What you will definitely need
Among the mandatory documentation that must be drawn up by the administration of enterprises is a written order and a report on expenses incurred. The decision on secondment is made by the employer, and written consent must be obtained from representatives of some categories. In this case, before applying for a business trip in 2021, you will need to obtain another mandatory document. This norm is enshrined in Article 264 of the Labor Code, it applies to the following persons:
- Women raising children under 14 years of age (disabled);
- Single parents;
- Employees who actually care for sick relatives.
If your organization tells you, “We will arrange and pay for business trips in 2021,” then you should at least sign the order before leaving. Proper registration of temporary movements guarantees employees payment of expenses incurred (for example, in the absence of an advance payment), provision of various benefits and compensation (rest days or overtime pay).
Business trip 2018
Official decision of the employer in writing
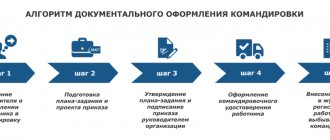
The consolidated daily order for the organization is the main legal document, which contains all orders for personnel. To clarify how to properly register a business trip in 2021, you should refer to the provisions of Article 166 of the Labor Code and Government Decree 749 of 2008. The recommended form for registering business trips is T9 (T9a) for individual or group trips.
A written decision can be drawn up not only according to the samples recommended by the legislator. According to the specifics of some enterprises, local regulations may develop and approve their own documents for business trips in 2021. The following remain the required details:
- Belonging to date, case number;
- Company name;
- Staff details of the departing employee;
- Place of performance of the official task and time interval of the employee’s absence;
- Purpose of departure;
- Responsible for receiving the advance report.
Business trip in 2021 - instructions for an accountant
The employer often practices business trips within the company. The accounting employee must know what documents are submitted by the posted employee upon return and how to correctly record all expenses. From 2021, the taxation procedure has changed. So before you fill out anything, please re-read the law and the guidelines.
How to arrange a business trip for an employee in 2021?
The general rule as of January 8, 2015 states that there is no need to issue a job assignment or travel certificate. But a company may have internal regulations that are actively enforced. They may say that the trip should be issued only on the basis of these documents. This is stated in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Articles 8 and 22 . The manager must make a decision about this. If it is positive, then when sending an employee on a trip, these documents must be drawn up by the employer without fail. But many companies have given up on this. Therefore, from 2021, registration and payment are made without these standard official papers.
Business trip for 1 day - registration
The rules for compiling documentation for a one-day business trip are in many ways similar to other types of business trips. The order is issued in any case, even if the trip is one day. Use the following forms for registration:
- N-T9 - used if the employee goes alone;
- N-T9a - used when several employees are assigned to it.
The employer or department head is required to sign the travel assignment and its completion report. A brief report on the work done is drawn up after the employee arrives. This document is pre-agreed with the director of the company where the seconded employee works.
On a business trip in a personal car 2021 - how to apply
The employee has the right to go to the destination in his own vehicle. An agreement on additional funds that will be needed for a car for purely business purposes is preliminarily agreed upon with the employer. The amount of compensation is paid in accordance with the agreement. Payment options may vary:
- The compensation amount includes additional fuel costs;
- Fuel costs are paid additionally according to pre-confirmed documents.
How to arrange a foreign business trip in 2021?
The Labor Code is still considered the main provision in accordance with which business trips are issued both within the country and abroad. Arranging for a trip abroad does not involve any difficulties. The list of official documents from the personnel service is standard. It includes a job assignment and an order. It is worth noting that the job assignment is no longer a mandatory document. The final deadlines are confirmed by tickets, as well as additional marks in the foreign passport of the customs officer.
Documents for business trips in 2021
Documentation of a business trip this year does not require the provision of a business travel certificate. The company can arrange it if necessary. The internal regulations of the organization may oblige the director of the unit or the personnel department to do this. Such a certificate is a document that confirms the employee’s arrival date for the trip. Not only the date of arrival is recorded, but also the date of departure. Therefore, everything depends solely on the company.
An order is an important document, without which you have no right to send an employee. A job assignment is an additional document that is not required to be drawn up since 2015. It all depends on the specific organization
How to issue a business trip order?
The main purpose of a business trip is to solve the problem that was set by the manager. An order for a business trip is issued only to an employee who works under an employment contract. If a contract has not been drawn up for it, it should not go through the documents presented above. It depends on the decision of the manager whether the employee will be sent or not. Until 2021, a certificate and official assignment were issued on the basis of the order. However, from January 1, only an order is issued. Without it, spontaneous work can be assessed as absenteeism. The travel order is issued according to the sample.
Sample order
Expense report
The final document summarizing the trip is the advance report. This is an estimate of the employee’s expenses, to which supporting documents are attached. The employee must submit the report for approval to the head of the company within 3 days. It is understood that within this period the employee must return the balance of the unused advance (receive a settlement if the amount issued is exceeded) and attach the following documents for business trips in 2018:
- Electronic coupons, travel tickets;
- Contracts and receipts confirming the employee’s residence and the amount of expenses incurred;
- A copy of the pages of the passport that contain marks affixed by the border service (when leaving abroad);
- When traveling to the place of performance of a work assignment in a personal (corporate) car, gas station receipts and a waybill are attached.
Important: when leaving on a business trip, you should take into account the maximum daily allowance standards - 700 rubles for Russia and 2,500 rubles for Abroad, respectively. Typically, companies do not exceed this limit, since they will have to show such expenses in the declaration.
Currently, organizations practice purchasing travel tickets and paying for reservations from the company's bank account. This method is often used to arrange local business trips. In any case, supporting documents must be submitted along with the advance report upon return.
How else can you check travel expenses?
Despite the fact that the procedure for registering an employee’s business trip has been simplified as much as possible since 2018, there are still forms in which it is necessary to duplicate information on all departures. In time sheets, it is necessary to indicate the suppression of dates and employees who performed their duties outside the office or production. For the days in which the employee was listed as having left, he will be paid the average salary and given a day of rest. If the work assignment was performed on a day off, the employee will receive double pay.
Secondment of employees is an integral part of the activities of many organizations. From the outside, the process seems simple - a person receives money and leaves with an official task (oral or written) to the place of execution. For the administration, this is always an attentive attitude to detail, because foreign business trips for registration and other types of departures may have their own characteristics. To eliminate risks, directors and entrepreneurs use both the recommended set of documents and resort to drawing up already canceled forms. This helps to avoid disputes with inspection inspectors and minimize the risk of fines.
Similar articles
- The travel permit has been canceled in 2021
- Business trip 2018
- How to write a business trip report example
- Business travel allowances in 2021
- Job assignment and business trip report (sample + form)
Business trips. Procedure for processing travel expenses
Any company may sooner or later need to send an employee on a business trip*.
*In accordance with Article 166 of the Labor Code, a business trip is a trip by an employee by order of the employer for a certain period of time to carry out an official assignment outside the place of permanent work.
Business trips of employees whose permanent work is carried out on the road or has a traveling nature are not recognized .
The specifics of sending employees on business trips are established by the Regulations “On the specifics of sending employees on business trips,” approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008. No. 749.
At the same time, taxpayers need to remember that the guarantees and compensations provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, including those related to business trips, apply only to employees who have entered into an employment contract with the organization.
Employees working under a GPC agreement are not subject to the norms of labor legislation and other acts containing labor law norms in accordance with the provisions of Article 11 of the Labor Code.
A similar rule is contained in paragraph 2 of Resolution No. 749:
Employees who have an employment relationship with the employer are sent on business trips.
Accordingly, if an employee works for a company under a GPC agreement, then sending him on a trip for official purposes is not a business trip . This means that the organization has no obligation to compensate such an employee for travel expenses.
Therefore, in order not to increase the price of the GPC agreement (remuneration amount) by the amount of expenses associated with the business trip, as well as not to pay “extra” taxes, the possibility of paying compensation amounts to the executor of the assignment must be provided for in the GPC agreement.
Both in tax and accounting, when reflecting business transactions related to business trips, a whole range of tasks and issues arise that accounting must solve.
Sending employees on business trips is part of the employment relationship between employees and the organization.
Chapter 24 of the Labor Code is devoted to this issue.
In accordance with this chapter, it is necessary to apply a special procedure for calculating wages with traveling employees. After all, when an employee is sent on a business trip, he is guaranteed to retain:
- places of work (positions),
- average earnings,
as well as reimbursement of expenses associated with a business trip in accordance with the provisions of Article 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The article will discuss the norms of the current legislation regulating the procedure for registration and accounting of business transactions related to sending employees on business trips.
REQUIREMENTS OF CURRENT LEGISLATION FOR THE PROCEDURE FOR executing official business trips
In accordance with the requirements of Article 168 of the Labor Code, in the event of being sent on a business trip, the employer is obliged to compensate the employee for:
- travel expenses to and from your destination;
- expenses for renting residential premises;
- daily allowance - additional expenses associated with living outside the place of permanent residence;
- other expenses incurred by the employee with the permission or knowledge of the employer.
In addition to the above, travel expenses include:
- expenses for travel to the airport or train station at places of departure, destination or transfers,
- baggage costs,
- expenses for communication services,
- expenses for obtaining and registering a service foreign passport, visas, and other travel documents,
- fees for the right of entry or transit of motor transport,
- costs for obtaining compulsory health insurance,
- expenses associated with the exchange of cash or a bank check for cash foreign currency,
- airport service fees, commission fees,
- other mandatory payments and fees.
The procedure and amount of reimbursement of expenses related to business trips are determined by a collective agreement or local regulations.
Thus, the Labor Code does not establish standards for compensation payments for reimbursement of travel allowances.
Employers are given the right to independently determine in a collective agreement or local regulation (for example, regulations on business trips), the procedure and amount of reimbursement of expenses associated with business trips, including the amount of daily allowances paid.
Employees are sent on business trips by order of the employer for a certain period of time to fulfill an official assignment outside their place of permanent work (clause 3 of Resolution No. 749).
In accordance with paragraph 6 of Resolution No. 749, the purpose of the employee’s business trip is determined by the head of the sending organization and is indicated in the job assignment , which is approved by the employer.
Based on the employer’s decision, the employee is issued a travel certificate confirming the length of his stay on the business trip:
- date of arrival at the point(s) of destination,
- date of departure from it (of them),
with the exception of the following cases:
An employee is sent on a business trip outside the Russian Federation by order of the employer without issuing a travel certificate, except for cases of business trips to CIS member states with which intergovernmental agreements have been concluded, on the basis of which marks are not made in entry and exit documents by border authorities on crossing the state border (clause 15 of Resolution No. 749).
The travel certificate is issued in one copy and signed by the employer, handed to the employee and kept by him for the entire duration of the business trip.
The actual period of stay at the place of assignment is determined by the marks on the date of arrival at the place of assignment and the date of departure from it, which are made on the travel certificate and certified by the signature of an authorized official and the seal of the organization to which the employee is posted.
If an employee is seconded to organizations located in different localities, notes on the travel certificate about the date of arrival and date of departure are made in each of the organizations to which he is seconded.
At the moment, for documenting business transactions related to business trips, unified forms are used, approved by the Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004. No. 1 “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation of labor and its payment”:
1. No. T-9 “Order (instruction) on sending an employee on a business trip”,
2. No. T-9a “Order (instruction) on sending workers on a business trip”,
is issued when sending an employee (employees) on a business trip. Filled out on the basis of a job assignment (form T-10a).
The storage period for these documents is 5 years (for long-term foreign business trips - 10 years).
3. No. T-10 “Travel certificate”,
serves to confirm the time spent on a business trip. The certificate indicates the time of arrival of the employee at the destination, as well as the time of departure. This document is drawn up on the basis of an order for sending on a business trip (form T-9) and is certified by the receiving party.
The storage period for certificates is 5 years (for business trips to the Far North and equivalent areas - 75 years).
4. No. T-10a “Official assignment for sending on a business trip and a report on its implementation,”
contains information about the purpose of the employee’s trip and its final results. It is the basis for issuing an order in the T-9 form and serves to confirm the economic justification of business trip expenses.
The storage period for official assignments and reports is 5 years (for long-term foreign business trips - 10 years).
DURATION OF BUSINESS TRIP
In accordance with paragraph 4 of Resolution No. 749, the duration of the business trip is determined by the employer, taking into account the volume, complexity and other features of the official assignment.
In this case, the day of departure on a business trip is considered to be the date of departure:
- trains,
- airplane,
- bus,
- another vehicle
from the place of permanent work of the business traveler, and on the day of arrival from the business trip - the date of arrival of the specified vehicle at the place of permanent work.
When a vehicle is sent before 24 hours inclusive, the day of departure for a business trip is considered the current day, and from 00 hours and later - the next day.
If a station, pier or airport is located outside a populated area, the time required to travel to the station, pier or airport is taken into account.
The day the employee arrives at his place of permanent work is determined similarly.
The issue of an employee’s attendance at work on the day of departure on a business trip and on the day of arrival from a business trip is resolved by agreement with the employer.
When an employee travels from the territory of the Russian Federation, the date of crossing the state border of the Russian Federation is included in the days for which daily allowances are paid in foreign currency, and when traveling to the territory of the Russian Federation, the date of crossing the state border of the Russian Federation is included in the days for which daily allowances are paid in rubles.
The dates of crossing the state border of the Russian Federation are determined by the marks of the border authorities in the passport.
PAYMENT OF EXPENSES ASSOCIATED WITH AN OFFICE TRIP TO AN EMPLOYEE
In accordance with paragraph 10 of Resolution No. 749, when an employee is sent on a business trip, he is given a cash advance to pay expenses:
- on the way,
- renting a living space,
- daily allowance.
At the same time, daily allowances are reimbursed to the employee for each day he is on a business trip, including (clause 11 of Resolution No. 749):
- weekends and non-working holidays,
- days on the road (including during a forced stopover).
Payment of daily allowance, as well as reimbursement of travel expenses, can be carried out by the organization both in cash and in non-cash forms.
In the case of issuing cash from the cash desk of an enterprise, an employee going on a business trip, as an accountable person, is required to draw up a written application in any form for the issuance of accountable amounts.
This application must contain a handwritten note from the head of the company about the amount of cash and the period for which it is issued.
The application must also be dated and signed by the head of the company.
Currently, companies are increasingly using non-cash means for settlements with accountable persons. And when employees are on a business trip, non-cash payments become especially relevant.
However, when transferring accountable amounts to employees’ “salary” plastic cards, certain tax risks may arise.
They are associated with the re-qualification of funds transferred as accountable to wages.
When conducting an audit, tax authorities may charge additional insurance premiums, personal income tax, penalties and fines for such amounts.
In order to avoid conflicts with tax authorities and minimize tax risks, organizations can protect themselves in the following ways:
- To reflect in the accounting policies for the purposes of accounting and tax accounting of organizations the possibility of transferring non-cash funds for the issuance of accountable amounts using any employee details.
- Clearly indicate the purpose of the payment as “transfer of accountable funds” and insist on your position if the servicing bank tries to change the purpose of the payment.
- Keep records of advance reports and supporting documents attached to them in a timely and complete manner.
When an employee is sent on a business trip to the territory of 2 or more foreign states, daily allowances for the day of crossing the border between states are paid in foreign currency according to the standards established for the state to which the employee is sent (clause 18 of Resolution No. 749).
If an employee falls ill during his stay on a business trip, then he:
- expenses for renting living quarters are reimbursed (except for cases when the posted employee is undergoing inpatient treatment),
- daily allowances are paid for the entire time until he is unable, for health reasons, to begin fulfilling the official assignment assigned to him or to return to his place of permanent residence.
During the period of temporary disability, the employee is paid temporary disability benefits in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
In this case, temporary disability must be documented in the prescribed manner (clause 25 of Resolution No. 749).
DOCUMENTARY PROOF OF TRAVEL EXPENSES
In accordance with paragraph 24 of Resolution No. 749, reimbursement of other expenses related to business trips in cases, procedures and amounts determined by a collective agreement or local regulations is carried out upon presentation of documents confirming these expenses.
Upon returning from a business trip, the employee is obliged to provide the employer within 3 working days (clause 26 of Resolution No. 749):
an advance report on the amounts spent in connection with the business trip, as well as to make a final payment for the cash advance for travel expenses issued to him before leaving for the business trip.
The following documents, duly executed, are attached to the advance report:
- travel certificate,
- about renting residential premises,
- confirming travel expenses (including insurance premium for compulsory personal insurance of passengers on transport, payment for services for issuing travel documents and providing bedding on trains),
- about other expenses related to the business trip;
- a report on the work performed on a business trip, agreed upon with the head of the employer’s structural unit, in writing.
In accordance with Article 252 of the Tax Code, the organization's expenses must be justified and documented.
This requirement also applies to travel expenses incurred by the organization. Below we will look at some Letters from the Ministry of Finance regarding documents confirming expenses associated with business trips.
1. Documents confirming the costs of paying for travel documents (tickets) and hotel services.
In his Letter dated November 10, 2011. No. 03-03-07/51, the Ministry of Finance indicated a list of documents required to confirm the costs of paying for travel documents by seconded employees.
“When sending an employee on a business trip, documents confirming his expenses for paying for tickets and (or) hotel services are:
— check of cash register equipment;
— slips, checks of electronic terminals when conducting transactions using a bank card, the holder of which is the employee;
— confirmation of the credit institution in which the employee has a bank account, which provides for transactions using a bank card, and the payment transaction carried out;
- or another document confirming the payment made, drawn up on an approved strict reporting form.”
Please note: Seconded employees should not forget about documents confirming payment of expenses incurred (cash register receipts and slips).
2. How to confirm expenses if electronic travel documents are issued.
The procedure for confirming expenses when issuing electronic tickets is disclosed in the Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated February 27, 2012. No. 03−03−07/6: “In the case of issuing travel documents with electronic passenger tickets, it is necessary to take into account that in accordance with clause 2 of Order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated November 8, 2006 No. 134 “On establishing the form of an electronic passenger ticket and baggage check in civil aviation” route /receipt of an electronic passenger ticket and baggage receipt (extract from the automated information system for registration of air transportation) is a document of strict accountability and is used for organizations and individual entrepreneurs to carry out cash payments and (or) payments using payment cards without the use of cash register equipment.
Thus, if an air ticket was purchased in undocumented form (electronic ticket), then the supporting documents confirming the costs of purchasing the air ticket for tax purposes are the route/receipt of the electronic document (air ticket) generated by the automated information system for registration of air transportation on paper, which indicates the cost of the flight, a boarding pass confirming the flight of the accountable person on the route specified in the electronic ticket.”
3. What documents are needed to confirm expenses in the form of daily allowances issued to a posted employee.
Expenses in the form of daily allowance can be confirmed by a travel certificate. This is precisely the point of view that the Ministry of Finance adheres to in its Letter dated November 11, 2011. No. 03-03-06/1/741.
“Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2008 N 749 approved the Regulations on the specifics of sending employees on business trips (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations).
In accordance with paragraph 11 of the Regulations, additional expenses associated with living outside the place of residence (per diems) are reimbursed to the employee for each day he is on a business trip, including weekends and non-working holidays, as well as for days en route, including during a forced stop. on the way, taking into account the provisions provided for in paragraph 18 of the Regulations.
According to paragraph 7 of the Regulations, based on the employer’s decision, the employee is issued a travel certificate confirming the period of his stay on a business trip (date of arrival at the destination point(s) and date of departure from it (from them)), except for the cases specified in paragraph 15 of the Regulations.
Taking into account that the daily allowance is reimbursed to the employee for each day he is on a business trip, and at the same time, the length of stay on the business trip is confirmed by a travel certificate, we believe that expenses in the form of daily allowance can be confirmed by a travel certificate. At the same time, the provision of checks and receipts confirming the employee’s expenditure of daily allowance is not required.”