Art. 6 of the Federal Law of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ “On Currency Regulation and Currency Control” establishes that currency transactions between residents and non-residents are carried out without restrictions, with the exception of transactions provided for in Art. 11 of Federal Law No. 173-FZ.
When selling goods (providing services) for export, their price is usually determined in foreign currency.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 781 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the customer pays for services in the manner prescribed by the contract. Consequently, the parties have the right to include in the contract a condition on preliminary (full or partial) payment for services.
Advances in foreign currency. Determining the VAT base
If the agreement provides for the transfer of an advance payment in foreign currency, then VAT will have to be calculated twice. Let's consider when the tax base arises and how to calculate its amount taking into account changes in the exchange rate.
General rules for calculating tax
If settlements with a foreign counterparty are carried out in foreign currency, value added tax payers should be guided by the provisions of paragraph 3 of Article 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. To determine the tax base and calculate the amount of VAT, you need to know: 1) the moment of determining the tax base; 2) rate of conversion of foreign currency earnings into rubles.
Determination of the tax base
According to Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, under contracts in foreign currency, the moment of determining the tax base is the earliest of the following dates: 1) the day of shipment (transfer) of goods (work, services), property rights; 2) the day of payment, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights.
Revenue conversion rate
Based on the rules established by paragraph 3 of Article 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the tax base for value added tax, the taxpayer's revenue in foreign currency is recalculated into rubles at the Bank of Russia exchange rate on the date corresponding to the moment the tax base is determined.
If the agreement provides for the transfer of an advance
According to Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the moment of determining the tax base for VAT arises for the seller at the moment of receiving a foreign currency advance from the buyer. In this case, revenue for the purpose of calculating value added tax must be recalculated into rubles at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in effect on the date of receipt of the prepayment (clause 3 of Article 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the rate of 18/118 or 10/110 is applied to calculate the amount of VAT. No later than five calendar days from the date of receipt of the advance payment, the taxpayer issues an invoice for it. In addition, it should be taken into account that when shipping goods (work, services, property rights), the seller also has the moment of determining the tax base for VAT on the basis of paragraph 14 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the tax amount should be calculated based on the official exchange rate to the ruble on the date of shipment. Thus, it turns out that when an advance payment is received in foreign currency, the tax base must be recalculated into rubles twice. The first time - upon receipt of an advance payment (at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in effect on the date of its receipt). The second time - upon shipment of goods (work, services, property rights) (at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation valid on the date of shipment). No later than five days from the date when the goods are shipped, an invoice is issued (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the amount of VAT previously calculated from the advance payment received on account of the upcoming supply of goods (work, services, property rights) is accepted for deduction. This point of view is expressed in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 4, 2012 No. 03-07-15/130, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 24, 2012 No. ED-4-3/15921.
Example 1.
The amount of the foreign exchange contract is USD 10,000 (including VAT). The terms of the contract require a 40 percent advance payment (i.e. $4,000). The advance payment from the foreign customer was received on October 10, 2012 (the official rate is 31 rubles per dollar). The goods were shipped on October 12, 2012 (the official rate is 32 rubles per dollar). On the date of receipt of the prepayment in the organization's accounting, the accountant made the appropriate entries. They look like this: DEBIT 52LOAN 62 subaccount “Advances received”
– 124,000 rub.
(4000 USD x 31 rubles/USD) – prepayment for goods has been received; DEBIT 76 subaccount “Calculations for VAT from advance payment”
CREDIT 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT”– 18,915 rub.
(RUB 124,000: 118% x 18%) – VAT is charged on the prepayment. On the date of shipment of the goods, the following was recorded in accounting: DEBIT 90 subaccount “VAT”
CREDIT 68 subaccount “VAT Calculations”– 48,813 rub.
(10,000 USD: 118% x 18% x 32 rubles/USD) – VAT added; DEBIT 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT”
CREDIT 76 subaccount “Calculations for VAT from advance payment”– 18,915 rub. – the VAT previously accrued on the prepayment received has been restored.
Accounting under an export contract
When selling goods (work, services) provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (for example, when exporting goods), the organization has the right to apply a VAT rate of 0 percent. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, prepayment amounts received for future deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), taxed at a tax rate of 0 percent, are not included in the tax base. Thus, when receiving a foreign currency advance on transactions taxed at a zero VAT rate, the moment of determining the tax base does not arise. Accordingly, there is no need to prepare an advance invoice for a foreign counterparty. According to paragraph 9 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the moment for determining the tax base for the sale of goods for export is the last day of the quarter in which the full package of documents provided for in Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is collected. In this case, an organization selling goods (work, services) subject to VAT at a zero rate, on account of previously received advance payment in foreign currency, in order to determine the VAT tax base on the last day of the quarter in which the full package of necessary documents has been collected, carries out a recalculation foreign currency received in rubles at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services). This point of view is expressed in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 12, 2012 No. 03-07-15/123. In this case, the invoice is drawn up according to the general rules - no later than five days from the date when the goods are shipped (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is registered in the sales book on the last day of the quarter, which contains documents confirming the right to a zero rate (clause 2 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137). Separately, it should be noted that if within 180 days the exporter has not collected documents confirming the zero VAT rate, then he will have to charge VAT on top of the cost of the goods in the quarter in which it was shipped. In this case, to convert foreign currency earnings into rubles, the foreign exchange rate on the date of shipment of goods is used.
Example 2.
The amount of the export foreign exchange contract is USD 15,000. Its terms require an advance payment of $5,000. The advance payment from a foreign buyer was received on October 10, 2012 (the official rate is 31 rubles per dollar). The goods were shipped on October 12, 2012 (the official rate is 32 rubles per dollar). On the date of receipt of the prepayment, the accountant recorded:DEBIT 52 CREDIT 62 subaccount “Advances received”
– 155,000 rub.
(5000 USD x 31 rubles/USD) – the received prepayment is reflected. For the purposes of calculating value added tax, the tax base does not arise on the date of receipt of the advance. And on the date of shipment of the goods, revenue for the purposes of calculating VAT is determined at the exchange rate on the date of shipment - 480,000 rubles. (15,000 USD x32 rubles/USD). This amount should be reflected in section 4 of the VAT return as export earnings. Important to remember
If an advance is made, the VAT tax base will have to be recalculated into rubles twice. Upon receipt of an advance payment - at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in effect on the date of its receipt. And also when shipping goods - at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation valid on the date of shipment.
What it is
An invoice is a document that confirms the company's legal right to deductions prescribed by law. The paper establishes goods, works and services with VAT added to the price structure.
Article 168 of the Tax Code establishes that the seller must receive an invoice before receiving an advance payment for services or goods, or before actually fulfilling his obligations to the customer.
Article 171 of the Tax Code establishes that if an invoice is in hand, an organization has the right to apply for a tax deduction, as if it had already received a shipping document.
When considering Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it is noticeable that invoices are in the same legal group, but are divided into 3 categories:
- a document that the customer issues when selling goods, providing services or performing work, or when transferring the rights of one subject to a transaction to another. Such invoices are informally called “Shipping”;
- a document that the supplier presents to the buyer at the time of receipt of a service, work or product. They are called advance and are the most common;
- adjustment documents that appeared in Russia in 2011. They are issued when the supplier reduces the quantity or price of an item to clarify current information.
How to fill it out and its sample
Article 169 of the Tax Code establishes the rules on how to issue and fill out an invoice:
- the date of preparation of the document along with the serial number is written in the first line;
- identification information about the seller and buyer, including address, checkpoint, tax identification number and organization name;
- information about the payment document proving receipt of the advance, including its number and date;
- code and name of the settlement currency taking into account OKV;
- the name of the service, product or work for which the advance was received, with the same wording as in the contract;
- the VAT rate taking into account a specific product or service, which is established in calculated form and written in column 7 (for example, 10/110 and 18/118, and not 18% or 10%);
- the amount of accrued tax in rubles and kopecks, rounding is prohibited;
- the amount of the transferred advance payment, also without rounding.
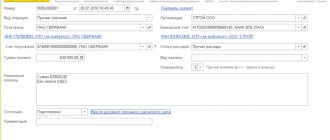
Blank form.
Sample of a completed advance invoice:
Term
The Tax Code establishes that when payment is received from the buyer, the seller has 5 days to issue an advance invoice to the counterparty.
The buyer has the right to receive a deduction in the amount of VAT, which he writes in the document, from the advance payment. Article 171 of the Tax Code controls the procedure and methods for obtaining tax deductions.
Within 5 calendar days or working days
The Tax Code does not establish exceptions to the rules in the form of permission not to draw up a document after receiving an advance or partial payment.
There are 5 calendar days within which the invoice must be issued and transferred to the contractor.
Is it necessary to put up an advance?
The basis for issuing an invoice for an advance payment is the receipt of an advance payment from the buyer in material or monetary terms. In some cases, the company arranges payments for regular deliveries from the contractor, for example, telecommunications enterprises that operate on a prepaid basis.
The Tax Code allows you to issue an invoice at the end of the billing period for the amount of all payments received from the customer, minus the actual work or services provided.
There are several cases when an advance payment for upcoming work, services and goods has already been received, but an invoice is not required:
- the product has a production and delivery time of six months;
- the order is not subject to tax or has a rate of 0%.
The Ministry of Finance issued a clarification confirming that it is not required to issue a document when the shipment occurred within 5 calendar days from the date of transfer of the advance payment for the goods or services.
Average conversion rate
The new edition of paragraph 6 of PBU 3/2006 has been supplemented with a paragraph that allows you to convert currency into rubles at the average rate for a month or a shorter period, say a week. This can be done if several conditions are met. Firstly, exchange rate fluctuations should be insignificant. And secondly, it is necessary to have a large number of homogeneous operations. The materiality criteria, as well as a deciphering of what number of similar transactions the company considers to be large, must be given in the accounting policy.
However, the 5% deviation rule is hardly appropriate here. In our opinion, we can talk about insignificant changes when the rates for different days differ from each other within a penny. But at the moment, even over a week, not to mention a month, there is often a much more significant fluctuation in the exchange rate. Therefore, it is too early to use the granted right to recalculate at the average rate. This amendment is a foundation for the future.
Errors during checkout
Despite the rules and deadlines for issuing advance invoices established by the Tax Code, some taxpayers violate their obligations. The most common mistake an accountant makes is refusing to issue an advance payment document for each buyer's preliminary payment document.
Some entrepreneurs add the total amount to the received advance payment, subtract the shipment amount and, if an advance payment remains, draw up a document. As a rule, the procedure is performed every quarter.
Some people do not issue invoices if they received the product or service in full during the tax period (that is, there was a transfer of property rights in accordance with the contract).
Such methods of accounting are contrary to the law. If an inspector from the tax office comes, he will establish the presence of issued tax documents on advances. If the document is not completed, penalties will be charged for each day of delay.
How to display purchases and sales in the ledger
The buyer who has received an invoice for an advance payment is obliged to keep records and draw up a document in the purchase book. The book must be filled out in the tax period when the invoice arrived.
A registration entry is permitted if the invoice is drawn up correctly, has no corrections or errors, and complies with current legal requirements.
The standard requirements are:
- the client's details are entered in accordance with the invoice;
- details of the principal whose valuables will be sold;
- information about the currency in which the document is drawn up;
- total invoice value;
- the total tax amount for the entire document.
The seller must retain the issued invoice to confirm the entry in the sales book. Registration is carried out on the day the document is issued. The entry relates to the tax period in which the seller received the funds.
The standard design rules are:
- information about the buyer from whom the funds were received is entered in accordance with the invoice;
- information about the intermediary, if he takes part in the transaction;
- Column 12 is filled in if the invoice is made in the currency of another state;
- fields 13a and 13b are filled in in accordance with column 9 of the invoice (13a is entered if the currency is Russian, 13b - if the money is from another state).
What to do if the contract is terminated
If before the day the buyer decided to terminate the contract with the seller, he made an advance payment, and the amount that needs to be returned does not exceed what was received, then there is no need to reconcile mutual settlements and it is possible to disperse in a few days.
If during the current contract the seller shipped goods against the transferred amount, and only an advance payment not covered by the products is required, then it is recommended to sign a reconciliation report.
It is also required when the advance payment was received into a bank account in several payments or the amount was received not from the buyer, but from his representative with a power of attorney.
Most often, reconciliation is required if the initiator of the break in legal relations is the buyer.
There are 2 ways to terminate the contract: sending a letter of offer or drawing up a new document that the parties sign. In the first case, you will need to send a response letter after returning the advance. Documentation is kept in the archives of the enterprise for 75 years, or until the company ceases to exist.
Responsibility for violations
If the tax office discovers a violation during an audit, the manager will not be able to submit an application and clarify the information in the declaration, correct the invoice or explain his mistake. Despite the fact that the advance will be repaid by shipment in the tax period, the lack of documents is a serious mistake.
If an advance is discovered for which no document has been issued, the tax inspector will charge additional VAT for the entire tax period for each advance. The taxpayer will lose the opportunity to deduct, since he did not declare such a right in the VAT return.
If an entrepreneur deliberately does not issue an invoice, the tax office will be able to fine him for a gross violation of the law.
The amount of punishment is established by Article 120 of the Tax Code and is equal to 10 thousand rubles if the violation occurred in the current tax period. If the inspector finds that there were problems with the documents before, the fine will be 30 thousand rubles.
When receiving an advance payment for goods, work or services, the supplier is obliged to issue invoices for the advance payment according to the template established by law. This document serves as evidence when paying tax and receiving a tax deduction.
There are several registration nuances, for example, the requirement to indicate the current tax rate and provide the document within 5 days after receiving the funds. Willful violators of the rules are required to pay a fine.