In modern society, any employee knows that failure to pay wages on time entails very real consequences for the employer.
There are different cases, each of which is interpreted by current legislation, based on existing norms and requirements of the labor code. You should consider them in more detail in order to know about your rights in the event of such a problem. Let us dwell more on the criminal liability of the employer. For the procedure for collecting wages from an employer, please follow the link.
Non-payment of salary upon dismissal
There are specific deadlines, if violated, non-payment of wages upon dismissal will be considered a punishable event. The following situations are acceptable:
- the salary is issued to the employee on the last day of his work in cash;
- if wages are transferred to the employee’s card or bank account, the procedure is carried out the next day after dismissal;
- in case of going on vacation with further termination of the employment contract, the entire salary is given to the employee on the last day before the specified vacation date.
If the mentioned standards are not observed, an individual can write a statement to the prosecutor's office about non-payment of wages upon dismissal, after which the relevant government agency will investigate the mentioned case. Sometimes a simple complaint to the employer upon dismissal can help solve the problem, if not, then now you will know how to act.
If during supervisory activities it is established that the employer is guilty of non-payment of wages, then the employee, quite reasonably, based on these results, can apply to the judicial authorities to protect his labor rights.
There are often cases when neither supervisory nor control authorities find any violations in the actions of the employer. This circumstance cannot become an obstacle to the protection of the employee’s rights; in any case, only the court can put a final point in this dispute. Do not forget that there are cases when labor rights are restored on the basis of a judicial act of the appellate authority. Moreover, we should not forget about the practice of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, since sometimes it is these acts that put an end to a labor dispute.
Where to go if the employer has not paid the settlement
Violation of payment deadlines or failure to provide payment for time worked is a violation of the labor rights of a specialist. If the period established by law has expired and the funds have not yet been accrued, the employee has the right to contact the authorities competent to resolve the problems.
If the contract is terminated, but the employee was not paid upon dismissal, an appropriate step would be to file a complaint with the labor inspectorate, labor dispute commission, prosecutor's office or court. These authorities are authorized to resolve the issue in favor of the applicant and facilitate the receipt of the unpaid settlement.
Labor Dispute Commission
The first instance where a former employee of a company can turn is the commission that resolves labor issues when the interests of working citizens are infringed. Article 386 of the Labor Code sets a period of 3 months when an employee can submit an application to this organization if he discovers a violation of the law.
Labor dispute commissions are created at enterprises by order of management with the consent of the trade union committee (if there is one in the organization).
ATTENTION! The CTS includes a circle of people who also work in this institution - representatives of different departments who are not interested in taking the side of one or another participant in the conflict.
To resolve a conflict situation, an employee must submit a written application, which is reviewed within 10 working days. At least half of the commission members must participate; it is also necessary to interview witnesses, study and analyze documents related to the resolution of the issue.
Labour Inspectorate
If a citizen has not been paid upon dismissal, and the CTS has not been created, the second authority where one can apply for protection of interests becomes the institution that accepts statements of violation of labor laws. The labor inspectorate is empowered to restore justice to the employee and take measures to punish those responsible. Article 356 of the Labor Code establishes a list of such events:
- sending a request to eliminate deficiencies within a specified time frame;
- a petition to bring the violator to administrative punishment;
- temporary suspension of the work of structural units, branches, departments until the circumstances of infringement of the applicant’s interests are clarified;
- removal of those responsible from performing duties according to job descriptions.
You can contact this department within 3 months from the moment the conflict situation arises.
Prosecutor's office
When, in the event of non-payment of wages upon dismissal, the above methods did not bring results, the best step would be to file an application with the prosecutor's office. This structure has the right to organize an inspection of the company or request the necessary documents to analyze the situation and determine corrective measures.
ATTENTION! If prosecutors identify a violation of the interests of workers, they can prepare materials for drawing up a protocol if the case concerns administrative punishment, or to begin investigative actions in the case of criminal proceedings.
After the inspection, the prosecutor's office sends the manager a report describing the identified violations of the law and demanding their correction within a specified period.
You may be interested in : What to do if your employer does not pay wages
Judicial authorities
The courts are the last option for resolving a controversial issue. They are contacted when previous authorities were unable to influence the employer regarding the delay in wages. An application is filed with the court, to which is attached a package of documents confirming the applicant’s position. When considering a case, the judge is interested in whether the parties tried to resolve the conflict pre-trial, since the opportunity to reach an agreement on their own always remains.
After this, a court hearing is scheduled, where both parties are invited, and the issue is considered on its merits. If a positive decision is made for the employee, the company is obliged to pay wages. According to judicial practice, if the verdict is negative, it can be challenged within 1 month in a higher authority.
IMPORTANT! Article 392 of the Labor Code establishes a statute of limitations during which the applicant has the right to go to court to resolve a conflict in the labor sphere - 1 year from the date of recording the fact of non-payment of wages.
If an enterprise does not pay money by court decision, bailiffs receive the right to further influence it.
Samples of complaints for downloading: to the CTS, labor inspectorate, prosecutor's office, example of going to court.
How to punish an employer for non-payment of wages?
In this case, criminal liability for non-payment of wages is assigned by Article Art. 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, but only for managers. It begins to take effect if not only the fact of non-payment is proven, but also selfish intent in which the debt was spent for one’s own purposes.
If violations are detected, the employer’s criminal liability for non-payment of wages partially includes a number of such consequences:
- the fine can be up to 120 thousand rubles;
- imprisonment for up to one year;
- prohibition on carrying out any activity or holding a certain position for a period of up to one year;
- ordering corrective labor for two years.
Grave consequences require a different court decision. The fine can vary from 200 to 500 thousand rubles. Imprisonment increases to five years. For the same period, a person may be prohibited from holding the same position or carrying out a specific type of activity. But it should be remembered that criminal liability will arise only if the employer’s selfish intentions towards the employee are revealed.
How to apply to the State Tax Inspectorate for salary after dismissal
If the employer does not pay the dismissal payment and direct negotiations with him did not lead to anything, you can contact the labor inspectorate. To do this, an application is drawn up in any form indicating the following information (Article 7 Federal Law No. 59-FZ dated 02.05.2006):
- the name of the territorial department of the labor inspectorate to which the appeal is sent;
- Full name of the applicant;
- contact information for receiving a response: postal address, email address, telephone number;
- the name of the employer who committed the abuse;
- the content of the violation, with a description of all the circumstances of its commission and the requirements for payment of the debt;
- date of writing and personal signature of the applicant.
The application can be submitted in person, by registered mail with notification, or electronically on the government services website and the portal of the territorial office of the State Tax Inspectorate. To further confirm that he is right, the employee can attach copies of documents (dismissal orders, time sheets, written requests to the employer for debt repayment).
The received application is registered within 3 days and after that is considered within no more than 30 days (Part 1, Article 12 of Law No. 59-FZ). During this time, an unscheduled inspection of the employer is carried out and if violations are detected, a report is drawn up and an order is issued to the employer.
In exceptional cases, it is possible to extend the period for consideration of an application by another 30 days, of which the applicant must be notified in writing.
The order specifies the deadline for its implementation and, if the debt is not repaid before its end, the inspectorate has the right to make a decision on forced collection. Such a decision will have the force of an executive document. If it is not executed within the time period specified therein, then it is handed over to the bailiffs (Article 360.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The applicant is sent a written response with a detailed explanation of the results of the verification and recommendations on further steps that he can take to restore his rights.
How can an employer defend himself against accusations of non-payment of wages?
The whole point is that in order to bring the head of an organization to criminal liability, the conditions for liability for non-payment of wages to employees must be met. It should be noted that in order to impose criminal liability for unlawful actions of an employer in the form of non-payment of wages, in addition to a selfish motive, a number of conditions must be met based on the legislation of the Russian Federation, in particular:
- The employer has a real opportunity to liquidate the resulting debt to the employee or employees, but sells these funds for other purposes, for example, the purchase of equipment, renovation of premises, personal needs;
- Non-payment of wages must be made over a certain period , based on the legislation, this period is more than two months, that is, during this period the employee must not receive any funds from the employer as wages;
- For partial payment of wages, a different period is established; in this case, in relation to an employee, the employer allows partial payment of wages for more than three months. It should be taken into account that partly received wages are considered to be wages in the amount of less than half of the monthly salary.
If the conditions are not met, the accusation against you is brought prematurely and unfoundedly, then our criminal lawyer will build a defense for the accused against this composition and defend the honest name of a law-abiding manager. Read the advice of a criminal lawyer at the link and carry out your defense 100%.
ATTENTION : watch a video about defending the rights of the accused by a lawyer and subscribe to our YouTube channel, you will have access to free legal assistance from a lawyer through comments on the video.
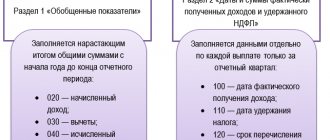
Compensation payment processing
When paying wages, the organization is obliged to notify the employee in writing about the components of his remuneration, deductions and compensation. All this is indicated on the pay slip. It also needs to indicate the amount of compensation for delayed wages, so that the employee knows how much he received and for what.
The calculation of compensation looks like this: debit 91-2 credit 73.
Payment through the cash register: debit 73 credit 50.
Payment via current account: debit 73 credit 51.
Civil liability of the employer for non-payment of wages
Do not forget that the employer’s liability may be limited only to a fine from regulatory authorities or criminal liability. Labor legislation also provides for a number of measures aimed at restoring the labor rights of an employee (read about how to force an employer to pay black wages, for example).
In particular, the Labor Code reflects that in case of delay on the part of the employer, the employee has the right to receive compensation, the amount of which is determined as 1/150 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for each day of delay in payment of wages.
In addition, the law provides for compensation for moral damage when it is established that the employer is guilty of violating the labor rights of an employee.
These circumstances and compensation are established and awarded in court, which is why the help of our experienced lawyer from the Law Office “Katsailidi and Partners” in Yekaterinburg is simply necessary in this matter. The employer has all the documentation and the ability to prepare other written evidence for the court, and an experienced lawyer will equalize your chances for a fair decision.
How to resolve a salary issue through the prosecutor's office
If payment is delayed after the dismissal of a worker, he can file a written complaint with the prosecutor's office. It is also drawn up in any form and must necessarily include the following details (clause 2.8 Order of the Prosecutor General’s Office of Russia dated January 30, 2013 No. 45):
- the name of the prosecutor's office and the official to whom the application is sent;
- Full name and contact details of the applicant;
- the essence of the dispute, a list of violated rights, as well as requirements to eliminate abuses on the part of the employer.
- date of writing and personal signature of the applicant.
Documents substantiating the requirements contained in it must be attached to the application. For example: a copy of the employment contract, extracts from time sheets, copies of work orders, an order to terminate the employment contract. Applications are allowed to be submitted:
- by post (registered letter with acknowledgment of delivery);
- through the official website of the prosecutor's office;
- through a personal visit to the prosecutor's office.
The received appeal is also subject to registration within 3 days. If its consideration requires an inspection of the employer, then it is considered within 30 days. In cases where additional actions are not required to confirm the facts stated in the application, it can be considered within 15 days.
If, as a result of requesting explanations from the employer and checking the requested documentation, the fact of non-payment of wages is confirmed, he is issued an order to eliminate the violation. The applicant must receive a written response to the submitted application. The prosecutor's office also has the right to independently file a lawsuit on behalf of the applicant to protect his rights.
What threatens an employer who delays payment?
Upon dismissal, the employee receives all due payments, a work book, a 2-NDFL certificate and other documents upon request. If the employee was given the documents, but was not paid the money, he has the right to take measures of influence on the administration of the enterprise. The head of the company and the chief accountant are considered responsible for timely payment.
The interests of a dismissed employee are protected by:
- commission for dispute resolution (not available everywhere, mainly at large enterprises);
- regional division of the state labor inspection;
- prosecutor's office;
- judicial authorities.
In all cases of delay in due payments, you should begin protecting your rights with a written appeal to management. A negligent employer can be punished in several ways.
Material liability
If the management of the organization is in no hurry to pay the money earned, then, under Article 236 of the Labor Code, the court imposes certain obligations on the director:
- payment of compensation for late payment upon dismissal. During the delay period, inflation may depreciate the size of the monetary settlement. The employee has the right to demand indexation of the salary amount;
- compensation for late payment. The penalty is calculated as a percentage of the amount of detained funds.
To receive the money due, the dismissed employee must apply to the judicial authorities. The organization must pay compensation even if the payment is delayed due to circumstances beyond the control of management.
Fine or warning
An employer who delays payment upon dismissal, in addition to assigning compensation, is held administratively liable. Such measures are used to reduce irresponsibility, fraud and negligence in labor relations.
A director found to have failed to fulfill obligations to an employee is punished with a warning. If a repeated offense occurs, the manager may be removed from his position.
Fines are imposed in different amounts, the amount is influenced by the following parameters:
- degree of guilt;
- the amount of damage caused to the employee;
- the total number of detected offenses in the organization;
- status of the guilty official.
For example, the fine for non-payment of compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal will be 30-50 thousand rubles for the organization. An individual entrepreneur will pay 1000-5000 rubles. A specific official will be fined in the same amount and given a warning.
A minimum amount of 1000 rubles is assigned to individual entrepreneurs brought to justice for the first time. Limited liability companies that repeatedly violate payment deadlines with employees may pay up to 100 thousand rubles. Payment of fines is credited to the municipal fund or state treasury.
Criminal liability for non-payment of money
If the organization’s actions violate the provisions of Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, a criminal case is opened. During the trial, the guilt of the act and the motives of the defendant are established. Instead of the director, the head of a department or an accountant may be found guilty. Late payment with delays in payments longer than 60 days is subject to criminal prosecution.
As a result of judicial review, one of the following types of punishment is assigned:
- fine;
- removal from office for a certain period;
- forced labor;
- restriction of freedom.
In some cases, the types of punishment complement each other.
Fines in criminal prosecution are much higher than in administrative proceedings. If more than 50% of the salary is not paid for longer than three months, the culprit will be required to pay up to 120 thousand rubles. If the payment has not been made at all for more than 2 months, the amount increases to 100-500 thousand.
Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
— contact the on-duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call:
+7
— Moscow and region.
+7
— St. Petersburg and region.
8
- Other regions of the Russian Federation
You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will take care of solving all your problems!