Let us pay attention to one of the types of periodic inspections of the organization’s condition. Today, inventory before drawing up annual financial statements is carried out, in fact, without fail, and below we will look at why this happens, why, and what it gives. We will separately touch on the tasks and deadlines and go through all its stages. So much information - so that you understand how to act, and also realize the importance and relevance of the measures being taken.
Let us immediately note that literally all the nuances of this complex procedure are regulated by various documents. And this is even convenient in practice, since it protects against repeated mistakes: having corrected all the mistakes, you will not make them the second time. Below we will try to highlight all the nuances and pitfalls in as much detail as possible, so that there are initially fewer “filled bumps”.
What it is
Essentially, this is a check, an accounting of objects: whether they exist, whether they are located in warehouses, counters, or are in the process of being transported from one warehouse to another. And also accounting for whether the written-off products were actually withdrawn from circulation and sent for disposal.
Although the frequency itself directly depends on the manager or owner of the enterprise, the timing and regulations, as well as the corresponding decisions based on the results, are identified through the basic provisions on accounting.
Basically, the process has two main tasks. The first is the actual reconciliation. The second is derivative in nature. If any discrepancies are identified, then it is necessary to determine the amount of surplus or deficiency for various items.
Several responsible persons take part in the preparation of inventory of inventory items. The start occurs through the decision of the manager, who issues the appropriate order. It immediately notes a lot of initial data. Whether the inspection is scheduled or unscheduled, whether it concerns a specific location, department, branch, warehouse, or, in principle, all the property of the enterprise will be taken into account. The form of implementation is revealed. As well as the composition of the commission that will carry out this activity. Moreover, it is heterogeneous; among the members there is also a leader who will be responsible for making decisions and reporting on the results. And he bears obligations for the correct execution of the task by all members of the commission. Materially responsible persons are also involved in the actual verification of inventories and balances of goods. In most cases, this is the storekeeper. Who will be interested in ensuring that accounting occurs as correctly as possible. Otherwise, he will often have to compensate for the defects of lost products personally.
The summed up results are processed, analyzed, and after that a certain verdict is made. If the results are satisfactory, then activities continue as normal. If there are unaccounted losses, which, however, are quite understandable, for example, burned in a fire, the economic plan for the next period changes. The new course is being developed taking into account new information. And if subsequent documentation of the inventory of goods and materials reveals discrepancies, but the reason for them has not been established, a special investigation is often initiated within the enterprise. Its purpose, naturally, is to establish the source of expenses.
Inventory as an element of accounting policy
The accounting policy of an organization is a set of accounting methods. One of these methods is inventory. How often should an inventory be taken? When? What assets and liabilities should be checked? The organization has the right to resolve all these issues independently. But the answers to them are better reflected in the accounting policies for accounting purposes.
Auditing and consulting ESSENCE AND GOALS OF INVENTORY
Inventory is a method of accounting, which is a regulatory procedure for periodic verification and documentary confirmation of the presence, condition and assessment of the property and liabilities of an organization, carried out to confirm the reliability of accounting data and financial statements <*>.
————————
<*> Audits, audits, current operations for accounting for valuables that require checking their availability and determining their quantity, and procedures for accounting for property for management purposes (management inventory) are not included in the routine inventory procedure.
The main goals of the inventory are: - identifying the actual availability of the enterprise’s property; — comparison of the actual availability of property with accounting data; — identification of substandard material resources, formation of informed conclusions with the involvement of the necessary specialists and special organizations, as well as preparation of documents for their markdown or write-off (disposal); — identification of those responsible in the event of detection of shortages, surpluses, or damage to material resources; — checking the completeness of the reflection of obligations in the accounting of compliance by performers with fulfilling contractual deadlines, taking measures to collect receivables and pay off accounts payable, writing off obligations in the prescribed manner after the expiration of the statute of limitations. According to clause 1.3 of the Methodological Guidelines for Inventorying Property and Financial Liabilities (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 N 49), “all property of the organization is subject to inventory, regardless of its location, and all types of financial liabilities. In addition, inventories are subject to inventory and other types of property that do not belong to the organization, but are listed in the accounting records (those in custody, rented, received for processing), as well as property that is not accounted for for any reason.” This provision does not say anything about property recorded off the balance sheet or in operational accounting. However, the need for an inventory of this property is undoubted, especially if we take into account the following provision of PBU 6/01 (clause 18): “Fixed assets with a value of no more than 10,000 rubles per unit or another limit established in the accounting policy based on technological features, as well as purchased books, brochures, etc. publications are allowed to be written off as production costs (sales costs) as they are released into production or operation. In order to ensure the safety of these objects in production or during operation, the organization must organize proper control over their movement.” The results of the inventory of property recorded on the balance sheet or in operational accounting are primarily of interest to the organization from the point of view of management accounting and internal control.
PROCEDURE FOR CONDUCTING INVENTORY
The procedure for conducting an inventory refers to the number of inventories in the reporting year, the date of their conduct, the list of property and liabilities checked during each inventory, etc. (clause 26 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation). The procedure for conducting an inventory was previously determined in the letter of the USSR Ministry of Finance dated December 30, 1982 N 179 “On the main provisions for the inventory of fixed assets, inventory, cash and settlements.” Currently, it is regulated by the Methodological Guidelines for the Inventory of Property and Financial Liabilities (Appendix to Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 N 49). The procedure for conducting an inventory is determined by the head of the organization, except in cases where an inventory is required. Carrying out an inventory is mandatory in the following cases (clause 2 of article 12 “Inventory of property and liabilities” of the Law “On Accounting”): - before drawing up annual financial statements; — when changing financially responsible persons (on the day of acceptance and transfer of cases); — when establishing facts of theft, abuse, and damage to valuables; — in case of natural disasters, fires, accidents or other emergency circumstances; — during liquidation or reorganization of an enterprise before drawing up a liquidation (separation) balance sheet; - when transferring the property of an enterprise for rent, redemption, sale and in other cases specifically provided for by law. In accordance with clause 27 of the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting, if an inventory of any property was carried out after October 1 of the reporting year, this property is not included in the list of property checked during the inventory before drawing up the annual financial statements. To compile annual reporting, the results of an already completed inventory of this property are used. To carry out an inventory in an organization, as a rule, a permanent inventory commission is created. When the volume of work is large, working inventory commissions are created to simultaneously carry out an inventory of property and financial obligations. If the amount of work is small and the organization has an audit commission, it can be entrusted with carrying out inventories. During the inter-inventory period, by order of the head of the organization, selective inventories can be carried out.
FACTORS INFLUENCED DECISION MAKING IN THE FORMATION OF ACCOUNTING POLICIES IN PART OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF INVENTORY PROCEDURE
Decision-making in the formation of accounting policies in terms of developing an inventory procedure can be influenced by the scale of the organization’s activities, the number of types of activities, the ramifications of the organizational structure, the total volume of property and liabilities of the organization, the volume and specifics of the warehouse, the geographical location of the organization itself and its divisions, features of accounting systems accounting and internal control. So, for example, for a relatively small enterprise with a limited number of enterprise activities, a compact structure and a small warehouse volume, the number of proactive inventories can be reduced to a minimum.
ISSUES THAT AN ORGANIZATION SHOULD ADDRESS WHEN DEVELOPING AN INVENTORY PROCEDURE
1. According to clause 27 of the Accounting Regulations, the organization must independently choose the frequency of conducting an inventory of fixed assets (at least once every three years). Organizations located in the regions of the Far North and similar areas need to decide when to carry out an inventory of goods, raw materials and materials, since clause 27 of the Regulations allows for an inventory to be carried out both at normal times and during the period of the smallest balances of goods, raw materials and supplies. 2. To document the inventory and reflect its results in accounting, standard unified forms of primary accounting documentation are used, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated 08/18/1998 N 88 (as amended on 05/03/2000 N 36) “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for accounting of cash transactions, accounting of inventory results.” If there are no standard forms of documents for recording inventory results, the organization must develop its own forms. The development of your own forms will be required, for example, when: - inventory of investments in the acquisition of individual fixed assets and intangible assets; — inventory of investments in non-current assets (except for investments in the acquisition of individual fixed assets and intangible assets); - inventory of fixed assets leased and for the safety of which financially responsible persons - employees of the organization are no longer responsible; — inventory of inventory items transferred for storage (secured storage, for processing); — inventory of financial investments (except for securities in documentary form); — inventory of estimated reserves and reserves for future expenses and payments. 3. The actual data obtained during the inventory process is verified in the organization’s accounting department with accounting indicators, and in the event of a discrepancy between the inventory data and the accounting or warehouse accounting data, matching statements are filled out. There are two standard comparison forms: N INV-18 “Comparison statement of the results of the inventory of fixed assets and intangible assets” and N INV-19 “Comparison statement of the results of the inventory of inventory items.” For other assets and liabilities, standard forms of matching statements are not provided. Therefore, if necessary, the organization must develop its own forms of matching statements.
PROCEDURE FOR COMPLETING INVENTORY FORMS
When conducting an inventory of property and liabilities, it is necessary to take into account the following features of the inventory. Inventory is carried out in kind on objects, for the safety of which financially responsible persons - employees of the organization - are responsible. In this case, inventory lists are compiled, which indicate the actual quantity according to the inventory data. An exception is the inventory of precious metals and precious stones that are part of material assets. The actual quantity of precious metals and stones is established on the basis of confirmation of the actual availability of material assets containing precious metals and stones, and technical documentation containing information on the amount of precious metals and stones in the specified material assets. Inventory lists for objects that are under the accountability of financially responsible persons - employees of the organization, are compiled: in two copies - for values owned by the organization (accounted for on the balance sheet); in triplicate - for valuables of other organizations and individuals (accounted for on the balance sheet). All inventories are signed by the financially responsible person(s). One copy of the inventory is transferred to the accounting department, the second - to the financially responsible person, the third (if compiled) - to the owner of the property. If an inventory is carried out: of material assets owned by the organization (accounted for on the balance sheet), but for the safety of which the organization’s employees are not responsible (such assets include material assets: in transit, shipped, transferred for storage to other organizations, transferred for processing, rent, management); all types of settlements (with debtors, creditors, borrowers and lenders); intangible objects (for example, intangible assets, financial investments in non-documentary form, valuation reserves, reserves for future expenses and payments, etc.), then such an inventory is carried out on the basis of primary documents (commodity transport, invoices, acts, statements etc.) and is drawn up not with an inventory list, but with an inventory act. As primary documents, it is possible to use documents from third-party organizations compiled by them in the process of inventorying the organization’s property. Such documents, in particular, include: - an inventory list drawn up by the tenant organization in Form N INV-1 for the leased property; — safety receipts reissued on a date close to the inventory date; — turnover statements for safekeeping provided as of the date preceding the inventory date. When conducting an inventory based on documents, it is not the actual data and accounting data that are subject to comparison, but the data from documents and accounting data. Acts are drawn up and signed by employees of inventory commissions without the participation of financially responsible persons. One copy of the act is transferred to the accounting department, the second remains with the commission. When making an inventory of unfinished capital investments in the form of the acquisition of individual fixed assets, intangible assets, and capital construction, the inventory is carried out both in kind and according to documents. The data identified by the commission is subject to comparison with accounting data and planned indicators (estimates, investment programs). Identified excess consumption in relation to the estimated (planned) indications should be considered separately. Inventory acts are drawn up in two copies. The acts are signed by members of the commission and the financially responsible person(s). One copy is transferred to the accounting department, the second - to the financially responsible person. In the case when the same form of inventory or act is used to inventory different groups of property or liabilities, then it is advisable to indicate the use case in the header part of the table. For example, in the inventory according to form N INV-1, in the heading part of the form after the word “located” it is indicated “in lease”, “in storage”, etc. All cost indicators in inventory records and acts are filled out in rubles and kopecks. Matching statements are compiled for fixed assets and material assets. Inventory results for other inventory items are reflected either directly in inventory acts or in matching statements developed by the organization.
WHICH PROVISIONS REGARDING INVENTORY SHOULD BE INCLUDED IN THE ACCOUNTING POLICY ORDER
The order on accounting policy must indicate the internal regulatory document regulating the procedure for conducting an inventory, the forms developed by the organization for recording and processing the inventory results, the frequency of the inventory of fixed assets, as well as the library collection, if any. The order may also establish the number of initiative inventories in the reporting year, the date of their conduct, and the list of inspected property and liabilities.
INTERNAL DOCUMENTS ON INVENTORY CARRYING OUT
In addition to document forms for recording inventory results, in the absence of standard ones, the organization must develop other internal documents for conducting inventory. These should include specific methods for conducting an inventory of individual objects, the procedure for obtaining confirmation of accounting data from counterparties, the procedure for resolving claims to the inventory commission, the procedure for offsetting shortages of valuables with surpluses by re-grading, etc. One of the issues that is not sufficiently regulated is the inventory of investments in non-current assets. Let's consider some aspects of this issue. In order to carry out an inventory of investments in non-current assets, the following types of objects can be distinguished: - objects that have not been completed with capital construction; - objects completed by construction, actually put into operation in whole or in part, the acceptance and commissioning of which are not documented with proper documents; — objects completed, but for some reason not put into operation; at the same time, the inventories must indicate the reasons for the delay in formalizing the commissioning of these facilities; — objects stopped under construction; at the same time, the act provides data on the nature of the work performed and its cost, indicating the reasons for the termination of construction. For this purpose, the appropriate technical documentation (drawings, estimates, financial estimates), certificates of completion of work, stages, logs of work performed at construction sites and other documentation must be used; — construction projects transferred to conservation; at the same time, the act indicates documents confirming the transfer of objects for conservation, as well as the reasons for conservation; — design and survey work for unfinished construction; at the same time, the act provides data on the nature of the work performed and its cost, indicating the reasons for non-construction. To do this, appropriate technical documentation (drawings, estimates, financial estimates), work completion certificates, stages, logs of work performed at construction sites and other documentation must be used. During the inventory process, both a physical check of the objects being built and a documentary check of construction costs are carried out. A natural inspection of constructed objects consists of inspecting construction sites. The result of the inspection is compared with the data from acts on the cost of work performed and expenses (Form N KS-3) or the general work log (Form N KS-6a), if the manufacturer of the work is an organization. In cases where control inspections are impossible (for example, when laying a sewer system), data is entered into the reports on the basis of acts of hidden work. The act reflects the actual volume of work performed and costs incurred. At the same time, it is checked: - whether the equipment that was handed over for installation, but has not actually begun installation, is included in the unfinished capital construction; — the condition of mothballed and temporarily stopped construction facilities, as well as the availability of completed documents for the mothballing of facilities. Additional explanations also require the procedure for offsetting shortages of valuables with surpluses based on re-grading. Since the concept of “regrading” is not defined normatively, the organization needs to define this concept for itself, taking into account the specifics of its warehouse facilities. For example, the following version of the definition of the concept of “misgrading” is possible. For the purpose of offsetting the shortage of material assets with surpluses by misgrading, misgrading is understood as a discrepancy between accounting and actual data on quantity in relation to the nomenclature of material assets of the same name with different distinctive features (grade, type). In this case, the values of one item are considered, which are under the accountability of one financially responsible person, for the same reporting period and in identical quantities. For the purpose of offsetting shortages of material assets with surpluses according to re-grading, the discrepancy between accounting and actual data is not recognized as re-grading: - in terms of quantity in relation to the nomenclature of material assets of the same name, listed in the account of one person in different reporting periods; - by quantity in relation to the nomenclature of material assets of the same name, which are not listed in the accounts of one person in identical quantities; - by quantity in relation to the nomenclature of material assets of the same name, listed in the accounts of different persons (even in identical quantities). The same name of material assets should be understood as material assets of the same name, the same type and purpose, similar in shape and size. For example, a credit can be made for oils and lubricants packaged in small containers that are similar in appearance. Materially responsible persons provide detailed explanations to the inventory commission about any misgrading. Proposals on the possibility of mutual offset of misgrading are submitted by the working inventory commission for consideration by the permanent commission. The issue of credit is finally decided by the head of the organization. The result of the offset by regrading can be negative (in the case when the value of the missing values was greater than the value of the values remaining in the surplus) or positive (in the case when the value of the missing values was less than the value of the values remaining in the surplus). In the event that, after a regrading test carried out in the prescribed manner, a shortage of valuables has arisen, then the norms of natural loss should be applied only for the name of the valuables for which the shortage has been established. In the absence of norms, the loss is considered as a shortage in excess of the norms. If, after offsetting the shortages with surpluses by re-grading and applying the norms of natural loss, a shortage still arises, the inventory commission decides on the sources of its coverage. The difference can be attributed to the guilty parties, and in cases where they are not identified, the differences are considered as shortfalls in excess of loss norms and are written off as a debit to account 91 “Other income and expenses.” For the difference in value from misgrading to shortages that were not caused by the fault of financially responsible persons, the protocols of the inventory commission must provide comprehensive explanations of the reasons why such a difference is not attributed to the guilty persons.
ERRORS IN CONDUCTING INVENTORY AND THEIR CONSEQUENCES
In order to ensure the legitimacy and reliability of the inventory results, measures should be taken to comply with the rules of paperwork and inventory procedures. The table below shows cases of violations of the inventory procedure and describes the impact of these violations on the legitimacy and reliability of the inventory results.
| Violation | Consequence |
| 1 | 2 |
| The manager’s order to carry out an inventory was incorrectly executed (the timing of the inventory, the composition of the commission, the list of property are not indicated) | There are no grounds for conducting an inventory, and therefore, for recognizing its results |
| The absence of at least one commission member during the inventory is documented | Inventory results are invalid |
| The inventory list is compiled in one copy | Inventory results are invalid |
| If it is impossible to stop business activities, incoming and outgoing documents are not endorsed by the chairman of the inventory commission | Violations identified as a result of the inventory can be challenged by presenting documents drawn up during the inventory period. |
| Receipts were not taken from financially responsible persons that all incoming and outgoing documents were submitted to the accounting department | Violations identified as a result of the inventory can be challenged by presenting documents drawn up during the inventory period. |
| The inventory procedure is violated: accounting data is compared with actual availability, and not vice versa | Violations may not be detected due to possible distortion of the actual availability |
| On each page of the inventory, the totals are not verified: the number in words, the number of rooms and the amount of material assets, as well as the overall total in physical terms | There is a possibility of unauthorized corrections of inventory results |
| On each page there is no entry “Prices, totals checked” and “Signature of the financially responsible person” (for forms in which such signatures are provided) | It is impossible to make claims against the financially responsible person on the basis of such a document |
| On the last page of the inventory list there is no signature of the financially responsible person stating that he has no claims against the members of the commission, as well as that he accepts the property specified in the inventory for safekeeping (for forms in which such signatures are provided) | It is impossible to make claims against the financially responsible person if shortages are identified |
| Errors and corrections are not signed or certified by members of the commission | Corrections are considered invalid |
| After approval of the results, inventory lists contain blank lines (lines not crossed out) | There is a possibility of unauthorized corrections of inventory results |
| During breaks in the work of the commission, access to the premises where the inventory records are stored is not blocked for outsiders | There is a possibility of unauthorized corrections of inventory results |
The Inventory Commission is not responsible for the unreliability of data provided by other organizations and used for the purpose of drawing up inventory acts for material assets, for the safety of which at the time of inventory the organization’s employees are not responsible.
Check Features
This procedure is a means of preserving the organization’s property, as well as controlling the existing array. Therefore, in addition to planned actions, it is often a response to an external factor. The storekeeper quit - we need to check whether this is part of a scam to steal funds. A reorganization took place; most likely, some of the products were greatly affected; they could have been transported or written off. Again you should check that everything is in place.
Due to the different purposes and related tasks, the study location is highlighted. In a general sense, when it comes to annual audits, scheduled audits, reconciliations before filing financial statements, this is general coverage. That is, all inventory items will be strictly taken into account. And if we are talking about the dismissal of a specific responsible person, then the coverage area will be narrower, only the one where this person made decisions and conducted activities. Usually there is a target warehouse or, in extreme cases, several. It is noteworthy that the algorithm for conducting an inventory of inventory items does not change depending on the volume involved. But the documentation may well. It is worth understanding that each object needs registration and its own inventory. The order and general reporting are just the tip of the iceberg. During the process, each object will receive its own documentation.
And all possible documentation options have a strictly prescribed format in legal acts. These are precise forms, where any discrepancy will call into question, in principle, the correctness of the entire procedure as a whole. Although this is often an internal matter of the enterprise, an incorrect format can have a very negative impact. For example, such a document cannot become evidence in court if a legal entity wants to accuse its employee of theft.
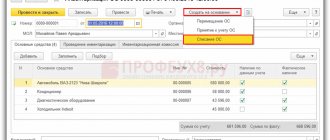
Postings during OS inventory: example
before the annual reporting, conducted an inventory of fixed assets. As a result of comparison of accounting and actual data, the following was revealed:
- shortage of a hydraulic machine with a purchase price of 42 thousand rubles. (28 thousand rubles residual value and 14 thousand rubles depreciation);
- shortage of a laptop (the culprit is Samokhin L. E.) worth 52 thousand rubles. (36 thousand rubles residual value and 16 thousand rubles depreciation);
- surplus hydraulic pump with a market value of 45 thousand rubles.
In accounting, the accountant recorded the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Amount (thousand rubles) | Wiring Description | Documentation | ||
| ||||||
| 01 disposal | 01 | 42 | The original cost of the hydraulic machine was written off | Act on write-off of fixed assets in form OS-4 | ||
| 02 | 01 disposal | 14 | depreciation of the hydraulic machine was written off | Accounting information | ||
| 94 | 01 disposal | 28 | The residual value of the hydraulic machine has been written off | |||
| 91 | 94 | 28 | Loss from machine write-off | |||
| ||||||
| 01 disposal | 01 | 52 | The original cost of the laptop has been written off | Act on write-off of fixed assets in form OS-4 | ||
| 02 | 01 | 16 | Laptop depreciation written off | Accounting information | ||
| 94 | 01 disposal | 36 | The residual value of the laptop has been written off | |||
| 73 | 94 | 36 | The shortage was attributed to Samokhina L.E. | |||
| 73 | 98.4 | 16 | The difference between the residual value of a laptop and the market value | |||
| 70 | 73 | 52 | The cost of the laptop was withheld from L. E. Samokhina’s salary. | |||
ATTENTION! The amount of damage caused by the shortage can be withheld from the employee’s salary within the limit - no more than 20% of the monthly salary (Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
According to paragraph 36 of the Methodological Recommendations for the accounting of fixed assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 13, 2013 No. 91n, unaccounted for fixed assets identified during the audit are taken into account in the fixed assets accounts at market value. Therefore, the hydraulic pump should be registered with the following wiring:
- Dt 08 Kt 91 - the hydraulic pump discovered during the inventory was capitalized;
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - hydraulic pump put into operation
Reasons for conducting an inventory of goods and materials
You need to understand that management independently determines the regulations and periodicity of scheduled inspections. Depending on how intensive the turnover is in the company, processes may be more frequent or less frequent. Only before submitting financial statements is there always a major reconciliation. Then it is at the discretion of the directors. But at the same time, usually serious companies with large turnover strive for indicators once every three months. That is, 4 times a year.
But this is what concerns planned variations. And there are still a lot of unplanned ones. They arise for various reasons. The most common reasons include the following:
- Transfer of property. These are often a variety of options, renting part of production or other assets, selling or buying. For example, a batch of new equipment was purchased. And they were placed in a specific storage facility. It would be a good idea to check after checking both the availability of the entire supply and whether previous models have disappeared and will need to be transferred to another department.
- The emergence of a new responsible person. Even before a new employee begins his work, it is worth checking everything of value accurately. Otherwise, it is not clear whether the shortage was the fault of the previous employee or the mistakes of the new one.
- Change of leader. The principle is approximately the same, only this employee could carry out illegal manipulations with property on a much larger scale. Therefore, you need to understand whether after his departure the property part of the company remained intact.
- Also, an inventory of inventory items is carried out if there has been a change in the organizational structure of a legal entity. Including the complete liquidation of an existing enterprise. It is necessary to understand that this is especially important if liquidation in bankruptcy is implied. The presence of debts presupposes the formation of a bankruptcy estate, which includes all the company’s material assets in full.
- Emergency situations, force majeure circumstances and similar. Various natural disasters, fires in a warehouse, sales area. As well as minor local problems. For example, flooding due to problems with plumbing. It is unclear how many objects could have deteriorated and lost their usability as a result.
Justification for the mandatory annual inventory
Yes, the audit is not carried out at will - it must be carried out by legal entities of any legal entity (organizational form), no matter what tax regime they apply. Two documents talk about this at once:
- Federal Law No. 402 of December 6, 2011, namely paragraph three of Article 11;
- PBU (accounting regulations) approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 34n dated July 29, 1998 - clause 27.
According to them, the procedure is necessary to ensure up-to-date accounting data. On the other hand, Article 14 of the same Federal Law No. 402 says that the results of the audit are not included in the reporting. This means that in the standard case, the tax office will not look at whether you performed an inventory at all. But if they suspect something and come with an inspection, it will turn out that you acted illegally, and this will entail sanctions.
However, it’s not just about compliance with regulations and legal business, but also about practical benefits. This procedure will allow you to assess the real state of affairs: directly verify the presence/absence of inventories (inventories) and debts, detect thefts and arrears, unaccounted income and expenses, violations by employees, and the like. So we suggest that you think positively and perceive it as an opportunity to analyze the state of the company, and not as an inappropriate necessity.
Documents for conducting an inventory of inventory items
It is fundamentally important to understand that this process operates through a mass of accompanying acts. And every action of the commission, as well as the responsible persons, must be recorded. The results of the reconciliation are strict. If any errors, discrepancies, or contradictions in opinions are made, an additional check is immediately carried out. And appropriate corrections are made.
The regulations are strict; the required form is used for each action. For reconciliation - yours, for write-off - yours. So, let's look at what formats we need for this:
- Inventory INV-3. This is the main document that the head submits to the formed commission. Or rather, specifically to the leader of the group. It reflects the balances of inventory items for the current period. These are the ones that need to be verified. This, so to speak, is the basis on which to focus. The form contains a column indicating actual availability. In fact, this is exactly what you need to fill out, going through all the positions indicated in the paper. The order remains at the discretion of the inspectors.
- INV-19. It is also called a comparison sheet. This is a kind of main report, which is generated in the form of the results of the work done.
- INV-6. On the question of how to register and conduct an inventory of goods and materials that are currently in transport. That is, they are transported, delivered to a warehouse or point of sale, and taken from the supplier. It is this act that is used in this case.
- INV-5. This act is drawn up only for a certain category of goods or other property. What is accepted for safekeeping. High security facilities. And they are checked especially carefully, entering information in a separate inventory.
- TORG-16. This act already applies to the write-off of goods. In principle, it is issued if it turns out that the product is available, but its performance properties have been exhausted. This is usually a planned write-off. It was known that by this date the expiration date would have already expired. Or the storage conditions have been violated. And then the search for the culprit is added to the situation. In addition, there is a certain category of goods whose expiration date does not have a clearly defined date. So, when conducting an inventory of inventory items, this act is also drawn up for products that have unexpectedly reached the end of their useful life.
Inventory report
Inventory list
(act) is a document that reflects the results of the inventory. For each type of property and liability, a separate form is drawn up. For example, when taking inventory of cash, an act is filled out in form No. INV-15, goods or materials - an inventory in form No. INV-3, etc. These forms are approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88.
The inventory of property is carried out with the participation of financially responsible persons (storekeepers, cashiers, etc.). From these employees they take receipts stating that the received assets have been capitalized, the released assets have been written off, and all primary documents for them have been submitted to the accounting department.
The inventory is signed by all members of the commission and employees responsible for the safety of the property. If the document does not contain at least one required signature, the inventory results may be invalidated. The inventory is stored in the company archives for at least five years.
Procedure and algorithm
This action is carried out in strict accordance with the adopted regulations. First of all, the reason is always identified, even before the stage of forming the corresponding order. The second point is the appointment of commission members; this already occurs simultaneously with the publication of the order. Next, deadlines are determined, which are also entered into the document. Violating the established time range is unacceptable. Otherwise, a re-verification will be initiated.
The last point is summing up the results, generating reports, sending them to the accounting department for analysis. In the future, the management team already holds a meeting on the results and takes appropriate steps, if they are needed at all.
We compare the results with the credentials
All endorsed materials are sent to the accounting department, whose employees make comparisons and fill out statements for fixed assets and intangible assets in a general manner or separately - in relation to assets temporarily owned by the company.
The reasons for the discrepancies are clarified and recorded in special protocols. These documents are submitted to the head of the organization, who approves them within 5 working days, along with the decisions and recommendations of experts. Thus, business papers acquire administrative power and become primary. It is on their basis that accounting entries are updated.
Composition of the commission
Let us remind you that an inventory of material assets at an enterprise is a reconciliation of storage locations. Personal, which is carried out by employees, not remote, not documentary, not electronic. This means that you will have to create a list of people who will do this.
Separately, I would like to say that there is always:
- Chairman. The person responsible for making key decisions, summing up results, and transmitting reports. At the same time, all obligations regarding the quality of the procedures performed fall on the shoulders of this particular person.
- Administration members. And the position in this case is no longer of fundamental importance. These can be local or general level administrators assigned to a specific branch or from the central office.
- Accounting representatives. Again, not necessarily the chief accountant himself. Even an intern who has not yet been hired under an employment contract, but is only undergoing training, will do.
Considering how the inventory of goods and materials is carried out, the documents are usually prepared by accountants. They are simply more competent in this matter. And the chairman is often appointed from this department.
What happens if inventory is not carried out before the annual report?
There are no separate penalties for this, but a completed check will help show that everything is in order at the enterprise if the tax office suddenly discovers something suspicious and comes with an inspection. If you do not have convincing evidence of the transparency of business, you will receive a fine of up to 20 thousand rubles, although the main trouble is the possible blocking of the company’s activities for a period of 1 to 3 years. Plus, if the violation is considered gross, from a tax point of view, you will be charged an additional 10 to 40 thousand rubles.
In addition, it is better to carry out audits regularly to optimize your work. Because it will give an idea of the real state of assets, the amount of stored products and raw materials, the obsolescence of equipment and many other important things.
Instructions for conducting an inventory of inventory items
Under no circumstances should an order be issued if the latest receipt documentation is not yet in hand. After all, then the inspectors will simply have nothing to guide them. The transfer of papers takes place under the signature of all inspectors. The same goes for subsequent reporting.
All data must be reflected clearly, in full, without unacceptable abbreviations. And all actions are carried out under the supervision of persons who are personally responsible for the products stored in the area. It is unacceptable to begin reconciliation without their knowledge or presence.
Separately, it is worth informing that any correction, even of the smallest nature, is made only upon obtaining the consent of each member of the commission. The activity is transparent; workers from this zone or workshop may be present at inspection sites.
Since with a large volume of products the procedure becomes complex and lengthy, it is logical to use special software. It will help simplify the process, filling out reports, reconciliation, and identifying results. Reduce complex paperwork to a minimum.
How to understand the expression inventory outsourcing?
In economic theory, there is such a term as outsourced services. To put it simply, this is a purchase by the owner of a company of a certain type of service that must be performed within a certain time period. This method is becoming increasingly popular among owners of medium and large businesses. The fact is that for each officially registered labor unit, a certain amount of financial contributions must be paid to the state treasury. This is a stable tax that is mandatory for every employer. If services are attracted from outside, and are of a so-called seasonal nature, then it will be much cheaper for the owner of any company to use the knowledge and work of temporarily hired specialists, for whom another company pays taxes. She is also responsible for their qualifications.
Inventory outsourcing is a service for recounting goods and determining the degree of their compliance with the regulatory framework, leased and performed by specialists who deal with specific types of tasks professionally.
Documentation of results
Since the list of documents is quite extensive, not all personnel know how to work with them. Therefore, it is precisely in this matter that the use of “smart” programs from Cleverence, which will help avoid errors associated with the human factor, is completely justified.
And for those who are already very familiar with the technique of filling out papers, such help definitely won’t hurt. No activity has ever become worse because it was simplified. While maintaining or even increasing overall productivity levels.
Inventorying material assets is a complex process. Why not make it simpler?
WMI and Powershell
In WinNT 4.0SP4, administrators received a new tool for centralized management and monitoring of the operation of various parts of the operating system - WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation). True, in the first versions there were few components included (only 15). But in subsequent Win2k+ their number increased along with the capabilities. Today WMI is available for all versions of Windows OS, including Se7en. By querying various WMI classes of local and remote systems, we can obtain all the necessary information on the company’s software and hardware.
In the examples, I suggest not using VBScript, JScript or other scripting languages, they are too cumbersome and inconvenient, especially since we already have the luxurious PowerShell that can do the lion’s share of the work for us (read more about PS in ][ 09.2009 and 05.2010). First, let's get a list of BIOS on slave computers:
PS> Get-WMIObject Win32_BIOS -computerName synack.ru
As you understand, after '-computerName' the host name is indicated. Although when polling the local system, this parameter can be omitted, which we will do in the future for the sake of brevity. By writing a simple script, you can easily pass Get-WMIObject a list of systems from which information will be collected. If necessary, save the result to a text file for further analysis.
We conduct a survey of the remaining parameters in the same way. For example, we request information about the CPU:
PS> Get-WMIObject Win32_Processor
As a rule, a complete list of data is not needed, so we select only the necessary parameters:
PS> Get-WmiObject Win32_ComputerSystem | Select Manufacturer, Model
Let's see what kind of motherboard we have:
PS> Win32_Baseboard | Select Manufacturer, Name, Product | ft -a
The Win32_ComputerSystem, Win32_ComputerSystemProduct and Win32_ OperatingSystem classes will allow you to collect general data on your computer and system:
PS> “127.0.0.1”, “synack.ru”, “pc01” | Check-Online | Foreach-Object { Get-WMIObject Win32_ComputerSystem -computerName $_ }
We request the OS version:
PS> Get-WmiObject Win32_OperatingSystem | Select CSName,Buil dNumber,ServicePackMajorVersion
If desired, the result can be saved to a file, for example “Export-CliXML C:\check.xml”, and then filtered or processed:
PS> Import-CliXML C:\check.xml | Out-GridView
A complete list of Win32_* classes and properties is available in the MSDN documentation “Win32_Classes” (https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa394084%28v=VS.85%29.aspx). An alternative option is to use the search function.
For example, let's look at the list of objects whose names contain the word disk:
PS> Get-WmiObject -List | where {$_. name -match "disk"}
Document forms
It is worth downloading the necessary forms in advance. As already mentioned, strict compliance with the samples in this case is mandatory.
- . The order itself is about the start of the process.
- . Description of the object.
- . Products that have been shipped.
- . Already accepted objects.
- . Inventory and materials during transportation.
- . Reporting on results.
- Collation statement.
- . Control check of the correctness of the procedure.
- A general journal with notes on the actions taken and their compliance with the regulations.
Ready-made utilities and applications
If you search the Internet well, you can find dozens of ready-made WMI scripts in a variety of programming languages that can easily be adapted to your needs.
My attention was drawn to the HTA application Hardware Inventory (www.robvanderwoude.com/hardware.php) with a web shell. Just enter the computer name and get information about the installed equipment. If necessary, you can edit the raw file in a text editor, adding the necessary parameters to it (poll of WMI objects is implemented in VBScript).
Third-party developers have created a number of special cmdlets that simplify writing scripts. The Computer Inventory Script (CompInv), which is available on the website powershellpro.com, allows you to obtain information about hardware, OS and save all collected data in an Excel file for further analysis. After launching, the script will ask several questions, answering which the administrator selects the data collection mode. The list of computers to scan is determined using a special text file, and the script can also automatically scan all systems or servers included in the domain. As an option, the computer name is specified manually. By default, the current account is used, but by answering “Yes” to the question “Would you like to use an alternative credential?”, you can specify the required account.
In order not to run the created script yourself, we will entrust this to SchTasks. For example:
> SchTasks /CREATE /TN CheckScript /TR "powershell.exe ` -noprofile -executionpolicy Unrestricted ` -file check.ps1" /IT /RL HIGHEST /SC DAILY
As a result, a task called CheckScript is created, which will execute the PS script check.ps1 daily, and with the highest priority. Together with the NetPoint hardware and installed applications inventory system (www.neutex.net), a set of PS scripts (GetNet*) is offered, designed specifically for collecting a certain type of data about slave systems. For example, let's look at the availability of free space on the hard drive:
PS> Get-NetLogicalDisk -DriveType "Local Disk" | where { $_.FreeSpace / $_.Size -lt .10 } | % { $_.ComputerSystemName }
Now let's try to collect information about installed programs:
PS> Get-NetProgram -System synack.ru -Uninstalled $False | % { $_.DisplayName } | sort -unique
In total, the delivery includes 20 cmdlets. A free version of NetPoint Express Edition is available and runs on 32/64-bit WinXP/2k3/2k8/Vista/Se7en and can be used in networks of any size. To install NetPoint you will need PS 2.0, IIS and SQL server (Express Edition is sufficient).
By the way, you can get a list of installed programs by simply reading the desired registry branch:
PS> Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\ Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Format-Table DisplayName,Publisher | Out-GridView
The Out-GridView cmdlet displays data in a separate window with the ability to search and sort.
Installing Ocsng
The required package is available in the repositories of most distributions, although it is usually not the most current version. Self-assembly from source texts should not cause difficulties if you are careful. The setup.sh installation script, located inside the archive, will check for the presence of the required components and provide recommendations for troubleshooting, if necessary. In Debian/Ubuntu, for manual assembly you need to download the following packages:
$ sudo apt-get install libapache2-mod-perl2 libdbi-perl libapache-dbi-perl libdbd-mysqlperl libsoap-lite-perl libxml-simple-perl libnet-ip-perl libcompress-zlib-perl php5-gd
And XML::Entities from the CPAN repository:
$ sudo cpan -i XML::Entities
During the installation process, all necessary configuration files and aliases for the web server will be created. Since the files that can be distributed using OCSNG are often large, you should set the desired values for the post_max_size and upload_max_filesize variables in the /etc/php5/apache2/php.ini files (8 and 2 MB by default) and ocsinventory-reports. conf. After all the settings, call the browser and run the installation script https://localhost/ocsreports/install.php, where we specify the parameters for accessing the database. During the installation process, an “ocs” account with a “ocs” password will be created to access the ocsweb database. If access to the database is not limited to the local system, for security purposes the default password should be changed. To install the agent on Linux, you will need to have some Perl modules (XML and Zlib) and dmidecode.
$ sudo apt-get install libcompress-zlib-perl libnet-ipperl libnet-ssleay-perl libwww-perl libxml-simple-perl po-debconf ucf dmidecode pciutils
After which the agent is installed in the standard way for Perl applications:
$ tar xzvf Ocsinventory-Agent-1.1.2.tar.gz $ cd Ocsinventory-Agent-1.1.2 $ perl Makefile.PL $ make $ sudo make install
Next, the script will begin asking a series of questions about the placement of configuration files. We enter the server data, create a tag (to group systems), activate the cron task. Once the setup is complete, the collected computer configuration data is sent to the server. If the connection is established and we receive a “Success!” response, the agent installation can be considered complete. Its data will appear in the web console, in the “ All computers” section. An XML file containing the current computer configuration will be created in the /var/lib/ocsinventory-agent directory. If the connection does not occur, run the agent in debug mode:
$ ocsinventory-agent -l /tmp –debug –server https://ocsng-server/ocsinventory
Usually the information obtained is enough to diagnose errors. Agent for Windows can be installed in several ways. The simplest is manually or using the included logon script.
After installing the server, the agent installation file can be imported into the OCSNG database. Simply select the “Agent” tab and indicate the location of the file, after which it will be accessible from any computer on the network. The installation is standard: at the last stage we report the name or IP address of the OCSNG server, and in order to immediately generate and send a report, check the “Immediately launch inventory” checkbox. Next, the agent is registered in startup and starts as a service.