canceling maternity capital.
How to renew old contracts
The contractual base of the enterprise must be grouped and reissued depending on the type of contract:
- If the text contains a figure with VAT 18%, you will need to sign an additional agreement or re-register the transaction with VAT 20%.
- If the price list is stated, but there is no mention of indirect deductions to the budget, it is recommended to supplement the transaction with more detailed explanations, indicating separately the price and the taxable tax of 20%.
- If the price list is displayed only in shipping documents, the general agreement does not need to be amended.
- The text of the sales document may provide for the seller’s ability to change the conditions unilaterally, taking into account significant adjustments in legislation or the economy; it is not necessary to re-register the transaction, but it is very advisable to warn the buyer.
- The text of agreements with preferential terms of 0% and 10% does not need to be adjusted.
What happens if the rate increases
Privileges
Prime Minister D. A. Medvedev explained that all benefits for services and goods of special social significance will be fully preserved.
Today the rate on essential goods, such as milk and bread, as well as on medications and goods for children, is 10%. For domestic flights the rate is zero.
According to the Ministry of Finance, the preferential rate will continue to be maintained for a third of the goods included in the standard consumption basket.
Inflation
The Minister of Finance explained that an increase in VAT by 2% will actually accelerate the growth of inflation: if now it is about 3 - 3.5%, then the forecast for 2021 is 4.5%.
Alexander Shoshin, Chairman of the Russian Union of Industrialists and Entrepreneurs, believes that the Central Bank and the Russian government will be able to contain inflation at a level not exceeding 4%. Anton Tabakh, managing director of the Expert RA agency, has a different opinion. He believes that an increase in VAT will lead to a more serious acceleration of inflation, which will force the Central Bank to increase the key rate. According to the expert, the increase in inflation in 2019 will be 0.5–0.75 percentage points. If the tariffs of natural monopolists increase, the increase in inflation will actually be much higher than the planned threshold. According to Anton Tabakh, VAT is planned to be raised because it is much easier to collect than other taxes: the Federal Tax Service has today significantly improved its work on collecting and processing data.
Compensation procedure
It is planned to reduce the timing of inspections for VAT compensation carried out desk-wise (such inspections are carried out directly at the offices of the Federal Tax Service, visits to enterprises are not provided for them). The number of enterprises for which VAT compensation will be accelerated will also be increased. If today only companies that have transferred taxes amounting to 7 billion rubles can count on expedited verification. in 3 years, this threshold will soon drop to 2 billion rubles.
When is a correction invoice needed?
If the parties agree on an increase in price, the buyer pays the difference. When an additional payment is made in 2021, it should be accounted for using an adjustment invoice, which is generated in addition to the original advance invoice.
The adjustment invoice contains information about the change in the tax amount and total shipment amount compared to the original invoice. The letter of the Federal Tax Service dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] provides examples of an adjustment invoice.
Adjustment invoice
It happens that for some reason an invoice issued in 2018 was not taken into account on time. In this case, in order to determine the period for which the deduction is applied, the date of receipt of the document is important.
The invoice relating to the 4th quarter of 2021 will be received in 2021. This document includes VAT at the rate of 18%. Depending on the date of receipt of the invoice, the deduction is applied in the following order:
- If it was received earlier than the deadline established for submitting a VAT return for the 4th quarter of 2021 (i.e. before 01/25/19) - include a deduction on the invoice in this declaration (clause 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- If it was received after January 25, take into account the deduction in the declaration for the 1st quarter of 2021. Since the shipment took place in the previous period, there is no reason to increase the deduction - take VAT for deduction at a rate of 18%.
As of the date of writing this article (November 2021), no changes have been made to the VAT return form. But there is already a draft order of the Federal Tax Service, published on the Unified Portal of Draft Regulatory Legal Acts. In accordance with the project, lines will be added to section 3 reflecting increased tax rates. Due to the transitional situation, the declaration for the 1st quarter of 2021 will use old and new lines.
Draft new VAT declaration form
Arguments of the Minister of Finance
A.G. Siluanov considers the rate increase to be a great boon for business and the economy as a whole. He stated this on television on Rossiya-1. The funds received from this tax maneuver will go not only to such social projects as medicine and education, social infrastructure, digitalization, and preferences for business.
The minister believes that the updated quality of healthcare will be achieved within 6 years. As a result, mortality from oncology and diseases of the cardiovascular system will decrease, which is what people die from most often today. And as a final result, the minister plans to increase the overall life expectancy of the population.
The released resources will be invested in digitalization. This means a different quality of life, for example, the availability of high-speed Internet where it is needed - in hospitals or small towns. The funds will be used only for those activities that should produce results and will not be “wasted,” the minister emphasized.
The result of an increase in the VAT rate will be an increase in investment activity in our country, and the growth rate of its economy will also increase. This can be explained by the fact that additional budget funds will be invested specifically in infrastructure, in particular such facilities as roads and airports. The minister considers the impact on inflation not so significant, but he also sees certain disadvantages in its increase. However, in his opinion, the advantages of obtaining additional resources and their more competent distribution significantly outweigh the disadvantages.
Anton Siluanov promised that preferential rates for businesses on a number of product categories will be maintained. In particular, he named such categories as food, medications; school uniform, some other items.
The minister called the abolition of the movable property tax and the simplification of VAT compensation a step towards business. This will allow businessmen to immediately receive 100 billion rubles. working capital next year.
At the same time, the minister claims that talking about the theft of resources is the wrong position. The Federal Tax Service works clearly, so it will become impossible to avoid paying VAT, and that is why the government makes such decisions.
The VAT increase will affect wage growth and important sectors of the economy. The minister suggested remembering that price increases had previously been in double digits. Now the price increase will not affect those goods for which the VAT rate will remain preferential, just as now.
What contracts do not need to be amended?
Agreements where the net price is indicated do not need to be renegotiated, but it is recommended to supplement them with an additional agreement with new tax accounting rules.
When the price is included in the add. agreements for each delivery separately, then the general agreement most likely is not subject to adjustment.
There is no need to correct the supply document, which provides for preferential value added tax, since its amount does not change:
- 0% – export operations;
- 10%, what goods are sold in the Russian Federation using this benefit: basic food products (cereals, meat, fish, dairy, vegetables, sugar, flour, bread, butter, baby food, products for diabetics); some assortment items for children (basic clothing and shoes, diapers, stationery, mattresses, cribs); medicines; books and educational magazines.
Expert forecasts, or who is against
Experts' forecasts are not as optimistic as the position of the Minister of Finance.
This is how the State Duma has already announced the expected inflation figures. They can reach 12%, which, naturally, is not at all as optimistic as the Minister of Finance suggests.
Alexander Kalinin, head of Opora Rossii, believes that problems from raising rates may arise in construction, trade and mechanical engineering. Even before taxes begin to rise, prices will already begin to rise: food, all imports, and housing and communal services will become more expensive.
Robert Aloyan, an expert at the consultancy, believes that raising taxes will affect both business and all groups of the population. And the inevitable acceleration of inflation will reduce to zero the entire promised effect of raising pensions and will provoke the growth of the shadow economy. The effect of the innovations itself, according to the expert, will be quite small.
Alexey Korenev, an expert at FINAM Group of Companies, believes that it will not be possible to avoid rising prices. The government, let’s say, is not telling the whole truth that prices for social goods will definitely not rise, since the main preferential rates will remain. Firstly, in a free market it is impossible for goods with the same quality but different prices to exist in parallel; in this case, their prices will still be equalized. Secondly, the goods will need to be delivered to the consumer and stored, and VAT on these services will be raised. The same applies to sales, and the VAT of retail chains will also be raised. That is, the introduced additional VAT rate will necessarily affect all types of goods. And 2% is not at all small, since the tax will be returned to the price of the product several more times.
Yulia Vymyatnina, a professor at the Faculty of Economics at ENERPO, believes that with an increase in VAT, goods that are currently taxed at a preferential ten percent rate will also become more expensive, because their production requires raw materials and services, and the rate on them is a basic one, not a preferential one.
The management of , a large manufacturer of meat products, believes that the price of any meat products in general will rise, due to the fact that they will have to buy feed at much higher prices, in addition, veterinary and transport services will become more expensive. In response to the high price, people will start saving, which will lead to a decrease in sales. Thus, both producers and buyers will suffer.
They express similar opinions about the rise in price of the entire product line. However, it will be impossible to sell all this at a higher price, and it will not be possible to reduce it due to rising costs.
Impact of the increase on real estate
The purchase of residential property is not subject to value added tax, but the updated rules will have a direct negative impact on this segment.
What will the VAT increase on the real estate market lead to:
- Prices for apartments will rise due to rising prices for construction work and materials.
- Direct price increases will affect non-residential premises.
- The reduction in bank interest rates on mortgages may stop due to the acceleration of inflation.
- Increase in tenant expenses.
- Sales volumes may decrease due to a decrease in the solvency of the population.
The addition to the cost of apartments by 1-2% due to the VAT increase will be insignificant compared to the jump of 15-20% due to the entry into force of project financing and the abolition of shared-equity construction.
Petition against
The authors of the petition against increasing the VAT rate believe that such a decision will lead to an increase in prices for most goods, which will further reduce the purchasing power of Russians, which is already at a low level today. The authors are sending a petition to the government and personally to President V.V. Putin. The petition states that the rate increase will take 360 rubles out of the pocket of every resident of the country. per month.
The authors of the petition believe that officials who claim that the VAT increase will only minimally affect ordinary citizens should not be trusted. According to the authors, officials deliberately do not mention that the preferential categories for which they do not plan to increase the rate do not even include essential products included in the consumer basket of any Russian (cereals, milk, butter).
The reaction of the Russian population to the future increase in VAT is very negative. The Confederation of Labor of the Russian Federation states that applications for holding rallies and pickets are registered daily, more than 70 cities are included in them, the number of expected actions is approaching 100. The protest rally, organized by the Communist Party of the Russian Federation, is scheduled for July 28.
How to calculate VAT 20% of the established amount
The question from what period the 20% VAT will be applied is not entirely correct. The new value will come into force on a specific date - the first of January. But you should prepare for this in advance.
First, let's look at how to calculate the increased tax levy. Under the old value, the settlement rate of 18/118 or 15.25% applies. The calculation of VAT 20% implies other parameters: 20/120 or 16.67%.
For example, you receive cash (advance payment) for a shipment of electronics in the amount of 300,000 rubles. including the fee. The premium in this case will be 50,010 rubles. That is, in order to allocate VAT of 20%, the price must be multiplied by 16.67%.
If 300,000 rub. - this is the price without collection, then you should add 60,000 to it. The final amount will be 360,000 rubles. How to calculate VAT 20% of the amount in this case is quite clear: price + price * 20%.
Tax adjustments should be taken into account if work under the contract is carried out in different years. Even if the advance payment was fully transferred to the supplier's account before the new value was introduced, one of the parties will have to pay an additional 2% difference in state tax when shipping in 2021. All modifications to contractual obligations should be discussed by partners in advance.
It is advisable to send a letter to the counterparty about changing the VAT rate and a sample amendment to the contract, which will take into account updated legal requirements, revised prices and other aspects of the contractual relationship, even before the law comes into force.
1. Ask our specialist a question at the end of the article. 2. Get detailed advice and a full description of the nuances! 3. Or find a ready-made answer in the comments of our readers.
Why did they decide to raise VAT to 20%?
Deputy Prime Minister T.A. explained why it was decided to increase the rate by 2%. Golikova. Previously, the government discussed in detail another option for changing the rate: 22\22%, that is, it was planned to raise VAT by 4% and also change the amount of insurance premiums to 22%. But this option had to be abandoned, since such growth would have had a much greater impact on accelerating inflation than the accepted option. And 2% is the result at the limit of sensitivity; when passing through it, you will have to make other decisions. The increase in inflation, according to the Deputy Prime Minister, will be immediately compensated by indexation of pensions. Since the beginning of February, indexation has been carried out by the amount of actual inflation calculated for the past year.
How much will the rate increase?
Indirect fiscal obligations from sales increase by two percentage points - up to twenty percent. History shows that this is not a record value, chronology of values:
- 1992 – 28%;
- 1993-2004 – 20%, and since 2008 another +5% of sales volume;
- 2004-2018 - 18%;
- From 2021 - 20%.
In some developed countries, VAT even exceeds the value of the Russian Federation, but there are completely different tax rules: Sweden - 25%, Finland - 24%, Italy - 22%, Germany - twenty%.
VAT Law and the relationship between taxation and pricing
The amount of VAT paid to the supplier is compensated by tax deductions to the taxpayer. According to Andrei Makarov, head of the Committee on Budget and Taxes in the State Duma, Russian business should not raise prices at all when the rate increases. After all, he doesn’t reduce them, even symbolically, when the government reduces taxes? The deputy believes that an interesting situation is being created. Businessmen, including representatives of big business, argue that prices are determined by taxation. However, they are determined only when taxes increase. But when taxes become lower, for some reason this fact ceases to influence pricing. After the sales tax was eliminated, prices did not fall as a result. Also with the VAT reduction in 2004 at the peak of economic growth. According to the deputy, a decision was made not to increase the VAT, but to return to the rate that already existed in 2004. And it would be worth calculating the amount that the business received after the rate reduction, without lowering prices in connection with this. It is clear that no one likes an increase in the tax burden as such, but what should be more important for business is not the rates themselves, but the constancy of the rules for a long period. And tax rules are constant over long and significant business periods. Other taxes will also remain unchanged. The establishment of stable rules is also indicated by the fact that other options for replenishing the budget, such as increasing personal income tax or introducing a sales tax, were not adopted.
What to do if a legal entity refuses to increase the price?
If all parties agree to the updated terms, then the amount of net proceeds does not change, and the buyer pays 2% more.
If the buyer’s reaction to the increase in prices is negative, then in order to maintain the sale, the supplier will have to make a two% discount, that is, pay part of the new tax liability from its revenue.
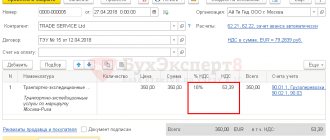
For example: delivery amount is 250 thousand rubles. excluding VAT 18% (+45 thousand rubles). If taxation changes, the deduction amount will increase to 50 thousand rubles. Two calculation options are possible:
- The buyer pays 300 thousand rubles, of which the seller’s revenue is 250 thousand rubles, payment of taxes is 50 thousand rubles.
- The buyer pays the previously agreed upon amount, 295 thousand rubles: VAT 20% – 49 thousand rubles, and the seller’s income is 4 thousand less – 246 thousand rubles.
When will the new rate be introduced?
The bill submitted to the State Duma states that VAT will be increased on January 1, 2021. This means that it should often be applied to those shipments of goods that will occur after the specified date.
VAT is an indirect tax, so its increase will be felt by all consumers. Changes in the taxation of products and goods, for which VAT is currently 10%, are not provided for by the bill.
If the State Duma does not have time to fully adopt the bill to increase the rate by the end of this year, and the likelihood of this is quite high, then it will be postponed until the next quarter. And therefore, it will start working on April 1, 2021.
Personal Tax Management
From January 1, 2021, the VAT rate will increase from 18% to 20% in relation to goods (work, services), property rights shipped (performed, rendered), starting from January 1, 2021. With the fact that in contracts and agreements concluded from January 1, 2019, it will be necessary to indicate the VAT rate of 20%, everything is clear.
Questions remain regarding changes and the need to make such changes to contracts concluded before January 1, 2021. Making changes to existing agreements will allow companies to eliminate future disputes with counterparties and avoid claims from tax authorities regarding the calculation of VAT.
Taxpayer questions boil down to the following:
Is it possible to apply a VAT rate of 18% to payments and supplies/provision of services/performance of work if the contract was concluded by the parties before January 1, 2021?
Is it necessary to conclude additional agreements to existing contracts?
Is it possible now to include in contracts a condition that a VAT rate of 20% is applied to goods (work, services) shipped (performed, rendered) from January 1, 2019?
What should be indicated in the additional agreement to the contract if its conclusion is related to a change in the VAT rate?
How to calculate VAT if no changes are made to the contract?
Is it possible to require (including in court) the counterparty to pay an increased amount?
Let's consider each of the questions separately:
1. Is it possible to apply a VAT rate of 18% to payments and supplies/provision of services/performance of work if the contract was concluded by the parties before January 1, 2021?
The law does not make the amount of the applicable VAT rate dependent on the date of signing the agreement.
Federal Law No. 303-FZ of August 3, 2018 “On Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation on Taxes and Fees” does not provide for exceptions in relation to goods (work, services), property rights sold under contracts concluded before January 1, 2021 , including providing for the transfer of advance payments. This position was also taken by the Russian Ministry of Finance in its Letter dated 08/06/2018 N 03-07-05/55290.
Therefore, if the seller ships the goods and the contractor provides services in 2021, he must charge a tax at a rate of 20%. The new VAT rate is applied to goods/services/works shipped/performed starting from January 1, 2021, as specified in clause 4 of Art. 5 of the Federal Law of August 3, 2018 No. 303-FZ.
2. Is it necessary to conclude additional agreements to existing contracts?
It all depends on the terms of your agreement with the counterparty. There is no need to conclude additional agreements to the following contracts:
- if the parties agree on a condition in the contract that gives the seller/performer/contractor the right to unilaterally increase the price if legislators increase the VAT rate;
- if the terms of the contract provide for agreement on the price of goods/services/work in separate specifications/additional agreements/applications and other additional documents to the contract;
- if the contract sets the price of the product/service/work without VAT and the wording “excluding VAT” is directly stated in the contract. In this case, the supplier/contractor must charge VAT on top of the price of the product/service/work. In 2021, the supplier/contractor calculates VAT in the amount of 18 rubles. (100 ₽ × 18%). And in 2021 the tax will be 20 rubles. (100 ₽ × 20%).
3. Is it possible now to include in contracts a condition that a VAT rate of 20% is applied to goods (work, services) shipped (performed, provided) from January 1, 2021?
Can. The legislation of the Russian Federation does not establish such obstacles. The norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation state that the execution of a contract is paid at the price established by agreement of the parties (clause 1 of Article 424).
We consider it necessary to differentiate between prices for 2021 and 2021 and subsequent years in newly concluded contracts. For example, you can use the following wording:
- “The monthly cost of services provided up to December 31, 2018 (inclusive) is 118 rubles. (including VAT 18%), and the monthly cost of services provided from January 1, 2021 is 120 rubles. (including VAT 20%)";
- “In 2021, the price of the product is 1180 (One thousand one hundred and eighty) rubles. per unit of goods, including VAT at a rate of 18 percent - 180 (One hundred and eighty) rubles. From January 1, 2021, the price of the product is 1200 (One thousand two hundred) rubles. per unit of goods, including VAT at a rate of 20 percent - 200 (Two hundred) rubles";
- “The monthly cost of services is 100 rubles. excluding VAT. VAT is applied additionally to the cost of services at the rates established by clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: until December 31, 2018 - at a rate of 18%, from January 1, 2019 - at a rate of 20%.”
As for the conditions for calculating the amounts of advance payments, we propose to use the following wording in contracts:
- “Advance payments paid in 2021 for the supply of goods/provision of services in 2021 are transferred by the Buyer/Customer based on the price of the goods for 2021, established taking into account VAT at a rate of 18 percent. The difference in price is 20 rubles. for each unit of goods/services arising in connection with an increase in the price of goods/services from January 1, 2021 due to an increase in the legally established VAT rate, the Buyer/Customer pays to the Seller/Contractor within___ calendar days after the Parties sign the invoice/act of delivery.
4.What should be included in the additional agreement to the contract if its conclusion is related to a change in the VAT rate?
If the agreement was concluded by the parties before January 1, 2021 and it indicates the price of the product/service/work with VAT at a rate of 18%, then when concluding an additional agreement it is necessary to fix the price of the product/service/work, the rate and the amount of VAT from January 1, 2021.
The terms of the additional agreement may be as follows:
- “From January 1, 2021, the price of the product is 1200 (One thousand two hundred) rubles. per unit of goods, including VAT at a rate of 20 percent - 200 (Two hundred) rubles.”
- “From January 1, 2021, the monthly cost of services is 100 rubles. excluding VAT. VAT is applied additionally to the cost of services at a rate of 20%.”
Of course, it would be optimal if such an additional agreement was signed with the counterparty in 2021. However, if the signing of the additional agreement takes place only after January 1, 2021, then in terms of determining the cost of services and the VAT rate, the additional agreement will need to be extended to the relations of the parties established from January 1, 2019 (in accordance with paragraph 2 Article 425 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
5. How to calculate VAT if no changes are made to the contract?
Many people wonder what to do if the counterparty does not agree to make changes to the contract and sign an additional agreement? Or, if circumstances arise in which it is not possible to draw up and sign such an additional agreement?
For example, the contract says that the price of the goods is 118 rubles, including VAT. You proposed to the counterparty to increase the price of goods/services/work from January 1, 2021 due to the fact that, in accordance with the Federal Law, the VAT rate was increased. But the counterparty did not agree with this. Then the amount of tax should be determined based on the price indicated in the contract, at the calculated rate. So, the tax amount will be 19.67 rubles. (118 ₽ × × 20/120). Therefore, the price without tax will be equal to 98.33 rubles. (118 – 19.67).
As you can see, it is still safer to separate VAT from the price that the parties established in the contract.
6. Is it possible to require (including in court) the counterparty to pay an increased amount?
Can. There is a possibility that the counterparty will respond to the request and will pay the cost of goods/services/work, applying a 20% VAT rate to the price.
As for satisfying such a requirement in court, it is quite difficult to predict the outcome of judicial consideration of such disputes.
The Tax Code states that the supplier presents the buyer with the amount of VAT in addition to the price of the goods (clause 1 of Article 168 of the Tax Code). Indeed, if the price of goods excluding VAT is 100 rubles, then in 2021 the supplier/contractor must charge this tax in the amount of 20 rubles.
But there is no judicial practice on the price of goods in connection with an increase in the VAT rate. And in controversial situations with VAT, judges can shift the risks to the supplier/executor (ruling of the Supreme Court dated April 23, 2018 in case No. A32-4803/2015). Perhaps they will offer the supplier/contractor to allocate VAT from the contract price at the estimated rate (clause 17 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court dated May 30, 2014 No. 33).
In a similar situation, when since 2004 the VAT rate changed from 20% to 18%, the courts also indicated that changing the cost of goods (work, services) taking into account the new tax rate is possible only by agreement of the parties. For example: the lessee demanded a price reduction of 2%, since the tax rate had been reduced since 2004. But the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District, in Resolution No. F09-4928/08-S5 dated July 8, 2008, indicated that even if the cost of services is indicated taking into account 20% VAT - “120, incl. VAT 20%”, then the lease payment can be recalculated only by agreement of the parties.
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 422 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the contract must comply with the rules mandatory for the parties, established by law and other legal acts in force at the time of its conclusion. The execution of the contract is paid at the price established by agreement of the parties (clauses 1, 2 of Article 424 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
If, after the conclusion of an agreement, a law is adopted that establishes rules binding on the parties, other than those that were in force at the conclusion of the agreement, the terms of the concluded agreement remain in force, except in cases where the law establishes that its effect extends to relations arising from previously concluded agreements (Clause 2 of Article 422 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Federal Law No. 303-FZ dated August 3, 2018 (on increasing the VAT rate from 18% to 20%) does not directly establish that its effect applies to contracts concluded before January 1, 2021. Consequently, for the purpose of calculating VAT, the seller/ the contractor is obliged to calculate the amount of VAT at a rate of 20%, but in accordance with the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the seller/contractor has no grounds for automatically increasing the cost of goods/services/work established by an agreement concluded before January 1, 2021, by 2% VAT, i.e. e. the total cost specified in the contract, including VAT, must remain unchanged.
A change in the VAT rate can also be qualified as a significant change in circumstances (Article 451 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
A significant change in the circumstances from which the parties proceeded when concluding the contract is the basis for its modification or termination, unless otherwise provided for by the contract or follows from its essence. But a change in circumstances is considered significant when they have changed so much that, if the parties could have reasonably foreseen it, the contract would not have been concluded by them at all or would have been concluded on significantly different terms.
However, a contract can be terminated or amended under certain circumstances only if an increase in the VAT rate, which the parties did not anticipate when concluding the contract, will lead to significant damage to the seller/performer if he performs the contract on the same terms.
Moreover, if the parties have not reached an agreement to bring the contract into compliance with significantly changed circumstances or to terminate it, the contract may be terminated, and on the grounds provided for in paragraph 4 of Article 451 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, amended by the court at the request of the interested party if there are simultaneously the following conditions (clause 2 of article 451 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- at the time of concluding the contract, the parties assumed that such a change in circumstances would not occur (i.e., we can only talk about contracts concluded before the publication of Law No. 303-FZ - until 08/03/2018);
- the change in circumstances was caused by reasons that the interested party could not overcome after their occurrence with the degree of care and prudence that was required of it by the nature of the contract and the conditions of turnover;
- execution of the contract without changing its terms would so violate the relationship of property interests of the parties corresponding to the contract and would entail such damage for the interested party that it would largely lose what it had the right to count on when concluding the contract;
- It does not follow from customs or the essence of the contract that the risk of changes in circumstances is borne by the interested party.
Amendment of the contract due to a significant change in circumstances is permitted by a court decision in exceptional cases when termination of the contract is contrary to public interests or will entail damage for the parties that significantly exceeds the costs necessary to execute the contract on the terms changed by the court (Clause 4 of Article 451 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) .
As you can see, it is possible to require the counterparty to pay an increased amount due to an increase in the VAT rate, but such a process will be very costly not only financially, but also in time, and this is without a guarantee of completion of the process in your favor.
Possible alternative solution
To increase budget revenues, other measures need to be taken, says Valery Hartung, deputy head of the State Duma Committee on Economic Policy. He believes that it is necessary to leave VAT at the same level, and at the same time deny compensation to exporters of raw materials. Where does VAT come from? The enterprise produced some added value, while the state took a certain amount from it into the budget. It turns out that the more an enterprise produces, the more it develops, creates jobs and technological products, the more taxes are collected from the enterprise. If oil is pumped abroad, then VAT is not only less, it is compensated for, since the raw materials (oil and gas) are pumped abroad.
It turns out that those who use natural rent pay less than those who work productively, and even receive compensation. The deputy opposes the VAT increase and proposes the Chinese option as an alternative. For 35 years now, the Chinese government has not refunded VAT to enterprises that export raw materials. VAT is lower in this country, it is 17%.
What is the reason for the increase?
Value added tax accounts for more than a third of the budget revenues of the Russian Federation (34%), in 2021. the amount amounted to 5.1 trillion. ₽, the increase will allow us to collect 620 billion rubles more.
In May, Putin signed a decree with a list of a number of social projects, the implementation of which requires 8 trillion over 6 years. ₽ or ≈1300 billion ₽ per year. The law had to be adopted because there were not enough available funds in the budget. In order to accumulate additional resources, the retirement age in Russia has already been raised (women to 63, men to 65). Other alternative sources of filling the state treasury could be: a trade tax, an increase in personal income tax or the use of a progressive scale for calculation, the use of a different oil sales scheme. The arguments in favor of adopting 20% VAT were:
- Non-critical impact on business: firstly, enterprises receive compensation for the paid fiscal obligation for raw materials; secondly, the growth of indirect fiscal obligations is included in the final price tag;
- Theoretically, low-income citizens should not suffer, since essential food products are taxed on preferential terms, which are not subject to adjustment.
Who will live better or targeted projects for financing:
- Growth of pension payments and wages in the public sector.
- Free medical examination.
- Preferential mortgage.
- Payment of maternity capital.
- Infrastructure development.
- Export support.
- Reforms in the educational sector.
- Improvements in health services.
- Support for the scientific and technological sector.