What is the PA index
This is a coefficient that shows what part of non-current assets, including fixed assets, is financed by the enterprise’s own capital.
Exceeding the KPA indicates an unstable financial position of the company, since:
- in the absence of long-term borrowed funds, this situation suggests that PAs are formed not only from their own, but also from external short-term sources, and withdrawing money from circulation for such purposes can lead to the inability to pay off short-term obligations;
- if there are long-term borrowed funds on the balance sheet, a CPA of more than 1 also signals possible financial problems in the event of money being withdrawn from circulation with the obligation to return it to creditors.
Login to the site
wrote: Help, please, with exam 0035 (Financial Management). Nothing fits. Same topic with 1505 (Insurance). Maybe someone has unanswered questions. Help......Hurray, I found everything myself. For financial management, it is not 0035 that is suitable, but 4373.Ex.01;EE.02;1, but it is only available on paid sites. 100% suitable. Answer text 4373.Ex.01;EE.02;1 _______ is a forward transaction that is concluded to insure the price against a possible fall Futures _______ is a document of title with the help of which sea transportation of goods is issued Bill of lading _______ risk is the risk of an undesirable change in the exchange rate currencies on the international or national market Foreign exchange ________ is an agreement between two entities for the exchange of obligations or assets in order to improve their structure, reduce risks, costs Swap ________ assets are the totality of property assets of an enterprise that serve current production and commercial activities and are fully consumed within one production and commercial cycle Working ________ are models that allow you to compare actual results of activity with expected results calculated according to the budget Regulatory ________ financial planning is the identification of the financial goals of the company, establishing the degree of compliance of these goals with the current financial state, forming a sequence of actions to achieve set goals Process _________ is an initial placement on the securities market. Underwriting _________ is the coordination of the work of all parts of the risk management system, the management apparatus and each employee Coordination _________ is an agreement on the purchase and sale of a commodity or financial instrument at a fixed price with delivery and settlement in the future Futures _________ bill of exchange is a security that is used in relations between companies to finance commodity transactions Trade _________ cash flows is the process of selecting the best forms of their organization in an enterprise, taking into account the conditions and characteristics of its business activities Optimization _________ risk of an enterprise is the likelihood of adverse financial consequences in the form of loss of income or capital Financial _________ rate used to increase the amount of debt. Cumulative _________ management is the direction and method of using funds to achieve a set long-term goal. The _________ price strategy shows how much the market price of a selected consumer basket for analysis of a group of goods has changed in the reporting period compared to the price in the base period. Index __________ assets is the totality of the property assets of the enterprise , which are formed at the expense of both own and borrowed capital Gross __________ leverage is the relationship between changes in net profit and changes in sales volume Production __________ project is a document that justifies the need to invest and contains organizational, legal and technical and economic characteristics of the planned investment processes The investment __________ rate is used to discount the amount of debt. Accounting ___________ is the time during which the interest rate remains unchanged. Interest period ___________ is the process of allocating capital among different investments that are not directly related to each other Diversification ___________ is that cash flow that consists of an initial investment made at one time or over several successive base periods and subsequent cash inflows Ordinary ___________ management is an integrated process of research, planning, organization and control, aimed at optimizing the formation, distribution and use of financial resources. Financial ___________ certificate of a bank - any document, the right of claim for which can be assigned by one person to another, which is the bank’s obligation to repay deposits placed with of deposits Deposit ___________ management are specific methods and techniques for achieving a set goal in specific conditions Tactics ___________ function is a function that provides a system for stimulating the implementation of management decisions in the field of financial activities Incentive ____________ models are predictive models designed to predict the income of an enterprise and its future financial condition Predictive ____________ policy of an enterprise - this is part of the general business policy of the enterprise, which consists in ensuring the attraction of the required amount of financial resources through the issue and placement of its own shares on the stock market Emission ____________ risk - the risk of choosing the wrong method of investing capital or type of securities for investment Selective ____________ risk is a risk that represents random fluctuations of individual securities relative to the market trend, which is reduced when forming an investment portfolio from a variety of stocks and bonds Non-systematic ________________ in financial management is the identification of optimal options for financing an enterprise using forecast calculations and models Forecasting _________________ financial management is a system of theoretical and cognitive categories, basic concepts, scientific tools and regulatory principles for managing the financial activities of business entities. Method __________________ growth rates are the maximum achievable rate of operation of a company for a given capital structure. Sustainable ___________________ leverage is the relationship between the profitability of business capital entity and the volume of accounts payable Financial “___________” is the business reputation and business communications of an organization that can bring property benefits and have an economic assessment Goodwill A letter of credit, a bill of exchange, a bill of lading and a savings certificate are among the main _________ securities of Russia. _______ reflects indicators of the financial condition of the enterprise on the balance sheet In __________, the assessment of the liquidity of investments is measured in days. Depending on the strategic goal and business concept, a business plan is developed for ___ year(s) (give the answer in numbers) 1 In the case of _________ share of borrowed capital, the level of financial leverage increases increases The composition of the financial mechanism includes legal, regulatory , information, personnel, technical, software subsystems, financial instruments, financial techniques, methods and models The probability of losses and the amount of possible damage is the degree of risk Investments in commercial organizations or investments in securities for a period of up to one year are _______________ financial investments short-term Internal financial ________ - a process organized by an enterprise to verify the execution and ensure the implementation of all management decisions in the field of financial strategy and prevent crisis situations leading to its bankruptcy control Expression of a unit of a certain currency in units of another currency is a quote Group of tax payments included in the price of products, - this is value added tax, excise tax and ____ customs duties A document issued by the cargo carrier to the cargo owner, which certifies ownership of the shipped goods - this is a bill of lading A document that clearly and visually reveals the essence of the proposed new direction of the company’s activity, reflecting key indicators that justify the feasibility project, is a _______ business plan. The share of preferred shares in the total issue volume cannot exceed ____% (give the answer in numbers). 10 The tasks of financial management are to ensure the maximization of the enterprise’s profit, to ensure the constant financial balance of the enterprise, to ensure the formation of the volume of financial resources, to optimize cash flow From the above: 1) analysis of the financial position of companies; 2) drawing up forecast estimates and budgets; 3) determining the company’s overall need for financial resources; 4) analysis of market conditions; 5) forecasting and making a profit; 6) purchase and sale of securities at a favorable rate stages of the financial planning process are 1, 2, 3 From the following: 1) accounts receivable; 2) short-term financial investments; 3) non-current assets; 4) money surrogates; 5) currency values in the composition of current assets include only 1, 2, 3 of the following: 1) creditors of the enterprise; 2) investors; 3) audit firms; 4) government bodies; 5) shareholders of the enterprise; 6) employees of the enterprise - external users of the enterprise’s financial information include: 1, 2, 3, 4 From the following: 1) according to the form of functioning; 2) by the degree of liquidity; 3) according to the degree of balance; 4) by the nature of ownership; 5) according to the degree of profitability, the assets of the enterprise are classified: 1, 2, 4 From the following: 1) profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise; 2) depreciation charges on fixed assets used; 3) the enterprise receives free financial assistance; 4) attraction of share capital internal sources of funds formation include 1, 2 From the following: 1) production fixed assets; 2) intangible assets; 3) current assets; 4) long-term financial investments; 5) reserves; 6) financial assets the operating assets of the enterprise include 1, 2, 3 From the following: 1) indicators of the financial condition and results of financial activities of the enterprise as a whole; 2) indicators of financial performance of individual divisions; 3) normative and planned indicators; 4) indicators of the composition of assets and capital used; 5) performance indicators of branches and representative offices - the main groups of internal indicators of the financial management of an enterprise include 1, 2, 3 Of the listed indicators: 1) coefficient of variation; 2) beta coefficient; 3) standard deviation; 4) cumulative rate; 5) financial measurement; 6) investment efficiency in assessing the level of investment risks is used 1, 2, 3 A company with a significant share of borrowed capital is called a company with a high level of _______. financial leverage A control system that ensures the concentration of control actions on the highest priority areas of the financial activity of an enterprise, the timely identification of deviations of its actual results from those envisaged and the adoption of operational management decisions that ensure its normalization is called financial __________. controlling The concept of cost ____________ provides for the determination of the minimum level of income necessary to cover the costs of maintaining a given source of financing and allowing not to end up in a capital loss Self-financing coefficient for the upcoming development of the enterprise (KSF), where SFR is the planned volume of formation of own financial resources, ∆A is the planned increase in the assets of the enterprise , calculated by the formula Ksf = SFR / ∆A The sustainability coefficient of an enterprise's economic growth is used to characterize ______ business activity Any security or contact for which there is a simultaneous increase in the financial assets of one business entity and the financial liabilities of another business entity is a financial instrument Methods of factor analysis , operations research and decision-making theory are among the main ________ analytical methods of financial analysis. The tax payment included in the price of products is a tax on _____________ value added. One of the indicators of profitability of sales is ______ gross profit per unit. The danger of losses in the process of activities of business entities in as a result of the excess of interest rates paid by them on borrowed funds over the rates on loans provided - this is ______________ interest risk. Operation ________ is an agreement to borrow securities guaranteed by funds or borrow funds against repo securities Determination of objects in which financial resources should be invested , is ___________ investment portfolio formation Fixed assets, funds, the amount of capital invested in the totality of material objects and values used in the production process to influence objects of labor and their transformation into consumable products are _________ non-current assets Basic elements the mechanism of financial management is state legal regulation, market regulation, a system of methods and techniques for managing the financial activities of an enterprise, financial regulation in the field of an enterprise. Refers to indicators for assessing the property and financial status of an enterprise - these are indicators: business activity, property status, , liquidity and solvency, financial stability Assessing the potential financial capabilities of an enterprise for the coming periods and ensuring the maximization of the welfare of the owners of the enterprise through rational financial policy is the _______ financial management goal. Assessing financial ________ is the determination of the ratio of equity and borrowed capital, taking into account the income tax rate and gross return on assets leverage A bill of exchange or _______ is a document in which the exporter instructs the importer to pay a certain amount to a specified person within a certain time (60, 90 days) draft A plan drawn up for the next period regulating the formation, distribution and use of financial resources, is called the budget. The formula ___________ calculates the ratio of net profit to fixed production costs (DOLP), where FC is semi-fixed production costs and Pn is net profit DOLP = Pn / FC. The formula ___________ calculates the ratio of fixed and variable costs (DOLd), where VC - variable production costs and FC - conditionally fixed production costs DOLd = FC / VC The formula _________________ determines the value of the net assets (NA) of the enterprise, where A is the total amount of all assets of the enterprise at book value, ZK is the total amount of the company's borrowed capital used . NA = A - ZK Based on the nature of participation in certain types of activities, assets are divided into operating and _________. investment Indicators of the situation _________ and __________ are the main subgroups of indicators of the situation in the financial market, money market, stock market An order from the payer's bank to the recipient's bank to pay a certain amount to an individual or legal entity upon fulfillment of certain conditions - this is a letter of credit The need to attract own financial resources from external sources (SFRvnesh), where Psfr is the total need for own financial resources planned to be attracted from internal sources, SFRvnut is the amount of own financial resources planned to be attracted from internal sources, calculated by the formula SFRvnesh = Psfr - SFRvnut Entrepreneurial ________ is a danger shortfall in earnings before interest and taxes. risk Principles _________, ____________, ____________ are the basic principles of financial management of material interest, independence, self-financing The process of anticipating and neutralizing negative consequences associated with their identification, assessment, prevention and insurance is ________ financial risk management of an enterprise By assessing the following indicators : __________, production and financial expenses and net profit, the influence of production and financial leverage of revenue is determined. There are types of assets: _______ and gross net assets. There are statistical, regulatory, analytical ________ ways of presenting information about securities. Risk ________ benefits is the risk of non-receipt of income, which omissions could be obtained Risk _________ there is a danger as a result of the wrong choice of method of investing capital, loss of equity capital and inability to pay off bankruptcy obligations An increase in the purchasing power of money and a decrease in price entails the possibility of ______________ risk of deflation A market in which international transactions take place with various national currencies, called ____________ world currency market The risk management system consists of ______ subsystems (give the answer in numbers) 2 The ratio of two or more monetary units, currencies of different countries, established by their purchasing power in relation to a certain set of goods and services, is called purchasing power parity Article of the Civil Code The Russian Federation, which determines the nature of the property rights of the enterprise for assets 128, the amount of debts due to the enterprise, company, companies by other enterprises, companies, companies, as well as citizens who are their debtors, is called ____________ debtor's debt and ____________ Types of financial plans, the short -term sett correspondence Dold == The share of permanent production costs in the total amount of expenses, Dolp == The ratio of net profit to permanent production expenses, Dolr == Relationship of the rate of change of profit before deducting interest and taxes to the pace of change of sales in natural units establish the correspondence between the concepts between the concepts and their definition of the policy of the anti -crisis financial management == part of the general financial strategy of the enterprise, which consists in the development of a system of preliminary diagnostic methods for the threat of bankruptcy and “inclusion” of the mechanisms of financial “recovery” of the enterprise, ensuring its exit from the crisis state, the policy of attracting borrowed funds == part The general business policy of the enterprise, which consists in ensuring the most effective forms and conditions for attracting borrowed capital from various sources in accordance with the needs of the enterprise,, a policy of managing non-current assets == Part of the general financial strategy of the enterprise, which consists in financial support of the timely update and high efficiency of use Set the correspondence between the concepts and their determination of the account of receivables and the part of the general business policy of the enterprise, aimed at expanding the volume of sales of products and consisting in optimizing the total amount of receivables and ensuring its timely collection, and part of the management of monetary assets == Part The general business policy of the enterprise, which consists in optimizing the total size of their balance in order to ensure constant solvency and efficient use,, a policy of reserves management == part of the general economic policy, which consists in optimizing the total size and structure of stocks of inventory, minimizing the costs of their costs Maintenance and ensuring effective control over their movement establish the correspondence between the concepts and their determination by the management of the financial risks of the enterprise == The process of foresight and neutralization of their negative financial consequences associated with their identification, evaluation, prevention, insurance, and financial investment tool == financial securities which meets the interests of the company and is attractive for potential creditors and investors, as well as for investing the company, the financial risk of the enterprise == The probability of adverse financial consequences in the form of a loss of income or capital establish a correspondence between the concepts and their definition of the method of critical sales == Determination of the threshold volume of product sales for each specific situation in accordance with existing production costs and profit, the method of financial management as science == system of theoretical and cognitive categories, basic (fundamental) concepts, scientific instruments (apparatus) and regulatory principles for managing financial activities Management, a mechanism of financial management == System of the main elements governing the process of developing and implementing managerial decisions in the field of financial activities of the enterprise establish a corresponding between concepts and their definition, assessment of financial leverage == determination of the ratio of your own and borrowed capital, taking into account the rate of income tax and gross tax rate Profitability of assets, production leverage == The relationship of changes in net profit and changes in sales, financial leverage == The relationship between the profitability (profitability) of the capital of the economic entity and the volume of accounts of this subject establish the correspondence between the concepts and their determination of the financial and independent company == A company that finances its activities only at the expense of its own funds, financial leverage == The relationship between the profitability (profitability) of the capital of the economic entity and the volume of accounts payable of this subject, financial management == Integrated process of research, planning, organization and control aimed at optimizing Activities on the formation, distribution and use of financial resources, establish a correspondence between concepts and their definition, financial strategy == Aggregated scheme (model) of financial activity at a long -term temporary interval, financial tactics == detailed scheme (model) of financial activity on a short -term temporary interval ,, Financial plan == The document that characterizes financial goals and the methods of achieving them establish a correspondence between the concepts and their definition of transactional currency risk == Conscious danger of losses due to a decrease in profit during transactions in different currencies, a broadcast currency risk == Conscious probability of the danger of losses due inconsistencies in the assessment of assets and obligations expressed in different currencies, economic currency risk == The risk of incorrect prediction of inflation and the long -term dynamics of the currency course establish the correspondence between the concepts and their determination of investment == investment in all its forms in order to improve economic potential, increase the volume of economic activity, the development of new types of activities, the capital of the enterprise == The total value of the funds of the enterprise in monetary, material and intangible forms invested in the formation of its assets, the current current assets == The set of property values of the enterprise serving the current production and commercial (operating room ) Activities and fully consumed during one production and commercial cycle establish a correspondence between the concepts and their definition of the concept of a compromise between the risk and profitability == achievement of a reasonable ratio between risk and profitability, the concept of capital == Determination of the minimum income level required to cover costs to maintain this source of financing and allows not to be at a loss, the concept of securities market efficiency == The speed of reflection of information about the securities market at the securities market prices, the degree of completeness and freedom of access to all market participants to information establish a correspondence between the concepts and their determination of their definition Concept of agency relations == Leveling the group interests of conflicting subgroups of managerial workers and owners of the company, the concept of asymmetric information == certain categories of persons can own information inaccessible to all market participants, the concept of the efficiency of the securities market == Speed of reflection of information about the market securities of securities of securities market prices, the degree of completeness and freedom of access to all market participants to information, establish a correspondence between the concepts and their definition The concept of agency relations == Leveling the group interests of conflicting subgroups of managerial workers and owners of the company, the concept of alternative costs == Assessment of alternative options possible investment of capital, the use of production facilities, choosing options for customer lending policy, etc., the concept of asymmetric information == individual categories of persons can own information, inaccessible to all market participants, equally establish a correspondence between concepts and their definition of currency risk == Conscious danger of losses due to changes in the exchange rate, and entrepreneurial risk == The danger of receiving profit before deducting interest and taxes, percentage risk == The risk of losses in the process of business entities as a result of the exceeding the interest rates paid by the funds raised over the rates. on loans provided by the actual losses of the entrepreneur, the costs of reducing these losses, as well as the costs of reimbursing these losses and consequences - this is __________ Risk cost the cost of financial (OE) ____________ - this is an aggregated model of financial activity at a long -term temporary interval, financial strategy ________ is an active form of effective the use of temporarily free capital or the tool for implementing strategic goals related to the diversification of the operating activity of the investment enterprise financial __________ is a document that characterizes the method of achieving the financial goals of the company and the financial plan and expenses, the financial plan ___________ is the relationship between the profitability of the economic entity and the volume of the payable Leveridge debts, financial menths are an integrated process of research, planning, organization and control aimed at optimizing the formation, distribution and use of ________________. Financial resources financial option and a forwarding contract are derivatives financial ________ tools _________ is a process of studying the financial condition and basic results of the financial activity of the enterprise in order to identify reserves to increase its market value and ensure effective development of financial analysis _____________ is the process of developing a financial system. plans and regulatory indicators to ensure the development of the enterprise with the necessary financial resources and increase the efficiency of its financial activity in the upcoming period by planning a formula, which allows you to calculate the amount of economic funds that are owned and the disposal of the NBV = TA formula, which calculates the coefficient of concentration of their own capital (KEQ ), where tel is the total amount of sources of funds (long -term and short -term) and E - the own capital KEQ = E / Tel The formula, which calculates the ratio of its own and attracted funds (KDTE), where LTD is long -term liability, Cl are short -term liabilities and short -term liabilities and E - equity KDTE = (LTD + CL) / E formula, which calculates the coefficient of the structure of the coating of long -term investments (KLTA), where LTD is long -term liabilities and LTA - fixed assets and other non -current assets KLTA = LTD / LTA formula for which The current liquidity coefficient of KLT = Return Formulas Formula is calculated by the formula for which the coefficient of the stability of the economic growth of the enterprise (KG) is calculated, which is used to characterize business activity, where the net profit accessible to the distribution among shareholders, D are dividends paid to shareholders and E - equity KG = [(pn - d) / e] × 100% formula, which calculates the determination of the overall need for its own financial resources (PSFR), where PC is the general need for capital at the end of the planned period, the USC is the planned specific the weight of its own capital in its total amount (in %), SKN - the amount of equity at the beginning of the planned period, pr - the amount of profit aimed at consumption in the planned period PSFR = (PC × Usk / 100) - SKN + formula, according to which The liquidity and solvency indicator WC = equity + long -term obligations - fixed assets and investments (current assets and current obligations) formula, for which the profitability of total capital (ROA) is calculated, where PN is net profit, atic - interest on payment in the post -a -term deduction and CT-total capital (the result of the balance sheet for liability) ROA = (pn + atic) / ct formula for which the specific gross profit (GPM) is calculated, where S is the sales revenue, cogs is the cost of sold products and (s- COGS)-gross profit GPM = (s-cogs) / s functions that perform the finances of the business entity: ensuring current financial and economic activities, ensuring the participation of the economic entity in the implementation of social policy, the formation, maintenance of the optimal structure and the increase in the economic potential of the enterprise The function __________ is a function that ensures effective control over the implementation of the adopted management decisions in the field of financial activity of control ___________ is a function that ensures the development of a system of strategic current plans and operational budgets in the main areas of financial activity, various structural units and the enterprise as a whole. ensuring the substantiation of several possible alternative options for managerial decisions is ______________________ Function The Information Futures Market functions performs a hedging part of the property with a useful life exceeding 12 months used as a means of labor for the production and sale of goods (work, services) or for the provision of services) or for The organization’s management is ____________ funds are the main ones to answer and instead of the code 1505, most likely 4344. EKZ.01; EE.02; 1. (There are only paid sites). I will unsubscribe how to check. Thank you!!!!! Very helped out!
How to calculate
The permanent asset ratio is equal to the ratio of non-current assets to equity:
KPA = BOA/SC.
Permanent asset index (balance sheet formula) = line 1100 / line 1300.
The value of the indicator, of course, depends on the company’s field of activity. Thus, in capital-intensive industries its value will be higher than in enterprises, the availability of fixed assets in whose activities is not a decisive factor. For example, for trading enterprises, working capital will prevail in the balance sheet structure.
The generally accepted standard value of KPA is in the range from 0 to 1.
KPA is directly related to the agility coefficient, which, on the contrary, shows what part of the working capital is financed by the organization’s own capital.
The sum of these two indicators must equal one.
What is a permanent asset
A permanent asset (PA) refers to the organization's obligations to counterparties, constantly reflected in the balance sheet (Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n dated July 2, 2010).
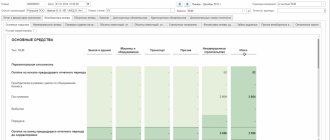
These constants are always present in the final financial statements and move from each previous balance sheet to the next. They are long-term and are reflected in the first section of the balance sheet. Permanent assets are identical to non-current assets. Thus, permanent funds consist of the following types:
- intangible - line 1110 BB;
- research and development results - 1120;
- intangible search - 1130;
- material search - 1140;
- fixed assets - 1150;
- profitable investments in materiel - 1160;
- financial investments - 1170;
- deferred taxes - 1180;
- other non-current - 1190.
The institution's own capital, consisting of authorized, additional and reserve capital, etc., is displayed in the balance sheet in line 1300 (section III).
Current liabilities in accounting. balance sheet: composition, line-by-line distribution
So, short-term liabilities are those obligations that are repaid in a period of no more than a year. In the form of an updated balance sheet, they are reflected in Section V. The composition of this section and the line-by-line distribution of liabilities is as follows.
| Borrowed funds | Creditor. debt | Future income periods | Estimated liabilities | Other obligations | Summary of Section V |
| Page 1510 | Page 1520 | Page 1530 | Page 1540 | Page 1550 | Page 1500 |
The total for the entire section (line 1500) or the sum of all completed lines of this section minus line 1520 (accounts payable) is the value of P2 (short-term liabilities). In other words:
When calculating, a question may arise as to where to include future income. Despite the fact that they are formed at the current moment, and the obligations under them are in the short term, they last more than 2 years. That is, we are talking about future income. In this regard, it is assumed that such future income is usually equal to zero, so it does not matter where they are taken into account. Meanwhile, in many services that provide financial analysis services, they are taken into account in long-term liabilities.
Taking into account the above, the above formula may be modified. The calculation can also be done like this:
Another option for calculating P2, in addition to the above lines, includes one more:
Formula 2 is considered the most optimal calculation option. What is important is that there is no separate standard for P2. But it is recognized that a decrease in this indicator is a positive factor.
Comparison of groups of assets and liabilities: division of assets, current standards and their meanings
When assessing the liquidity of an enterprise, it is customary to compare groups of liabilities and assets. Before moving on to this issue, you should take into account some important factors accompanying the division of assets and liabilities into groups.
The division of liabilities has already been described above. As for assets, they, like liabilities, can be divided into 4 groups: A1 (the most liquid), A2 (quickly liquid). A3 (slowly liquid) and, accordingly, A4 (slowly liquid).
Among other features of this classification of assets, the use of different names for the same groups should also be separately noted. They can be consonant, synonymous, or not differ significantly, but in practice they still designate the same group and do not change their purpose.
For example, the most liquid assets from gr. A1 can be called the most liquid, and, for example, quickly liquid assets from gr. A2 – urgently liquid or quickly marketable. In fact, this phenomenon occurs very often in practice during analysis. Therefore, you just need to know and take this point into account so as not to be misled due to some difference in the name of one or another group of assets (liabilities).
Important! When assessing the liquidity of an enterprise, all groups of assets and liabilities should be compared, and not just one of the groups.
Thus, they compare: A1 with P1, A2 with P2, A3 with P3, A4 with P4. It is appropriate to make such comparisons for any period (for a month, a quarter, a year, two years, etc.). That is, essentially, if necessary. Comparisons over several periods are considered the most effective, since this allows you to track ongoing changes in dynamics. Based on the results of such comparisons, the overall liquidity indicator of the book is derived. balance sheet and determine the level of financial viability of the enterprise as a whole.
The following ratios are recognized as standard: A1>P1, A2>P2, A3>P3, A4 < or = P4. The ideal option is to meet all three standards. Then they “automatically” imply compliance with the third relationship: A4 < or = P4, and b. the balance is recognized as absolutely liquid. But in practice, such an “ideal” option does not occur very often.
A direct comparison of quickly liquid assets and short-term liabilities, subject to the ratio A2>P2, will mean the following:
- The company is able to pay off debt obligations using quickly liquid assets.
- Repayment of these debts is possible in the near future (relatively speaking, in the short and medium term).
It should be taken into account that if, after a comprehensive comparison of assets and liabilities, it turns out that A4>P4, then the enterprise can be called illiquid.
| Business valuation | Financial analysis according to IFRS | Financial analysis according to RAS |
| Calculation of NPV, IRR in Excel | Valuation of stocks and bonds |
Short-term liabilities P2 in formulas for calculating liquidity indicators
Liabilities from group P2 are used in calculating a number of liquidity ratios. In particular, when calculating KTL, KSL, KAL. These are the main ratios of current, urgent and, accordingly, absolute liquidity. Each of them has a specific purpose.
For example, CTL (current ratio), the most famous and often used in financial analysis. It is calculated as follows:
In the said formula there is a group of short-term liabilities P2, as well as P1, A1, A2 and A3. That is, by itself, separately, the P2 indicator indicated in formula 4 is not analyzed, but only participates in the calculation. But without it, calculation and analysis of the KTL value is not possible.
If, based on the calculation results, KTL = 1.5–2, then this will mean compliance with the norm. A KTL value that is less than 1 indicates the enterprise’s inability to pay current obligations on time. There is a destabilization of the financial situation, which, according to the logic of events, implies the presence of significant financial risks for the enterprise.
The remaining liquidity ratios are calculated and analyzed in a similar way. For comparison, the calculation of the CLR (urgent, critical or quick liquidity ratio) is considered below. Using it, you can find out the ability of a particular enterprise to pay current obligations in a difficult financial situation using A1 and A2. Formula for calculating KSL:
This formula uses A1, A2 and P1, P2. That is, there is more than one P2 indicator. The result of calculation with his participation in the situation under consideration must be at least 0.7. If the value of the CFL is less than this minimum, then we can talk about a drop in the solvency of the enterprise. The best result is considered to be a value of KSL = from 0.8 to 1.2.
Some features of entering data into Section V of the account. balance
Passive buh. The balance sheet is presented in two sections: “Long-term liabilities” (Section IV) and “Short-term liabilities” (Section V). According to the last, fifth section, it is necessary to display information about short-term financial sources attracted by the enterprise. It is recommended to take into account the following features of filling out lines:
- on page 1510, register data using the account. 66 and partially 67 (settlements for short-term and long-term loans, credits);
- on page 1520 indicate the generalized amount of all types of short-term debt (data for accounts 60, 62, 68, 69, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76).
- line 1530 is completed if this accounting object is recognized in accordance with accounting provisions;
- on page 1540 show credit. account balance 96;
- page 1550 is intended to display those types of short-term liabilities that were not included in the previous lines mentioned above;
- page 1500 reproduces the total for all previous lines 1510–1550.
Thus, the total amount of short-term borrowed capital of the enterprise is the result according to section. V, i.e. page 1500. When forming the book. balance sheet and, in particular, section. V, one should also take into account the fact that enterprises autonomously detail the indicators for the relevant items of the generated reports. This right is reserved for all organizations and is justified. So, for example, an enterprise has the right to supplement p. 1520 in section. V in the appropriate lines, detailing, deciphering in this way, this or that indicator.
Definition
P4 Constant liabilities are liabilities that - unlike other groups of liabilities - firstly, are not obligations, and secondly, do not require payments to external parties.
This category traditionally includes the result of Section 3 “Capital and Reserves”.
That is, permanent liabilities are your own sources of financing.
Some authors include deferred income and reserves for future expenses and payments (estimated liabilities) or one of these items in this category.
Either of these options is wrong because both clauses are obligations.